The Impact of Polyurethane on Interior Design Trends
JUN 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Polyurethane Evolution
Polyurethane has undergone a remarkable evolution since its inception in the 1930s, significantly impacting interior design trends over the decades. Initially developed as a versatile material for industrial applications, polyurethane quickly found its way into the realm of interior design due to its unique properties and adaptability.
In the 1950s and 1960s, polyurethane foam revolutionized furniture design, enabling the creation of innovative, sculptural forms that defined the mid-century modern aesthetic. This period saw the emergence of iconic pieces like Verner Panton's Panton Chair and Eero Aarnio's Ball Chair, which showcased the material's ability to mold into complex shapes while providing comfort and durability.
The 1970s and 1980s witnessed a shift towards more practical applications of polyurethane in interior design. The material's insulating properties led to its widespread use in building construction, particularly for thermal insulation and weatherproofing. This period also saw the development of polyurethane-based paints and coatings, offering enhanced durability and protection for various surfaces within interior spaces.
As environmental concerns gained prominence in the 1990s and 2000s, the polyurethane industry responded by developing more sustainable formulations. Water-based polyurethane coatings emerged as a low-VOC alternative to traditional solvent-based products, aligning with the growing demand for eco-friendly interior design solutions. This period also saw advancements in polyurethane foam recycling technologies, addressing end-of-life concerns for furniture and other polyurethane-based products.
The 2010s marked a new era of innovation in polyurethane applications for interior design. Smart materials incorporating polyurethane began to emerge, offering features such as self-healing properties and enhanced energy efficiency. Polyurethane-based 3D printing materials also gained traction, enabling designers to create intricate, customized interior elements with unprecedented precision and flexibility.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards developing bio-based polyurethanes derived from renewable resources such as plant oils and recycled materials. This trend aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainability in interior design, offering designers environmentally responsible alternatives without compromising on performance or aesthetics.
The evolution of polyurethane in interior design has been characterized by continuous innovation, adapting to changing design trends, environmental concerns, and technological advancements. From revolutionizing furniture design to enabling smart and sustainable interiors, polyurethane has proven to be a versatile and enduring material in the field of interior design, with its journey far from over as new applications and formulations continue to emerge.
In the 1950s and 1960s, polyurethane foam revolutionized furniture design, enabling the creation of innovative, sculptural forms that defined the mid-century modern aesthetic. This period saw the emergence of iconic pieces like Verner Panton's Panton Chair and Eero Aarnio's Ball Chair, which showcased the material's ability to mold into complex shapes while providing comfort and durability.
The 1970s and 1980s witnessed a shift towards more practical applications of polyurethane in interior design. The material's insulating properties led to its widespread use in building construction, particularly for thermal insulation and weatherproofing. This period also saw the development of polyurethane-based paints and coatings, offering enhanced durability and protection for various surfaces within interior spaces.
As environmental concerns gained prominence in the 1990s and 2000s, the polyurethane industry responded by developing more sustainable formulations. Water-based polyurethane coatings emerged as a low-VOC alternative to traditional solvent-based products, aligning with the growing demand for eco-friendly interior design solutions. This period also saw advancements in polyurethane foam recycling technologies, addressing end-of-life concerns for furniture and other polyurethane-based products.
The 2010s marked a new era of innovation in polyurethane applications for interior design. Smart materials incorporating polyurethane began to emerge, offering features such as self-healing properties and enhanced energy efficiency. Polyurethane-based 3D printing materials also gained traction, enabling designers to create intricate, customized interior elements with unprecedented precision and flexibility.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards developing bio-based polyurethanes derived from renewable resources such as plant oils and recycled materials. This trend aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainability in interior design, offering designers environmentally responsible alternatives without compromising on performance or aesthetics.
The evolution of polyurethane in interior design has been characterized by continuous innovation, adapting to changing design trends, environmental concerns, and technological advancements. From revolutionizing furniture design to enabling smart and sustainable interiors, polyurethane has proven to be a versatile and enduring material in the field of interior design, with its journey far from over as new applications and formulations continue to emerge.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for polyurethane in interior design has been steadily increasing over the past decade, driven by its versatility, durability, and aesthetic appeal. This synthetic material has found widespread application in various aspects of interior design, from furniture and flooring to wall coverings and decorative elements.
In the furniture sector, polyurethane-based foams and coatings have become increasingly popular due to their ability to provide comfort, support, and longevity. The demand for polyurethane-based furniture has grown significantly, particularly in the residential and hospitality sectors. This growth is attributed to the material's resistance to wear and tear, ease of maintenance, and ability to mimic the look and feel of more expensive materials.
The flooring industry has also seen a surge in demand for polyurethane-based products. Polyurethane flooring systems offer superior durability, chemical resistance, and ease of cleaning, making them ideal for both residential and commercial applications. The market for polyurethane flooring is expected to continue its upward trajectory, especially in high-traffic areas and industrial settings.
Wall coverings and decorative elements incorporating polyurethane have gained traction in the interior design market. The material's flexibility allows for the creation of intricate designs and textures, providing designers with a wide range of creative possibilities. This has led to an increased demand for polyurethane-based wall panels, moldings, and other decorative elements in both residential and commercial spaces.
The eco-friendly trend in interior design has also influenced the polyurethane market. Manufacturers have responded to the growing demand for sustainable materials by developing bio-based polyurethanes and improving recycling processes. This shift towards more environmentally conscious products has opened up new market opportunities and is expected to drive further growth in the sector.
In terms of regional demand, North America and Europe continue to be significant markets for polyurethane in interior design. However, the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing the fastest growth, driven by rapid urbanization, increasing disposable incomes, and a growing middle class. This regional shift is reshaping the global market landscape for polyurethane-based interior design products.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also influenced market demand, with an increased focus on home improvement and renovation projects. This trend has led to a surge in demand for polyurethane-based products for residential applications, as consumers seek durable and easy-to-maintain materials for their living spaces.
Looking ahead, the market demand for polyurethane in interior design is projected to continue its growth trajectory. Factors such as technological advancements, increasing urbanization, and the ongoing trend towards sustainable and multifunctional living spaces are expected to drive this growth. As the material continues to evolve and improve, its impact on interior design trends is likely to become even more pronounced in the coming years.
In the furniture sector, polyurethane-based foams and coatings have become increasingly popular due to their ability to provide comfort, support, and longevity. The demand for polyurethane-based furniture has grown significantly, particularly in the residential and hospitality sectors. This growth is attributed to the material's resistance to wear and tear, ease of maintenance, and ability to mimic the look and feel of more expensive materials.
The flooring industry has also seen a surge in demand for polyurethane-based products. Polyurethane flooring systems offer superior durability, chemical resistance, and ease of cleaning, making them ideal for both residential and commercial applications. The market for polyurethane flooring is expected to continue its upward trajectory, especially in high-traffic areas and industrial settings.
Wall coverings and decorative elements incorporating polyurethane have gained traction in the interior design market. The material's flexibility allows for the creation of intricate designs and textures, providing designers with a wide range of creative possibilities. This has led to an increased demand for polyurethane-based wall panels, moldings, and other decorative elements in both residential and commercial spaces.
The eco-friendly trend in interior design has also influenced the polyurethane market. Manufacturers have responded to the growing demand for sustainable materials by developing bio-based polyurethanes and improving recycling processes. This shift towards more environmentally conscious products has opened up new market opportunities and is expected to drive further growth in the sector.
In terms of regional demand, North America and Europe continue to be significant markets for polyurethane in interior design. However, the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing the fastest growth, driven by rapid urbanization, increasing disposable incomes, and a growing middle class. This regional shift is reshaping the global market landscape for polyurethane-based interior design products.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also influenced market demand, with an increased focus on home improvement and renovation projects. This trend has led to a surge in demand for polyurethane-based products for residential applications, as consumers seek durable and easy-to-maintain materials for their living spaces.
Looking ahead, the market demand for polyurethane in interior design is projected to continue its growth trajectory. Factors such as technological advancements, increasing urbanization, and the ongoing trend towards sustainable and multifunctional living spaces are expected to drive this growth. As the material continues to evolve and improve, its impact on interior design trends is likely to become even more pronounced in the coming years.
Technical Challenges
The integration of polyurethane in interior design has brought about significant advancements, yet it also presents several technical challenges. One of the primary obstacles is achieving the perfect balance between durability and aesthetic appeal. While polyurethane offers excellent resistance to wear and tear, maintaining its visual appeal over time remains a concern, especially in high-traffic areas or when exposed to direct sunlight.
Another challenge lies in the formulation of polyurethane coatings that can effectively adhere to a wide range of surfaces commonly found in interior spaces. Different substrates, such as wood, metal, or synthetic materials, require specific formulations to ensure proper bonding and longevity. This necessitates ongoing research and development to create versatile polyurethane products that can be universally applied across various interior design elements.
The environmental impact of polyurethane production and application poses a significant technical hurdle. Traditional polyurethane formulations often contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that can negatively affect indoor air quality. Developing low-VOC or VOC-free alternatives that maintain the desirable properties of polyurethane is a complex task that requires innovative chemical engineering approaches.
Color stability and consistency present another technical challenge in the use of polyurethane for interior design. Ensuring that polyurethane coatings maintain their original color and finish over time, without yellowing or fading, is crucial for preserving the intended aesthetic of interior spaces. This challenge is particularly pronounced in applications involving light or vibrant colors.
The curing process of polyurethane coatings in interior environments can also be problematic. Achieving optimal curing conditions while minimizing disruption to occupants or other ongoing interior work requires careful consideration of factors such as temperature, humidity, and ventilation. Developing fast-curing formulations that do not compromise on quality or durability is an ongoing area of research.
Lastly, the recyclability and end-of-life management of polyurethane products used in interior design pose significant technical challenges. As sustainability becomes increasingly important in design practices, finding efficient methods to recycle or repurpose polyurethane materials at the end of their lifecycle is crucial. This involves developing new technologies for breaking down polyurethane into its constituent components or finding innovative ways to upcycle the material without compromising its structural integrity.
Another challenge lies in the formulation of polyurethane coatings that can effectively adhere to a wide range of surfaces commonly found in interior spaces. Different substrates, such as wood, metal, or synthetic materials, require specific formulations to ensure proper bonding and longevity. This necessitates ongoing research and development to create versatile polyurethane products that can be universally applied across various interior design elements.
The environmental impact of polyurethane production and application poses a significant technical hurdle. Traditional polyurethane formulations often contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that can negatively affect indoor air quality. Developing low-VOC or VOC-free alternatives that maintain the desirable properties of polyurethane is a complex task that requires innovative chemical engineering approaches.
Color stability and consistency present another technical challenge in the use of polyurethane for interior design. Ensuring that polyurethane coatings maintain their original color and finish over time, without yellowing or fading, is crucial for preserving the intended aesthetic of interior spaces. This challenge is particularly pronounced in applications involving light or vibrant colors.
The curing process of polyurethane coatings in interior environments can also be problematic. Achieving optimal curing conditions while minimizing disruption to occupants or other ongoing interior work requires careful consideration of factors such as temperature, humidity, and ventilation. Developing fast-curing formulations that do not compromise on quality or durability is an ongoing area of research.
Lastly, the recyclability and end-of-life management of polyurethane products used in interior design pose significant technical challenges. As sustainability becomes increasingly important in design practices, finding efficient methods to recycle or repurpose polyurethane materials at the end of their lifecycle is crucial. This involves developing new technologies for breaking down polyurethane into its constituent components or finding innovative ways to upcycle the material without compromising its structural integrity.
Current Applications
01 Polyurethane synthesis and composition
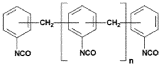
This category focuses on the synthesis and composition of polyurethane materials. It includes various methods for producing polyurethane with specific properties, such as improved durability, flexibility, or chemical resistance. The synthesis may involve different types of isocyanates, polyols, and additives to achieve desired characteristics.- Polyurethane synthesis and composition: This category focuses on the synthesis and composition of polyurethane materials. It includes various methods for producing polyurethane with specific properties, such as improved durability, flexibility, or chemical resistance. The synthesis often involves the reaction of polyols with isocyanates, and may incorporate additives or modifiers to enhance specific characteristics.
- Polyurethane applications in coatings and films: This point covers the use of polyurethane in various coating and film applications. Polyurethane coatings and films are utilized in industries such as automotive, construction, and electronics due to their excellent adhesion, durability, and weather resistance. The formulations may be tailored for specific performance requirements like UV stability or chemical resistance.
- Polyurethane foam technology: This category encompasses the development and production of polyurethane foams. It includes various types of foams such as flexible, rigid, and spray foams, each with unique properties and applications. The technology involves controlling the foam structure, density, and cell size to achieve desired characteristics for insulation, cushioning, or structural purposes.
- Polyurethane in adhesives and sealants: This point focuses on the use of polyurethane in adhesive and sealant formulations. Polyurethane-based adhesives and sealants offer excellent bonding strength, flexibility, and resistance to environmental factors. The technology includes developing formulations for specific substrates, curing mechanisms, and performance requirements in various industries such as construction, automotive, and packaging.
- Sustainable and bio-based polyurethane: This category covers the development of sustainable and bio-based polyurethane materials. It includes research into renewable raw materials, such as plant-based polyols, to replace petroleum-based components. The focus is on creating environmentally friendly polyurethane products with reduced carbon footprint while maintaining or improving performance characteristics.
02 Polyurethane applications in coatings and films
This point covers the use of polyurethane in various coating and film applications. It includes formulations for protective coatings, adhesive films, and specialty surface treatments. The polyurethane-based coatings and films may offer properties such as weather resistance, chemical resistance, and improved adhesion to different substrates.Expand Specific Solutions03 Polyurethane foam technology
This category encompasses innovations in polyurethane foam production and properties. It includes advancements in foam formulations, manufacturing processes, and the development of specialized foam products. The foams may have applications in insulation, cushioning, packaging, and other industries requiring lightweight, durable materials.Expand Specific Solutions04 Polyurethane in textile and fiber applications
This point focuses on the use of polyurethane in textile and fiber-related applications. It includes the development of polyurethane-based fibers, coatings for textiles, and treatments for enhancing fabric properties. Applications may include waterproof and breathable fabrics, elastic textiles, and durable clothing materials.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmentally friendly polyurethane innovations
This category covers advancements in making polyurethane more environmentally friendly. It includes the development of bio-based polyurethanes, recyclable formulations, and production methods with reduced environmental impact. These innovations aim to address sustainability concerns while maintaining or improving the performance of polyurethane materials.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The polyurethane market in interior design is experiencing rapid growth, driven by increasing demand for innovative and sustainable materials. The industry is in a mature stage, with a global market size expected to reach $79.2 billion by 2025. Major players like BASF Corp., Covestro Deutschland AG, and Dow Global Technologies LLC are at the forefront of technological advancements, focusing on developing eco-friendly and high-performance polyurethane products. Companies such as Vitra Patente AG and LX Hausys Ltd. are integrating these materials into cutting-edge furniture and interior solutions, while research institutions like South China University of Technology and University of Strasbourg are pushing the boundaries of polyurethane applications, indicating a high level of technical maturity and ongoing innovation in the field.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF Corp. has developed innovative polyurethane solutions for interior design, focusing on sustainability and performance. Their Elastoflex® E system is a flexible polyurethane foam that combines comfort with durability for furniture applications. This technology allows for the creation of lightweight, yet sturdy furniture pieces that maintain their shape and resilience over time. Additionally, BASF has introduced eco-friendly polyurethane coatings, such as their Elastocoat® C range, which provides excellent surface protection while reducing VOC emissions, making it ideal for interior finishes and decorative elements.
Strengths: Industry-leading research capabilities, wide range of sustainable solutions, global presence. Weaknesses: Higher costs compared to traditional materials, potential for off-gassing in some applications.
Sika Technology AG
Technical Solution: Sika Technology AG has developed advanced polyurethane systems for interior design applications, focusing on flooring and wall coatings. Their Sika ComfortFloor® system utilizes polyurethane technology to create seamless, comfortable, and durable flooring solutions for various interior spaces. This system offers excellent sound absorption, impact resistance, and design flexibility, allowing for customized colors and patterns. Sika has also introduced Sikagard® polyurethane-based wall coatings that provide superior protection against wear and tear while offering decorative finishes, contributing to the overall aesthetics of interior spaces.
Strengths: Specialized in construction chemicals, high-performance products, strong focus on sustainability. Weaknesses: Limited product range compared to larger chemical companies, potentially higher costs for specialized solutions.
Material Advancements
Polyurethane and rigid substrate composite with fasteners
PatentInactiveUS20050287347A1
Innovation
- A composite product comprising a substrate core, polyurethane foam made with pentane as a blowing agent, and at least one fastener pin, where the foam fully encapsulates the substrate core to provide a wood grain appearance and securely attaches it to a furniture frame, using a semi-rigid fastener pin to anchor the core to a heavy-gage furniture frame.
Polyurethane composition for creating flooring patterns
PatentWO2018114991A1
Innovation
- A polyurethane composition comprising a polyol component, a hardener component, and metallic or pearlescent pigments is used to create concrete-like and wood-like patterns, where the composition is applied and patterned before curing, utilizing metallic pigments to achieve a realistic appearance.
Sustainability Factors
Sustainability has become a crucial factor in the use of polyurethane in interior design trends. As environmental concerns continue to grow, designers and manufacturers are increasingly focusing on developing eco-friendly alternatives and sustainable practices in the production and application of polyurethane materials.
One of the primary sustainability challenges associated with polyurethane is its reliance on fossil fuels as raw materials. However, significant progress has been made in developing bio-based polyurethanes derived from renewable resources such as vegetable oils, corn, and other plant-based materials. These alternatives reduce the carbon footprint of polyurethane products and contribute to a more sustainable supply chain.
Recycling and waste reduction are also key sustainability factors in the polyurethane industry. Manufacturers are implementing closed-loop systems to recycle and reuse polyurethane waste, minimizing environmental impact. Additionally, advancements in chemical recycling technologies are enabling the breakdown of polyurethane into its original components, allowing for more efficient recycling processes.
Energy efficiency is another important aspect of sustainability in polyurethane production. Manufacturers are adopting more energy-efficient production methods and investing in renewable energy sources to power their facilities. This not only reduces the overall environmental impact but also helps to lower production costs in the long term.
The durability and longevity of polyurethane products contribute to their sustainability profile. High-quality polyurethane materials used in interior design can last for many years, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing waste generation. This longevity aligns with the growing consumer demand for durable, long-lasting products that offer better value for money and reduced environmental impact.
Water-based polyurethane formulations are gaining popularity as a more environmentally friendly alternative to solvent-based systems. These formulations significantly reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, improving indoor air quality and minimizing the environmental impact during application and curing processes.
Certifications and standards play a crucial role in promoting sustainability in the polyurethane industry. Many manufacturers are pursuing certifications such as GREENGUARD, which ensures low chemical emissions, and cradle-to-cradle certification, which assesses the overall sustainability of products throughout their lifecycle.
As the demand for sustainable interior design solutions continues to grow, the polyurethane industry is likely to see further innovations in eco-friendly formulations, production processes, and end-of-life management. These advancements will not only address environmental concerns but also shape future interior design trends, as consumers increasingly prioritize sustainability in their purchasing decisions.
One of the primary sustainability challenges associated with polyurethane is its reliance on fossil fuels as raw materials. However, significant progress has been made in developing bio-based polyurethanes derived from renewable resources such as vegetable oils, corn, and other plant-based materials. These alternatives reduce the carbon footprint of polyurethane products and contribute to a more sustainable supply chain.
Recycling and waste reduction are also key sustainability factors in the polyurethane industry. Manufacturers are implementing closed-loop systems to recycle and reuse polyurethane waste, minimizing environmental impact. Additionally, advancements in chemical recycling technologies are enabling the breakdown of polyurethane into its original components, allowing for more efficient recycling processes.
Energy efficiency is another important aspect of sustainability in polyurethane production. Manufacturers are adopting more energy-efficient production methods and investing in renewable energy sources to power their facilities. This not only reduces the overall environmental impact but also helps to lower production costs in the long term.
The durability and longevity of polyurethane products contribute to their sustainability profile. High-quality polyurethane materials used in interior design can last for many years, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing waste generation. This longevity aligns with the growing consumer demand for durable, long-lasting products that offer better value for money and reduced environmental impact.
Water-based polyurethane formulations are gaining popularity as a more environmentally friendly alternative to solvent-based systems. These formulations significantly reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, improving indoor air quality and minimizing the environmental impact during application and curing processes.
Certifications and standards play a crucial role in promoting sustainability in the polyurethane industry. Many manufacturers are pursuing certifications such as GREENGUARD, which ensures low chemical emissions, and cradle-to-cradle certification, which assesses the overall sustainability of products throughout their lifecycle.
As the demand for sustainable interior design solutions continues to grow, the polyurethane industry is likely to see further innovations in eco-friendly formulations, production processes, and end-of-life management. These advancements will not only address environmental concerns but also shape future interior design trends, as consumers increasingly prioritize sustainability in their purchasing decisions.
Regulatory Compliance
The regulatory landscape surrounding polyurethane in interior design is complex and ever-evolving. As the use of polyurethane in various interior design applications continues to grow, manufacturers and designers must navigate a web of regulations to ensure compliance and safety.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating polyurethane products. Under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), the EPA has established guidelines for the production, use, and disposal of polyurethane-based materials. These regulations aim to minimize potential health and environmental risks associated with polyurethane exposure.
The Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) also oversees the safety of polyurethane products used in interior design. They have set standards for flammability and off-gassing, particularly for furniture and mattresses containing polyurethane foam. Manufacturers must adhere to these standards to ensure their products meet safety requirements for consumer use.
In the European Union, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation governs the use of polyurethane in interior design applications. REACH requires manufacturers to register chemicals used in their products and provide safety information to consumers. This regulation has led to increased transparency and safer practices in the polyurethane industry.
Many countries have implemented specific regulations regarding volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions from polyurethane products. These regulations aim to improve indoor air quality and reduce potential health risks associated with long-term exposure to VOCs. Manufacturers must ensure their polyurethane-based products meet these stringent emission standards to comply with local and international regulations.
The fire safety of polyurethane products is another critical area of regulatory focus. Building codes and fire safety standards often dictate the use of flame retardants in polyurethane foams used in furniture and construction materials. However, concerns about the potential health effects of certain flame retardants have led to ongoing revisions of these regulations.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important in interior design, regulations are emerging to address the environmental impact of polyurethane products. Some jurisdictions have implemented extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs, requiring manufacturers to manage the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal and recycling.
Compliance with these diverse regulations presents challenges for the polyurethane industry. Manufacturers must invest in research and development to create products that meet safety and environmental standards while maintaining performance and aesthetic qualities. This regulatory landscape has driven innovation in the development of bio-based and low-emission polyurethane formulations, aligning with broader sustainability goals in interior design.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating polyurethane products. Under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), the EPA has established guidelines for the production, use, and disposal of polyurethane-based materials. These regulations aim to minimize potential health and environmental risks associated with polyurethane exposure.
The Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) also oversees the safety of polyurethane products used in interior design. They have set standards for flammability and off-gassing, particularly for furniture and mattresses containing polyurethane foam. Manufacturers must adhere to these standards to ensure their products meet safety requirements for consumer use.
In the European Union, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation governs the use of polyurethane in interior design applications. REACH requires manufacturers to register chemicals used in their products and provide safety information to consumers. This regulation has led to increased transparency and safer practices in the polyurethane industry.
Many countries have implemented specific regulations regarding volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions from polyurethane products. These regulations aim to improve indoor air quality and reduce potential health risks associated with long-term exposure to VOCs. Manufacturers must ensure their polyurethane-based products meet these stringent emission standards to comply with local and international regulations.
The fire safety of polyurethane products is another critical area of regulatory focus. Building codes and fire safety standards often dictate the use of flame retardants in polyurethane foams used in furniture and construction materials. However, concerns about the potential health effects of certain flame retardants have led to ongoing revisions of these regulations.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important in interior design, regulations are emerging to address the environmental impact of polyurethane products. Some jurisdictions have implemented extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs, requiring manufacturers to manage the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal and recycling.
Compliance with these diverse regulations presents challenges for the polyurethane industry. Manufacturers must invest in research and development to create products that meet safety and environmental standards while maintaining performance and aesthetic qualities. This regulatory landscape has driven innovation in the development of bio-based and low-emission polyurethane formulations, aligning with broader sustainability goals in interior design.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!