Ammonium hydroxide in the synthesis of amino acid derivatives
AUG 14, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ammonium Hydroxide in Amino Acid Synthesis: Background
Ammonium hydroxide has played a significant role in the synthesis of amino acid derivatives, marking a crucial development in organic chemistry and biochemistry. This compound, also known as aqueous ammonia, has been utilized for decades as a key reagent in various synthetic pathways leading to the production of amino acids and their derivatives.
The use of ammonium hydroxide in amino acid synthesis can be traced back to the early 20th century when researchers began exploring efficient methods for producing these essential building blocks of proteins. Its popularity stems from its dual nature as both a base and a source of nitrogen, making it an ideal candidate for introducing amino groups into organic molecules.
One of the earliest and most notable applications of ammonium hydroxide in this field was the Strecker synthesis, developed by Adolph Strecker in 1850. This reaction involves the condensation of an aldehyde with ammonium hydroxide and hydrogen cyanide to form an α-aminonitrile, which can then be hydrolyzed to yield an α-amino acid. The Strecker synthesis laid the foundation for many subsequent developments in amino acid production.
As research in organic synthesis progressed, ammonium hydroxide found its way into numerous other methodologies for creating amino acid derivatives. Its role expanded beyond being a simple nitrogen source to include functions such as pH regulation, nucleophilic addition, and as a reagent in various coupling reactions.
The versatility of ammonium hydroxide in amino acid synthesis is further exemplified by its use in the Gabriel synthesis, where it serves to cleave phthalimide derivatives, releasing primary amines that can be further functionalized into amino acids. This method has been particularly valuable in the synthesis of non-proteinogenic amino acids and other specialized derivatives.
In recent decades, the application of ammonium hydroxide has evolved to meet the demands of modern synthetic chemistry. It has been incorporated into greener and more sustainable synthetic routes, aligning with the principles of green chemistry. Researchers have explored its use in aqueous reaction media, reducing the need for harmful organic solvents and improving the overall environmental impact of amino acid synthesis.
The ongoing research into the use of ammonium hydroxide in amino acid derivative synthesis reflects the compound's enduring importance in the field. As new synthetic challenges arise, particularly in the realm of unnatural amino acids and peptide mimetics, ammonium hydroxide continues to be a valuable tool in the chemist's arsenal, offering both versatility and efficiency in the creation of these vital molecular building blocks.
The use of ammonium hydroxide in amino acid synthesis can be traced back to the early 20th century when researchers began exploring efficient methods for producing these essential building blocks of proteins. Its popularity stems from its dual nature as both a base and a source of nitrogen, making it an ideal candidate for introducing amino groups into organic molecules.
One of the earliest and most notable applications of ammonium hydroxide in this field was the Strecker synthesis, developed by Adolph Strecker in 1850. This reaction involves the condensation of an aldehyde with ammonium hydroxide and hydrogen cyanide to form an α-aminonitrile, which can then be hydrolyzed to yield an α-amino acid. The Strecker synthesis laid the foundation for many subsequent developments in amino acid production.
As research in organic synthesis progressed, ammonium hydroxide found its way into numerous other methodologies for creating amino acid derivatives. Its role expanded beyond being a simple nitrogen source to include functions such as pH regulation, nucleophilic addition, and as a reagent in various coupling reactions.
The versatility of ammonium hydroxide in amino acid synthesis is further exemplified by its use in the Gabriel synthesis, where it serves to cleave phthalimide derivatives, releasing primary amines that can be further functionalized into amino acids. This method has been particularly valuable in the synthesis of non-proteinogenic amino acids and other specialized derivatives.
In recent decades, the application of ammonium hydroxide has evolved to meet the demands of modern synthetic chemistry. It has been incorporated into greener and more sustainable synthetic routes, aligning with the principles of green chemistry. Researchers have explored its use in aqueous reaction media, reducing the need for harmful organic solvents and improving the overall environmental impact of amino acid synthesis.
The ongoing research into the use of ammonium hydroxide in amino acid derivative synthesis reflects the compound's enduring importance in the field. As new synthetic challenges arise, particularly in the realm of unnatural amino acids and peptide mimetics, ammonium hydroxide continues to be a valuable tool in the chemist's arsenal, offering both versatility and efficiency in the creation of these vital molecular building blocks.
Market Analysis for Amino Acid Derivatives
The market for amino acid derivatives has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by their diverse applications across various industries. These derivatives find extensive use in pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, cosmetics, and agriculture sectors. The pharmaceutical industry, in particular, has been a major consumer of amino acid derivatives, utilizing them in the synthesis of peptides, proteins, and other biologically active compounds.
In the pharmaceutical sector, amino acid derivatives play a crucial role in drug development and manufacturing processes. They are essential components in the production of antibiotics, antihypertensive agents, and various other therapeutic drugs. The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases and the growing demand for personalized medicine have further boosted the market for amino acid derivatives in this sector.
The food and beverage industry represents another significant market for amino acid derivatives. These compounds are widely used as flavor enhancers, nutritional supplements, and preservatives. With the rising consumer awareness about health and wellness, there has been a surge in demand for functional foods and dietary supplements, which often incorporate amino acid derivatives.
The cosmetics and personal care industry has also emerged as a promising market for amino acid derivatives. These compounds are valued for their moisturizing, anti-aging, and skin-conditioning properties. As consumers become more conscious about the ingredients in their personal care products, the demand for natural and amino acid-based formulations has increased substantially.
In the agricultural sector, amino acid derivatives are utilized in the production of fertilizers and animal feed additives. They contribute to improved crop yields and enhanced animal nutrition, addressing the growing need for sustainable agricultural practices and food security.
The global market for amino acid derivatives is projected to continue its upward trajectory, with Asia-Pacific region expected to witness the highest growth rate. This can be attributed to the rapid industrialization, increasing population, and rising disposable incomes in countries like China and India. North America and Europe remain significant markets, driven by advancements in pharmaceutical research and development.
Key market trends include the increasing adoption of plant-based amino acid derivatives, driven by the growing preference for vegan and vegetarian products. Additionally, there is a rising focus on sustainable production methods and the development of novel amino acid derivatives with enhanced functionalities.
In the pharmaceutical sector, amino acid derivatives play a crucial role in drug development and manufacturing processes. They are essential components in the production of antibiotics, antihypertensive agents, and various other therapeutic drugs. The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases and the growing demand for personalized medicine have further boosted the market for amino acid derivatives in this sector.
The food and beverage industry represents another significant market for amino acid derivatives. These compounds are widely used as flavor enhancers, nutritional supplements, and preservatives. With the rising consumer awareness about health and wellness, there has been a surge in demand for functional foods and dietary supplements, which often incorporate amino acid derivatives.
The cosmetics and personal care industry has also emerged as a promising market for amino acid derivatives. These compounds are valued for their moisturizing, anti-aging, and skin-conditioning properties. As consumers become more conscious about the ingredients in their personal care products, the demand for natural and amino acid-based formulations has increased substantially.
In the agricultural sector, amino acid derivatives are utilized in the production of fertilizers and animal feed additives. They contribute to improved crop yields and enhanced animal nutrition, addressing the growing need for sustainable agricultural practices and food security.
The global market for amino acid derivatives is projected to continue its upward trajectory, with Asia-Pacific region expected to witness the highest growth rate. This can be attributed to the rapid industrialization, increasing population, and rising disposable incomes in countries like China and India. North America and Europe remain significant markets, driven by advancements in pharmaceutical research and development.
Key market trends include the increasing adoption of plant-based amino acid derivatives, driven by the growing preference for vegan and vegetarian products. Additionally, there is a rising focus on sustainable production methods and the development of novel amino acid derivatives with enhanced functionalities.
Current Challenges in Ammonium Hydroxide Utilization
The utilization of ammonium hydroxide in the synthesis of amino acid derivatives faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread adoption and efficiency. One of the primary issues is the control of reaction selectivity. Ammonium hydroxide, being a strong base, can lead to multiple side reactions, resulting in the formation of unwanted by-products. This not only reduces the yield of the desired amino acid derivatives but also complicates the purification process.
Another challenge lies in the pH control during the reaction. Ammonium hydroxide's high alkalinity can cause rapid pH fluctuations, which may affect the stability and reactivity of both reactants and products. Maintaining a consistent pH throughout the synthesis is crucial for optimal yield and product quality, but it requires sophisticated monitoring and control systems.
The volatility of ammonium hydroxide presents additional difficulties in handling and storage. Its tendency to evaporate at room temperature can lead to concentration variations, affecting reaction stoichiometry and reproducibility. This volatility also raises safety concerns, necessitating specialized equipment and protocols for its safe use in laboratory and industrial settings.
Furthermore, the environmental impact of ammonium hydroxide usage is a growing concern. Its production and application can contribute to ammonia emissions, which have implications for air quality and ecosystem health. Developing more environmentally friendly alternatives or improving the efficiency of ammonium hydroxide use is becoming increasingly important in the context of sustainable chemistry practices.
The scalability of processes involving ammonium hydroxide in amino acid derivative synthesis also poses challenges. What works efficiently at a laboratory scale may encounter significant hurdles when scaled up to industrial production levels. Issues such as heat dissipation, mixing efficiency, and reaction kinetics can become more pronounced at larger scales, necessitating extensive process optimization and potentially costly equipment modifications.
Lastly, the purity of commercially available ammonium hydroxide can vary, potentially affecting reaction outcomes and product quality. Trace impurities can catalyze undesired side reactions or introduce contaminants into the final product. Ensuring consistent high-quality ammonium hydroxide supply and developing robust purification methods for the synthesized amino acid derivatives are ongoing challenges in this field.
Another challenge lies in the pH control during the reaction. Ammonium hydroxide's high alkalinity can cause rapid pH fluctuations, which may affect the stability and reactivity of both reactants and products. Maintaining a consistent pH throughout the synthesis is crucial for optimal yield and product quality, but it requires sophisticated monitoring and control systems.
The volatility of ammonium hydroxide presents additional difficulties in handling and storage. Its tendency to evaporate at room temperature can lead to concentration variations, affecting reaction stoichiometry and reproducibility. This volatility also raises safety concerns, necessitating specialized equipment and protocols for its safe use in laboratory and industrial settings.
Furthermore, the environmental impact of ammonium hydroxide usage is a growing concern. Its production and application can contribute to ammonia emissions, which have implications for air quality and ecosystem health. Developing more environmentally friendly alternatives or improving the efficiency of ammonium hydroxide use is becoming increasingly important in the context of sustainable chemistry practices.
The scalability of processes involving ammonium hydroxide in amino acid derivative synthesis also poses challenges. What works efficiently at a laboratory scale may encounter significant hurdles when scaled up to industrial production levels. Issues such as heat dissipation, mixing efficiency, and reaction kinetics can become more pronounced at larger scales, necessitating extensive process optimization and potentially costly equipment modifications.
Lastly, the purity of commercially available ammonium hydroxide can vary, potentially affecting reaction outcomes and product quality. Trace impurities can catalyze undesired side reactions or introduce contaminants into the final product. Ensuring consistent high-quality ammonium hydroxide supply and developing robust purification methods for the synthesized amino acid derivatives are ongoing challenges in this field.
Existing Ammonium Hydroxide-Based Synthesis Protocols
01 Use of ammonium hydroxide in chemical processes
Ammonium hydroxide is widely used in various chemical processes as a reactant, catalyst, or pH regulator. It plays a crucial role in the synthesis of organic compounds, production of fertilizers, and treatment of industrial waste. Its alkaline properties make it suitable for neutralization reactions and as a cleaning agent in industrial applications.- Use in chemical processes: Ammonium hydroxide is widely used in various chemical processes as a reactant, catalyst, or pH regulator. It plays a crucial role in the synthesis of organic compounds, production of fertilizers, and treatment of industrial waste. Its alkaline properties make it useful for neutralizing acids and controlling pH levels in different applications.
- Application in cleaning and surface treatment: Ammonium hydroxide is utilized in cleaning formulations and surface treatment processes. It is effective in removing grease, oils, and other contaminants from various surfaces. In the semiconductor industry, it is used for etching and cleaning silicon wafers. It also finds applications in the textile industry for fabric treatment and in the leather industry for dehairing hides.
- Role in environmental applications: Ammonium hydroxide is employed in environmental applications, particularly in air pollution control and water treatment. It is used to neutralize acidic gases in flue gas desulfurization processes and to remove nitrogen oxides from industrial emissions. In water treatment, it helps in adjusting pH levels and removing heavy metals through precipitation.
- Use in personal care and cosmetic products: Ammonium hydroxide is utilized in various personal care and cosmetic products. It acts as a pH adjuster in shampoos, hair dyes, and other hair care products. In some cosmetic formulations, it helps to stabilize emulsions and adjust the overall pH of the product. Its alkaline nature also makes it useful in certain depilatory creams and hair relaxers.
- Application in food processing: Ammonium hydroxide finds applications in food processing as a leavening agent and pH regulator. It is used in the production of certain types of caramel coloring and as a processing aid in cocoa and chocolate manufacturing. In some countries, it is approved as a food additive for specific purposes, such as regulating acidity in baked goods.
02 Application in hair coloring and treatment
Ammonium hydroxide is commonly used in hair dye formulations and hair treatment products. It helps to open the hair cuticle, allowing color molecules to penetrate the hair shaft more effectively. Additionally, it can be used to adjust the pH of hair care products, enhancing their performance and stability.Expand Specific Solutions03 Role in textile processing and dyeing
In the textile industry, ammonium hydroxide is utilized for various purposes, including fabric treatment, dyeing, and printing processes. It can act as a pH regulator, dye fixative, or assist in the removal of impurities from textiles. Its alkaline nature helps in improving the color fastness and overall quality of dyed fabrics.Expand Specific Solutions04 Use in cleaning and surface treatment
Ammonium hydroxide is an effective cleaning agent and is used in various household and industrial cleaning products. It can remove grease, grime, and stubborn stains from surfaces. In addition, it is employed in surface treatment processes, such as etching and polishing of metals and semiconductors, due to its ability to dissolve certain materials and modify surface properties.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and agricultural applications
Ammonium hydroxide finds applications in environmental remediation and agriculture. It can be used to neutralize acidic soils, control emissions from industrial processes, and as a component in fertilizers. In wastewater treatment, it helps in the removal of pollutants and adjustment of pH levels. Its role in nitrogen fixation makes it valuable for improving soil fertility and crop yields.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Amino Acid Derivative Industry
The research on ammonium hydroxide in amino acid derivative synthesis is in a mature phase, with a substantial market size due to its wide applications in pharmaceuticals and chemical industries. The technology has reached a high level of maturity, as evidenced by the involvement of major players like Novartis AG, Bayer AG, and Ajinomoto Co., Inc. These companies, along with others such as Solvay SA and UCB Pharma GmbH, have established strong positions in the field, leveraging their extensive R&D capabilities and global presence. The competitive landscape is characterized by ongoing innovation and strategic collaborations, with academic institutions like Dresden University of Technology contributing to advancements in the field.
Solvay SA
Technical Solution: Solvay has developed an innovative approach to the synthesis of amino acid derivatives using ammonium hydroxide, leveraging their expertise in chemical manufacturing and process optimization. Their method involves a carefully controlled reaction between ammonium hydroxide and specific amino acid precursors in a specially designed reactor system. Solvay's process incorporates advanced process intensification techniques, such as microreactor technology, to enhance reaction efficiency and product selectivity[1]. The company has also developed a proprietary catalyst system that facilitates the desired transformations while minimizing side reactions[2]. Furthermore, Solvay has implemented a sustainable manufacturing approach, utilizing ammonium hydroxide not only as a reactant but also as a key component in their closed-loop recycling system, significantly reducing waste and improving overall process economics[3]. Their technology also includes advanced separation and purification techniques, ensuring high-quality amino acid derivatives suitable for various industrial applications[4].
Strengths: Highly efficient and sustainable process, versatile production capabilities, advanced reactor and catalyst technologies. Weaknesses: May require significant capital investment for implementation, potential challenges in scaling up for certain types of amino acid derivatives.
Ajinomoto Co., Inc.
Technical Solution: Ajinomoto has developed an innovative approach for the synthesis of amino acid derivatives using ammonium hydroxide. Their method involves a controlled reaction between ammonium hydroxide and specific precursor molecules in a carefully optimized environment. This process allows for the efficient production of various amino acid derivatives with high purity and yield[1]. The company has also implemented a green chemistry approach, utilizing ammonium hydroxide as both a reactant and a pH regulator, reducing the need for additional chemicals[2]. Ajinomoto's technology incorporates advanced catalysts that enhance selectivity and reduce side reactions, leading to improved product quality and reduced waste[3]. Furthermore, they have developed a continuous flow reactor system that allows for better control of reaction parameters and increased scalability[4].
Strengths: High efficiency and yield, environmentally friendly approach, versatile production of various amino acid derivatives. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment and expertise, potential safety concerns with handling ammonium hydroxide at scale.
Innovative Approaches in Ammonium Hydroxide Application
Process for producing amino acid derivative from hydroxyimino acid
PatentInactiveEP1806408A4
Innovation
- Use of microorganisms and/or enzymes to catalyze the conversion of hydroxyimino acids to amino acid derivatives.
- Broad applicability of the method to various hydroxyimino acids with different R1 substituents and alkyl groups.
- Industrial scalability of the process for producing amino acid derivatives.
Process for the preparation of amino acid derivatives
PatentWO2012041986A1
Innovation
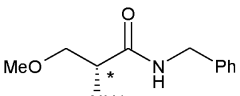
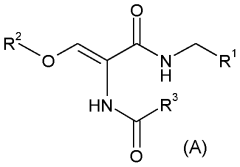
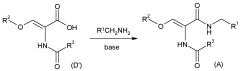
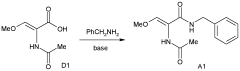
- A novel process involving the synthesis of (Z)-2-acetamido-N-benzyl-3-methoxyacrylamide using specific base and solvent conditions, followed by catalytic asymmetric hydrogenation with rhodium-based chiral catalysts, eliminates the need for costly chiral ligands and separation methods, achieving high enantiomeric excess and scalability.
Environmental Impact of Ammonium Hydroxide Use
The use of ammonium hydroxide in the synthesis of amino acid derivatives has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. This chemical compound, while essential for certain industrial processes, can pose risks to ecosystems and human health if not properly managed.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with ammonium hydroxide is its potential to contribute to eutrophication in aquatic ecosystems. When released into water bodies, excess ammonia can lead to algal blooms, which deplete oxygen levels and harm aquatic life. This impact is particularly pronounced in freshwater systems, where even small increases in ammonia concentrations can disrupt the delicate balance of aquatic ecosystems.
Atmospheric emissions of ammonia from industrial processes using ammonium hydroxide can also contribute to air pollution. Ammonia is a precursor to particulate matter formation, which can have adverse effects on air quality and human respiratory health. Moreover, ammonia emissions can lead to the formation of acid rain when combined with other atmospheric pollutants, potentially damaging vegetation and acidifying soil and water bodies.
The production and transportation of ammonium hydroxide also carry environmental risks. Accidental spills or leaks during handling and transport can result in localized environmental damage, affecting soil quality and potentially contaminating groundwater resources. Such incidents may require extensive remediation efforts and can have long-lasting impacts on local ecosystems.
However, it is important to note that the environmental impact of ammonium hydroxide use in amino acid derivative synthesis can be mitigated through proper management and control measures. Implementing closed-loop systems, improving process efficiency, and employing advanced treatment technologies for waste streams can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of these industrial processes.
Furthermore, research into green chemistry alternatives and sustainable synthesis methods is ongoing, aiming to develop more environmentally friendly approaches to amino acid derivative production. These efforts focus on reducing the reliance on harsh chemicals like ammonium hydroxide and exploring bio-based or catalytic processes that minimize environmental impact.
In conclusion, while the use of ammonium hydroxide in amino acid derivative synthesis presents environmental challenges, ongoing research and technological advancements offer promising avenues for mitigating these impacts. Balancing the industrial need for this chemical with environmental protection requires a comprehensive approach, incorporating best practices in chemical management, innovative process design, and continuous improvement in environmental performance.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with ammonium hydroxide is its potential to contribute to eutrophication in aquatic ecosystems. When released into water bodies, excess ammonia can lead to algal blooms, which deplete oxygen levels and harm aquatic life. This impact is particularly pronounced in freshwater systems, where even small increases in ammonia concentrations can disrupt the delicate balance of aquatic ecosystems.
Atmospheric emissions of ammonia from industrial processes using ammonium hydroxide can also contribute to air pollution. Ammonia is a precursor to particulate matter formation, which can have adverse effects on air quality and human respiratory health. Moreover, ammonia emissions can lead to the formation of acid rain when combined with other atmospheric pollutants, potentially damaging vegetation and acidifying soil and water bodies.
The production and transportation of ammonium hydroxide also carry environmental risks. Accidental spills or leaks during handling and transport can result in localized environmental damage, affecting soil quality and potentially contaminating groundwater resources. Such incidents may require extensive remediation efforts and can have long-lasting impacts on local ecosystems.
However, it is important to note that the environmental impact of ammonium hydroxide use in amino acid derivative synthesis can be mitigated through proper management and control measures. Implementing closed-loop systems, improving process efficiency, and employing advanced treatment technologies for waste streams can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of these industrial processes.
Furthermore, research into green chemistry alternatives and sustainable synthesis methods is ongoing, aiming to develop more environmentally friendly approaches to amino acid derivative production. These efforts focus on reducing the reliance on harsh chemicals like ammonium hydroxide and exploring bio-based or catalytic processes that minimize environmental impact.
In conclusion, while the use of ammonium hydroxide in amino acid derivative synthesis presents environmental challenges, ongoing research and technological advancements offer promising avenues for mitigating these impacts. Balancing the industrial need for this chemical with environmental protection requires a comprehensive approach, incorporating best practices in chemical management, innovative process design, and continuous improvement in environmental performance.
Regulatory Framework for Chemical Synthesis Processes
The regulatory framework for chemical synthesis processes involving ammonium hydroxide in the production of amino acid derivatives is complex and multifaceted. Regulatory bodies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States, as well as their counterparts in other countries, play crucial roles in overseeing these processes.
Environmental regulations are a primary concern, focusing on the potential impacts of ammonium hydroxide and its byproducts on air and water quality. The Clean Air Act and Clean Water Act in the U.S. set stringent standards for emissions and effluents from chemical synthesis facilities. Companies must obtain permits and implement control technologies to minimize the release of ammonia and other potentially harmful substances.
Workplace safety regulations are equally important, given the hazardous nature of ammonium hydroxide. OSHA's Hazard Communication Standard requires proper labeling, safety data sheets, and employee training on the safe handling of this chemical. Additionally, specific standards for personal protective equipment, emergency response procedures, and ventilation systems must be adhered to in facilities using ammonium hydroxide.
The transportation of ammonium hydroxide is regulated by the Department of Transportation (DOT) in the U.S. and similar agencies worldwide. These regulations cover packaging, labeling, and shipping requirements to ensure safe transport of this corrosive material.
Product safety and quality regulations also apply to amino acid derivatives synthesized using ammonium hydroxide. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the production of amino acids intended for human consumption or pharmaceutical use, enforcing Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and conducting inspections to ensure product safety and efficacy.
International regulations, such as the European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) program, add another layer of complexity for global manufacturers. These regulations require extensive documentation and testing of chemical substances, including those used in and produced by the synthesis of amino acid derivatives.
Compliance with these diverse regulations requires a comprehensive management system, including regular audits, employee training, and meticulous record-keeping. Companies must stay abreast of regulatory changes and adapt their processes accordingly to maintain compliance and ensure the safety of workers, consumers, and the environment.
Environmental regulations are a primary concern, focusing on the potential impacts of ammonium hydroxide and its byproducts on air and water quality. The Clean Air Act and Clean Water Act in the U.S. set stringent standards for emissions and effluents from chemical synthesis facilities. Companies must obtain permits and implement control technologies to minimize the release of ammonia and other potentially harmful substances.
Workplace safety regulations are equally important, given the hazardous nature of ammonium hydroxide. OSHA's Hazard Communication Standard requires proper labeling, safety data sheets, and employee training on the safe handling of this chemical. Additionally, specific standards for personal protective equipment, emergency response procedures, and ventilation systems must be adhered to in facilities using ammonium hydroxide.
The transportation of ammonium hydroxide is regulated by the Department of Transportation (DOT) in the U.S. and similar agencies worldwide. These regulations cover packaging, labeling, and shipping requirements to ensure safe transport of this corrosive material.
Product safety and quality regulations also apply to amino acid derivatives synthesized using ammonium hydroxide. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the production of amino acids intended for human consumption or pharmaceutical use, enforcing Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and conducting inspections to ensure product safety and efficacy.
International regulations, such as the European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) program, add another layer of complexity for global manufacturers. These regulations require extensive documentation and testing of chemical substances, including those used in and produced by the synthesis of amino acid derivatives.
Compliance with these diverse regulations requires a comprehensive management system, including regular audits, employee training, and meticulous record-keeping. Companies must stay abreast of regulatory changes and adapt their processes accordingly to maintain compliance and ensure the safety of workers, consumers, and the environment.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!