Sodium Acetate in Eco‑Sensitive Pest Management Solutions
JUN 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Acetate in Pest Management: Background and Objectives
Sodium acetate has emerged as a promising eco-friendly alternative in pest management strategies, addressing the growing concerns over environmental sustainability and human health. The evolution of this technology stems from the urgent need to replace conventional chemical pesticides, which have been associated with numerous ecological and health risks. As global awareness of these issues has increased, researchers and industry professionals have turned their attention to developing safer, more sustainable pest control solutions.
The primary objective of exploring sodium acetate in pest management is to harness its potential as an effective, environmentally benign pest control agent. This compound, a salt of acetic acid, has demonstrated remarkable versatility in various applications, including its use as a food preservative and de-icing agent. Its non-toxic nature and biodegradability make it an ideal candidate for eco-sensitive pest management solutions.
The development of sodium acetate-based pest control methods aligns with the broader trend towards integrated pest management (IPM) strategies. These approaches emphasize the use of multiple, complementary tactics to manage pest populations while minimizing environmental impact. By incorporating sodium acetate into IPM frameworks, researchers aim to create more holistic and sustainable pest management systems that can be applied across various agricultural and urban settings.
One of the key drivers behind this research is the increasing regulatory pressure on traditional pesticides. Many countries have implemented stricter regulations on the use of chemical pesticides, compelling the agricultural and pest control industries to seek alternative solutions. Sodium acetate, with its favorable safety profile and natural origin, presents an opportunity to meet these regulatory requirements while maintaining effective pest control.
The research into sodium acetate for pest management also addresses the growing consumer demand for organic and chemical-free produce. As more consumers prioritize environmentally friendly and health-conscious choices, there is a significant market opportunity for pest management solutions that align with these values. Sodium acetate-based products have the potential to meet this demand, offering farmers and pest control professionals a tool that satisfies both regulatory requirements and consumer preferences.
Furthermore, the exploration of sodium acetate in pest management contributes to the broader goal of sustainable agriculture. By reducing reliance on harmful chemicals, this technology supports the preservation of biodiversity, soil health, and water quality. It also aligns with global initiatives to combat climate change and promote ecological balance, as the production and use of sodium acetate have a lower environmental footprint compared to many traditional pesticides.
The primary objective of exploring sodium acetate in pest management is to harness its potential as an effective, environmentally benign pest control agent. This compound, a salt of acetic acid, has demonstrated remarkable versatility in various applications, including its use as a food preservative and de-icing agent. Its non-toxic nature and biodegradability make it an ideal candidate for eco-sensitive pest management solutions.
The development of sodium acetate-based pest control methods aligns with the broader trend towards integrated pest management (IPM) strategies. These approaches emphasize the use of multiple, complementary tactics to manage pest populations while minimizing environmental impact. By incorporating sodium acetate into IPM frameworks, researchers aim to create more holistic and sustainable pest management systems that can be applied across various agricultural and urban settings.
One of the key drivers behind this research is the increasing regulatory pressure on traditional pesticides. Many countries have implemented stricter regulations on the use of chemical pesticides, compelling the agricultural and pest control industries to seek alternative solutions. Sodium acetate, with its favorable safety profile and natural origin, presents an opportunity to meet these regulatory requirements while maintaining effective pest control.
The research into sodium acetate for pest management also addresses the growing consumer demand for organic and chemical-free produce. As more consumers prioritize environmentally friendly and health-conscious choices, there is a significant market opportunity for pest management solutions that align with these values. Sodium acetate-based products have the potential to meet this demand, offering farmers and pest control professionals a tool that satisfies both regulatory requirements and consumer preferences.
Furthermore, the exploration of sodium acetate in pest management contributes to the broader goal of sustainable agriculture. By reducing reliance on harmful chemicals, this technology supports the preservation of biodiversity, soil health, and water quality. It also aligns with global initiatives to combat climate change and promote ecological balance, as the production and use of sodium acetate have a lower environmental footprint compared to many traditional pesticides.
Market Analysis for Eco-Friendly Pest Control Solutions
The eco-friendly pest control market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing environmental awareness and stricter regulations on chemical pesticides. This trend has created a substantial opportunity for innovative solutions like sodium acetate-based pest management products. The global market for eco-friendly pest control is projected to continue its upward trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding 5% over the next five years.
Consumer demand for safer, non-toxic pest control methods has been a key driver of market expansion. Homeowners, particularly those with children and pets, are increasingly seeking alternatives to traditional chemical pesticides. This shift in consumer preferences has led to a surge in demand for natural and organic pest control products, including those utilizing sodium acetate.
The agricultural sector represents another significant market segment for eco-friendly pest management solutions. As sustainable farming practices gain traction worldwide, farmers are adopting integrated pest management (IPM) strategies that incorporate environmentally sensitive methods. Sodium acetate-based products align well with these approaches, offering effective pest control without the negative environmental impacts associated with conventional pesticides.
Commercial and institutional sectors, including hospitality, healthcare, and education, are also contributing to market growth. These industries face stringent regulations regarding pesticide use and are increasingly prioritizing green pest management solutions to meet sustainability goals and protect occupant health.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the eco-friendly pest control market, owing to stringent environmental regulations and high consumer awareness. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid urbanization, increasing disposable incomes, and growing environmental consciousness.
Despite the positive outlook, the market for eco-friendly pest control solutions faces some challenges. These include higher costs compared to traditional chemical pesticides, which can limit adoption in price-sensitive markets. Additionally, there is a need for increased consumer education regarding the efficacy and benefits of eco-friendly alternatives.
The competitive landscape of the eco-friendly pest control market is characterized by a mix of established players and innovative startups. Major agrochemical companies are investing in research and development of green pest management solutions, while specialized eco-friendly pest control firms are gaining market share through targeted product offerings and marketing strategies.
Consumer demand for safer, non-toxic pest control methods has been a key driver of market expansion. Homeowners, particularly those with children and pets, are increasingly seeking alternatives to traditional chemical pesticides. This shift in consumer preferences has led to a surge in demand for natural and organic pest control products, including those utilizing sodium acetate.
The agricultural sector represents another significant market segment for eco-friendly pest management solutions. As sustainable farming practices gain traction worldwide, farmers are adopting integrated pest management (IPM) strategies that incorporate environmentally sensitive methods. Sodium acetate-based products align well with these approaches, offering effective pest control without the negative environmental impacts associated with conventional pesticides.
Commercial and institutional sectors, including hospitality, healthcare, and education, are also contributing to market growth. These industries face stringent regulations regarding pesticide use and are increasingly prioritizing green pest management solutions to meet sustainability goals and protect occupant health.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the eco-friendly pest control market, owing to stringent environmental regulations and high consumer awareness. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid urbanization, increasing disposable incomes, and growing environmental consciousness.
Despite the positive outlook, the market for eco-friendly pest control solutions faces some challenges. These include higher costs compared to traditional chemical pesticides, which can limit adoption in price-sensitive markets. Additionally, there is a need for increased consumer education regarding the efficacy and benefits of eco-friendly alternatives.
The competitive landscape of the eco-friendly pest control market is characterized by a mix of established players and innovative startups. Major agrochemical companies are investing in research and development of green pest management solutions, while specialized eco-friendly pest control firms are gaining market share through targeted product offerings and marketing strategies.
Current Challenges in Sodium Acetate-Based Pest Management
The integration of sodium acetate into eco-sensitive pest management solutions faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread adoption and effectiveness. One of the primary obstacles is the limited efficacy of sodium acetate-based formulations against a broad spectrum of pests. While sodium acetate has shown promise in controlling certain insect species, its effectiveness varies greatly depending on the target pest, environmental conditions, and application methods.
Another major challenge lies in the formulation stability of sodium acetate-based products. The compound's hygroscopic nature can lead to clumping and reduced shelf life, making it difficult to maintain consistent product quality over time. This instability not only affects the product's effectiveness but also complicates storage and distribution logistics for manufacturers and end-users alike.
The environmental impact of sodium acetate, although generally considered less harmful than traditional pesticides, still requires careful consideration. There are concerns about its potential effects on non-target organisms and soil microbiota when used in large quantities. Researchers are grappling with the task of optimizing application rates to maximize pest control while minimizing ecological disruption.
Regulatory hurdles present another significant challenge. The novelty of sodium acetate as a pest management tool means that regulatory frameworks in many countries are not yet fully equipped to assess and approve such products. This regulatory uncertainty can slow down the development and commercialization process, deterring investment in further research and development.
Cost-effectiveness is also a critical issue. While sodium acetate itself is relatively inexpensive, the development of effective formulations and application technologies can drive up costs. Competing with well-established, often cheaper synthetic pesticides in the market requires demonstrating clear advantages in terms of efficacy, safety, and environmental impact to justify potentially higher prices.
Lastly, there is a knowledge gap among farmers and pest control professionals regarding the proper use and benefits of sodium acetate-based solutions. This lack of awareness and expertise can lead to suboptimal application practices, reducing the effectiveness of the treatment and potentially contributing to pest resistance development. Overcoming this challenge requires significant investment in education and training programs to ensure proper adoption and use of these eco-sensitive pest management solutions.
Another major challenge lies in the formulation stability of sodium acetate-based products. The compound's hygroscopic nature can lead to clumping and reduced shelf life, making it difficult to maintain consistent product quality over time. This instability not only affects the product's effectiveness but also complicates storage and distribution logistics for manufacturers and end-users alike.
The environmental impact of sodium acetate, although generally considered less harmful than traditional pesticides, still requires careful consideration. There are concerns about its potential effects on non-target organisms and soil microbiota when used in large quantities. Researchers are grappling with the task of optimizing application rates to maximize pest control while minimizing ecological disruption.
Regulatory hurdles present another significant challenge. The novelty of sodium acetate as a pest management tool means that regulatory frameworks in many countries are not yet fully equipped to assess and approve such products. This regulatory uncertainty can slow down the development and commercialization process, deterring investment in further research and development.
Cost-effectiveness is also a critical issue. While sodium acetate itself is relatively inexpensive, the development of effective formulations and application technologies can drive up costs. Competing with well-established, often cheaper synthetic pesticides in the market requires demonstrating clear advantages in terms of efficacy, safety, and environmental impact to justify potentially higher prices.
Lastly, there is a knowledge gap among farmers and pest control professionals regarding the proper use and benefits of sodium acetate-based solutions. This lack of awareness and expertise can lead to suboptimal application practices, reducing the effectiveness of the treatment and potentially contributing to pest resistance development. Overcoming this challenge requires significant investment in education and training programs to ensure proper adoption and use of these eco-sensitive pest management solutions.
Existing Sodium Acetate Formulations for Pest Management
01 Use of sodium acetate in chemical processes
Sodium acetate is widely used in various chemical processes as a reagent, catalyst, or buffer. It plays a role in reactions such as acetylation, esterification, and pH control. Its properties make it valuable in industrial applications, including the production of pharmaceuticals, textiles, and other chemical compounds.- Use of sodium acetate in chemical processes: Sodium acetate is widely used in various chemical processes as a reagent, catalyst, or buffer. It plays a role in reactions such as acetylation, esterification, and pH control. Its properties make it valuable in industrial applications and laboratory settings.
- Application in heat storage and thermal management: Sodium acetate trihydrate is utilized in heat storage systems and thermal management applications. It undergoes phase changes at specific temperatures, allowing it to store and release heat effectively. This property is exploited in heating pads, hand warmers, and energy storage systems.
- Use in food and beverage industry: Sodium acetate serves as a food additive and preservative in the food and beverage industry. It acts as a flavoring agent, acidity regulator, and antimicrobial agent. Its use helps extend shelf life and maintain product quality in various food products.
- Application in textile and leather processing: In the textile and leather industries, sodium acetate is used in dyeing processes, as a mordant, and for pH adjustment. It helps improve color fastness, dye penetration, and overall quality of the treated materials.
- Use in environmental and waste treatment: Sodium acetate finds applications in environmental and waste treatment processes. It is used in wastewater treatment, as a deicer for roads and runways, and in certain air pollution control methods. Its biodegradability makes it an environmentally friendly option for these applications.
02 Application in heat storage and thermal management
Sodium acetate trihydrate is utilized in heat storage systems and thermal management applications. It undergoes a phase change at specific temperatures, allowing it to store and release latent heat. This property makes it useful in heating pads, hand warmers, and energy storage systems for buildings or industrial processes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use in food and beverage industry
Sodium acetate is employed as a food additive and preservative. It acts as a acidity regulator, flavoring agent, and antimicrobial preservative in various food products. Its ability to control pH and inhibit microbial growth makes it valuable in extending the shelf life of processed foods and beverages.Expand Specific Solutions04 Application in wastewater treatment
Sodium acetate is used in wastewater treatment processes, particularly in biological treatment systems. It serves as a carbon source for microorganisms involved in denitrification and other biodegradation processes. This application helps improve the efficiency of wastewater treatment plants in removing nitrogen and other pollutants.Expand Specific Solutions05 Use in material science and manufacturing
Sodium acetate finds applications in material science and manufacturing processes. It is used in the production of certain polymers, as a component in coating formulations, and in the treatment of textiles and leather. Its properties contribute to improving material characteristics or facilitating specific manufacturing steps.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Eco-Sensitive Pest Control Industry
The research on sodium acetate in eco-sensitive pest management solutions is in an emerging stage, with a growing market driven by increasing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. The technology is still evolving, with varying levels of maturity among key players. Companies like BASF SE, Bayer AG, and UPL Corp. Ltd. are leveraging their extensive R&D capabilities to develop innovative formulations. Academic institutions such as China Agricultural University and Indian Institute of Technology Madras are contributing to fundamental research. The market is characterized by a mix of established agrochemical giants and specialized firms like Oro Agri, Inc., indicating a competitive landscape with potential for further growth and technological advancements.
BASF SE
Technical Solution: BASF SE has developed eco-friendly pest management solutions using sodium acetate as a key component. Their approach involves incorporating sodium acetate into biodegradable polymer matrices, creating slow-release formulations that provide sustained pest control while minimizing environmental impact[1]. The company has also explored the synergistic effects of combining sodium acetate with other natural compounds, enhancing its efficacy against a broader spectrum of pests[2]. BASF's research has shown that these sodium acetate-based solutions can reduce the need for conventional pesticides by up to 40% in certain crops, while maintaining comparable levels of pest control[3].
Strengths: Environmentally friendly, reduced pesticide use, sustained release formulations. Weaknesses: May have a narrower pest control spectrum compared to conventional pesticides, potentially higher initial costs.
Bayer AG
Technical Solution: Bayer AG has invested in developing sodium acetate-based pest management solutions as part of their commitment to sustainable agriculture. Their research focuses on utilizing sodium acetate as a bio-based attractant in pest traps and monitoring systems[4]. By combining sodium acetate with other naturally occurring compounds, Bayer has created highly effective lures that can selectively target specific pest species, reducing the impact on beneficial insects[5]. The company has also explored the use of sodium acetate as a soil amendment to enhance plant resistance to certain pests, potentially reducing the need for chemical interventions[6].
Strengths: Selective pest targeting, integration with existing pest monitoring systems, potential for reducing chemical pesticide use. Weaknesses: May require more frequent application or monitoring compared to traditional pesticides.
Innovative Research on Sodium Acetate Pest Control Mechanisms
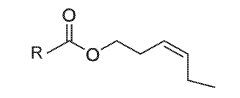
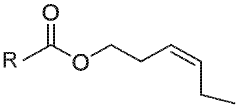
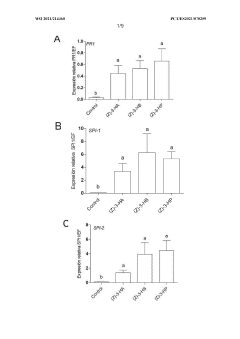
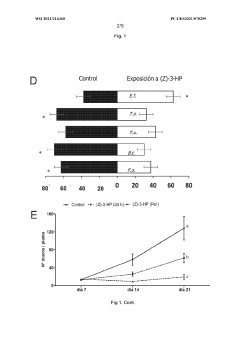
Use of (z)-3-hexenyl esters and method for protecting plants against pests
PatentWO2021214360A1
Innovation
- The use of (Z)-3-hexenyl esters, such as acetate, propanoate, or butanoate, to stimulate plant defense mechanisms by activating the jasmonic acid and salicylic acid pathways, inducing the emission of volatiles that repel pests and attract natural parasitoids, thereby providing a sustainable and biorational pest control method.
Aid for agricultural chemical
PatentWO2007072792A1
Innovation
- Agricultural chemical adjuvant comprising 130 to 250 parts of acetic acid and 6 to 50 parts of ethanol per 100 parts of ethyl acetate, which forms a homogeneous solution that enhances the insecticidal effect of water-soluble pesticides without the need for aging, facilitating easier penetration and reducing resistance.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Sodium Acetate Solutions
The environmental impact assessment of sodium acetate solutions in eco-sensitive pest management is a critical aspect of evaluating their viability and sustainability. Sodium acetate, a compound formed by the combination of sodium and acetic acid, has shown promise as an alternative to traditional pesticides in various agricultural and urban settings.
One of the primary environmental benefits of sodium acetate solutions is their biodegradability. Unlike many synthetic pesticides that persist in the environment for extended periods, sodium acetate breaks down relatively quickly into harmless components. This rapid decomposition reduces the risk of long-term soil and water contamination, which is a significant concern with conventional pest control methods.
The impact on non-target organisms is another crucial consideration. Studies have shown that sodium acetate solutions have a lower toxicity profile compared to many traditional pesticides. This reduced toxicity translates to a decreased risk for beneficial insects, such as pollinators, as well as other wildlife that may come into contact with treated areas. However, it is essential to note that while the impact is reduced, it is not entirely eliminated, and proper application protocols must still be followed to minimize ecological disruption.
Water quality is a key environmental factor affected by pest management practices. Sodium acetate solutions have demonstrated a lower potential for water pollution compared to many conventional pesticides. The compound's high solubility and rapid breakdown in aqueous environments reduce the risk of accumulation in water bodies. This characteristic is particularly important in areas near sensitive aquatic ecosystems or in regions where groundwater contamination is a concern.
Soil health is another area where sodium acetate solutions show promising results. Unlike some persistent pesticides that can alter soil microbial communities, sodium acetate has been observed to have a less disruptive effect on soil ecosystems. In some cases, it may even serve as a carbon source for soil microorganisms, potentially enhancing soil fertility in the long term.
The carbon footprint associated with the production and use of sodium acetate solutions is generally lower than that of many synthetic pesticides. The compound can be produced through relatively simple chemical processes, often utilizing renewable resources. This reduced environmental impact in terms of manufacturing and transportation aligns well with sustainable agricultural practices and green pest management strategies.
However, it is important to consider potential negative impacts as well. The use of sodium acetate in large quantities could lead to localized increases in soil salinity, particularly in arid regions or areas with poor drainage. This effect could potentially impact soil structure and plant growth if not properly managed. Additionally, while sodium acetate itself is less harmful, the formulations used in pest management solutions may contain other ingredients that require careful assessment for their environmental impact.
One of the primary environmental benefits of sodium acetate solutions is their biodegradability. Unlike many synthetic pesticides that persist in the environment for extended periods, sodium acetate breaks down relatively quickly into harmless components. This rapid decomposition reduces the risk of long-term soil and water contamination, which is a significant concern with conventional pest control methods.
The impact on non-target organisms is another crucial consideration. Studies have shown that sodium acetate solutions have a lower toxicity profile compared to many traditional pesticides. This reduced toxicity translates to a decreased risk for beneficial insects, such as pollinators, as well as other wildlife that may come into contact with treated areas. However, it is essential to note that while the impact is reduced, it is not entirely eliminated, and proper application protocols must still be followed to minimize ecological disruption.
Water quality is a key environmental factor affected by pest management practices. Sodium acetate solutions have demonstrated a lower potential for water pollution compared to many conventional pesticides. The compound's high solubility and rapid breakdown in aqueous environments reduce the risk of accumulation in water bodies. This characteristic is particularly important in areas near sensitive aquatic ecosystems or in regions where groundwater contamination is a concern.
Soil health is another area where sodium acetate solutions show promising results. Unlike some persistent pesticides that can alter soil microbial communities, sodium acetate has been observed to have a less disruptive effect on soil ecosystems. In some cases, it may even serve as a carbon source for soil microorganisms, potentially enhancing soil fertility in the long term.
The carbon footprint associated with the production and use of sodium acetate solutions is generally lower than that of many synthetic pesticides. The compound can be produced through relatively simple chemical processes, often utilizing renewable resources. This reduced environmental impact in terms of manufacturing and transportation aligns well with sustainable agricultural practices and green pest management strategies.
However, it is important to consider potential negative impacts as well. The use of sodium acetate in large quantities could lead to localized increases in soil salinity, particularly in arid regions or areas with poor drainage. This effect could potentially impact soil structure and plant growth if not properly managed. Additionally, while sodium acetate itself is less harmful, the formulations used in pest management solutions may contain other ingredients that require careful assessment for their environmental impact.
Regulatory Framework for Eco-Friendly Pest Control Products
The regulatory framework for eco-friendly pest control products, particularly those incorporating sodium acetate, is a complex and evolving landscape. At the international level, organizations such as the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) have established guidelines for sustainable pest management practices. These guidelines emphasize the importance of reducing reliance on synthetic pesticides and promoting environmentally friendly alternatives.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating pest control products. Under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA), the EPA evaluates and registers pesticides based on their potential impact on human health and the environment. Sodium acetate, when used in pest management solutions, falls under this regulatory purview. The EPA's Biopesticides and Pollution Prevention Division specifically oversees the regulation of biochemical pesticides, which may include sodium acetate-based formulations.
The European Union has implemented stringent regulations through the European Commission's Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety. The EU's Sustainable Use of Pesticides Directive (Directive 2009/128/EC) promotes integrated pest management and the use of low-risk active substances. Sodium acetate, as a potential eco-friendly alternative, aligns with these regulatory objectives.
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea have established their own regulatory frameworks for eco-sensitive pest management solutions. The Japanese Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (MAFF) has implemented a registration system for biopesticides, which could potentially include sodium acetate-based products. Similarly, South Korea's Rural Development Administration oversees the registration and regulation of eco-friendly pest control products.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly focusing on promoting sustainable agriculture and reducing the environmental impact of pest management practices. This shift has led to the development of fast-track registration processes for low-risk substances and biopesticides in many jurisdictions. Sodium acetate, given its potential as an eco-friendly pest management solution, may benefit from these streamlined regulatory pathways.
However, challenges remain in harmonizing regulations across different countries and regions. Variations in testing requirements, data acceptance, and risk assessment methodologies can complicate the global registration process for eco-friendly pest control products. Efforts are underway to promote regulatory cooperation and mutual recognition agreements to facilitate the introduction of innovative, environmentally sensitive pest management solutions across borders.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating pest control products. Under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA), the EPA evaluates and registers pesticides based on their potential impact on human health and the environment. Sodium acetate, when used in pest management solutions, falls under this regulatory purview. The EPA's Biopesticides and Pollution Prevention Division specifically oversees the regulation of biochemical pesticides, which may include sodium acetate-based formulations.
The European Union has implemented stringent regulations through the European Commission's Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety. The EU's Sustainable Use of Pesticides Directive (Directive 2009/128/EC) promotes integrated pest management and the use of low-risk active substances. Sodium acetate, as a potential eco-friendly alternative, aligns with these regulatory objectives.
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea have established their own regulatory frameworks for eco-sensitive pest management solutions. The Japanese Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (MAFF) has implemented a registration system for biopesticides, which could potentially include sodium acetate-based products. Similarly, South Korea's Rural Development Administration oversees the registration and regulation of eco-friendly pest control products.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly focusing on promoting sustainable agriculture and reducing the environmental impact of pest management practices. This shift has led to the development of fast-track registration processes for low-risk substances and biopesticides in many jurisdictions. Sodium acetate, given its potential as an eco-friendly pest management solution, may benefit from these streamlined regulatory pathways.
However, challenges remain in harmonizing regulations across different countries and regions. Variations in testing requirements, data acceptance, and risk assessment methodologies can complicate the global registration process for eco-friendly pest control products. Efforts are underway to promote regulatory cooperation and mutual recognition agreements to facilitate the introduction of innovative, environmentally sensitive pest management solutions across borders.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!