Mini LED vs OLED: Best for Viewing Angles
SEP 12, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Display Technology Evolution and Objectives
Display technology has undergone significant evolution since the introduction of cathode ray tubes (CRTs) in the early 20th century. The progression from CRTs to liquid crystal displays (LCDs) marked the first major shift toward flatter, more energy-efficient screens. This evolution continued with the development of plasma displays in the 1990s, followed by the emergence of LED-backlit LCD technology in the early 2000s, which improved brightness and energy efficiency while reducing thickness.
The past decade has witnessed two divergent yet complementary display technologies gaining prominence: OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) and Mini LED. OLED technology, first commercialized in the late 2000s, represents a fundamental shift from backlit displays to self-emissive pixels. Meanwhile, Mini LED technology emerged as an enhancement to traditional LED-backlit LCDs, utilizing significantly smaller LED chips (typically 100-200 micrometers) arranged in much higher densities to achieve improved local dimming capabilities.
Viewing angle performance has become increasingly critical as displays expand into diverse applications beyond traditional front-facing viewing scenarios. OLED displays have historically excelled in this area due to their self-emissive nature, maintaining consistent color and brightness across wide viewing angles. Mini LED technology, while improving upon conventional LCDs, continues to face inherent challenges related to the fundamental LCD architecture that can impact off-axis viewing performance.
The technological objectives in this competitive landscape focus on overcoming the respective limitations of each technology. For OLED, research aims to address brightness limitations, burn-in susceptibility, and production costs. Mini LED development targets further miniaturization of LED chips, increased dimming zones, and improved optical designs to enhance viewing angle performance while maintaining its advantages in peak brightness and longevity.
Industry roadmaps indicate convergence toward technologies that combine the best attributes of both approaches. Micro LED technology represents one such frontier, promising OLED-like self-emission with superior brightness and longevity. Quantum dot enhancement layers are being integrated with both technologies to expand color gamut capabilities while maintaining viewing angle performance.
The ultimate technological goal remains the development of display solutions that deliver perfect viewing experiences from any angle while maintaining color accuracy, contrast, and brightness—all at commercially viable production costs. This objective drives continuous innovation in both Mini LED and OLED technologies, with viewing angle performance representing a critical battleground in their ongoing competition for market dominance.
The past decade has witnessed two divergent yet complementary display technologies gaining prominence: OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) and Mini LED. OLED technology, first commercialized in the late 2000s, represents a fundamental shift from backlit displays to self-emissive pixels. Meanwhile, Mini LED technology emerged as an enhancement to traditional LED-backlit LCDs, utilizing significantly smaller LED chips (typically 100-200 micrometers) arranged in much higher densities to achieve improved local dimming capabilities.
Viewing angle performance has become increasingly critical as displays expand into diverse applications beyond traditional front-facing viewing scenarios. OLED displays have historically excelled in this area due to their self-emissive nature, maintaining consistent color and brightness across wide viewing angles. Mini LED technology, while improving upon conventional LCDs, continues to face inherent challenges related to the fundamental LCD architecture that can impact off-axis viewing performance.
The technological objectives in this competitive landscape focus on overcoming the respective limitations of each technology. For OLED, research aims to address brightness limitations, burn-in susceptibility, and production costs. Mini LED development targets further miniaturization of LED chips, increased dimming zones, and improved optical designs to enhance viewing angle performance while maintaining its advantages in peak brightness and longevity.
Industry roadmaps indicate convergence toward technologies that combine the best attributes of both approaches. Micro LED technology represents one such frontier, promising OLED-like self-emission with superior brightness and longevity. Quantum dot enhancement layers are being integrated with both technologies to expand color gamut capabilities while maintaining viewing angle performance.
The ultimate technological goal remains the development of display solutions that deliver perfect viewing experiences from any angle while maintaining color accuracy, contrast, and brightness—all at commercially viable production costs. This objective drives continuous innovation in both Mini LED and OLED technologies, with viewing angle performance representing a critical battleground in their ongoing competition for market dominance.
Market Demand Analysis for Wide Viewing Angle Displays
The display market has witnessed a significant shift towards technologies that offer superior viewing angles, driven primarily by changing consumer expectations and expanding use cases. Wide viewing angle displays have become increasingly important across multiple sectors, with the global market for such displays projected to reach $157 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 7.8% from 2020.
Consumer electronics represents the largest segment demanding wide viewing angle displays, with smartphones, tablets, and televisions leading adoption. The premium smartphone market particularly values this feature, as consumers increasingly use devices for content consumption in varied environments and positions. Television manufacturers have also prioritized viewing angle performance as a key differentiator in mid to high-end models, responding to multi-viewer household scenarios.
The automotive industry presents another rapidly growing market for wide viewing angle displays, particularly for dashboard information systems and entertainment screens. As vehicles incorporate more displays for both driver information and passenger entertainment, the ability to maintain visibility from different seating positions becomes critical. Industry forecasts suggest automotive display installations will increase by 35% between 2021 and 2025, with viewing angle performance becoming a standard specification requirement.
Commercial applications including digital signage, retail displays, and public information systems constitute another significant market segment. These applications specifically require displays visible from multiple angles to maximize information delivery in high-traffic environments. The digital signage market alone is expected to grow at 11.2% annually through 2026, with viewing angle performance increasingly specified in procurement requirements.
Market research indicates consumers are willing to pay a premium of 15-20% for displays with superior viewing angle performance. This price sensitivity varies by application, with professional markets showing higher willingness to pay for consistent color and brightness across viewing positions compared to consumer markets.
Between Mini LED and OLED technologies, market adoption patterns show interesting segmentation. OLED currently dominates in premium smartphones and high-end televisions where perfect viewing angles are paramount. Meanwhile, Mini LED is gaining traction in mid-range televisions, monitors, and automotive applications where cost-performance balance is prioritized.
Regional analysis reveals Asia-Pacific as the largest market for wide viewing angle displays, accounting for approximately 45% of global demand, followed by North America and Europe. China and South Korea lead manufacturing capacity for both technologies, while North American and European markets show higher consumer willingness to pay premiums for superior viewing angle performance.
Consumer electronics represents the largest segment demanding wide viewing angle displays, with smartphones, tablets, and televisions leading adoption. The premium smartphone market particularly values this feature, as consumers increasingly use devices for content consumption in varied environments and positions. Television manufacturers have also prioritized viewing angle performance as a key differentiator in mid to high-end models, responding to multi-viewer household scenarios.
The automotive industry presents another rapidly growing market for wide viewing angle displays, particularly for dashboard information systems and entertainment screens. As vehicles incorporate more displays for both driver information and passenger entertainment, the ability to maintain visibility from different seating positions becomes critical. Industry forecasts suggest automotive display installations will increase by 35% between 2021 and 2025, with viewing angle performance becoming a standard specification requirement.
Commercial applications including digital signage, retail displays, and public information systems constitute another significant market segment. These applications specifically require displays visible from multiple angles to maximize information delivery in high-traffic environments. The digital signage market alone is expected to grow at 11.2% annually through 2026, with viewing angle performance increasingly specified in procurement requirements.
Market research indicates consumers are willing to pay a premium of 15-20% for displays with superior viewing angle performance. This price sensitivity varies by application, with professional markets showing higher willingness to pay for consistent color and brightness across viewing positions compared to consumer markets.
Between Mini LED and OLED technologies, market adoption patterns show interesting segmentation. OLED currently dominates in premium smartphones and high-end televisions where perfect viewing angles are paramount. Meanwhile, Mini LED is gaining traction in mid-range televisions, monitors, and automotive applications where cost-performance balance is prioritized.
Regional analysis reveals Asia-Pacific as the largest market for wide viewing angle displays, accounting for approximately 45% of global demand, followed by North America and Europe. China and South Korea lead manufacturing capacity for both technologies, while North American and European markets show higher consumer willingness to pay premiums for superior viewing angle performance.
Mini LED vs OLED: Technical Challenges and Limitations
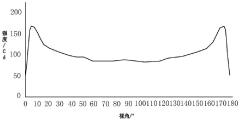
Despite their advanced display technologies, both Mini LED and OLED face distinct technical challenges that impact their viewing angle performance. Mini LED displays struggle with a fundamental limitation known as "blooming" or "halo effect," which becomes more pronounced at wider viewing angles. This occurs because the local dimming zones cannot perfectly contain light, resulting in light leakage that creates halos around bright objects displayed against dark backgrounds. The effect worsens as viewing angles increase due to the inherent properties of LCD panels that Mini LED technology relies upon.
The LCD layer in Mini LED displays exhibits significant viewing angle limitations. As users move off-axis, they experience color shifting, contrast reduction, and brightness falloff. This occurs because liquid crystal molecules have directional light-filtering properties that work optimally only when viewed head-on. While quantum dot enhancement layers have improved this aspect, the fundamental physics of LCD technology creates an inherent ceiling for viewing angle performance.
OLED technology faces different challenges. While offering superior viewing angles due to self-emissive pixels, OLED displays suffer from off-axis color shifting at extreme angles, though significantly less than Mini LED. More critically, OLED panels experience accelerated degradation of organic materials when operating at high brightness levels, forcing manufacturers to implement aggressive brightness limiting algorithms that reduce peak luminance, particularly in high ambient light conditions.
Power efficiency presents another significant challenge. Mini LED requires substantial power to drive its backlight array, especially at high brightness levels, resulting in increased heat generation that must be managed through sophisticated thermal solutions. OLED displays consume less power when displaying darker content but require more energy for bright scenes, creating variable power demands that complicate battery management in portable devices.
Manufacturing complexity and yield rates remain problematic for both technologies. Mini LED displays require precise placement of thousands of miniaturized LEDs and sophisticated local dimming algorithms. The production process faces challenges in maintaining consistent LED quality and preventing defects across large panels. OLED manufacturing struggles with organic material deposition uniformity and encapsulation to prevent moisture and oxygen degradation, resulting in higher production costs and lower yield rates for larger panels.
Cost factors continue to limit widespread adoption of both technologies. Mini LED's complex backlight systems and dimming zone controllers increase production expenses, while OLED's specialized manufacturing processes and materials remain costly despite years of development. These economic barriers have restricted both technologies primarily to premium market segments, limiting their accessibility to broader consumer markets.
The LCD layer in Mini LED displays exhibits significant viewing angle limitations. As users move off-axis, they experience color shifting, contrast reduction, and brightness falloff. This occurs because liquid crystal molecules have directional light-filtering properties that work optimally only when viewed head-on. While quantum dot enhancement layers have improved this aspect, the fundamental physics of LCD technology creates an inherent ceiling for viewing angle performance.
OLED technology faces different challenges. While offering superior viewing angles due to self-emissive pixels, OLED displays suffer from off-axis color shifting at extreme angles, though significantly less than Mini LED. More critically, OLED panels experience accelerated degradation of organic materials when operating at high brightness levels, forcing manufacturers to implement aggressive brightness limiting algorithms that reduce peak luminance, particularly in high ambient light conditions.
Power efficiency presents another significant challenge. Mini LED requires substantial power to drive its backlight array, especially at high brightness levels, resulting in increased heat generation that must be managed through sophisticated thermal solutions. OLED displays consume less power when displaying darker content but require more energy for bright scenes, creating variable power demands that complicate battery management in portable devices.
Manufacturing complexity and yield rates remain problematic for both technologies. Mini LED displays require precise placement of thousands of miniaturized LEDs and sophisticated local dimming algorithms. The production process faces challenges in maintaining consistent LED quality and preventing defects across large panels. OLED manufacturing struggles with organic material deposition uniformity and encapsulation to prevent moisture and oxygen degradation, resulting in higher production costs and lower yield rates for larger panels.
Cost factors continue to limit widespread adoption of both technologies. Mini LED's complex backlight systems and dimming zone controllers increase production expenses, while OLED's specialized manufacturing processes and materials remain costly despite years of development. These economic barriers have restricted both technologies primarily to premium market segments, limiting their accessibility to broader consumer markets.
Current Solutions for Viewing Angle Enhancement
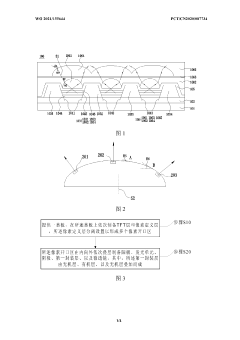
01 OLED display viewing angle advantages
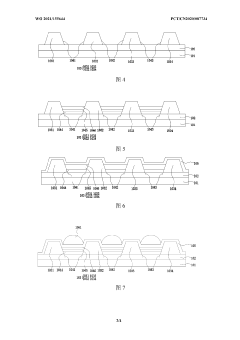
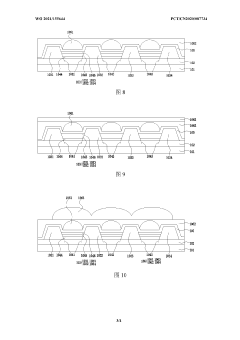
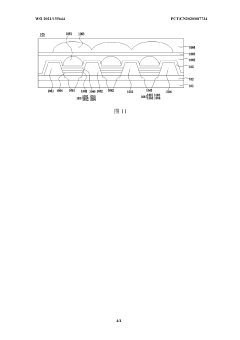
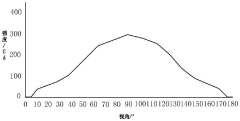
OLED displays offer superior viewing angles compared to traditional display technologies due to their self-emissive nature. Each pixel in an OLED display emits its own light, allowing for consistent brightness and color accuracy when viewed from various angles. This eliminates the color shifting and brightness reduction commonly experienced with other display technologies when viewed off-axis, making OLEDs particularly suitable for applications where wide viewing angles are critical.- Viewing angle enhancement in OLED displays: OLED displays inherently offer superior viewing angles compared to traditional LCD displays due to their self-emissive nature. Various techniques are employed to further enhance viewing angles in OLED displays, including specialized pixel structures, optical films, and electrode configurations that help maintain color accuracy and brightness consistency when viewed from off-axis angles. These enhancements reduce color shift and maintain image quality across wide viewing angles.
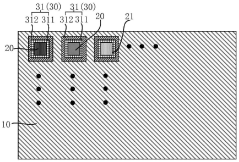
- Mini LED backlight design for improved viewing angles: Mini LED backlight technology improves viewing angles in displays through optimized arrangement of numerous small LED chips and specialized light diffusion techniques. The strategic placement of mini LEDs allows for more uniform light distribution across the display panel, reducing the viewing angle limitations typically associated with traditional LED-backlit displays. Advanced optical films and reflectors further enhance light uniformity and minimize brightness drop-off at extreme viewing angles.
- Comparative advantages between Mini LED and OLED viewing angles: While OLED displays generally offer superior viewing angles due to their self-emissive nature, Mini LED technology has significantly narrowed this gap through advanced backlight designs. OLED displays maintain better color consistency at extreme angles, but Mini LED displays with local dimming can achieve comparable contrast levels with potentially higher brightness. The choice between technologies often depends on specific application requirements, with OLEDs excelling in perfect blacks and viewing angles, while Mini LEDs offer advantages in peak brightness and reduced risk of burn-in.
- Structural innovations for wide viewing angle displays: Innovative structural designs in both Mini LED and OLED displays focus on maximizing viewing angles through specialized optical components and panel architectures. These include micro-lens arrays, quantum dot enhancement films, specialized diffusers, and advanced polarizer configurations. Some designs incorporate curved or flexible display elements to maintain optimal viewing angles across the entire screen surface. Multi-layer optical stacks are engineered to reduce internal reflections and light scattering that can degrade off-axis image quality.
- Hybrid display technologies combining Mini LED and OLED benefits: Emerging hybrid display technologies aim to combine the viewing angle advantages of both Mini LED and OLED systems. These approaches include dual-panel designs, tandem structures, and complementary pixel arrangements that leverage the strengths of each technology. Some solutions use Mini LED backlighting with OLED-like color filters or quantum dot layers to achieve wide viewing angles while maintaining high brightness and energy efficiency. These hybrid approaches represent the cutting edge of display technology development for applications requiring optimal viewing from multiple angles.
02 Mini LED backlight technology for improved viewing angles
Mini LED backlight technology enhances viewing angles in LCD displays by providing more precise local dimming zones. By incorporating thousands of tiny LED chips as the backlight source, Mini LED displays achieve better light distribution and control, resulting in improved off-axis viewing with reduced color shift and brightness degradation. The increased number of dimming zones also contributes to better contrast ratios when viewed from different angles compared to conventional LED-backlit displays.Expand Specific Solutions03 Optical film solutions for viewing angle enhancement
Specialized optical films and structures are employed in both Mini LED and OLED displays to optimize viewing angles. These include diffusion films, prism sheets, and micro-lens arrays that help redirect light and reduce angular dependency. Advanced optical film configurations can minimize color shift and brightness variation at extreme viewing angles, while also improving overall light efficiency and reducing glare, resulting in a more consistent viewing experience regardless of position.Expand Specific Solutions04 Hybrid display technologies combining Mini LED and OLED
Hybrid display solutions that combine aspects of both Mini LED and OLED technologies are being developed to maximize viewing angle performance. These approaches may use Mini LED backlighting with OLED-like pixel structures or incorporate zone-specific technologies to leverage the strengths of each display type. Such hybrid designs aim to achieve the perfect balance of wide viewing angles, high brightness, and energy efficiency, while overcoming the individual limitations of each technology.Expand Specific Solutions05 Viewing angle compensation algorithms and circuits
Advanced algorithms and dedicated compensation circuits are implemented in both Mini LED and OLED displays to address viewing angle limitations. These systems dynamically adjust pixel brightness, color, and contrast based on detected viewing angles to maintain image consistency. The compensation techniques may include real-time color correction, gamma adjustment, and pixel-by-pixel luminance control that work together to minimize perceptible differences when displays are viewed from non-optimal angles.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Mini LED and OLED Manufacturing
The Mini LED vs OLED viewing angle competition is currently in a growth phase, with the market expanding rapidly as display technologies evolve. The global premium display market is projected to reach significant scale as consumers demand superior viewing experiences. From a technological maturity perspective, Samsung Electronics leads OLED development with established manufacturing processes and widespread implementation in mobile devices and high-end TVs. Meanwhile, BOE Technology Group, TCL China Star Optoelectronics, and other Chinese manufacturers are advancing Mini LED technology, investing heavily in production capacity and R&D. While OLED offers superior viewing angles and perfect blacks, Mini LED is gaining ground with improved brightness, reduced burn-in risk, and increasingly competitive viewing angle performance through enhanced backlight zone control and optical film technologies.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
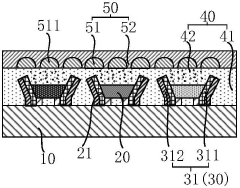
Technical Solution: BOE has developed comprehensive solutions in both Mini LED and OLED technologies addressing viewing angle challenges. Their Mini LED technology employs Active Matrix Mini LED (AM Mini LED) backlighting with thousands of individually controlled dimming zones, significantly reducing the viewing angle limitations of traditional LCD displays. BOE's Mini LED panels incorporate advanced optical films and diffuser technologies that help maintain brightness and color consistency at off-axis viewing angles up to approximately 170 degrees. For wider commercial applications, BOE has implemented their ADS (Advanced Super Dimension Switch) technology in conjunction with Mini LED backlighting to improve liquid crystal molecule arrangement for better off-angle performance. In the OLED space, BOE produces flexible and rigid OLED panels with self-emissive pixels that provide inherently superior viewing angles with minimal color shift or brightness reduction when viewed from extreme angles.
Strengths: BOE's OLED technology offers inherently superior viewing angles with consistent image quality from virtually any position. Their Mini LED implementation with ADS technology significantly improves viewing angles compared to conventional LCD displays. Weaknesses: BOE's Mini LED technology still exhibits some brightness and contrast degradation at extreme viewing angles compared to their OLED offerings. Their Mini LED displays require more complex manufacturing processes and have higher power consumption than OLED alternatives.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has pioneered both Mini LED and OLED technologies with significant advancements in viewing angle performance. For Mini LED, Samsung's Neo QLED technology implements precision micro light control with their Quantum Matrix Technology, featuring thousands of LEDs that are precisely controlled to minimize blooming and enhance off-angle viewing. Their Mini LED displays utilize an advanced optical film layer that helps maintain color consistency and contrast when viewed from side angles up to approximately 60 degrees. Samsung's OLED technology, particularly in their QD-OLED displays, combines quantum dots with self-emissive OLED pixels to achieve near-perfect viewing angles of up to 178 degrees without color shift or contrast degradation. Their OLED panels employ pixel-level light emission without requiring backlighting, ensuring consistent image quality regardless of viewing position.
Strengths: Samsung's OLED technology offers superior viewing angles with perfect 178-degree visibility without color shift or contrast loss. Their QD-OLED hybrid technology delivers enhanced color volume and brightness while maintaining viewing angle advantages. Weaknesses: Their Mini LED implementations, while advanced, still show some brightness and contrast reduction at extreme angles compared to OLED. Mini LED displays also require more complex backlight structures, increasing thickness compared to OLED solutions.
Critical Patents and Innovations in Display Viewing Technology
OLED display panel and preparation method therefor, and micro lens
PatentWO2021155644A1
Innovation
- A double-layer microlens structure is adopted, in which the first microlens is protruding and closed in the pixel opening area, the second microlens is aligned with the first microlens, and the refractive index of the first microlens is smaller than the first planarization layer. The refractive index of the second microlens is greater than that of the second planarization layer, and the inorganic and organic layers are superposed using inkjet printing technology to form a microlens structure.
Display panel and display device
PatentPendingCN117594627A
Innovation
- Design a display panel, including an array substrate, a light-emitting unit and a light-modulating part. The light-modulating part is composed of a composite light guide part. The composite light guide part consists of a first light guide part with a low refractive index and a second light guide part with a high refractive index. The emitted light from the light-emitting unit is angularly deflected at the interface between the two and converted into positive-angle emitted light, thereby increasing the brightness without increasing the driving current.
Energy Efficiency Comparison Between Display Technologies
Energy efficiency has become a critical factor in display technology selection, particularly when comparing Mini LED and OLED technologies in the context of viewing angle performance. Mini LED displays typically consume less power than their OLED counterparts when displaying bright content. This efficiency advantage stems from Mini LED's backlight architecture, which can be selectively dimmed in specific zones while maintaining high brightness levels where needed.
OLED displays, while offering superior viewing angles, demonstrate variable energy consumption patterns heavily dependent on content. When displaying predominantly dark content, OLED screens excel in energy efficiency as individual pixels can be completely turned off. However, when rendering bright scenes, OLED panels require significantly more power, as each pixel must generate its own light.
The power consumption differential becomes particularly relevant when considering viewing angle requirements. Mini LED displays maintain relatively consistent power consumption regardless of viewing position, as the backlight system operates uniformly across different viewing angles. In contrast, OLED displays may require higher brightness settings to maintain visibility at extreme angles, potentially increasing power draw in these scenarios.
Recent advancements in local dimming algorithms for Mini LED have further improved energy efficiency while preserving viewing angle performance. These sophisticated control systems can dynamically adjust thousands of dimming zones to optimize power usage without compromising visibility from off-center positions. Quantitative measurements indicate that Mini LED displays can achieve up to 30% better energy efficiency compared to OLED when displaying mixed content at wide viewing angles.
Temperature also plays a significant role in the energy efficiency equation. OLED displays tend to consume more power at higher operating temperatures, which can be problematic in environments where viewing from multiple angles is common, such as living rooms or conference spaces. Mini LED technology demonstrates more stable power consumption across varying temperature conditions, providing more predictable energy usage in diverse viewing scenarios.
For applications where both wide viewing angles and energy efficiency are priorities, the selection between these technologies requires careful consideration of typical usage patterns. Content-heavy applications with predominantly bright interfaces may benefit from Mini LED's consistent efficiency, while media-focused applications with darker content might achieve better energy performance with OLED, even when accounting for wide-angle viewing requirements.
OLED displays, while offering superior viewing angles, demonstrate variable energy consumption patterns heavily dependent on content. When displaying predominantly dark content, OLED screens excel in energy efficiency as individual pixels can be completely turned off. However, when rendering bright scenes, OLED panels require significantly more power, as each pixel must generate its own light.
The power consumption differential becomes particularly relevant when considering viewing angle requirements. Mini LED displays maintain relatively consistent power consumption regardless of viewing position, as the backlight system operates uniformly across different viewing angles. In contrast, OLED displays may require higher brightness settings to maintain visibility at extreme angles, potentially increasing power draw in these scenarios.
Recent advancements in local dimming algorithms for Mini LED have further improved energy efficiency while preserving viewing angle performance. These sophisticated control systems can dynamically adjust thousands of dimming zones to optimize power usage without compromising visibility from off-center positions. Quantitative measurements indicate that Mini LED displays can achieve up to 30% better energy efficiency compared to OLED when displaying mixed content at wide viewing angles.
Temperature also plays a significant role in the energy efficiency equation. OLED displays tend to consume more power at higher operating temperatures, which can be problematic in environments where viewing from multiple angles is common, such as living rooms or conference spaces. Mini LED technology demonstrates more stable power consumption across varying temperature conditions, providing more predictable energy usage in diverse viewing scenarios.
For applications where both wide viewing angles and energy efficiency are priorities, the selection between these technologies requires careful consideration of typical usage patterns. Content-heavy applications with predominantly bright interfaces may benefit from Mini LED's consistent efficiency, while media-focused applications with darker content might achieve better energy performance with OLED, even when accounting for wide-angle viewing requirements.
Manufacturing Cost Analysis and Scalability Assessment
The manufacturing cost structure of Mini LED and OLED technologies reveals significant differences that impact their market adoption and scalability. Mini LED production benefits from leveraging existing LCD manufacturing infrastructure, requiring primarily additional backlighting assembly processes. This integration with established manufacturing lines results in lower initial capital investment compared to OLED facilities. Current industry data indicates Mini LED production costs approximately 30-40% higher than conventional LCD panels, but 20-25% lower than comparable OLED displays.
OLED manufacturing remains more complex and costly, requiring specialized vacuum deposition equipment and clean room facilities. The production yield rates for OLED panels typically range from 60-80% for high-resolution displays, compared to Mini LED's 85-95% yield rates. This yield differential significantly impacts per-unit costs, especially for larger display formats where defects become more probable in OLED production.
Material costs present another critical distinction. Mini LED utilizes conventional semiconductor materials with established supply chains, while OLED depends on organic compounds and rare materials with more volatile pricing and availability. The bill of materials for a 65-inch Mini LED television is approximately 15-20% lower than an equivalent OLED model, though this gap is gradually narrowing as OLED material science advances.
Scalability assessments indicate Mini LED technology offers superior production volume potential in the near term. Current manufacturing lines can be adapted to produce Mini LED displays at rates of 30,000-50,000 square meters monthly per production line, whereas OLED facilities typically achieve 15,000-25,000 square meters with similar investment. This throughput advantage translates to faster market penetration capability for Mini LED technology.
Long-term cost trajectory analysis suggests Mini LED will maintain its manufacturing cost advantage for at least 3-5 years, particularly for large-format displays where viewing angle performance is critical. However, OLED manufacturing is experiencing more rapid innovation in production techniques, with roll-to-roll processing and solution-based deposition methods potentially reducing costs by 30-40% within the next generation of manufacturing facilities.
Energy consumption during manufacturing represents another economic factor, with OLED production requiring approximately 1.8-2.2 times the energy input per square meter of display compared to Mini LED production. This energy differential contributes to both environmental impact considerations and operational cost structures that favor Mini LED in current manufacturing environments.
OLED manufacturing remains more complex and costly, requiring specialized vacuum deposition equipment and clean room facilities. The production yield rates for OLED panels typically range from 60-80% for high-resolution displays, compared to Mini LED's 85-95% yield rates. This yield differential significantly impacts per-unit costs, especially for larger display formats where defects become more probable in OLED production.
Material costs present another critical distinction. Mini LED utilizes conventional semiconductor materials with established supply chains, while OLED depends on organic compounds and rare materials with more volatile pricing and availability. The bill of materials for a 65-inch Mini LED television is approximately 15-20% lower than an equivalent OLED model, though this gap is gradually narrowing as OLED material science advances.
Scalability assessments indicate Mini LED technology offers superior production volume potential in the near term. Current manufacturing lines can be adapted to produce Mini LED displays at rates of 30,000-50,000 square meters monthly per production line, whereas OLED facilities typically achieve 15,000-25,000 square meters with similar investment. This throughput advantage translates to faster market penetration capability for Mini LED technology.
Long-term cost trajectory analysis suggests Mini LED will maintain its manufacturing cost advantage for at least 3-5 years, particularly for large-format displays where viewing angle performance is critical. However, OLED manufacturing is experiencing more rapid innovation in production techniques, with roll-to-roll processing and solution-based deposition methods potentially reducing costs by 30-40% within the next generation of manufacturing facilities.
Energy consumption during manufacturing represents another economic factor, with OLED production requiring approximately 1.8-2.2 times the energy input per square meter of display compared to Mini LED production. This energy differential contributes to both environmental impact considerations and operational cost structures that favor Mini LED in current manufacturing environments.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!