PLA in the Next Decade: Predictions and Impacts
JUN 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PLA Evolution and Objectives
The People's Liberation Army (PLA) has undergone significant evolution since its inception, adapting to changing geopolitical landscapes and technological advancements. Over the past decades, the PLA has transformed from a largely land-based force to a modern, multi-domain military capable of projecting power beyond China's borders.
In the coming decade, the PLA's primary objective will likely be to achieve full military modernization by 2035, as outlined in China's long-term strategic plans. This goal encompasses developing a world-class military force capable of winning informatized wars and protecting China's expanding global interests.
A key focus for the PLA will be the continued integration of advanced technologies into its force structure and operational concepts. This includes the development and deployment of artificial intelligence, quantum computing, hypersonic weapons, and space-based assets. These technologies are expected to enhance the PLA's ability to conduct joint operations across multiple domains, including cyber and electromagnetic spectrum.
Another critical objective for the PLA will be to improve its expeditionary capabilities. As China's economic and strategic interests expand globally, the PLA will likely seek to enhance its ability to project power and protect Chinese assets abroad. This may involve the establishment of more overseas military bases and the development of long-range precision strike capabilities.
The PLA is also expected to prioritize the modernization of its nuclear forces. This includes expanding its nuclear arsenal, diversifying delivery systems, and improving command and control structures. The goal is to ensure a credible deterrent against potential adversaries and to support China's ambition of becoming a global military power.
In terms of force structure, the PLA will likely continue its efforts to streamline and professionalize its personnel. This involves reducing overall troop numbers while increasing the quality and specialization of its forces. The emphasis will be on creating a leaner, more agile force capable of rapid deployment and sustained operations in high-intensity conflicts.
Maritime capabilities will remain a crucial area of development for the PLA. The expansion and modernization of the PLA Navy (PLAN) are expected to continue, with a focus on aircraft carrier battle groups, advanced submarines, and amphibious assault capabilities. These enhancements aim to support China's territorial claims in the South China Sea and to protect its maritime trade routes.
As the PLA evolves, it will also face challenges in adapting its organizational culture and doctrine to match its technological advancements. Overcoming entrenched hierarchies and fostering innovation and initiative at all levels will be critical for the PLA to fully leverage its modernization efforts and achieve its strategic objectives in the coming decade.
In the coming decade, the PLA's primary objective will likely be to achieve full military modernization by 2035, as outlined in China's long-term strategic plans. This goal encompasses developing a world-class military force capable of winning informatized wars and protecting China's expanding global interests.
A key focus for the PLA will be the continued integration of advanced technologies into its force structure and operational concepts. This includes the development and deployment of artificial intelligence, quantum computing, hypersonic weapons, and space-based assets. These technologies are expected to enhance the PLA's ability to conduct joint operations across multiple domains, including cyber and electromagnetic spectrum.
Another critical objective for the PLA will be to improve its expeditionary capabilities. As China's economic and strategic interests expand globally, the PLA will likely seek to enhance its ability to project power and protect Chinese assets abroad. This may involve the establishment of more overseas military bases and the development of long-range precision strike capabilities.
The PLA is also expected to prioritize the modernization of its nuclear forces. This includes expanding its nuclear arsenal, diversifying delivery systems, and improving command and control structures. The goal is to ensure a credible deterrent against potential adversaries and to support China's ambition of becoming a global military power.
In terms of force structure, the PLA will likely continue its efforts to streamline and professionalize its personnel. This involves reducing overall troop numbers while increasing the quality and specialization of its forces. The emphasis will be on creating a leaner, more agile force capable of rapid deployment and sustained operations in high-intensity conflicts.
Maritime capabilities will remain a crucial area of development for the PLA. The expansion and modernization of the PLA Navy (PLAN) are expected to continue, with a focus on aircraft carrier battle groups, advanced submarines, and amphibious assault capabilities. These enhancements aim to support China's territorial claims in the South China Sea and to protect its maritime trade routes.
As the PLA evolves, it will also face challenges in adapting its organizational culture and doctrine to match its technological advancements. Overcoming entrenched hierarchies and fostering innovation and initiative at all levels will be critical for the PLA to fully leverage its modernization efforts and achieve its strategic objectives in the coming decade.
Global Security Implications
The global security landscape is poised for significant shifts as the People's Liberation Army (PLA) continues its modernization and expansion efforts over the next decade. The PLA's evolving capabilities and strategic posture will have far-reaching implications for regional stability and the global balance of power.
In East Asia, the PLA's growing naval and air capabilities will challenge the existing security architecture. The South China Sea, in particular, may become a flashpoint as China asserts its territorial claims more aggressively. This could lead to increased tensions with neighboring countries and potentially draw in external powers, such as the United States, raising the risk of military confrontation.
The PLA's advancements in long-range precision strike capabilities, including hypersonic weapons and improved ballistic missiles, will extend China's strategic reach beyond its immediate periphery. This development may prompt other regional powers to accelerate their own military modernization programs, potentially triggering an arms race in the Asia-Pacific region.
China's growing military presence in the Indian Ocean and its expanding network of overseas bases will have implications for global maritime security and trade routes. This expansion may lead to increased competition with other naval powers and could reshape the strategic dynamics in regions far from China's shores.
The PLA's focus on information warfare and cyber capabilities will present new challenges to global cybersecurity. As these capabilities mature, there is a heightened risk of cyber attacks on critical infrastructure, economic targets, and military systems of potential adversaries, blurring the lines between peacetime competition and conflict.
Space is likely to become an increasingly contested domain as the PLA enhances its space-based assets and anti-satellite capabilities. This could threaten the space-based systems that underpin global communications, navigation, and military operations, potentially destabilizing the existing space security regime.
The PLA's emphasis on artificial intelligence and autonomous systems in military applications may accelerate the global trend towards AI-enabled warfare. This shift could lower the threshold for military action and increase the speed of conflict, presenting new challenges for crisis management and strategic stability.
As the PLA's capabilities grow, traditional U.S. military superiority in the Asia-Pacific region may be eroded, potentially altering alliance dynamics and regional security arrangements. This could lead to a recalibration of U.S. defense commitments and force posture in the region, with cascading effects on global security partnerships.
In East Asia, the PLA's growing naval and air capabilities will challenge the existing security architecture. The South China Sea, in particular, may become a flashpoint as China asserts its territorial claims more aggressively. This could lead to increased tensions with neighboring countries and potentially draw in external powers, such as the United States, raising the risk of military confrontation.
The PLA's advancements in long-range precision strike capabilities, including hypersonic weapons and improved ballistic missiles, will extend China's strategic reach beyond its immediate periphery. This development may prompt other regional powers to accelerate their own military modernization programs, potentially triggering an arms race in the Asia-Pacific region.
China's growing military presence in the Indian Ocean and its expanding network of overseas bases will have implications for global maritime security and trade routes. This expansion may lead to increased competition with other naval powers and could reshape the strategic dynamics in regions far from China's shores.
The PLA's focus on information warfare and cyber capabilities will present new challenges to global cybersecurity. As these capabilities mature, there is a heightened risk of cyber attacks on critical infrastructure, economic targets, and military systems of potential adversaries, blurring the lines between peacetime competition and conflict.
Space is likely to become an increasingly contested domain as the PLA enhances its space-based assets and anti-satellite capabilities. This could threaten the space-based systems that underpin global communications, navigation, and military operations, potentially destabilizing the existing space security regime.
The PLA's emphasis on artificial intelligence and autonomous systems in military applications may accelerate the global trend towards AI-enabled warfare. This shift could lower the threshold for military action and increase the speed of conflict, presenting new challenges for crisis management and strategic stability.
As the PLA's capabilities grow, traditional U.S. military superiority in the Asia-Pacific region may be eroded, potentially altering alliance dynamics and regional security arrangements. This could lead to a recalibration of U.S. defense commitments and force posture in the region, with cascading effects on global security partnerships.
Technological Advancements
The People's Liberation Army (PLA) is poised for significant technological advancements in the coming decade, which will reshape its operational capabilities and strategic posture. One of the most prominent areas of development is artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. The PLA is expected to integrate AI into various aspects of military operations, including decision-making processes, autonomous weapons systems, and predictive maintenance for equipment.
Quantum technology is another field where the PLA is likely to make substantial progress. Quantum computing and quantum communications could revolutionize military cryptography and secure communications, potentially rendering current encryption methods obsolete. The PLA's investments in quantum radar and sensing technologies may also enhance its detection and surveillance capabilities.
Hypersonic weapons are set to become a key component of the PLA's arsenal. These weapons, capable of traveling at speeds exceeding Mach 5, pose significant challenges to existing missile defense systems. The PLA is expected to refine and expand its hypersonic capabilities, potentially altering the strategic balance in the region.
In the realm of space technology, the PLA is likely to enhance its satellite networks for communication, navigation, and reconnaissance. The development of anti-satellite weapons and space-based early warning systems will be crucial for the PLA's evolving space strategy.
Unmanned systems and robotics will see widespread adoption across the PLA. Advanced drones, autonomous underwater vehicles, and robotic ground units will augment human capabilities in various operational environments. These systems will enhance the PLA's ability to conduct reconnaissance, engage in combat, and perform logistical tasks with reduced risk to personnel.
Biotechnology and human performance enhancement are areas where the PLA may seek breakthroughs. Research into genetic engineering, brain-computer interfaces, and advanced pharmaceuticals could lead to enhanced soldier performance and resilience.
The PLA is also expected to make strides in directed energy weapons, such as high-power microwave and laser systems. These technologies could provide new options for both offensive and defensive capabilities, potentially changing the nature of battlefield engagements.
Advancements in materials science, including the development of metamaterials and nanomaterials, will likely contribute to improved armor, stealth technologies, and sensor systems. These innovations could significantly enhance the survivability and effectiveness of PLA platforms and personnel.
As these technologies mature and converge, the PLA will face the challenge of integrating them into a cohesive, network-centric warfare system. The successful implementation of these advancements will require substantial investments in research and development, as well as changes in doctrine, training, and organizational structure.
Quantum technology is another field where the PLA is likely to make substantial progress. Quantum computing and quantum communications could revolutionize military cryptography and secure communications, potentially rendering current encryption methods obsolete. The PLA's investments in quantum radar and sensing technologies may also enhance its detection and surveillance capabilities.
Hypersonic weapons are set to become a key component of the PLA's arsenal. These weapons, capable of traveling at speeds exceeding Mach 5, pose significant challenges to existing missile defense systems. The PLA is expected to refine and expand its hypersonic capabilities, potentially altering the strategic balance in the region.
In the realm of space technology, the PLA is likely to enhance its satellite networks for communication, navigation, and reconnaissance. The development of anti-satellite weapons and space-based early warning systems will be crucial for the PLA's evolving space strategy.
Unmanned systems and robotics will see widespread adoption across the PLA. Advanced drones, autonomous underwater vehicles, and robotic ground units will augment human capabilities in various operational environments. These systems will enhance the PLA's ability to conduct reconnaissance, engage in combat, and perform logistical tasks with reduced risk to personnel.
Biotechnology and human performance enhancement are areas where the PLA may seek breakthroughs. Research into genetic engineering, brain-computer interfaces, and advanced pharmaceuticals could lead to enhanced soldier performance and resilience.
The PLA is also expected to make strides in directed energy weapons, such as high-power microwave and laser systems. These technologies could provide new options for both offensive and defensive capabilities, potentially changing the nature of battlefield engagements.
Advancements in materials science, including the development of metamaterials and nanomaterials, will likely contribute to improved armor, stealth technologies, and sensor systems. These innovations could significantly enhance the survivability and effectiveness of PLA platforms and personnel.
As these technologies mature and converge, the PLA will face the challenge of integrating them into a cohesive, network-centric warfare system. The successful implementation of these advancements will require substantial investments in research and development, as well as changes in doctrine, training, and organizational structure.
Current PLA Capabilities
01 Military equipment and technology
The PLA has been developing and improving various military equipment and technologies. This includes advancements in communication systems, weaponry, and defensive gear. These innovations aim to enhance the operational capabilities and effectiveness of the armed forces.- Military equipment and technology: The PLA has been developing and improving various military equipment and technologies. This includes advancements in communication systems, weaponry, and defensive gear. These innovations aim to enhance the operational capabilities and effectiveness of the armed forces.
- Training and simulation systems: The PLA has been investing in advanced training and simulation systems to improve the skills and readiness of its personnel. These systems may include virtual reality training environments, combat simulators, and other technological tools to enhance military education and preparedness.
- Cybersecurity and information warfare: The PLA has been focusing on developing capabilities in cybersecurity and information warfare. This includes technologies for network defense, offensive cyber operations, and the protection of critical information infrastructure.
- Aerospace and missile technology: The PLA has been advancing its aerospace and missile technology capabilities. This includes the development of advanced aircraft, satellites, and missile systems to enhance its air and space defense capabilities.
- Artificial intelligence and autonomous systems: The PLA has been investing in artificial intelligence and autonomous systems for military applications. This includes the development of unmanned vehicles, AI-powered decision-making systems, and other autonomous technologies to enhance military operations and logistics.
02 Training and simulation systems
The PLA has been investing in advanced training and simulation systems to improve the skills and readiness of its personnel. These systems may include virtual reality training environments, combat simulators, and other technological tools to enhance military education and preparedness.Expand Specific Solutions03 Cybersecurity and information warfare
The PLA has been focusing on developing capabilities in cybersecurity and information warfare. This includes technologies for network defense, offensive cyber operations, and protection of critical information infrastructure to safeguard national security interests in the digital domain.Expand Specific Solutions04 Aerospace and satellite technology
The PLA has been advancing its capabilities in aerospace and satellite technology. This includes the development of satellite communication systems, space-based surveillance, and potentially anti-satellite weapons to enhance its strategic position and global reach.Expand Specific Solutions05 Artificial intelligence and autonomous systems
The PLA has been investing in artificial intelligence and autonomous systems for military applications. This may include the development of unmanned vehicles, AI-powered decision support systems, and autonomous weapons platforms to enhance combat effectiveness and reduce human casualties.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Military Powers Analysis
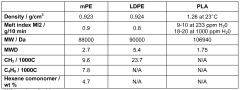
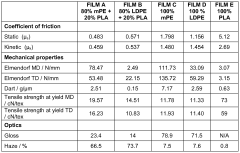
The PLA (Polylactic Acid) market is entering a mature growth phase, with significant expansion expected in the next decade. The global market size is projected to increase substantially, driven by growing demand for sustainable materials. Technologically, PLA is advancing rapidly, with companies like NatureWorks LLC and Total Research Corp leading innovation. Universities such as Shanghai Jiao Tong University and the University of Coimbra are contributing to research advancements. The competitive landscape is diverse, including established players like International Paper Co. and emerging specialists like Floreon Technology Ltd. Key areas of development include improving PLA's thermal stability, enhancing biodegradability, and expanding applications in sectors such as packaging and biomedical devices.
Honeywell International Technologies Ltd.
Technical Solution: Honeywell International Technologies Ltd. is developing advanced avionics, propulsion systems, and materials that could significantly impact PLA capabilities in the aerospace and defense sectors. Their focus includes enhancing aircraft performance through advanced flight management systems, developing more efficient and powerful engines, and creating new materials for improved stealth and durability. Honeywell is also working on integrating IoT and AI technologies into military logistics and maintenance systems, potentially revolutionizing PLA's operational readiness and efficiency.
Strengths: Diverse technological portfolio, strong presence in both commercial and military markets, proven track record in aerospace innovations. Weaknesses: Potential conflicts between commercial interests and military technology development, challenges in navigating complex international regulations.
Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique
Technical Solution: The Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS) is conducting fundamental research in areas that could have significant implications for future military technologies, including those relevant to PLA development. Key areas of focus include quantum technologies for secure communications and sensing, advanced materials science for next-generation armor and aerospace applications, and AI research for complex systems modeling and decision support. CNRS is also at the forefront of research in neuromorphic computing and brain-computer interfaces, which could revolutionize human-machine teaming in military contexts.
Strengths: World-class research capabilities, interdisciplinary approach, strong international collaborations. Weaknesses: Focus on fundamental research may result in longer timelines for practical military applications, potential limitations due to European regulations on military research.
Strategic Innovations
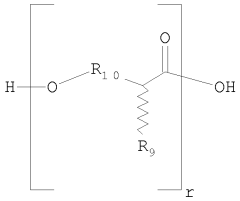
Process for cellular biosynthesis of poly d-lactic acid and poly l-lactic acid
PatentActiveUS20210324429A1
Innovation
- Engineering eukaryotic cells, such as yeast strains, to redirect metabolic pathways for the direct biological synthesis of PLLA and PDLA from carbon sources like glucose, using enzymes like D-lactate dehydrogenase, propionyl-CoA transferase, and polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase to convert pyruvate into lactyl-CoA and subsequently polymerize it into the desired polymers.
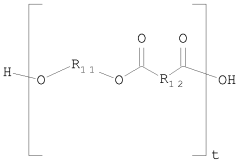
Polyethylene and poly(hydroxy carboxylic acid) blends
PatentWO2009027377A1
Innovation
- A resin composition comprising 0.1% to 50% by weight of poly(hydroxy carboxylic acid) blended with 50% to 99.9% by weight of polyethylene prepared using single-site metallocene catalysts, which achieves homogeneous blends without the need for compatibilizing agents, enhancing mechanical, gas barrier, and surface tension properties.
Geopolitical Considerations
The geopolitical landscape surrounding the People's Liberation Army (PLA) in the next decade is expected to be complex and dynamic. China's growing military capabilities and assertive stance in regional disputes will likely shape international relations and security dynamics in Asia-Pacific and beyond. The PLA's modernization efforts and strategic posture will have significant implications for regional stability, potentially altering the balance of power and influencing the foreign policies of neighboring countries.
One key consideration is the ongoing territorial disputes in the South China Sea and East China Sea. As the PLA enhances its naval and air capabilities, it may adopt a more assertive approach in these contested areas. This could lead to increased tensions with countries like Japan, Vietnam, and the Philippines, potentially drawing in other regional powers and the United States. The risk of miscalculation or unintended escalation in these maritime disputes may become a major concern for regional stability.
The Taiwan issue remains a critical geopolitical factor. The PLA's growing capabilities to project power across the Taiwan Strait could alter the strategic calculus for both Taiwan and the United States. This may lead to a reassessment of security commitments and alliances in the region, potentially triggering a recalibration of military postures and defense strategies among various stakeholders.
China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and its military implications will likely continue to shape geopolitical considerations. As the PLA expands its global presence to protect Chinese interests abroad, concerns may arise about the militarization of BRI projects and the establishment of overseas military bases. This could lead to increased competition with other major powers and reshape the strategic landscape in regions such as Africa and the Indian Ocean.
The PLA's advancements in emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence, hypersonic weapons, and space capabilities, will have far-reaching geopolitical implications. These developments may trigger arms races and prompt other nations to invest heavily in similar technologies to maintain strategic parity. The potential for technological surprises or breakthroughs could significantly alter military doctrines and strategic calculations globally.
Lastly, the PLA's role in China's overall national strategy and its impact on diplomatic relations will be crucial. As China seeks to assert itself as a global power, the PLA's capabilities and actions will influence perceptions of China's intentions and shape international responses. This could lead to the formation of new security alliances or the strengthening of existing ones, as countries seek to balance against perceived threats or align with emerging power structures.
One key consideration is the ongoing territorial disputes in the South China Sea and East China Sea. As the PLA enhances its naval and air capabilities, it may adopt a more assertive approach in these contested areas. This could lead to increased tensions with countries like Japan, Vietnam, and the Philippines, potentially drawing in other regional powers and the United States. The risk of miscalculation or unintended escalation in these maritime disputes may become a major concern for regional stability.
The Taiwan issue remains a critical geopolitical factor. The PLA's growing capabilities to project power across the Taiwan Strait could alter the strategic calculus for both Taiwan and the United States. This may lead to a reassessment of security commitments and alliances in the region, potentially triggering a recalibration of military postures and defense strategies among various stakeholders.
China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and its military implications will likely continue to shape geopolitical considerations. As the PLA expands its global presence to protect Chinese interests abroad, concerns may arise about the militarization of BRI projects and the establishment of overseas military bases. This could lead to increased competition with other major powers and reshape the strategic landscape in regions such as Africa and the Indian Ocean.
The PLA's advancements in emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence, hypersonic weapons, and space capabilities, will have far-reaching geopolitical implications. These developments may trigger arms races and prompt other nations to invest heavily in similar technologies to maintain strategic parity. The potential for technological surprises or breakthroughs could significantly alter military doctrines and strategic calculations globally.
Lastly, the PLA's role in China's overall national strategy and its impact on diplomatic relations will be crucial. As China seeks to assert itself as a global power, the PLA's capabilities and actions will influence perceptions of China's intentions and shape international responses. This could lead to the formation of new security alliances or the strengthening of existing ones, as countries seek to balance against perceived threats or align with emerging power structures.
Arms Control Implications
The modernization of the People's Liberation Army (PLA) over the next decade will have significant implications for arms control efforts globally. As China continues to expand and upgrade its military capabilities, existing arms control frameworks may face challenges in adapting to new realities. The development of advanced technologies such as hypersonic weapons, artificial intelligence, and space-based assets by the PLA could potentially destabilize strategic balances and trigger arms races in multiple domains.
One key concern is the potential impact on nuclear arms control agreements. China's expanding nuclear arsenal and the development of new delivery systems may necessitate the renegotiation of existing treaties or the creation of new multilateral frameworks that include China as a key party. The introduction of hypersonic glide vehicles and fractional orbital bombardment systems could undermine the effectiveness of early warning systems and complicate verification measures.
In the conventional realm, the PLA's focus on long-range precision strike capabilities and anti-access/area denial (A2/AD) systems may require new approaches to conventional arms control. Agreements limiting the deployment of certain weapon systems in specific regions or establishing "keep-out zones" could become more relevant. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence and autonomous systems into military operations may necessitate new international norms and regulations to prevent uncontrolled escalation.
The militarization of space by the PLA, including the development of anti-satellite weapons and space-based early warning systems, will likely drive efforts to establish or strengthen space arms control measures. This could include agreements on debris mitigation, non-interference with space assets, and limitations on the testing and deployment of anti-satellite weapons.
Cyber capabilities present another challenge for arms control efforts. As the PLA enhances its cyber warfare capabilities, there may be increased pressure to develop international norms and agreements governing the use of cyber weapons and defining thresholds for cyber attacks that could trigger kinetic responses.
Overall, the PLA's modernization will likely necessitate a reevaluation and potential overhaul of existing arms control frameworks. This may involve expanding the scope of agreements to cover new technologies, developing innovative verification mechanisms, and fostering greater transparency and confidence-building measures among major military powers. The international community will need to balance the imperative of maintaining strategic stability with the need to accommodate evolving military capabilities and geopolitical realities.
One key concern is the potential impact on nuclear arms control agreements. China's expanding nuclear arsenal and the development of new delivery systems may necessitate the renegotiation of existing treaties or the creation of new multilateral frameworks that include China as a key party. The introduction of hypersonic glide vehicles and fractional orbital bombardment systems could undermine the effectiveness of early warning systems and complicate verification measures.
In the conventional realm, the PLA's focus on long-range precision strike capabilities and anti-access/area denial (A2/AD) systems may require new approaches to conventional arms control. Agreements limiting the deployment of certain weapon systems in specific regions or establishing "keep-out zones" could become more relevant. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence and autonomous systems into military operations may necessitate new international norms and regulations to prevent uncontrolled escalation.
The militarization of space by the PLA, including the development of anti-satellite weapons and space-based early warning systems, will likely drive efforts to establish or strengthen space arms control measures. This could include agreements on debris mitigation, non-interference with space assets, and limitations on the testing and deployment of anti-satellite weapons.
Cyber capabilities present another challenge for arms control efforts. As the PLA enhances its cyber warfare capabilities, there may be increased pressure to develop international norms and agreements governing the use of cyber weapons and defining thresholds for cyber attacks that could trigger kinetic responses.
Overall, the PLA's modernization will likely necessitate a reevaluation and potential overhaul of existing arms control frameworks. This may involve expanding the scope of agreements to cover new technologies, developing innovative verification mechanisms, and fostering greater transparency and confidence-building measures among major military powers. The international community will need to balance the imperative of maintaining strategic stability with the need to accommodate evolving military capabilities and geopolitical realities.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!