Solvent Selection And Management For Continuous Flow Processes
SEP 3, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Continuous Flow Solvent Technology Background and Objectives
Continuous flow processing represents a paradigm shift in chemical manufacturing, transitioning from traditional batch processes to more efficient, controlled, and sustainable continuous operations. The evolution of this technology began in the early 2000s, primarily driven by the pharmaceutical industry's need for more efficient production methods. Over the past two decades, continuous flow technology has expanded across multiple sectors including fine chemicals, agrochemicals, and specialty materials manufacturing.
Solvent selection and management constitute critical aspects of continuous flow processes, directly impacting reaction efficiency, product quality, and process economics. Historically, solvent considerations were often secondary to reaction parameters in process development. However, as continuous manufacturing gained prominence, the unique demands of uninterrupted flow systems elevated solvent properties to primary design considerations.
The technological trajectory shows increasing sophistication in solvent systems, moving from simple single-solvent approaches to complex multi-solvent strategies that enable challenging chemistries and in-line separations. Recent advances in green chemistry principles have further shaped solvent selection criteria, emphasizing reduced environmental impact and improved safety profiles.
Current research focuses on developing solvent systems that maintain homogeneity throughout the process, prevent precipitation or crystallization that might cause clogging, and enable efficient downstream processing. The integration of real-time monitoring and control systems for solvent parameters represents another significant trend, allowing for dynamic adjustments during operation.
The primary technical objectives for continuous flow solvent technology include: developing universal solvent systems compatible with diverse reaction conditions; creating switchable solvent properties that can be modified in-line; establishing predictive models for solvent behavior under continuous flow conditions; and designing integrated solvent recovery and recycling systems to enhance sustainability.
Industry objectives center on cost reduction through solvent minimization, improved process robustness through better solvent management, and regulatory compliance through the elimination of problematic solvents. There is also growing interest in solvent-free or significantly reduced-solvent approaches that maintain the benefits of continuous processing while further reducing environmental impact.
The convergence of continuous flow technology with advances in computational chemistry and machine learning offers promising pathways for optimizing solvent selection. These tools enable rapid screening of solvent combinations and prediction of behavior under flow conditions, accelerating development cycles and expanding the range of feasible chemistries in continuous manufacturing.
Solvent selection and management constitute critical aspects of continuous flow processes, directly impacting reaction efficiency, product quality, and process economics. Historically, solvent considerations were often secondary to reaction parameters in process development. However, as continuous manufacturing gained prominence, the unique demands of uninterrupted flow systems elevated solvent properties to primary design considerations.
The technological trajectory shows increasing sophistication in solvent systems, moving from simple single-solvent approaches to complex multi-solvent strategies that enable challenging chemistries and in-line separations. Recent advances in green chemistry principles have further shaped solvent selection criteria, emphasizing reduced environmental impact and improved safety profiles.
Current research focuses on developing solvent systems that maintain homogeneity throughout the process, prevent precipitation or crystallization that might cause clogging, and enable efficient downstream processing. The integration of real-time monitoring and control systems for solvent parameters represents another significant trend, allowing for dynamic adjustments during operation.
The primary technical objectives for continuous flow solvent technology include: developing universal solvent systems compatible with diverse reaction conditions; creating switchable solvent properties that can be modified in-line; establishing predictive models for solvent behavior under continuous flow conditions; and designing integrated solvent recovery and recycling systems to enhance sustainability.
Industry objectives center on cost reduction through solvent minimization, improved process robustness through better solvent management, and regulatory compliance through the elimination of problematic solvents. There is also growing interest in solvent-free or significantly reduced-solvent approaches that maintain the benefits of continuous processing while further reducing environmental impact.
The convergence of continuous flow technology with advances in computational chemistry and machine learning offers promising pathways for optimizing solvent selection. These tools enable rapid screening of solvent combinations and prediction of behavior under flow conditions, accelerating development cycles and expanding the range of feasible chemistries in continuous manufacturing.
Market Analysis for Continuous Flow Processing Solutions
The continuous flow processing market has witnessed substantial growth over the past decade, driven by increasing demand for more efficient and sustainable manufacturing processes across multiple industries. The global market for continuous flow processing solutions was valued at approximately 1.2 billion USD in 2022 and is projected to reach 2.5 billion USD by 2028, representing a compound annual growth rate of 13.2%.
Pharmaceutical and fine chemical industries currently dominate the market landscape, accounting for nearly 60% of the total market share. This dominance stems from stringent regulatory requirements, pressure to reduce production costs, and the need for consistent product quality. The pharmaceutical sector, in particular, has embraced continuous flow technologies to address challenges in API manufacturing and formulation processes.
Emerging applications in specialty chemicals, agrochemicals, and polymer production are expanding the market footprint. These sectors are increasingly adopting continuous flow technologies to enhance reaction selectivity, improve yield, and reduce waste generation. The specialty chemicals segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate, with a projected CAGR of 15.7% through 2028.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the market with combined market share exceeding 65%. This dominance reflects the concentration of pharmaceutical and chemical manufacturing facilities, robust R&D infrastructure, and supportive regulatory frameworks in these regions. However, Asia-Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing market, driven by rapid industrialization in China and India, increasing investment in pharmaceutical manufacturing, and government initiatives promoting advanced manufacturing technologies.
Key market drivers include increasing pressure for sustainable manufacturing processes, rising demand for continuous manufacturing in pharmaceuticals, and technological advancements in process analytical technologies (PAT) and automation systems. The integration of digital technologies and Industry 4.0 concepts is further accelerating market growth by enabling real-time monitoring and control of continuous flow processes.
Challenges hindering market growth include high initial investment costs, technical complexity in solvent management systems, and regulatory uncertainties. The transition from batch to continuous processing requires significant capital expenditure and specialized expertise, creating barriers to adoption, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises.
Customer demand trends indicate growing interest in modular and flexible continuous flow systems that can be easily reconfigured for different processes. There is also increasing demand for integrated solutions that combine reaction, separation, and purification steps in a single continuous process train, with particular emphasis on efficient solvent management systems that minimize environmental impact.
Pharmaceutical and fine chemical industries currently dominate the market landscape, accounting for nearly 60% of the total market share. This dominance stems from stringent regulatory requirements, pressure to reduce production costs, and the need for consistent product quality. The pharmaceutical sector, in particular, has embraced continuous flow technologies to address challenges in API manufacturing and formulation processes.
Emerging applications in specialty chemicals, agrochemicals, and polymer production are expanding the market footprint. These sectors are increasingly adopting continuous flow technologies to enhance reaction selectivity, improve yield, and reduce waste generation. The specialty chemicals segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate, with a projected CAGR of 15.7% through 2028.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the market with combined market share exceeding 65%. This dominance reflects the concentration of pharmaceutical and chemical manufacturing facilities, robust R&D infrastructure, and supportive regulatory frameworks in these regions. However, Asia-Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing market, driven by rapid industrialization in China and India, increasing investment in pharmaceutical manufacturing, and government initiatives promoting advanced manufacturing technologies.
Key market drivers include increasing pressure for sustainable manufacturing processes, rising demand for continuous manufacturing in pharmaceuticals, and technological advancements in process analytical technologies (PAT) and automation systems. The integration of digital technologies and Industry 4.0 concepts is further accelerating market growth by enabling real-time monitoring and control of continuous flow processes.
Challenges hindering market growth include high initial investment costs, technical complexity in solvent management systems, and regulatory uncertainties. The transition from batch to continuous processing requires significant capital expenditure and specialized expertise, creating barriers to adoption, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises.
Customer demand trends indicate growing interest in modular and flexible continuous flow systems that can be easily reconfigured for different processes. There is also increasing demand for integrated solutions that combine reaction, separation, and purification steps in a single continuous process train, with particular emphasis on efficient solvent management systems that minimize environmental impact.
Current Solvent Management Challenges in Flow Chemistry
Flow chemistry processes face significant challenges in solvent management that impact efficiency, sustainability, and scalability. The selection of appropriate solvents represents a critical decision point, as many traditional batch chemistry solvents prove problematic in continuous flow environments. High viscosity solvents create excessive back-pressure in microreactors and narrow channels, leading to flow irregularities and potential system failures. This physical limitation restricts the use of certain otherwise chemically suitable solvents.
Solubility issues present another major challenge, as continuous processes require complete dissolution of reagents to prevent clogging of narrow channels. Precipitation during reactions can cause system blockages, leading to costly downtime and maintenance requirements. Unlike batch processes where precipitates can often be managed through stirring, flow systems have limited tolerance for solid formation.
Thermal management challenges are particularly pronounced in flow chemistry. The high surface-to-volume ratio in flow reactors, while beneficial for heat transfer, creates unique solvent demands. Solvents must maintain appropriate thermal properties across temperature ranges, especially in exothermic reactions where heat dissipation is critical for safety and reaction control.
Material compatibility represents a persistent challenge, as solvents must remain compatible with all system components including pumps, tubing, seals, and reactor materials. Aggressive solvents can degrade system components over time, leading to contamination, leaks, or equipment failure. This compatibility requirement often narrows the available solvent options significantly.
Multi-phase systems present particular difficulties in flow chemistry. Gas-liquid, liquid-liquid, or solid-liquid interfaces must be carefully managed to ensure consistent mixing and reaction conditions. Solvents that facilitate phase transitions or stabilize interfaces are highly valuable but challenging to identify and implement effectively.
Waste management and environmental considerations have become increasingly important. Traditional solvent-intensive processes face regulatory scrutiny and sustainability challenges. Flow chemistry offers potential advantages through reduced solvent volumes, but requires sophisticated recovery and recycling systems to fully realize these benefits.
Real-time monitoring and control of solvent parameters remains technically challenging. Unlike batch processes where periodic sampling is sufficient, continuous flow requires constant monitoring of solvent properties to ensure process stability. The development of inline analytical techniques for solvent monitoring represents an active area of research with significant technical hurdles.
Solubility issues present another major challenge, as continuous processes require complete dissolution of reagents to prevent clogging of narrow channels. Precipitation during reactions can cause system blockages, leading to costly downtime and maintenance requirements. Unlike batch processes where precipitates can often be managed through stirring, flow systems have limited tolerance for solid formation.
Thermal management challenges are particularly pronounced in flow chemistry. The high surface-to-volume ratio in flow reactors, while beneficial for heat transfer, creates unique solvent demands. Solvents must maintain appropriate thermal properties across temperature ranges, especially in exothermic reactions where heat dissipation is critical for safety and reaction control.
Material compatibility represents a persistent challenge, as solvents must remain compatible with all system components including pumps, tubing, seals, and reactor materials. Aggressive solvents can degrade system components over time, leading to contamination, leaks, or equipment failure. This compatibility requirement often narrows the available solvent options significantly.
Multi-phase systems present particular difficulties in flow chemistry. Gas-liquid, liquid-liquid, or solid-liquid interfaces must be carefully managed to ensure consistent mixing and reaction conditions. Solvents that facilitate phase transitions or stabilize interfaces are highly valuable but challenging to identify and implement effectively.
Waste management and environmental considerations have become increasingly important. Traditional solvent-intensive processes face regulatory scrutiny and sustainability challenges. Flow chemistry offers potential advantages through reduced solvent volumes, but requires sophisticated recovery and recycling systems to fully realize these benefits.
Real-time monitoring and control of solvent parameters remains technically challenging. Unlike batch processes where periodic sampling is sufficient, continuous flow requires constant monitoring of solvent properties to ensure process stability. The development of inline analytical techniques for solvent monitoring represents an active area of research with significant technical hurdles.
Current Solvent Selection Methodologies and Systems
01 Environmentally friendly solvent selection
Selection of environmentally friendly solvents is crucial for sustainable manufacturing processes. These solvents typically have lower toxicity, reduced environmental impact, and better biodegradability compared to traditional options. The selection process involves evaluating factors such as vapor pressure, boiling point, and environmental persistence. Green solvents can include bio-based alternatives, water-based systems, and those derived from renewable resources, which help reduce the carbon footprint of industrial processes.- Environmentally friendly solvent selection: Selection of environmentally friendly solvents is crucial for reducing environmental impact while maintaining process efficiency. These solvents typically have lower toxicity, reduced VOC emissions, and better biodegradability profiles. The selection process involves evaluating physical properties, environmental impact assessments, and compatibility with specific applications. Green solvents derived from renewable resources are increasingly preferred as alternatives to petroleum-based options.
- Solvent management systems and automation: Advanced solvent management systems incorporate automation technologies to optimize solvent usage, recovery, and disposal. These systems utilize sensors, monitoring equipment, and control algorithms to maintain optimal solvent conditions, reduce waste, and ensure consistent quality. Automated systems can track solvent parameters in real-time, adjust process variables, and implement predictive maintenance protocols to prevent system failures and minimize downtime.
- Solvent recovery and recycling techniques: Efficient solvent recovery and recycling techniques are essential for sustainable manufacturing processes. These techniques include distillation, membrane separation, adsorption, and condensation methods to capture and purify used solvents. Implementing closed-loop systems allows for continuous solvent reuse, reducing raw material costs and waste disposal requirements. Advanced recovery systems can achieve high purity levels, making recycled solvents suitable for reintroduction into sensitive manufacturing processes.
- Solvent compatibility and formulation optimization: Optimizing solvent formulations requires careful consideration of compatibility with active ingredients, substrates, and processing equipment. Proper solvent selection can enhance product stability, improve dissolution rates, and ensure consistent performance. Formulation techniques may include using solvent blends to achieve desired properties, incorporating co-solvents to improve solubility, and adjusting polarity parameters to optimize extraction or reaction efficiency. Compatibility testing protocols help identify potential interactions that could compromise product quality or process safety.
- Digital solutions for solvent inventory and compliance management: Digital platforms and software solutions enable comprehensive solvent inventory management and regulatory compliance. These systems track solvent usage, storage conditions, and disposal records while generating documentation for regulatory reporting. Advanced analytics can identify optimization opportunities, predict usage patterns, and ensure adherence to safety standards. Cloud-based solutions facilitate real-time monitoring across multiple facilities and enable integration with enterprise resource planning systems for improved supply chain management and cost control.
02 Solvent management systems and automation
Advanced solvent management systems utilize automation and digital technologies to optimize solvent usage, recovery, and disposal. These systems incorporate sensors, monitoring equipment, and control algorithms to maintain optimal solvent conditions, reduce waste, and ensure process efficiency. Automated solvent management can include real-time tracking of solvent properties, predictive maintenance scheduling, and integration with manufacturing execution systems, resulting in improved operational performance and reduced environmental impact.Expand Specific Solutions03 Solvent recovery and recycling techniques
Solvent recovery and recycling techniques are essential for cost reduction and environmental compliance in industrial processes. These techniques include distillation, membrane separation, adsorption, and condensation methods to capture and purify used solvents for reuse. Implementing effective solvent recovery systems can significantly reduce raw material costs, waste disposal expenses, and environmental emissions while helping facilities meet regulatory requirements for volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Solvent compatibility and stability assessment
Assessing solvent compatibility and stability is critical for ensuring product quality and process safety. This involves evaluating how solvents interact with other materials in the system, including active ingredients, containers, equipment surfaces, and other formulation components. Stability testing under various conditions such as temperature, light exposure, and storage duration helps predict shelf life and maintain product integrity. Proper compatibility assessment prevents issues like precipitation, degradation, corrosion, and unwanted chemical reactions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Regulatory compliance and safety protocols for solvents
Maintaining regulatory compliance and implementing robust safety protocols for solvent handling is essential in industrial settings. This includes adherence to local and international regulations regarding storage, handling, transportation, and disposal of solvents. Safety measures encompass proper ventilation systems, personal protective equipment requirements, emergency response procedures, and employee training programs. Comprehensive documentation and regular audits ensure ongoing compliance with evolving regulations and industry standards for solvent management.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies in Continuous Flow Solvent Technology
The continuous flow process solvent selection market is in a growth phase, with increasing adoption across pharmaceutical, chemical, and petrochemical industries. Market size is expanding as companies seek more efficient and sustainable manufacturing methods. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels, with established players like ExxonMobil Chemical and Saudi Aramco leading industrial applications, while academic institutions such as University of Barcelona and University of Strathclyde drive fundamental research. Companies like Illumina and Hovione Scientia are advancing specialized applications in life sciences, while equipment manufacturers including Siemens AG and Tokyo Electron are developing integrated solutions. Water treatment specialists Kurita and Ovivo are extending continuous flow technologies to environmental applications, creating a diverse competitive landscape balancing innovation with practical implementation.
ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, Inc.
Technical Solution: ExxonMobil has developed an integrated solvent selection framework for continuous flow processes that combines computational modeling with experimental validation. Their approach utilizes molecular dynamics simulations to predict solvent-solute interactions and reaction kinetics in flow conditions. The company has implemented a multi-parameter optimization system that evaluates solvents based on reaction efficiency, separation ease, environmental impact, and economic factors. Their technology includes real-time monitoring systems with inline spectroscopic tools (IR, Raman, UV-Vis) that provide feedback for automated solvent composition adjustments during continuous operation. ExxonMobil has also pioneered switchable solvent systems that can change properties (polarity, miscibility) through temperature or pH triggers, facilitating downstream separations without additional solvents. Their solvent recovery systems achieve up to 95% recycling rates, significantly reducing waste and operational costs in large-scale petrochemical processes.
Strengths: Superior computational modeling capabilities for solvent behavior prediction; extensive experience with industrial-scale implementation; highly efficient solvent recovery systems. Weaknesses: Solutions primarily optimized for petrochemical applications; high capital investment requirements; complex implementation requiring specialized expertise.
University of Strathclyde
Technical Solution: The University of Strathclyde has developed the Continuous Solvent Selection and Optimization Platform (CSSOP) for flow chemistry applications. This platform integrates machine learning algorithms with experimental data to rapidly identify optimal solvent systems for specific reaction classes. Their approach employs a combination of Hansen solubility parameters and quantum mechanical calculations to predict solvent effects on reaction rates and selectivity. The university has pioneered microfluidic-based high-throughput screening methods that can evaluate dozens of solvent combinations simultaneously under flow conditions. Their research has demonstrated particular success with multiphasic reactions, developing novel strategies for solvent selection that enhance mass transfer across phase boundaries. The CSSOP system incorporates sustainability metrics, evaluating solvents based on EHS (Environmental, Health and Safety) profiles alongside performance parameters. Recent publications have shown their methodology reduces solvent screening time by approximately 70% compared to traditional approaches, while identifying more efficient solvent systems for pharmaceutical and fine chemical synthesis.
Strengths: Cutting-edge integration of computational and experimental approaches; strong focus on green chemistry principles; excellent capabilities for multiphasic reactions. Weaknesses: Less experience with industrial-scale implementation; solutions may require adaptation for commercial manufacturing; primarily focused on pharmaceutical applications rather than broader chemical processing.
Key Innovations in Solvent Management for Flow Processes
Solvent selection process
PatentInactiveUS20140262961A1
Innovation
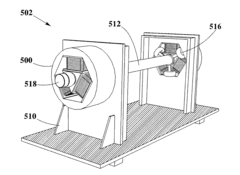
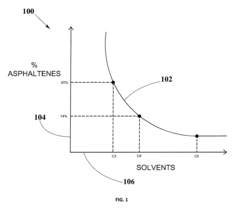
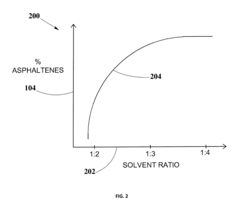
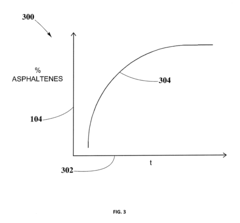
- A method for solvent selection using a computer-based analysis integrating market demands, oil characteristics, equipment capabilities, and solvent properties, including charts and algorithms to optimize solvent choice for asphaltenes separation, reducing solvent usage and equipment requirements.
Monitoring by means of an on-line sensor and fluidic operations involving unit separation and reaction operations
PatentInactiveEP1877768A2
Innovation
- The use of mechanical resonators, particularly flexural resonators, for real-time monitoring and control of fluid processes by contacting a sensing surface with the fluid and stimulating it to monitor responses, allowing for continuous composition analysis and process adjustments.
Sustainability Impact and Circular Economy Integration
The integration of sustainable practices in solvent selection and management for continuous flow processes represents a critical frontier in green chemistry evolution. Continuous flow technologies inherently offer environmental advantages through improved efficiency and reduced waste, but their full sustainability potential can only be realized through deliberate solvent considerations aligned with circular economy principles.
Solvent usage in continuous manufacturing accounts for approximately 80-90% of total mass in pharmaceutical and fine chemical processes, presenting both a significant environmental challenge and opportunity. Recent lifecycle assessments demonstrate that transitioning from batch to continuous processing with optimized solvent selection can reduce carbon footprints by 30-50% while decreasing water usage by up to 60%.
The circular economy approach to solvent management in flow chemistry encompasses three interconnected strategies: solvent elimination, substitution with greener alternatives, and recycling/recovery systems. Process intensification techniques unique to flow systems, such as microreactor technology and supercritical fluid applications, have enabled solvent-free or significantly reduced-solvent methodologies previously unattainable in batch processes.
Bio-derived solvents represent a growing alternative in continuous flow applications, with cyrene, 2-methyltetrahydrofuran, and ethyl lactate demonstrating comparable or superior performance to traditional petrochemical solvents in many reactions. These alternatives typically reduce ecotoxicity by 40-70% while maintaining or enhancing reaction efficiency when properly implemented in flow systems.
Integrated solvent recovery technologies specifically designed for continuous processes have advanced significantly, with membrane separation, adsorption systems, and in-line distillation achieving recovery rates exceeding 95% in many applications. These technologies, when incorporated into closed-loop continuous manufacturing, create near-circular solvent utilization pathways that dramatically reduce environmental impact and operating costs.
Economic analyses indicate that comprehensive solvent management strategies in continuous flow processes can reduce operational costs by 15-25% through decreased solvent consumption and waste treatment requirements. Additionally, these approaches mitigate regulatory compliance risks associated with increasingly stringent environmental legislation worldwide.
The pharmaceutical industry has emerged as a leader in this domain, with several major manufacturers implementing continuous flow platforms with integrated solvent recovery systems that align with green chemistry metrics and circular economy principles. These implementations serve as valuable case studies demonstrating both environmental and economic benefits achievable through thoughtful solvent management in continuous processing.
Solvent usage in continuous manufacturing accounts for approximately 80-90% of total mass in pharmaceutical and fine chemical processes, presenting both a significant environmental challenge and opportunity. Recent lifecycle assessments demonstrate that transitioning from batch to continuous processing with optimized solvent selection can reduce carbon footprints by 30-50% while decreasing water usage by up to 60%.
The circular economy approach to solvent management in flow chemistry encompasses three interconnected strategies: solvent elimination, substitution with greener alternatives, and recycling/recovery systems. Process intensification techniques unique to flow systems, such as microreactor technology and supercritical fluid applications, have enabled solvent-free or significantly reduced-solvent methodologies previously unattainable in batch processes.
Bio-derived solvents represent a growing alternative in continuous flow applications, with cyrene, 2-methyltetrahydrofuran, and ethyl lactate demonstrating comparable or superior performance to traditional petrochemical solvents in many reactions. These alternatives typically reduce ecotoxicity by 40-70% while maintaining or enhancing reaction efficiency when properly implemented in flow systems.
Integrated solvent recovery technologies specifically designed for continuous processes have advanced significantly, with membrane separation, adsorption systems, and in-line distillation achieving recovery rates exceeding 95% in many applications. These technologies, when incorporated into closed-loop continuous manufacturing, create near-circular solvent utilization pathways that dramatically reduce environmental impact and operating costs.
Economic analyses indicate that comprehensive solvent management strategies in continuous flow processes can reduce operational costs by 15-25% through decreased solvent consumption and waste treatment requirements. Additionally, these approaches mitigate regulatory compliance risks associated with increasingly stringent environmental legislation worldwide.
The pharmaceutical industry has emerged as a leader in this domain, with several major manufacturers implementing continuous flow platforms with integrated solvent recovery systems that align with green chemistry metrics and circular economy principles. These implementations serve as valuable case studies demonstrating both environmental and economic benefits achievable through thoughtful solvent management in continuous processing.
Regulatory Compliance for Industrial Solvent Applications
Regulatory compliance for industrial solvent applications in continuous flow processes represents a critical framework that manufacturers must navigate to ensure legal operation and environmental protection. The global regulatory landscape for solvent usage is complex and constantly evolving, with significant variations across different regions and jurisdictions. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) enforces regulations through the Clean Air Act and the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), which impose strict limitations on volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants (HAPs) commonly found in industrial solvents.
The European Union's regulatory framework is even more stringent, with the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation requiring comprehensive documentation and risk assessment for all chemical substances, including solvents used in continuous flow processes. Additionally, the EU's Solvent Emissions Directive (SED) specifically targets the reduction of VOC emissions from industrial activities involving organic solvents.
For continuous flow processes, compliance challenges are particularly acute due to the dynamic nature of solvent handling. Unlike batch processes, continuous operations require real-time monitoring and control systems to ensure ongoing compliance with emission limits and waste management requirements. This necessitates sophisticated analytical techniques and documentation protocols that can demonstrate consistent regulatory adherence.
Safety Data Sheets (SDS) management represents another critical compliance aspect, requiring regular updates to reflect the latest hazard information and handling protocols. For multinational operations, maintaining compliance across different regulatory regimes necessitates a comprehensive understanding of local requirements and the implementation of the most stringent standards across all facilities.
Waste management regulations further complicate solvent selection for continuous flow processes. The Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) in the US and the Waste Framework Directive in the EU establish strict protocols for the handling, storage, and disposal of spent solvents. Continuous processes must incorporate solvent recovery and recycling systems to minimize waste generation and associated compliance burdens.
Emerging regulations around greenhouse gas emissions and carbon footprints are increasingly influencing solvent selection decisions. Many traditional solvents with high global warming potentials face phase-out schedules, driving the industry toward greener alternatives that may require process modifications in continuous flow systems.
Compliance strategies for continuous flow processes must therefore incorporate proactive regulatory monitoring, comprehensive documentation systems, and flexible process designs that can adapt to evolving requirements. Companies implementing continuous flow technologies are increasingly adopting integrated compliance management systems that combine real-time monitoring with automated documentation to streamline regulatory reporting and reduce compliance risks.
The European Union's regulatory framework is even more stringent, with the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation requiring comprehensive documentation and risk assessment for all chemical substances, including solvents used in continuous flow processes. Additionally, the EU's Solvent Emissions Directive (SED) specifically targets the reduction of VOC emissions from industrial activities involving organic solvents.
For continuous flow processes, compliance challenges are particularly acute due to the dynamic nature of solvent handling. Unlike batch processes, continuous operations require real-time monitoring and control systems to ensure ongoing compliance with emission limits and waste management requirements. This necessitates sophisticated analytical techniques and documentation protocols that can demonstrate consistent regulatory adherence.
Safety Data Sheets (SDS) management represents another critical compliance aspect, requiring regular updates to reflect the latest hazard information and handling protocols. For multinational operations, maintaining compliance across different regulatory regimes necessitates a comprehensive understanding of local requirements and the implementation of the most stringent standards across all facilities.
Waste management regulations further complicate solvent selection for continuous flow processes. The Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) in the US and the Waste Framework Directive in the EU establish strict protocols for the handling, storage, and disposal of spent solvents. Continuous processes must incorporate solvent recovery and recycling systems to minimize waste generation and associated compliance burdens.
Emerging regulations around greenhouse gas emissions and carbon footprints are increasingly influencing solvent selection decisions. Many traditional solvents with high global warming potentials face phase-out schedules, driving the industry toward greener alternatives that may require process modifications in continuous flow systems.
Compliance strategies for continuous flow processes must therefore incorporate proactive regulatory monitoring, comprehensive documentation systems, and flexible process designs that can adapt to evolving requirements. Companies implementing continuous flow technologies are increasingly adopting integrated compliance management systems that combine real-time monitoring with automated documentation to streamline regulatory reporting and reduce compliance risks.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!