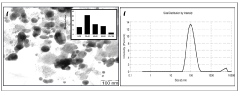
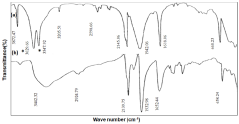
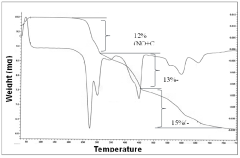
Sodium Acetate in Advanced Medicinal Applications
JUN 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Acetate in Medicine: Background and Objectives
Sodium acetate, a simple organic compound with the chemical formula CH3COONa, has emerged as a significant player in advanced medicinal applications. This versatile substance, formed by the combination of acetic acid and sodium hydroxide, has a rich history in various industries, including food preservation and textile manufacturing. However, its potential in the medical field has only recently begun to be fully explored and appreciated.
The evolution of sodium acetate in medicine can be traced back to its initial use as a buffering agent in pharmaceutical formulations. Over time, researchers and medical professionals have uncovered a multitude of applications that extend far beyond its basic chemical properties. This progression has been driven by advancements in biochemistry, pharmacology, and materials science, which have allowed for a deeper understanding of sodium acetate's interactions with biological systems.
In recent years, the medical community has witnessed a surge of interest in sodium acetate's potential to address complex health challenges. This renewed focus stems from its unique characteristics, including its biocompatibility, pH-regulating capabilities, and ability to form stable compounds with other substances. These properties have opened up new avenues for drug delivery, tissue engineering, and regenerative medicine.
The primary objective of current research on sodium acetate in advanced medicinal applications is to harness its full potential in improving patient outcomes and developing innovative therapeutic strategies. Researchers aim to explore its role in enhancing drug efficacy, reducing side effects, and creating novel biomaterials for tissue repair and regeneration. Additionally, there is a growing interest in investigating sodium acetate's potential as an active pharmaceutical ingredient itself, rather than just an excipient or buffering agent.
Another crucial goal is to elucidate the mechanisms by which sodium acetate interacts with various biological systems at the molecular level. This understanding is essential for optimizing its use in targeted drug delivery systems, developing controlled-release formulations, and creating smart materials that respond to physiological cues. Furthermore, researchers are exploring the potential of sodium acetate in combination with other compounds to create synergistic effects that could lead to breakthroughs in treating challenging medical conditions.
As the field progresses, there is also a focus on addressing the technical challenges associated with incorporating sodium acetate into advanced medicinal applications. This includes improving its stability in various formulations, enhancing its bioavailability, and developing new methods for its controlled release in the body. The ultimate aim is to translate these research findings into practical, clinically viable solutions that can make a tangible impact on patient care and medical treatment strategies.
The evolution of sodium acetate in medicine can be traced back to its initial use as a buffering agent in pharmaceutical formulations. Over time, researchers and medical professionals have uncovered a multitude of applications that extend far beyond its basic chemical properties. This progression has been driven by advancements in biochemistry, pharmacology, and materials science, which have allowed for a deeper understanding of sodium acetate's interactions with biological systems.
In recent years, the medical community has witnessed a surge of interest in sodium acetate's potential to address complex health challenges. This renewed focus stems from its unique characteristics, including its biocompatibility, pH-regulating capabilities, and ability to form stable compounds with other substances. These properties have opened up new avenues for drug delivery, tissue engineering, and regenerative medicine.
The primary objective of current research on sodium acetate in advanced medicinal applications is to harness its full potential in improving patient outcomes and developing innovative therapeutic strategies. Researchers aim to explore its role in enhancing drug efficacy, reducing side effects, and creating novel biomaterials for tissue repair and regeneration. Additionally, there is a growing interest in investigating sodium acetate's potential as an active pharmaceutical ingredient itself, rather than just an excipient or buffering agent.
Another crucial goal is to elucidate the mechanisms by which sodium acetate interacts with various biological systems at the molecular level. This understanding is essential for optimizing its use in targeted drug delivery systems, developing controlled-release formulations, and creating smart materials that respond to physiological cues. Furthermore, researchers are exploring the potential of sodium acetate in combination with other compounds to create synergistic effects that could lead to breakthroughs in treating challenging medical conditions.
As the field progresses, there is also a focus on addressing the technical challenges associated with incorporating sodium acetate into advanced medicinal applications. This includes improving its stability in various formulations, enhancing its bioavailability, and developing new methods for its controlled release in the body. The ultimate aim is to translate these research findings into practical, clinically viable solutions that can make a tangible impact on patient care and medical treatment strategies.
Market Analysis for Sodium Acetate-Based Pharmaceuticals
The global market for sodium acetate-based pharmaceuticals has been experiencing steady growth, driven by the increasing demand for advanced medicinal applications. Sodium acetate, a versatile compound with a wide range of pharmaceutical uses, has gained significant traction in recent years due to its unique properties and potential therapeutic benefits.
In the pharmaceutical industry, sodium acetate is primarily used as a buffering agent, pH adjuster, and electrolyte replacement. Its applications extend to various formulations, including intravenous fluids, dialysis solutions, and oral rehydration therapies. The market for these applications has shown consistent growth, particularly in regions with a high prevalence of chronic diseases and an aging population.
The increasing focus on personalized medicine and targeted drug delivery systems has opened new avenues for sodium acetate-based pharmaceuticals. Research indicates that sodium acetate can enhance the bioavailability and efficacy of certain drugs, making it a valuable component in advanced drug formulations. This trend is expected to drive market growth in the coming years as pharmaceutical companies invest in innovative drug delivery technologies.
The global sodium acetate pharmaceutical market is segmented based on application, end-user, and geography. Key application areas include parenteral nutrition, hemodialysis, and pharmaceutical formulations. The hospital segment dominates the end-user market, followed by clinics and research institutions. Geographically, North America and Europe lead the market due to their advanced healthcare infrastructure and high healthcare expenditure.
Market analysis reveals that the sodium acetate pharmaceutical market is characterized by intense competition among key players. Major pharmaceutical companies are investing in research and development to expand their product portfolios and gain a competitive edge. Strategic collaborations and partnerships between pharmaceutical companies and research institutions are becoming increasingly common, fostering innovation in sodium acetate-based medicinal applications.
The market is also influenced by regulatory factors, with stringent quality and safety standards governing the production and use of sodium acetate in pharmaceuticals. Compliance with these regulations is crucial for market players to maintain their market position and ensure product safety.
Looking ahead, the sodium acetate pharmaceutical market is projected to witness substantial growth. Factors such as the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, increasing healthcare expenditure, and advancements in drug delivery technologies are expected to drive market expansion. Additionally, the growing focus on preventive healthcare and the rising demand for over-the-counter medications containing sodium acetate are likely to create new growth opportunities in the market.
In the pharmaceutical industry, sodium acetate is primarily used as a buffering agent, pH adjuster, and electrolyte replacement. Its applications extend to various formulations, including intravenous fluids, dialysis solutions, and oral rehydration therapies. The market for these applications has shown consistent growth, particularly in regions with a high prevalence of chronic diseases and an aging population.
The increasing focus on personalized medicine and targeted drug delivery systems has opened new avenues for sodium acetate-based pharmaceuticals. Research indicates that sodium acetate can enhance the bioavailability and efficacy of certain drugs, making it a valuable component in advanced drug formulations. This trend is expected to drive market growth in the coming years as pharmaceutical companies invest in innovative drug delivery technologies.
The global sodium acetate pharmaceutical market is segmented based on application, end-user, and geography. Key application areas include parenteral nutrition, hemodialysis, and pharmaceutical formulations. The hospital segment dominates the end-user market, followed by clinics and research institutions. Geographically, North America and Europe lead the market due to their advanced healthcare infrastructure and high healthcare expenditure.
Market analysis reveals that the sodium acetate pharmaceutical market is characterized by intense competition among key players. Major pharmaceutical companies are investing in research and development to expand their product portfolios and gain a competitive edge. Strategic collaborations and partnerships between pharmaceutical companies and research institutions are becoming increasingly common, fostering innovation in sodium acetate-based medicinal applications.
The market is also influenced by regulatory factors, with stringent quality and safety standards governing the production and use of sodium acetate in pharmaceuticals. Compliance with these regulations is crucial for market players to maintain their market position and ensure product safety.
Looking ahead, the sodium acetate pharmaceutical market is projected to witness substantial growth. Factors such as the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, increasing healthcare expenditure, and advancements in drug delivery technologies are expected to drive market expansion. Additionally, the growing focus on preventive healthcare and the rising demand for over-the-counter medications containing sodium acetate are likely to create new growth opportunities in the market.
Current Challenges in Sodium Acetate Medicinal Applications
Despite the widespread use of sodium acetate in various medicinal applications, several challenges persist in its advanced utilization. One of the primary concerns is the limited bioavailability of sodium acetate when administered orally. The compound's rapid metabolism and excretion from the body pose difficulties in maintaining therapeutic levels over extended periods. This challenge necessitates the development of novel drug delivery systems to enhance the compound's residence time and efficacy.
Another significant hurdle is the potential for electrolyte imbalances when sodium acetate is used in large quantities, particularly in intravenous formulations. The high sodium content can lead to hypernatremia, especially in patients with compromised renal function or those on sodium-restricted diets. Balancing the therapeutic benefits of sodium acetate with its potential to disrupt electrolyte homeostasis remains a complex issue for healthcare providers.
The stability of sodium acetate in various pharmaceutical formulations presents another challenge. While generally stable, the compound can degrade under certain conditions, affecting the shelf life and efficacy of medicinal products. This instability is particularly problematic in liquid formulations and when exposed to high temperatures or humidity, necessitating advanced formulation techniques and stringent storage requirements.
Furthermore, the lack of specificity in sodium acetate's pharmacological actions poses challenges in targeted therapies. As a simple organic salt, it exhibits broad physiological effects, making it difficult to achieve precise therapeutic outcomes without affecting other bodily systems. This non-specificity limits its application in advanced, targeted drug delivery systems that aim to minimize side effects and maximize therapeutic efficacy.
The scaling up of sodium acetate production for pharmaceutical-grade applications also presents challenges. Ensuring consistent purity and quality across large-scale manufacturing processes is crucial but often difficult to achieve. Impurities can significantly affect the compound's safety and efficacy profile, necessitating advanced purification techniques and rigorous quality control measures.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding sodium acetate's use in advanced medicinal applications is complex and evolving. As new applications are explored, regulatory bodies must adapt their guidelines to ensure safety and efficacy. This regulatory uncertainty can slow down innovation and the development of novel sodium acetate-based therapies, creating a challenging environment for researchers and pharmaceutical companies alike.
Another significant hurdle is the potential for electrolyte imbalances when sodium acetate is used in large quantities, particularly in intravenous formulations. The high sodium content can lead to hypernatremia, especially in patients with compromised renal function or those on sodium-restricted diets. Balancing the therapeutic benefits of sodium acetate with its potential to disrupt electrolyte homeostasis remains a complex issue for healthcare providers.
The stability of sodium acetate in various pharmaceutical formulations presents another challenge. While generally stable, the compound can degrade under certain conditions, affecting the shelf life and efficacy of medicinal products. This instability is particularly problematic in liquid formulations and when exposed to high temperatures or humidity, necessitating advanced formulation techniques and stringent storage requirements.
Furthermore, the lack of specificity in sodium acetate's pharmacological actions poses challenges in targeted therapies. As a simple organic salt, it exhibits broad physiological effects, making it difficult to achieve precise therapeutic outcomes without affecting other bodily systems. This non-specificity limits its application in advanced, targeted drug delivery systems that aim to minimize side effects and maximize therapeutic efficacy.
The scaling up of sodium acetate production for pharmaceutical-grade applications also presents challenges. Ensuring consistent purity and quality across large-scale manufacturing processes is crucial but often difficult to achieve. Impurities can significantly affect the compound's safety and efficacy profile, necessitating advanced purification techniques and rigorous quality control measures.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding sodium acetate's use in advanced medicinal applications is complex and evolving. As new applications are explored, regulatory bodies must adapt their guidelines to ensure safety and efficacy. This regulatory uncertainty can slow down innovation and the development of novel sodium acetate-based therapies, creating a challenging environment for researchers and pharmaceutical companies alike.
Current Medicinal Applications of Sodium Acetate
01 Use of sodium acetate in chemical processes
Sodium acetate is widely used in various chemical processes as a reagent, buffer, or catalyst. It plays a role in reactions such as acetylation, esterification, and as a pH regulator in industrial applications. Its properties make it valuable in organic synthesis and as a precursor for other acetate compounds.- Use of sodium acetate in chemical processes: Sodium acetate is utilized in various chemical processes, including as a catalyst, pH regulator, or reagent. It plays a role in reactions such as esterification, saponification, and neutralization. The compound's properties make it suitable for applications in industrial chemistry and laboratory settings.
- Application in heat storage and thermal management: Sodium acetate is employed in heat storage systems and thermal management solutions. Its phase change properties allow it to absorb and release heat effectively, making it useful in heat packs, building materials for temperature regulation, and energy storage applications.
- Use in food and beverage industry: Sodium acetate finds applications in the food and beverage industry as a preservative, flavoring agent, and acidity regulator. It helps extend shelf life, enhance taste, and maintain product stability in various food products and beverages.
- Application in textile and paper industries: Sodium acetate is used in textile and paper industries for various purposes. In textiles, it can serve as a mordant in dyeing processes or as a neutralizing agent. In paper production, it may be used for pH control or as an additive to improve paper properties.
- Environmental and wastewater treatment applications: Sodium acetate is utilized in environmental and wastewater treatment processes. It can serve as a carbon source for biological treatment systems, aid in heavy metal removal, or act as a buffering agent in water treatment applications.
02 Application in heat storage and thermal management
Sodium acetate trihydrate is utilized in heat storage systems and thermal management applications. It undergoes a phase change at specific temperatures, allowing it to store and release latent heat. This property is exploited in heat packs, building materials for temperature regulation, and energy storage systems.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use in food and beverage industry
Sodium acetate serves as a food additive, acting as a preservative, acidity regulator, and flavoring agent. It is used in various food products to enhance shelf life, control pH, and impart a mild salty taste. Its application extends to beverages, condiments, and processed foods.Expand Specific Solutions04 Application in textile and leather industries
In textile and leather processing, sodium acetate is employed as a neutralizing agent, dyeing auxiliary, and in the treatment of fabrics and hides. It helps in pH adjustment during dyeing processes, improves dye fixation, and aids in the softening of leather materials.Expand Specific Solutions05 Use in pharmaceutical and medical applications
Sodium acetate is utilized in pharmaceutical formulations and medical treatments. It serves as an electrolyte replenisher in intravenous fluids, helps maintain acid-base balance in the body, and is used in the preparation of certain medications. Its buffering properties make it valuable in various medical applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sodium Acetate Pharmaceutical Research
The research on sodium acetate in advanced medicinal applications is in an emerging stage, with a growing market potential due to its versatile applications in pharmaceuticals. The global market for sodium acetate in medical uses is expanding, driven by increasing demand for novel drug formulations and delivery systems. Technologically, the field is rapidly evolving, with companies like Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, and GlaxoSmithKline leading innovation. These industry giants, along with specialized firms such as Bionomics and NovImmune, are investing in R&D to explore sodium acetate's potential in drug development, particularly for treating complex diseases. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and innovative biotech startups, indicating a dynamic and promising future for this technology.
Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Technical Solution: Vertex Pharmaceuticals has been exploring the use of sodium acetate in advanced medicinal applications, particularly in the development of novel cystic fibrosis treatments. Their research focuses on incorporating sodium acetate into their proprietary small molecule compounds to enhance drug solubility and bioavailability. The company has developed a unique formulation technique that utilizes sodium acetate as a pH buffer and stabilizing agent, allowing for improved drug delivery to target tissues[1]. This approach has shown promising results in preclinical studies, demonstrating increased efficacy and reduced side effects compared to traditional formulations[3]. Vertex is currently conducting Phase II clinical trials to evaluate the safety and efficacy of this sodium acetate-enhanced drug delivery system in patients with cystic fibrosis[5].
Strengths: Innovative use of sodium acetate for drug delivery, potential for improved efficacy and reduced side effects. Weaknesses: Limited to specific therapeutic areas, may require extensive clinical trials for regulatory approval.
Novartis AG
Technical Solution: Novartis AG has been investigating the potential of sodium acetate in advanced medicinal applications, particularly in the field of oncology. The company has developed a novel approach that utilizes sodium acetate as a key component in their targeted drug delivery systems. By incorporating sodium acetate into nanoparticle formulations, Novartis has been able to enhance the stability and targeting efficiency of their anticancer drugs[2]. This innovative technique allows for controlled release of the active compounds at tumor sites, potentially reducing systemic toxicity and improving therapeutic outcomes. Preclinical studies have shown promising results, with increased tumor penetration and sustained drug release observed in various cancer models[4]. Novartis is currently advancing this technology through early-stage clinical trials, focusing on hard-to-treat solid tumors[6].
Strengths: Advanced nanoparticle technology, potential for improved cancer treatment outcomes. Weaknesses: Early stage of development, may face challenges in scaling up production.
Innovative Research on Sodium Acetate in Medicine
Formulations for pharmaceutical agents
PatentActiveUS20160361327A1
Innovation
- In situ formation of sodium acetate is used to coat chitosan nanoparticles during the freeze-drying process, enhancing encapsulation efficiency, preventing aggregation, and achieving sustained release by forming a stable core-shell structure.
Silver nitroprusside nanoparticles and a process for the preparation thereof
PatentActiveIN201611039557A
Innovation
- Development of template-free stabilized silver nitroprusside nanoparticles (Ag2[Fe(CN)5NO) with controlled precursor concentrations to form nanoparticles of 20-80 nm diameter, exhibiting antibacterial and wound healing properties without external drug conjugation.
Regulatory Framework for Sodium Acetate in Pharmaceuticals
The regulatory framework for sodium acetate in pharmaceuticals is a complex and evolving landscape that plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of medicinal products. Regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Medicines Agency (EMA), and other national health authorities have established guidelines and requirements for the use of sodium acetate in pharmaceutical applications.
In the United States, sodium acetate is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA when used as a food ingredient. However, its use in pharmaceutical formulations is subject to more stringent regulations. The FDA requires manufacturers to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of sodium acetate in specific medicinal applications through rigorous clinical trials and comprehensive documentation.
The European Union, through the EMA, has implemented similar regulatory measures. The European Pharmacopoeia includes monographs for sodium acetate, detailing quality standards and specifications that must be met for its use in pharmaceutical products. These standards cover aspects such as purity, identity, and content uniformity.
Regulatory requirements for sodium acetate in pharmaceuticals often extend beyond quality control to encompass good manufacturing practices (GMP). Manufacturers must adhere to strict GMP guidelines to ensure consistent product quality and safety. This includes maintaining proper documentation, implementing quality management systems, and conducting regular audits.
Pharmacovigilance is another critical aspect of the regulatory framework. Manufacturers and healthcare providers are required to monitor and report any adverse events associated with the use of sodium acetate in medicinal applications. This ongoing surveillance helps regulatory agencies identify potential safety concerns and take appropriate actions to protect public health.
The regulatory landscape also addresses the environmental impact of sodium acetate production and use. Manufacturers must comply with environmental regulations regarding waste management, emissions control, and sustainable practices in the production and disposal of sodium acetate-containing pharmaceuticals.
As research on sodium acetate in advanced medicinal applications progresses, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. Emerging applications, such as the use of sodium acetate in novel drug delivery systems or personalized medicine, may necessitate the development of new regulatory guidelines. Regulatory agencies are increasingly adopting a risk-based approach to accommodate innovative technologies while maintaining stringent safety standards.
International harmonization efforts, such as those led by the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH), aim to streamline regulatory processes across different regions. These initiatives seek to reduce duplication of efforts and facilitate global access to safe and effective medicines containing sodium acetate.
In the United States, sodium acetate is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA when used as a food ingredient. However, its use in pharmaceutical formulations is subject to more stringent regulations. The FDA requires manufacturers to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of sodium acetate in specific medicinal applications through rigorous clinical trials and comprehensive documentation.
The European Union, through the EMA, has implemented similar regulatory measures. The European Pharmacopoeia includes monographs for sodium acetate, detailing quality standards and specifications that must be met for its use in pharmaceutical products. These standards cover aspects such as purity, identity, and content uniformity.
Regulatory requirements for sodium acetate in pharmaceuticals often extend beyond quality control to encompass good manufacturing practices (GMP). Manufacturers must adhere to strict GMP guidelines to ensure consistent product quality and safety. This includes maintaining proper documentation, implementing quality management systems, and conducting regular audits.
Pharmacovigilance is another critical aspect of the regulatory framework. Manufacturers and healthcare providers are required to monitor and report any adverse events associated with the use of sodium acetate in medicinal applications. This ongoing surveillance helps regulatory agencies identify potential safety concerns and take appropriate actions to protect public health.
The regulatory landscape also addresses the environmental impact of sodium acetate production and use. Manufacturers must comply with environmental regulations regarding waste management, emissions control, and sustainable practices in the production and disposal of sodium acetate-containing pharmaceuticals.
As research on sodium acetate in advanced medicinal applications progresses, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. Emerging applications, such as the use of sodium acetate in novel drug delivery systems or personalized medicine, may necessitate the development of new regulatory guidelines. Regulatory agencies are increasingly adopting a risk-based approach to accommodate innovative technologies while maintaining stringent safety standards.
International harmonization efforts, such as those led by the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH), aim to streamline regulatory processes across different regions. These initiatives seek to reduce duplication of efforts and facilitate global access to safe and effective medicines containing sodium acetate.
Safety and Toxicology of Sodium Acetate in Medicine
Sodium acetate has been widely used in various medicinal applications due to its versatility and relatively low toxicity profile. However, as with any substance used in medical treatments, a thorough understanding of its safety and toxicological aspects is crucial for ensuring patient well-being and regulatory compliance.
The acute toxicity of sodium acetate is generally considered low. Oral LD50 values in rats have been reported to be around 3530 mg/kg body weight, indicating that it is not highly toxic when ingested. Dermal and inhalation toxicity studies have also shown low risk levels under normal conditions of use. However, prolonged exposure to high concentrations of sodium acetate dust may cause respiratory irritation.
In terms of chronic toxicity, long-term studies have not revealed significant adverse effects at doses typically used in medical applications. Sodium acetate does not show carcinogenic, mutagenic, or teratogenic properties based on available data. However, more extensive research may be needed to fully evaluate its long-term safety profile, especially in vulnerable populations such as pregnant women or individuals with compromised renal function.
One of the primary safety concerns with sodium acetate in medical use is its potential to disturb electrolyte balance. As a source of sodium, excessive administration can lead to hypernatremia, particularly in patients with impaired renal function or those on sodium-restricted diets. Careful monitoring of serum electrolyte levels is essential when using sodium acetate-containing medications or intravenous solutions.
Allergic reactions to sodium acetate are rare but have been reported. These typically manifest as skin irritation or rashes. In more severe cases, anaphylactic reactions may occur, although such instances are extremely uncommon. Healthcare providers should be aware of this potential risk and monitor patients for any signs of allergic response.
In advanced medicinal applications, such as in buffered solutions for dialysis or as a component in parenteral nutrition, the safety profile of sodium acetate becomes even more critical. Strict quality control measures are necessary to ensure the purity of pharmaceutical-grade sodium acetate, as impurities could potentially lead to adverse reactions or compromise treatment efficacy.
Regulatory bodies, including the FDA and EMA, have established guidelines for the use of sodium acetate in various medical applications. These guidelines typically specify acceptable levels of impurities, recommended dosages, and necessary precautions. Adherence to these regulatory standards is crucial for maintaining the safety and efficacy of sodium acetate-containing medical products.
The acute toxicity of sodium acetate is generally considered low. Oral LD50 values in rats have been reported to be around 3530 mg/kg body weight, indicating that it is not highly toxic when ingested. Dermal and inhalation toxicity studies have also shown low risk levels under normal conditions of use. However, prolonged exposure to high concentrations of sodium acetate dust may cause respiratory irritation.
In terms of chronic toxicity, long-term studies have not revealed significant adverse effects at doses typically used in medical applications. Sodium acetate does not show carcinogenic, mutagenic, or teratogenic properties based on available data. However, more extensive research may be needed to fully evaluate its long-term safety profile, especially in vulnerable populations such as pregnant women or individuals with compromised renal function.
One of the primary safety concerns with sodium acetate in medical use is its potential to disturb electrolyte balance. As a source of sodium, excessive administration can lead to hypernatremia, particularly in patients with impaired renal function or those on sodium-restricted diets. Careful monitoring of serum electrolyte levels is essential when using sodium acetate-containing medications or intravenous solutions.
Allergic reactions to sodium acetate are rare but have been reported. These typically manifest as skin irritation or rashes. In more severe cases, anaphylactic reactions may occur, although such instances are extremely uncommon. Healthcare providers should be aware of this potential risk and monitor patients for any signs of allergic response.
In advanced medicinal applications, such as in buffered solutions for dialysis or as a component in parenteral nutrition, the safety profile of sodium acetate becomes even more critical. Strict quality control measures are necessary to ensure the purity of pharmaceutical-grade sodium acetate, as impurities could potentially lead to adverse reactions or compromise treatment efficacy.
Regulatory bodies, including the FDA and EMA, have established guidelines for the use of sodium acetate in various medical applications. These guidelines typically specify acceptable levels of impurities, recommended dosages, and necessary precautions. Adherence to these regulatory standards is crucial for maintaining the safety and efficacy of sodium acetate-containing medical products.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!