Sodium Acetate Impact on Textile Industry Processes
JUN 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Acetate in Textiles: Background and Objectives
Sodium acetate, a versatile chemical compound, has played a significant role in the textile industry for decades. Its journey in textiles began in the early 20th century when researchers discovered its potential as a mordant in dyeing processes. Since then, the applications of sodium acetate have expanded, revolutionizing various aspects of textile production and finishing.
The evolution of sodium acetate in textiles has been driven by the industry's constant pursuit of efficiency, sustainability, and product quality enhancement. Initially used primarily in dyeing, its properties were soon recognized as beneficial in other textile processes, including printing, finishing, and even fiber production. This expansion of applications has led to a growing interest in researching the compound's impact on textile industry processes.
The textile sector's increasing focus on environmentally friendly practices has further propelled the importance of sodium acetate. As a biodegradable and relatively non-toxic substance, it aligns well with the industry's sustainability goals. This has sparked renewed interest in exploring its potential as a replacement for more harmful chemicals traditionally used in textile manufacturing.
Current research objectives in this field are multifaceted. One primary goal is to optimize the use of sodium acetate in existing processes, aiming to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Researchers are investigating its role in enhancing dye fixation, improving fabric softness, and increasing the durability of finishes. Another objective is to explore novel applications of sodium acetate in emerging textile technologies, such as smart textiles and technical fabrics.
Additionally, there is a growing focus on understanding the molecular interactions between sodium acetate and various textile fibers. This fundamental research aims to provide insights that could lead to the development of innovative textile treatments and processes. The potential of sodium acetate in nanotechnology applications within textiles is also an area of increasing interest, with researchers exploring its use in creating functional nanocoatings for fabrics.
As the textile industry continues to evolve, the role of sodium acetate is expected to expand further. Future research directions may include its application in advanced textile recycling processes, its potential in developing self-cleaning fabrics, and its use in creating more sustainable synthetic fibers. The ongoing exploration of sodium acetate's properties and applications reflects the textile industry's commitment to innovation and sustainability, promising exciting developments in the years to come.
The evolution of sodium acetate in textiles has been driven by the industry's constant pursuit of efficiency, sustainability, and product quality enhancement. Initially used primarily in dyeing, its properties were soon recognized as beneficial in other textile processes, including printing, finishing, and even fiber production. This expansion of applications has led to a growing interest in researching the compound's impact on textile industry processes.
The textile sector's increasing focus on environmentally friendly practices has further propelled the importance of sodium acetate. As a biodegradable and relatively non-toxic substance, it aligns well with the industry's sustainability goals. This has sparked renewed interest in exploring its potential as a replacement for more harmful chemicals traditionally used in textile manufacturing.
Current research objectives in this field are multifaceted. One primary goal is to optimize the use of sodium acetate in existing processes, aiming to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Researchers are investigating its role in enhancing dye fixation, improving fabric softness, and increasing the durability of finishes. Another objective is to explore novel applications of sodium acetate in emerging textile technologies, such as smart textiles and technical fabrics.
Additionally, there is a growing focus on understanding the molecular interactions between sodium acetate and various textile fibers. This fundamental research aims to provide insights that could lead to the development of innovative textile treatments and processes. The potential of sodium acetate in nanotechnology applications within textiles is also an area of increasing interest, with researchers exploring its use in creating functional nanocoatings for fabrics.
As the textile industry continues to evolve, the role of sodium acetate is expected to expand further. Future research directions may include its application in advanced textile recycling processes, its potential in developing self-cleaning fabrics, and its use in creating more sustainable synthetic fibers. The ongoing exploration of sodium acetate's properties and applications reflects the textile industry's commitment to innovation and sustainability, promising exciting developments in the years to come.
Market Analysis: Sodium Acetate Demand in Textiles
The global textile industry has witnessed a significant increase in the demand for sodium acetate, driven by its versatile applications in various textile processes. This chemical compound plays a crucial role in dyeing, printing, and finishing operations, contributing to improved fabric quality and performance. The market for sodium acetate in the textile sector has experienced steady growth over the past decade, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 4-5%.
The textile industry's shift towards more sustainable and eco-friendly practices has further boosted the demand for sodium acetate. As a biodegradable and non-toxic substance, it aligns well with the industry's growing emphasis on environmental responsibility. This trend has led to increased adoption of sodium acetate in place of less environmentally friendly alternatives, particularly in regions with stringent environmental regulations.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the sodium acetate market for textiles, accounting for over 50% of the global demand. This is primarily due to the region's robust textile manufacturing sector, particularly in countries like China, India, and Bangladesh. North America and Europe follow, with growing demand driven by the increasing focus on technical textiles and high-performance fabrics.
The market dynamics of sodium acetate in the textile industry are influenced by several factors. Raw material availability and price fluctuations of acetic acid, a key ingredient in sodium acetate production, directly impact the market. Additionally, the overall health of the textile industry, which is subject to economic cycles and consumer spending patterns, plays a significant role in shaping demand.
Looking ahead, the sodium acetate market in the textile industry is poised for continued growth. The increasing adoption of advanced textile processing technologies and the growing demand for functional and smart textiles are expected to drive further market expansion. Moreover, the rising popularity of antimicrobial and moisture-wicking fabrics, where sodium acetate finds extensive use, is likely to contribute to market growth.
However, the market also faces challenges. The volatility in raw material prices and the emergence of alternative chemicals for certain textile processes could potentially impact the demand for sodium acetate. Additionally, the ongoing efforts to develop more sustainable and bio-based alternatives may influence market dynamics in the long term.
In conclusion, the demand for sodium acetate in the textile industry demonstrates a positive trajectory, underpinned by its versatile applications and alignment with sustainability trends. As the textile sector continues to evolve, the market for sodium acetate is expected to adapt and grow, presenting opportunities for both established players and new entrants in the chemical industry.
The textile industry's shift towards more sustainable and eco-friendly practices has further boosted the demand for sodium acetate. As a biodegradable and non-toxic substance, it aligns well with the industry's growing emphasis on environmental responsibility. This trend has led to increased adoption of sodium acetate in place of less environmentally friendly alternatives, particularly in regions with stringent environmental regulations.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the sodium acetate market for textiles, accounting for over 50% of the global demand. This is primarily due to the region's robust textile manufacturing sector, particularly in countries like China, India, and Bangladesh. North America and Europe follow, with growing demand driven by the increasing focus on technical textiles and high-performance fabrics.
The market dynamics of sodium acetate in the textile industry are influenced by several factors. Raw material availability and price fluctuations of acetic acid, a key ingredient in sodium acetate production, directly impact the market. Additionally, the overall health of the textile industry, which is subject to economic cycles and consumer spending patterns, plays a significant role in shaping demand.
Looking ahead, the sodium acetate market in the textile industry is poised for continued growth. The increasing adoption of advanced textile processing technologies and the growing demand for functional and smart textiles are expected to drive further market expansion. Moreover, the rising popularity of antimicrobial and moisture-wicking fabrics, where sodium acetate finds extensive use, is likely to contribute to market growth.
However, the market also faces challenges. The volatility in raw material prices and the emergence of alternative chemicals for certain textile processes could potentially impact the demand for sodium acetate. Additionally, the ongoing efforts to develop more sustainable and bio-based alternatives may influence market dynamics in the long term.
In conclusion, the demand for sodium acetate in the textile industry demonstrates a positive trajectory, underpinned by its versatile applications and alignment with sustainability trends. As the textile sector continues to evolve, the market for sodium acetate is expected to adapt and grow, presenting opportunities for both established players and new entrants in the chemical industry.
Current Applications and Challenges in Textile Industry
Sodium acetate has found widespread applications in the textile industry, primarily due to its versatile properties and cost-effectiveness. In fabric dyeing processes, it serves as a buffering agent, helping to maintain optimal pH levels for dye absorption and color fastness. This application is particularly crucial in reactive dyeing, where pH control is essential for achieving vibrant and long-lasting colors.
In textile printing, sodium acetate acts as a fixing agent, enhancing the adhesion of pigments to fabric fibers. This results in improved print quality and durability, especially in digital textile printing technologies. Additionally, it plays a role in reducing the environmental impact of printing processes by minimizing the need for harsh chemicals.
The compound is also utilized in fabric finishing treatments, where it contributes to softening and anti-wrinkling properties. When combined with other chemicals, sodium acetate can impart water repellency and flame retardancy to textiles, expanding the functional properties of finished products.
Despite its numerous applications, the use of sodium acetate in the textile industry faces several challenges. One primary concern is the environmental impact of chemical-intensive processes. As sustainability becomes increasingly important, there is pressure to reduce the use of chemicals and develop more eco-friendly alternatives. This has led to research into bio-based substitutes and green chemistry approaches to mitigate the environmental footprint of textile production.
Another challenge lies in the optimization of sodium acetate usage across various textile processes. Achieving the right balance between effectiveness and cost-efficiency requires continuous research and development. Manufacturers must fine-tune formulations to meet specific fabric requirements while minimizing resource consumption.
The textile industry also grapples with quality control issues related to sodium acetate applications. Inconsistencies in chemical purity or application methods can lead to variations in fabric properties, affecting the final product quality. Ensuring uniformity and reproducibility in large-scale production remains an ongoing challenge.
Furthermore, regulatory compliance poses a significant hurdle. As global regulations on chemical use in textiles become more stringent, manufacturers must adapt their processes to meet evolving standards. This often necessitates reformulation of existing treatments and the development of new, compliant solutions incorporating sodium acetate.
Lastly, the integration of sodium acetate-based treatments with emerging textile technologies, such as smart fabrics and wearable electronics, presents both opportunities and challenges. Researchers are exploring ways to leverage the compound's properties in these innovative applications while addressing compatibility issues and performance requirements.
In textile printing, sodium acetate acts as a fixing agent, enhancing the adhesion of pigments to fabric fibers. This results in improved print quality and durability, especially in digital textile printing technologies. Additionally, it plays a role in reducing the environmental impact of printing processes by minimizing the need for harsh chemicals.
The compound is also utilized in fabric finishing treatments, where it contributes to softening and anti-wrinkling properties. When combined with other chemicals, sodium acetate can impart water repellency and flame retardancy to textiles, expanding the functional properties of finished products.
Despite its numerous applications, the use of sodium acetate in the textile industry faces several challenges. One primary concern is the environmental impact of chemical-intensive processes. As sustainability becomes increasingly important, there is pressure to reduce the use of chemicals and develop more eco-friendly alternatives. This has led to research into bio-based substitutes and green chemistry approaches to mitigate the environmental footprint of textile production.
Another challenge lies in the optimization of sodium acetate usage across various textile processes. Achieving the right balance between effectiveness and cost-efficiency requires continuous research and development. Manufacturers must fine-tune formulations to meet specific fabric requirements while minimizing resource consumption.
The textile industry also grapples with quality control issues related to sodium acetate applications. Inconsistencies in chemical purity or application methods can lead to variations in fabric properties, affecting the final product quality. Ensuring uniformity and reproducibility in large-scale production remains an ongoing challenge.
Furthermore, regulatory compliance poses a significant hurdle. As global regulations on chemical use in textiles become more stringent, manufacturers must adapt their processes to meet evolving standards. This often necessitates reformulation of existing treatments and the development of new, compliant solutions incorporating sodium acetate.
Lastly, the integration of sodium acetate-based treatments with emerging textile technologies, such as smart fabrics and wearable electronics, presents both opportunities and challenges. Researchers are exploring ways to leverage the compound's properties in these innovative applications while addressing compatibility issues and performance requirements.
Existing Sodium Acetate Solutions for Textile Processes
01 Sodium acetate in chemical processes
Sodium acetate is widely used in various chemical processes, including as a catalyst, pH regulator, and reagent in organic synthesis. It plays a crucial role in industrial applications such as textile manufacturing, food processing, and pharmaceutical production.- Use of sodium acetate in heat storage materials: Sodium acetate is utilized in heat storage materials due to its phase change properties. It can absorb and release heat during phase transitions, making it suitable for thermal energy storage applications. These materials can be used in various heating and cooling systems to improve energy efficiency.
- Production methods for sodium acetate: Various methods are employed to produce sodium acetate, including the reaction of acetic acid with sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate. Some processes involve the use of catalysts or specific reaction conditions to improve yield and purity. These production methods are important for industrial-scale manufacturing of sodium acetate.
- Application of sodium acetate in food preservation: Sodium acetate is used as a food preservative and flavor enhancer. It helps to control acidity and inhibit microbial growth in various food products. This application is particularly important in the food industry for extending shelf life and maintaining food quality.
- Use of sodium acetate in textile processing: Sodium acetate finds applications in textile processing, particularly in dyeing and printing operations. It can act as a buffer or pH regulator in textile treatment solutions, helping to improve color fastness and overall fabric quality.
- Sodium acetate in pharmaceutical formulations: Sodium acetate is used in various pharmaceutical formulations as a buffering agent or to adjust pH. It can be found in injectable solutions, oral medications, and topical preparations. Its role in maintaining the stability and effectiveness of pharmaceutical products is significant in the medical field.
02 Sodium acetate in heat storage applications
Sodium acetate trihydrate is utilized as a phase change material for thermal energy storage. Its ability to absorb and release heat during phase transitions makes it valuable in heat packs, building materials for temperature regulation, and renewable energy systems.Expand Specific Solutions03 Sodium acetate in food preservation
Sodium acetate serves as a food preservative and flavoring agent. It helps control acidity, inhibit microbial growth, and enhance taste in various food products. Its use extends to beverages, baked goods, and processed meats.Expand Specific Solutions04 Sodium acetate in water treatment
Sodium acetate is employed in water treatment processes for pH adjustment and as a dechlorinating agent. It helps neutralize acidic water and remove excess chlorine, improving water quality in industrial and municipal applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Sodium acetate in medical applications
Sodium acetate is used in medical settings as a component of intravenous fluids for electrolyte replacement and pH balance. It also finds applications in hemodialysis solutions and as a buffering agent in pharmaceutical formulations.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sodium Acetate and Textile Manufacturing
The research on sodium acetate's impact on textile industry processes is in a developing stage, with growing market potential as the industry seeks more sustainable and efficient solutions. The technology's maturity varies across different applications, with some companies leading innovation. Key players like Covestro, Bayer, and BASF are leveraging their chemical expertise to explore sodium acetate's potential in textile processing. Universities such as Donghua University and Wuhan Textile University are contributing to fundamental research. Smaller specialized firms like AMSilk and Haiyan Jiayuan Color Technology are focusing on niche applications. The competitive landscape is diverse, with both established chemical giants and innovative startups vying for market share in this emerging field.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF Corp. has developed an innovative approach to utilizing sodium acetate in textile processing. Their method involves incorporating sodium acetate into a novel finishing treatment for fabrics. This treatment enhances the fabric's moisture-wicking properties while simultaneously improving its softness and durability. The process involves applying a solution containing sodium acetate and other proprietary compounds to the fabric, followed by a controlled heat treatment. This results in the formation of a thin, breathable layer on the fabric surface that improves its overall performance[1][3]. Additionally, BASF has integrated sodium acetate into their dyeing processes, where it acts as a pH buffer, ensuring more consistent and vibrant color results across various fabric types[5].
Strengths: Improved fabric performance, enhanced color consistency in dyeing, and potential for reduced water consumption in textile processing. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment for application and heat treatment, potentially increasing production costs.
Novozymes A/S
Technical Solution: Novozymes A/S has pioneered the use of sodium acetate in conjunction with their enzymatic textile processing technologies. Their approach involves using sodium acetate as a stabilizing agent for specialized enzymes used in fabric treatment. This combination allows for more efficient and environmentally friendly textile processing methods. The company has developed a range of enzyme formulations that, when used with sodium acetate, can effectively remove impurities from raw textiles, reduce fiber breakage during processing, and improve the overall quality of the finished product[2]. Furthermore, Novozymes has found that sodium acetate can enhance the performance of their cellulase enzymes in denim finishing processes, leading to more consistent and desirable fading effects[4]. The company has also explored the use of sodium acetate in bio-polishing treatments, where it helps to maintain optimal pH levels for enzyme activity, resulting in smoother and more pill-resistant fabrics[6].
Strengths: Enhanced enzyme performance, improved fabric quality, and more sustainable processing methods. Weaknesses: Requires careful control of process parameters and may necessitate changes to existing production lines.
Innovations in Sodium Acetate for Textile Applications
ECO-friendly fabric dyeing method using an organic dye fixing formulation to minimise waste discharge
PatentInactiveIN202343005698A
Innovation
- A method of fabric dyeing using an organic dye fixing formulation that replaces sodium sulphate, comprising a mixture of sodium carbonate monohydrate, sodium carbonate anhydrous, potassium nitrate, and sodium chloride, which reduces waste discharge, minimizes sludge, and maintains fabric strength.
Process for the treatment of synthetic textiles with cationic biocides
PatentWO2012136757A1
Innovation
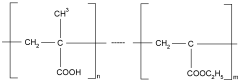
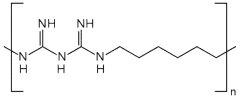
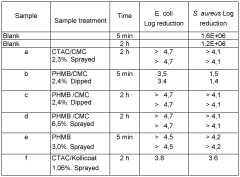
- A process involving the treatment of synthetic textiles with a specific ratio of cationic biocides and anionic polymers, such as carboxymethyl cellulose and copolymers of acrylic and methacrylic acid, to create a durable and fast-acting anti-microbial finish that prevents leaching, using an aqueous composition applied through spraying or dipping methods.
Environmental Impact of Sodium Acetate in Textiles
The use of sodium acetate in textile industry processes has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. This compound, while beneficial for certain textile applications, can have both positive and negative impacts on the environment throughout its lifecycle.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with sodium acetate in textiles is its potential to contribute to water pollution. When released into aquatic ecosystems, sodium acetate can lead to increased biological oxygen demand (BOD) and chemical oxygen demand (COD) levels. This can result in oxygen depletion in water bodies, adversely affecting aquatic life and ecosystem balance. Additionally, the discharge of sodium acetate-containing effluents from textile facilities may contribute to the eutrophication of water bodies, promoting excessive algal growth and further disrupting aquatic ecosystems.
However, it is important to note that sodium acetate is biodegradable and less harmful compared to many other chemicals used in textile processing. Its relatively low toxicity and ability to break down naturally in the environment make it a more environmentally friendly option in some applications. This characteristic has led to its increased adoption as a replacement for more hazardous substances in certain textile treatments.
The environmental impact of sodium acetate also extends to air quality considerations. During the production and application processes, volatile organic compounds (VOCs) may be released, contributing to air pollution and potentially affecting local air quality. However, the extent of these emissions is generally lower compared to many alternative chemicals used in textile manufacturing.
From a resource perspective, the production of sodium acetate requires energy and raw materials, contributing to the overall environmental footprint of textile manufacturing. However, its use can potentially lead to more efficient processes in some applications, potentially reducing overall resource consumption and waste generation in textile production.
In terms of waste management, sodium acetate presents both challenges and opportunities. While its biodegradability is advantageous, improper disposal or high concentrations in wastewater can still pose environmental risks. Effective wastewater treatment systems are crucial to mitigate these risks and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
As the textile industry continues to evolve towards more sustainable practices, the role of sodium acetate in environmentally friendly textile processes is likely to be subject to ongoing research and development. Efforts to optimize its use, minimize waste, and develop closed-loop systems for its recovery and reuse are areas of active investigation, aiming to further reduce its environmental impact while maximizing its benefits in textile applications.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with sodium acetate in textiles is its potential to contribute to water pollution. When released into aquatic ecosystems, sodium acetate can lead to increased biological oxygen demand (BOD) and chemical oxygen demand (COD) levels. This can result in oxygen depletion in water bodies, adversely affecting aquatic life and ecosystem balance. Additionally, the discharge of sodium acetate-containing effluents from textile facilities may contribute to the eutrophication of water bodies, promoting excessive algal growth and further disrupting aquatic ecosystems.
However, it is important to note that sodium acetate is biodegradable and less harmful compared to many other chemicals used in textile processing. Its relatively low toxicity and ability to break down naturally in the environment make it a more environmentally friendly option in some applications. This characteristic has led to its increased adoption as a replacement for more hazardous substances in certain textile treatments.
The environmental impact of sodium acetate also extends to air quality considerations. During the production and application processes, volatile organic compounds (VOCs) may be released, contributing to air pollution and potentially affecting local air quality. However, the extent of these emissions is generally lower compared to many alternative chemicals used in textile manufacturing.
From a resource perspective, the production of sodium acetate requires energy and raw materials, contributing to the overall environmental footprint of textile manufacturing. However, its use can potentially lead to more efficient processes in some applications, potentially reducing overall resource consumption and waste generation in textile production.
In terms of waste management, sodium acetate presents both challenges and opportunities. While its biodegradability is advantageous, improper disposal or high concentrations in wastewater can still pose environmental risks. Effective wastewater treatment systems are crucial to mitigate these risks and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
As the textile industry continues to evolve towards more sustainable practices, the role of sodium acetate in environmentally friendly textile processes is likely to be subject to ongoing research and development. Efforts to optimize its use, minimize waste, and develop closed-loop systems for its recovery and reuse are areas of active investigation, aiming to further reduce its environmental impact while maximizing its benefits in textile applications.
Regulatory Framework for Chemical Use in Textiles
The regulatory framework for chemical use in textiles is a complex and evolving landscape that significantly impacts the use of sodium acetate in textile industry processes. Governments and international organizations have established various regulations and standards to ensure the safety of textile products and minimize environmental impacts.
In the European Union, the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation plays a crucial role in controlling chemical use in textiles. While sodium acetate is not specifically restricted under REACH, manufacturers must still comply with general safety and environmental requirements. The EU has also implemented the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR), which may apply to sodium acetate when used as a preservative in textile treatments.
The United States regulates chemical use in textiles through multiple agencies. The Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) enforces the Federal Hazardous Substances Act and the Consumer Product Safety Improvement Act, which set safety standards for textile products. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates chemical use under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), which may impact the use of sodium acetate in textile processing.
In Asia, countries like China and India have their own regulatory frameworks. China's GB standards for textiles include restrictions on certain chemicals, while India's Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) sets guidelines for textile production and chemical use. These regulations may indirectly affect the use of sodium acetate in textile processes within these markets.
International standards also play a significant role in shaping the regulatory landscape. The OEKO-TEX Standard 100, a worldwide certification system for textiles, sets limits for harmful substances in textile products. While sodium acetate is not explicitly restricted, manufacturers must ensure that its use does not lead to the presence of prohibited substances in the final product.
The Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) is another influential certification that impacts chemical use in textiles. GOTS prohibits the use of certain chemicals and sets strict environmental criteria for textile processing. Sodium acetate, being a relatively benign chemical, may be permissible under GOTS if used in compliance with their guidelines for processing aids.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important in the textile industry, regulations are evolving to address environmental concerns. Many countries are implementing stricter wastewater treatment requirements, which may affect the use of sodium acetate in textile processes. Manufacturers must consider these regulations when developing and implementing sodium acetate-based treatments.
In the European Union, the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation plays a crucial role in controlling chemical use in textiles. While sodium acetate is not specifically restricted under REACH, manufacturers must still comply with general safety and environmental requirements. The EU has also implemented the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR), which may apply to sodium acetate when used as a preservative in textile treatments.
The United States regulates chemical use in textiles through multiple agencies. The Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) enforces the Federal Hazardous Substances Act and the Consumer Product Safety Improvement Act, which set safety standards for textile products. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates chemical use under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), which may impact the use of sodium acetate in textile processing.
In Asia, countries like China and India have their own regulatory frameworks. China's GB standards for textiles include restrictions on certain chemicals, while India's Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) sets guidelines for textile production and chemical use. These regulations may indirectly affect the use of sodium acetate in textile processes within these markets.
International standards also play a significant role in shaping the regulatory landscape. The OEKO-TEX Standard 100, a worldwide certification system for textiles, sets limits for harmful substances in textile products. While sodium acetate is not explicitly restricted, manufacturers must ensure that its use does not lead to the presence of prohibited substances in the final product.
The Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) is another influential certification that impacts chemical use in textiles. GOTS prohibits the use of certain chemicals and sets strict environmental criteria for textile processing. Sodium acetate, being a relatively benign chemical, may be permissible under GOTS if used in compliance with their guidelines for processing aids.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important in the textile industry, regulations are evolving to address environmental concerns. Many countries are implementing stricter wastewater treatment requirements, which may affect the use of sodium acetate in textile processes. Manufacturers must consider these regulations when developing and implementing sodium acetate-based treatments.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!