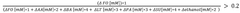Butyrate and Its Role in Gut Health Enhancement
Butyrate Research Background and Objectives
Butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid (SCFA), has emerged as a crucial player in gut health and overall well-being. The research on butyrate and its role in enhancing gut health has gained significant momentum in recent years, driven by the growing understanding of the gut microbiome's impact on human health. This field of study has evolved from early observations of butyrate's presence in the gut to a comprehensive exploration of its multifaceted functions and potential therapeutic applications.
The historical context of butyrate research dates back to the mid-20th century when scientists first identified SCFAs as byproducts of bacterial fermentation in the colon. However, it wasn't until the late 1990s and early 2000s that researchers began to unravel the specific roles of butyrate in maintaining intestinal health. This shift in focus was largely prompted by advancements in molecular biology techniques and the growing interest in the gut microbiome's influence on human physiology.
As research progressed, scientists discovered that butyrate serves as a primary energy source for colonocytes, the cells lining the colon. This finding opened up new avenues of investigation into butyrate's potential to support intestinal barrier function and protect against various gastrointestinal disorders. Subsequent studies revealed butyrate's anti-inflammatory properties, its ability to regulate gene expression, and its potential to modulate the immune system.
The objectives of current butyrate research are multifaceted and ambitious. Researchers aim to elucidate the precise mechanisms by which butyrate enhances gut health, including its effects on gut permeability, microbial composition, and immune function. There is a growing interest in understanding how dietary interventions and probiotic supplementation can increase butyrate production in the gut, potentially offering new strategies for managing gastrointestinal disorders and improving overall health.
Another key objective is to explore the therapeutic potential of butyrate in treating various conditions beyond gut health. Recent studies have suggested that butyrate may have beneficial effects on metabolic disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and even certain types of cancer. Researchers are working to develop novel delivery methods to overcome the challenges associated with butyrate's rapid metabolism and poor bioavailability.
The technological evolution in this field has been remarkable, with cutting-edge techniques such as metabolomics, metagenomics, and high-throughput sequencing enabling researchers to gain unprecedented insights into the complex interactions between butyrate, the gut microbiome, and host physiology. These advancements are paving the way for more targeted and personalized approaches to harnessing the power of butyrate for health enhancement.
Market Analysis of Gut Health Products
The global market for gut health products has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness of the importance of digestive health and its impact on overall well-being. This trend has been further accelerated by the growing interest in butyrate and its potential role in enhancing gut health.
The gut health product market encompasses a wide range of offerings, including probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and digestive enzymes. Among these, products targeting butyrate production or directly delivering butyrate to the gut have gained considerable attention. This segment is expected to witness robust growth as research continues to unveil the benefits of butyrate in maintaining gut health and potentially addressing various gastrointestinal disorders.
Consumer demand for gut health products is primarily driven by factors such as the rising prevalence of digestive disorders, increasing health consciousness, and a growing aging population. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has heightened consumer focus on immune health, which is closely linked to gut health, further boosting market growth.
The market for butyrate-related gut health products is still in its nascent stages but shows promising potential. Early adopters of these products are typically health-conscious consumers, individuals with digestive issues, and those seeking natural alternatives to traditional medications. As research on butyrate's benefits becomes more widely disseminated, it is anticipated that the consumer base will expand significantly.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the gut health product market, with Asia-Pacific emerging as a rapidly growing region. This growth is attributed to increasing disposable incomes, changing dietary habits, and rising health awareness in countries like China and India.
Key players in the gut health product market are investing heavily in research and development to create innovative formulations that can effectively deliver butyrate to the gut. Some companies are focusing on developing butyrate-producing probiotic strains, while others are exploring novel delivery mechanisms for butyrate supplements.
The market is characterized by intense competition, with both established pharmaceutical companies and emerging biotech firms vying for market share. This competitive landscape is driving innovation and is expected to lead to more effective and targeted gut health solutions in the coming years.
Looking ahead, the gut health product market, particularly the segment related to butyrate, is poised for substantial growth. As scientific understanding of the gut microbiome and the role of butyrate deepens, it is likely to open up new opportunities for product development and market expansion. However, regulatory challenges and the need for extensive clinical validation may pose hurdles to rapid market growth in some regions.
Current State of Butyrate Research
Butyrate research has made significant strides in recent years, with a growing body of evidence supporting its crucial role in gut health enhancement. Current studies focus on understanding the mechanisms by which butyrate influences intestinal homeostasis, immune function, and overall health outcomes.
One of the primary areas of investigation is the production of butyrate by gut microbiota. Researchers have identified specific bacterial species, particularly those belonging to the Firmicutes phylum, as key producers of butyrate through the fermentation of dietary fibers. The interplay between diet, gut microbiome composition, and butyrate production is a central theme in ongoing research efforts.
The molecular mechanisms of butyrate action are another major focus. Studies have elucidated its role as a histone deacetylase inhibitor, which influences gene expression and cellular processes. This epigenetic modulation has implications for various physiological functions, including intestinal barrier integrity, inflammation regulation, and cancer prevention.
Recent research has also explored the potential therapeutic applications of butyrate. Clinical trials are underway to assess its efficacy in treating inflammatory bowel diseases, colorectal cancer, and metabolic disorders. The development of novel butyrate delivery systems, such as encapsulation technologies and prodrugs, aims to overcome the challenges associated with its rapid absorption and metabolism in the gut.
The impact of butyrate on the gut-brain axis is an emerging area of interest. Studies suggest that butyrate may influence cognitive function, mood, and behavior through its effects on the enteric nervous system and systemic circulation. This research opens up new possibilities for understanding and potentially treating neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Technological advancements have enabled more sophisticated analyses of butyrate metabolism and its effects on host physiology. High-throughput sequencing, metabolomics, and advanced imaging techniques are providing unprecedented insights into the complex interactions between butyrate, the gut microbiome, and host cells.
Despite these advances, several challenges remain in butyrate research. Standardization of measurement techniques, elucidation of dose-dependent effects, and long-term safety assessments are areas that require further investigation. Additionally, the translation of preclinical findings to human applications presents ongoing challenges that researchers are actively addressing.
Existing Butyrate Delivery Methods
01 Butyrate production and gut microbiome modulation
Compositions and methods for enhancing butyrate production in the gut by modulating the microbiome. This approach aims to improve gut health by promoting beneficial bacteria that produce butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid known for its positive effects on intestinal health and function.- Butyrate production and gut microbiome modulation: Compositions and methods for enhancing butyrate production in the gut by modulating the microbiome. This approach aims to improve gut health by promoting beneficial bacteria that produce butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid known for its positive effects on intestinal health and function.
- Butyrate-producing probiotic formulations: Development of probiotic formulations containing butyrate-producing bacteria or bacterial strains engineered to enhance butyrate production in the gut. These formulations are designed to directly increase butyrate levels in the intestinal environment, supporting gut health and potentially addressing various gastrointestinal disorders.
- Dietary fiber and prebiotic compounds for butyrate production: Incorporation of specific dietary fibers and prebiotic compounds in food products or supplements to stimulate the growth of butyrate-producing bacteria in the gut. This approach focuses on providing the necessary substrates for endogenous butyrate production by the gut microbiota.
- Butyrate delivery systems for targeted gut health: Development of novel delivery systems for butyrate to ensure its effective release and absorption in the gut. These systems aim to overcome the challenges associated with butyrate's rapid metabolism and to target specific areas of the gastrointestinal tract for optimal therapeutic effects.
- Butyrate in combination with other bioactive compounds: Formulations combining butyrate with other bioactive compounds such as vitamins, minerals, or plant extracts to create synergistic effects for gut health. These combinations aim to address multiple aspects of gut health simultaneously, potentially offering more comprehensive benefits than butyrate alone.
02 Butyrate-based therapeutic formulations
Development of pharmaceutical formulations containing butyrate or its derivatives for treating gastrointestinal disorders. These formulations are designed to deliver butyrate effectively to the gut, potentially addressing conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease, irritable bowel syndrome, and other gut-related health issues.Expand Specific Solutions03 Dietary supplements for gut health
Creation of dietary supplements incorporating butyrate or butyrate-producing compounds to support gut health. These supplements aim to provide a convenient way for individuals to increase their butyrate intake, potentially improving gut barrier function, reducing inflammation, and promoting overall digestive wellness.Expand Specific Solutions04 Butyrate in combination with probiotics or prebiotics
Innovative approaches combining butyrate with probiotics or prebiotics to synergistically enhance gut health. These combinations aim to create a favorable environment for butyrate-producing bacteria while directly supplying butyrate, potentially offering more comprehensive gut health benefits.Expand Specific Solutions05 Butyrate delivery systems for targeted gut release
Development of advanced delivery systems to ensure targeted release of butyrate in specific regions of the gut. These technologies aim to overcome the challenges of butyrate's rapid absorption and metabolism, allowing for more effective delivery to the colon where it can exert its beneficial effects on gut health.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Butyrate Research
The research on butyrate and its role in gut health enhancement is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The global gut health market is expanding rapidly, driven by rising consumer awareness and demand for functional foods. Technologically, the field is progressing from basic research to more sophisticated applications. Companies like Nestlé, DSM, and Baxter International are leading in product development, while academic institutions such as Zhejiang University and The University of Chicago are contributing to fundamental research. Emerging players like PharmaBiome AG and Seed Health, Inc. are introducing innovative approaches, indicating a maturing but still evolving technological landscape in this domain.
Société des Produits Nestlé SA
DSM IP Assets BV
Core Innovations in Butyrate Studies
- Development of defined consortia of anaerobic bacterial strains, specifically including Agathobacter rectalis, Anaerostipes caccae, and Anaerobutyricum hallii, which are selected to enhance butyrate production through continuous co-culture fermentations, achieving metabolic equilibrium and stability, and are designed to treat conditions related to intestinal dysbiosis.
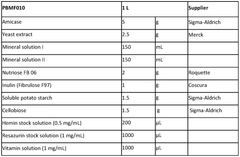
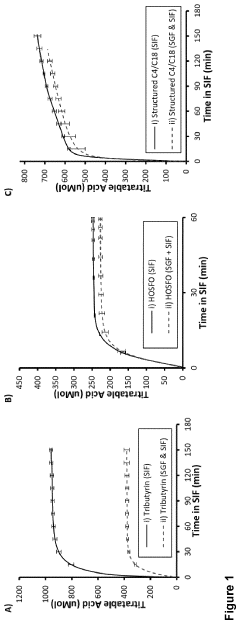
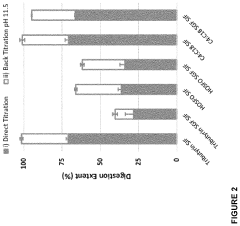
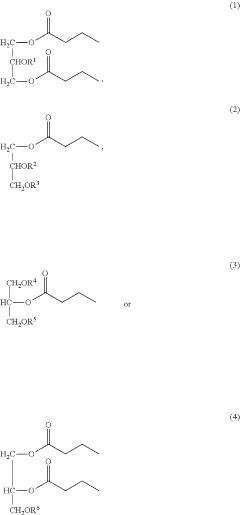
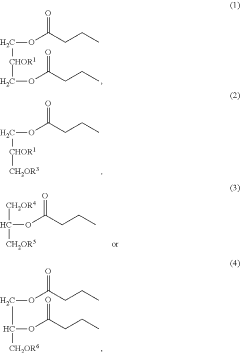
- Development of butyrate moiety containing triglycerides with improved organoleptic properties, such as 1,3-dibutyryl-2-palmitoylglycerol, which are synthesized through interesterification of tributyrin with high oleic sunflower oil, providing a dairy-free, cholesterol-free, and vegan alternative with reduced bitterness and odor, allowing effective delivery of butyric acid to the intestinal compartment.
Regulatory Landscape for Gut Health Supplements
The regulatory landscape for gut health supplements, particularly those involving butyrate, is complex and evolving. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees dietary supplements under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994. This framework allows for the sale of supplements without pre-market approval, provided they contain ingredients that were marketed prior to 1994 or have been deemed safe through a New Dietary Ingredient (NDI) notification process.
For butyrate-based supplements, manufacturers must ensure compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) and adhere to labeling requirements set forth by the FDA. Claims made on these products are limited to structure/function claims, which describe the role of a nutrient or dietary ingredient intended to affect the structure or function of the body. Disease claims are strictly prohibited without going through the rigorous drug approval process.
In the European Union, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) regulates food supplements. The EFSA has stringent requirements for health claims, necessitating substantial scientific evidence to support any statements about a product's effects on health. Butyrate supplements would need to undergo a thorough evaluation process before any gut health-related claims could be made on packaging or in marketing materials.
Japan's regulatory system for dietary supplements is notably different, with the Foods for Specified Health Uses (FOSHU) system allowing for more specific health claims if supported by scientific evidence. This could potentially provide a more favorable environment for butyrate supplements targeting gut health, provided the necessary research is conducted and approved.
Globally, there is an increasing focus on the gut microbiome and its impact on overall health. This has led to a growing interest in prebiotics, probiotics, and postbiotics, including butyrate. Regulatory bodies are adapting to this emerging field, with some countries developing specific guidelines for microbiome-related products.
As research on butyrate and gut health progresses, it is likely that regulatory frameworks will continue to evolve. Manufacturers and researchers must stay abreast of these changes to ensure compliance and maximize the potential for bringing effective gut health supplements to market.
Safety and Efficacy Considerations
When considering the safety and efficacy of butyrate in gut health enhancement, several key factors must be carefully evaluated. Butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid produced by gut bacteria during fermentation of dietary fiber, has shown promising potential in promoting intestinal health. However, its use as a therapeutic agent or dietary supplement requires thorough assessment.
The safety profile of butyrate is generally favorable, with minimal reported adverse effects when consumed in typical dietary amounts. Natural sources of butyrate, such as butter and certain fermented foods, have been consumed for centuries without significant safety concerns. However, when considering higher doses or concentrated forms for therapeutic purposes, potential risks must be carefully monitored.
One primary safety consideration is the potential for gastrointestinal distress. Some individuals may experience bloating, gas, or abdominal discomfort when consuming high amounts of butyrate or its precursors. These effects are typically mild and transient but should be taken into account when designing treatment protocols or dietary recommendations.
Efficacy studies have demonstrated several potential benefits of butyrate for gut health. It has been shown to possess anti-inflammatory properties, which may help in managing conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Butyrate also plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the intestinal barrier, potentially reducing the risk of leaky gut syndrome and associated complications.
Furthermore, butyrate has been linked to improved colonic motility and reduced risk of colorectal cancer. Its ability to regulate gene expression and modulate the gut microbiome composition contributes to its wide-ranging effects on intestinal health. However, the optimal dosage and delivery methods for achieving these benefits require further investigation.
When evaluating the efficacy of butyrate interventions, it is essential to consider individual variability in response. Factors such as baseline gut microbiome composition, diet, and overall health status can influence the effectiveness of butyrate supplementation. Long-term studies are needed to assess the sustained benefits and potential adaptations that may occur with prolonged use.
In conclusion, while butyrate shows promise in enhancing gut health, careful consideration of safety and efficacy is crucial. Continued research is necessary to establish optimal dosing regimens, identify potential contraindications, and develop targeted delivery systems to maximize the therapeutic potential of butyrate while minimizing any associated risks.