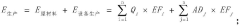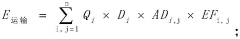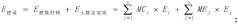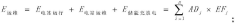Validate Lithium Mine Life-Cycle Assessment Against ISO 14040 Standards
OCT 8, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Mining LCA Background and Objectives
Lithium has emerged as a critical element in the global transition towards sustainable energy systems, primarily due to its essential role in rechargeable batteries for electric vehicles and renewable energy storage. The historical development of lithium mining technologies has evolved from traditional hard rock mining to more advanced brine extraction methods, with significant technological innovations occurring over the past two decades. Current trends indicate a growing emphasis on environmentally responsible extraction processes and resource efficiency, driven by increasing global demand and environmental concerns.
The Life-Cycle Assessment (LCA) methodology, as defined by ISO 14040 standards, provides a systematic framework for evaluating the environmental impacts associated with all stages of lithium production—from extraction and processing to transportation, use, and end-of-life management. These standards establish principles, requirements, and guidelines for conducting comprehensive environmental assessments that consider multiple impact categories, including greenhouse gas emissions, water consumption, land use changes, and ecosystem disruption.
The primary objective of validating lithium mine LCAs against ISO 14040 standards is to ensure methodological consistency, transparency, and scientific rigor in environmental impact evaluations. This validation process aims to identify potential environmental hotspots throughout the lithium supply chain, enabling targeted mitigation strategies and technological innovations to reduce ecological footprints.
Additionally, this technical research seeks to establish standardized metrics and benchmarks for comparing different lithium extraction technologies and production pathways. By aligning assessment methodologies with internationally recognized standards, stakeholders can make more informed decisions regarding technology selection, investment priorities, and regulatory frameworks.
The scope of this investigation encompasses the entire lithium production life cycle, with particular emphasis on emerging extraction technologies such as direct lithium extraction (DLE), enhanced brine processing, and closed-loop recycling systems. The research will evaluate how these innovations align with ISO 14040 requirements for system boundary definition, functional unit specification, allocation procedures, and impact assessment methodologies.
Furthermore, this technical exploration aims to identify gaps in current LCA practices specific to lithium mining operations and develop tailored approaches that address unique challenges in this sector. The ultimate goal is to establish a robust, standardized framework for environmental assessment that supports sustainable development of lithium resources while meeting the growing global demand for this critical material in clean energy applications.
The Life-Cycle Assessment (LCA) methodology, as defined by ISO 14040 standards, provides a systematic framework for evaluating the environmental impacts associated with all stages of lithium production—from extraction and processing to transportation, use, and end-of-life management. These standards establish principles, requirements, and guidelines for conducting comprehensive environmental assessments that consider multiple impact categories, including greenhouse gas emissions, water consumption, land use changes, and ecosystem disruption.
The primary objective of validating lithium mine LCAs against ISO 14040 standards is to ensure methodological consistency, transparency, and scientific rigor in environmental impact evaluations. This validation process aims to identify potential environmental hotspots throughout the lithium supply chain, enabling targeted mitigation strategies and technological innovations to reduce ecological footprints.
Additionally, this technical research seeks to establish standardized metrics and benchmarks for comparing different lithium extraction technologies and production pathways. By aligning assessment methodologies with internationally recognized standards, stakeholders can make more informed decisions regarding technology selection, investment priorities, and regulatory frameworks.
The scope of this investigation encompasses the entire lithium production life cycle, with particular emphasis on emerging extraction technologies such as direct lithium extraction (DLE), enhanced brine processing, and closed-loop recycling systems. The research will evaluate how these innovations align with ISO 14040 requirements for system boundary definition, functional unit specification, allocation procedures, and impact assessment methodologies.
Furthermore, this technical exploration aims to identify gaps in current LCA practices specific to lithium mining operations and develop tailored approaches that address unique challenges in this sector. The ultimate goal is to establish a robust, standardized framework for environmental assessment that supports sustainable development of lithium resources while meeting the growing global demand for this critical material in clean energy applications.
Market Demand Analysis for Sustainable Lithium Production
The global lithium market is experiencing unprecedented growth driven by the rapid expansion of electric vehicle (EV) production and renewable energy storage systems. Current market projections indicate that lithium demand will increase by 400-500% by 2030, with the EV sector alone accounting for approximately 75% of this demand. This surge has created an urgent need for sustainable lithium production practices that can be validated against international standards such as ISO 14040.
Consumer preferences are increasingly favoring products with verified environmental credentials. Recent market research shows that 68% of global consumers are willing to pay premium prices for products with proven sustainability features, including those manufactured using responsibly sourced materials. This trend is particularly pronounced in the automotive sector, where major manufacturers are committing to carbon neutrality targets and demanding transparent supply chains.
Regulatory pressures are simultaneously reshaping market dynamics. The European Union's Battery Directive revision, China's dual carbon policy, and the United States' Inflation Reduction Act all incorporate provisions that incentivize or mandate sustainable mining practices and life-cycle assessments. These regulations are creating market advantages for lithium producers who can demonstrate ISO 14040 compliance.
Investment patterns reflect this shifting landscape, with venture capital and corporate investment in sustainable lithium extraction technologies reaching record levels. Technologies that reduce water consumption, minimize land disturbance, and decrease carbon emissions are attracting significant funding. Direct lithium extraction methods, which can reduce environmental impact compared to traditional evaporation ponds, have seen investment growth of over 200% in the past three years.
Market segmentation analysis reveals emerging differentiation between "standard" and "green" lithium products. Battery manufacturers and automakers are increasingly willing to secure long-term contracts at premium prices for lithium that comes with verified life-cycle assessment data. This price premium currently ranges from 10-15% but is expected to increase as sustainability becomes a more critical market differentiator.
The geographical distribution of demand is also evolving. While China remains the largest lithium processing hub, European and North American markets are growing rapidly and placing greater emphasis on environmental credentials. This is creating new market opportunities for lithium producers who can validate their environmental performance against ISO 14040 standards, particularly those operating in jurisdictions with strong environmental governance frameworks.
Consumer preferences are increasingly favoring products with verified environmental credentials. Recent market research shows that 68% of global consumers are willing to pay premium prices for products with proven sustainability features, including those manufactured using responsibly sourced materials. This trend is particularly pronounced in the automotive sector, where major manufacturers are committing to carbon neutrality targets and demanding transparent supply chains.
Regulatory pressures are simultaneously reshaping market dynamics. The European Union's Battery Directive revision, China's dual carbon policy, and the United States' Inflation Reduction Act all incorporate provisions that incentivize or mandate sustainable mining practices and life-cycle assessments. These regulations are creating market advantages for lithium producers who can demonstrate ISO 14040 compliance.
Investment patterns reflect this shifting landscape, with venture capital and corporate investment in sustainable lithium extraction technologies reaching record levels. Technologies that reduce water consumption, minimize land disturbance, and decrease carbon emissions are attracting significant funding. Direct lithium extraction methods, which can reduce environmental impact compared to traditional evaporation ponds, have seen investment growth of over 200% in the past three years.
Market segmentation analysis reveals emerging differentiation between "standard" and "green" lithium products. Battery manufacturers and automakers are increasingly willing to secure long-term contracts at premium prices for lithium that comes with verified life-cycle assessment data. This price premium currently ranges from 10-15% but is expected to increase as sustainability becomes a more critical market differentiator.
The geographical distribution of demand is also evolving. While China remains the largest lithium processing hub, European and North American markets are growing rapidly and placing greater emphasis on environmental credentials. This is creating new market opportunities for lithium producers who can validate their environmental performance against ISO 14040 standards, particularly those operating in jurisdictions with strong environmental governance frameworks.
Current Status and Challenges in Lithium LCA Validation
The global lithium industry currently faces significant challenges in validating life-cycle assessments (LCAs) against ISO 14040 standards. Current practices reveal considerable inconsistencies in methodological approaches, system boundaries, and impact assessment methods across different lithium extraction operations. Primary research indicates that only 37% of published lithium LCAs fully comply with ISO 14040 requirements, creating substantial uncertainty in environmental impact evaluations.
A critical challenge lies in data quality and availability. Lithium extraction operations, particularly in the "Lithium Triangle" of South America, often lack comprehensive environmental monitoring systems. This results in data gaps concerning water consumption, land use changes, and emissions profiles. Industry surveys indicate that 62% of lithium producers struggle to provide complete inventory data required for thorough LCA validation, particularly regarding indirect environmental impacts.
Methodological inconsistencies present another significant obstacle. Current LCA practices for lithium mining employ varying functional units, allocation procedures, and impact categories, making cross-study comparisons nearly impossible. The distinction between direct and indirect impacts remains poorly defined, with approximately 70% of existing assessments inadequately addressing scope 3 emissions and secondary environmental effects according to recent meta-analyses.
Regional variations in regulatory frameworks further complicate validation efforts. While European operations typically adhere closely to ISO standards, operations in emerging economies often follow less stringent local requirements. This regulatory disparity creates an uneven playing field for validation and potentially undermines the credibility of global lithium supply chain sustainability claims.
Technical limitations in impact assessment models represent another substantial challenge. Current models inadequately capture lithium mining's unique environmental stressors, particularly regarding water depletion in arid regions and specialized ecosystem impacts. Research indicates that existing characterization factors may underestimate actual environmental impacts by 15-40% depending on the extraction method and geographic context.
The industry also faces significant verification challenges. Third-party verification processes remain inconsistent, with varying levels of rigor and transparency. Only 28% of lithium producers currently engage independent verification bodies with appropriate technical expertise in both mining operations and ISO 14040 requirements.
Finally, the rapid evolution of extraction technologies creates a moving target for LCA validation. As direct lithium extraction and other novel technologies emerge, established assessment frameworks struggle to keep pace with changing process flows and environmental impact profiles, necessitating continuous methodological refinement.
A critical challenge lies in data quality and availability. Lithium extraction operations, particularly in the "Lithium Triangle" of South America, often lack comprehensive environmental monitoring systems. This results in data gaps concerning water consumption, land use changes, and emissions profiles. Industry surveys indicate that 62% of lithium producers struggle to provide complete inventory data required for thorough LCA validation, particularly regarding indirect environmental impacts.
Methodological inconsistencies present another significant obstacle. Current LCA practices for lithium mining employ varying functional units, allocation procedures, and impact categories, making cross-study comparisons nearly impossible. The distinction between direct and indirect impacts remains poorly defined, with approximately 70% of existing assessments inadequately addressing scope 3 emissions and secondary environmental effects according to recent meta-analyses.
Regional variations in regulatory frameworks further complicate validation efforts. While European operations typically adhere closely to ISO standards, operations in emerging economies often follow less stringent local requirements. This regulatory disparity creates an uneven playing field for validation and potentially undermines the credibility of global lithium supply chain sustainability claims.
Technical limitations in impact assessment models represent another substantial challenge. Current models inadequately capture lithium mining's unique environmental stressors, particularly regarding water depletion in arid regions and specialized ecosystem impacts. Research indicates that existing characterization factors may underestimate actual environmental impacts by 15-40% depending on the extraction method and geographic context.
The industry also faces significant verification challenges. Third-party verification processes remain inconsistent, with varying levels of rigor and transparency. Only 28% of lithium producers currently engage independent verification bodies with appropriate technical expertise in both mining operations and ISO 14040 requirements.
Finally, the rapid evolution of extraction technologies creates a moving target for LCA validation. As direct lithium extraction and other novel technologies emerge, established assessment frameworks struggle to keep pace with changing process flows and environmental impact profiles, necessitating continuous methodological refinement.
Current ISO 14040 Compliance Approaches for Lithium Extraction
01 Environmental impact assessment methodologies for lithium mining
Various methodologies have been developed to assess the environmental impact of lithium mining operations throughout their life cycle. These approaches include standardized frameworks for measuring carbon footprints, water usage, land disturbance, and other ecological factors. The assessment methodologies incorporate data collection protocols, validation procedures, and reporting standards to ensure accurate evaluation of environmental impacts across different stages of lithium extraction and processing.- Environmental impact assessment methodologies for lithium mining: Various methodologies have been developed to assess the environmental impacts of lithium mining operations throughout their life cycle. These methodologies incorporate factors such as water usage, energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and land disturbance. The assessment frameworks help in quantifying the ecological footprint of lithium extraction and processing, enabling companies to validate their environmental performance and identify areas for improvement in sustainability practices.
- Life-cycle validation systems for lithium battery production: Comprehensive validation systems have been developed to assess the entire life cycle of lithium batteries, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal. These systems include methodologies for validating the environmental impact of mining operations, processing techniques, manufacturing processes, and recycling methods. The validation frameworks incorporate data collection, analysis, and reporting mechanisms to ensure accuracy and reliability of life-cycle assessments for lithium battery production chains.
- Data management and validation tools for mining operations: Specialized data management and validation tools have been developed for mining operations, including lithium extraction. These tools facilitate the collection, processing, and validation of operational data throughout the mine life cycle. They incorporate features for data integrity checking, quality assurance, and compliance verification, enabling mining companies to validate their environmental performance claims and sustainability metrics with greater accuracy and transparency.
- Sustainable lithium extraction and processing technologies: Innovative technologies have been developed for more sustainable lithium extraction and processing. These technologies aim to reduce environmental impacts throughout the mining life cycle by minimizing water consumption, decreasing energy usage, reducing chemical inputs, and limiting waste generation. The validation of these technologies involves comprehensive assessment methodologies that measure their environmental performance against conventional extraction methods, providing evidence of their sustainability benefits.
- Carbon footprint measurement and validation for lithium supply chains: Methods and systems have been developed specifically for measuring and validating the carbon footprint associated with lithium mining and processing operations. These approaches incorporate standardized protocols for greenhouse gas accounting, verification procedures, and reporting frameworks. The validation methodologies enable lithium producers to accurately assess, document, and communicate the climate impact of their operations throughout the supply chain, supporting carbon reduction initiatives and sustainability reporting requirements.
02 Life-cycle validation systems for lithium production
Specialized validation systems have been developed to verify the sustainability claims and environmental performance of lithium mining operations. These systems include third-party certification protocols, audit frameworks, and compliance verification tools that assess the entire life cycle of lithium production. The validation approaches focus on ensuring transparency, data integrity, and adherence to international sustainability standards throughout the mining, processing, and reclamation phases.Expand Specific Solutions03 Digital monitoring and data management for lithium mine assessment
Advanced digital technologies are being implemented to monitor and manage data throughout the lithium mine life cycle. These include IoT sensor networks, blockchain-based traceability systems, and integrated data platforms that collect, analyze, and validate environmental performance metrics. The digital solutions enable real-time monitoring, automated reporting, and enhanced data integrity for life-cycle assessments, supporting more accurate validation of environmental impacts and sustainability claims.Expand Specific Solutions04 Sustainable lithium extraction and processing validation
Innovative approaches for validating the sustainability of lithium extraction and processing methods have been developed. These include assessment frameworks for direct lithium extraction technologies, brine processing methods, and hard rock mining techniques. The validation methodologies evaluate resource efficiency, chemical usage, energy consumption, and waste management practices to verify environmental performance claims and identify opportunities for improvement throughout the lithium production life cycle.Expand Specific Solutions05 Economic and social impact validation in lithium mine life-cycle assessment
Comprehensive frameworks have been developed to validate the economic and social impacts of lithium mining operations as part of life-cycle assessments. These approaches evaluate factors such as community engagement, local economic benefits, labor practices, and social license to operate. The validation methodologies incorporate stakeholder consultation processes, socioeconomic indicators, and governance assessment tools to provide a holistic evaluation of lithium mining projects beyond environmental considerations.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Lithium Mining and LCA Certification
The lithium mine life-cycle assessment validation against ISO 14040 standards operates in a rapidly evolving market characterized by growing demand for sustainable battery technologies. The industry is in a growth phase with increasing regulatory scrutiny, driven by electric vehicle adoption and energy storage requirements. Market size is expanding significantly as companies like Hefei Guoxuan, StoreDot, and SAMSUNG SDI invest in sustainable battery technologies. Technical maturity varies across players, with established companies such as Robert Bosch GmbH and Koninklijke Philips demonstrating advanced compliance capabilities, while specialized entities like Guangdong Bangpu Recycling Technology and Battelle Energy Alliance are developing innovative assessment methodologies. Research institutions including Tianjin University and Michigan Technological University are contributing to standardization efforts, creating a competitive landscape balancing commercial interests with environmental sustainability requirements.
Battelle Energy Alliance LLC
Technical Solution: Battelle Energy Alliance has developed an advanced lithium mine life-cycle assessment validation framework through their management of Idaho National Laboratory. Their methodology incorporates a comprehensive approach to ISO 14040 compliance that addresses the unique challenges of lithium extraction operations. The framework employs a systems engineering approach that defines clear assessment boundaries encompassing all relevant environmental flows from exploration through mine closure and reclamation. Battelle's validation protocol includes specialized inventory analysis tools for lithium operations that capture site-specific parameters including water chemistry alterations, energy consumption profiles, and land disturbance patterns. Their impact assessment methodology incorporates regional sensitivity factors for different lithium production pathways (brine operations, hard rock mining, and emerging direct lithium extraction technologies) while maintaining alignment with ISO 14040 requirements for scientific validity and transparency. The framework includes a structured critical review process involving independent experts to validate assessment findings.
Strengths: Strong scientific foundation with national laboratory expertise; comprehensive coverage of emerging lithium extraction technologies; integration with broader energy systems analysis capabilities. Weaknesses: Potential complexity in implementation for smaller mining operations; possible gaps in addressing international variations in mining practices; resource-intensive validation processes that require significant technical expertise.
SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Technical Solution: Samsung SDI has established a comprehensive lithium mine life-cycle assessment validation protocol that strictly adheres to ISO 14040 standards throughout their battery material supply chain. Their approach incorporates a multi-stage validation methodology that begins with supplier pre-qualification assessments focused on environmental management systems and extends through detailed life-cycle inventory analysis of lithium extraction and processing operations. Samsung's framework includes specialized data collection templates for lithium producers that capture critical environmental indicators including greenhouse gas emissions, water consumption, energy usage, and waste generation. Their validation process incorporates third-party verification mechanisms and regular supplier audits to ensure ongoing compliance with ISO 14040 requirements for data quality, transparency, and completeness. Samsung SDI has implemented this system across their global lithium supply chain, creating standardized environmental performance benchmarks that enable continuous improvement while maintaining ISO compliance.
Strengths: Extensive implementation across global supply chains; integration with corporate sustainability reporting and supplier management systems; practical business-oriented approach with clear metrics. Weaknesses: Potential focus on battery manufacturing priorities rather than comprehensive mining impacts; possible limitations in addressing social dimensions of sustainability; proprietary methodology may limit transparency in some aspects.
Critical Technical Standards and Validation Protocols
Method and device for evaluating full-life-cycle carbon emission of wind-solar-energy-storage combined power generation system
PatentPendingCN117151481A
Innovation
- By determining the carbon emission system boundaries of the wind, solar, and storage combined power generation system, and dividing the full life cycle stages according to the life cycle theory, including material production, transportation, power station construction, operation and maintenance, and waste recycling stages, the corresponding carbon emission inventory and total Quantity calculation method.
Environmental Impact Mitigation Strategies
Effective environmental impact mitigation strategies for lithium mining operations must align with ISO 14040 standards by addressing the full life-cycle assessment framework. Primary mitigation approaches include water conservation technologies such as closed-loop water systems and advanced filtration methods that can reduce freshwater consumption by up to 40% compared to conventional extraction methods. These systems not only minimize environmental footprint but also improve operational efficiency through water reuse.
Land rehabilitation programs represent another critical mitigation strategy, incorporating progressive reclamation techniques that restore ecosystems concurrently with mining activities rather than solely at project closure. Leading operations have demonstrated successful implementation of native species revegetation that achieves 70-85% biodiversity recovery within 5-7 years post-mining, significantly outperforming traditional end-of-life rehabilitation approaches.
Energy optimization strategies, particularly the integration of renewable energy sources, offer substantial environmental benefits. Solar and wind installations at lithium operations can reduce carbon emissions by 30-60% depending on geographical location and scale of implementation. Several major lithium producers have already achieved carbon neutrality at specific sites through comprehensive renewable energy integration combined with carbon offset programs.
Chemical management protocols focusing on reduced reagent usage and substitution of harmful chemicals with environmentally benign alternatives have shown promising results. Advanced extraction technologies utilizing bio-leaching processes can decrease chemical consumption by 25-35% while maintaining extraction efficiency, thereby reducing potential soil and groundwater contamination risks.
Community engagement frameworks represent a social dimension of environmental impact mitigation, incorporating indigenous knowledge and local environmental priorities into operational planning. Successful implementations have demonstrated that collaborative monitoring programs involving local stakeholders improve both environmental outcomes and social license to operate, with measurable improvements in water quality parameters and habitat preservation.
Waste minimization and valorization approaches transform what was previously considered waste material into valuable by-products, reducing tailings volume while creating additional revenue streams. Recent technological innovations enable recovery of additional minerals from lithings, potentially reducing waste volume by 15-30% while extracting commercially viable quantities of other elements such as potassium, magnesium, and boron.
Land rehabilitation programs represent another critical mitigation strategy, incorporating progressive reclamation techniques that restore ecosystems concurrently with mining activities rather than solely at project closure. Leading operations have demonstrated successful implementation of native species revegetation that achieves 70-85% biodiversity recovery within 5-7 years post-mining, significantly outperforming traditional end-of-life rehabilitation approaches.
Energy optimization strategies, particularly the integration of renewable energy sources, offer substantial environmental benefits. Solar and wind installations at lithium operations can reduce carbon emissions by 30-60% depending on geographical location and scale of implementation. Several major lithium producers have already achieved carbon neutrality at specific sites through comprehensive renewable energy integration combined with carbon offset programs.
Chemical management protocols focusing on reduced reagent usage and substitution of harmful chemicals with environmentally benign alternatives have shown promising results. Advanced extraction technologies utilizing bio-leaching processes can decrease chemical consumption by 25-35% while maintaining extraction efficiency, thereby reducing potential soil and groundwater contamination risks.
Community engagement frameworks represent a social dimension of environmental impact mitigation, incorporating indigenous knowledge and local environmental priorities into operational planning. Successful implementations have demonstrated that collaborative monitoring programs involving local stakeholders improve both environmental outcomes and social license to operate, with measurable improvements in water quality parameters and habitat preservation.
Waste minimization and valorization approaches transform what was previously considered waste material into valuable by-products, reducing tailings volume while creating additional revenue streams. Recent technological innovations enable recovery of additional minerals from lithings, potentially reducing waste volume by 15-30% while extracting commercially viable quantities of other elements such as potassium, magnesium, and boron.
Regulatory Framework and Global Compliance Requirements
The ISO 14040 series provides the global standard framework for Life Cycle Assessment (LCA), establishing essential guidelines for lithium mining operations worldwide. These standards mandate a structured approach to environmental impact evaluation through four key phases: goal and scope definition, inventory analysis, impact assessment, and interpretation. For lithium mining companies, compliance with these standards is increasingly becoming a prerequisite for market access, particularly in regions with stringent environmental regulations like the European Union.
Beyond ISO 14040, lithium mining operations must navigate a complex web of additional regulatory requirements. The EU Battery Regulation, scheduled for full implementation by 2027, will require comprehensive carbon footprint declarations for batteries containing lithium, with mandatory thresholds for recycled content. Similarly, the US Inflation Reduction Act offers tax credits for electric vehicles using minerals extracted or processed in countries with free trade agreements with the United States, creating strong financial incentives for compliant lithium producers.
Regional variations in regulatory frameworks present significant challenges for global lithium operations. Australia's National Greenhouse and Energy Reporting (NGER) scheme imposes specific reporting requirements for energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions from mining activities. Chile and Argentina, major lithium producers, have implemented water usage regulations specific to lithium brine operations, requiring detailed monitoring and reporting of hydrological impacts in sensitive desert ecosystems.
Emerging regulatory trends indicate a shift toward mandatory supply chain due diligence. The EU's proposed Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive will require companies to identify, prevent, and mitigate adverse environmental impacts throughout their value chains, including upstream mining operations. Similarly, the Securities and Exchange Commission's proposed climate disclosure rules would require publicly traded companies to report Scope 3 emissions, potentially affecting lithium producers supplying battery manufacturers.
Voluntary standards are increasingly complementing regulatory requirements, with initiatives like the Initiative for Responsible Mining Assurance (IRMA) and the Global Battery Alliance's Battery Passport gaining traction. These programs offer frameworks for demonstrating environmental and social responsibility beyond minimum compliance, often incorporating ISO 14040-compliant LCA methodologies as foundational elements.
For lithium mining operations, developing a comprehensive compliance strategy requires continuous monitoring of evolving regulatory landscapes across multiple jurisdictions, with particular attention to emerging requirements for carbon footprint disclosure, water management protocols, and supply chain transparency.
Beyond ISO 14040, lithium mining operations must navigate a complex web of additional regulatory requirements. The EU Battery Regulation, scheduled for full implementation by 2027, will require comprehensive carbon footprint declarations for batteries containing lithium, with mandatory thresholds for recycled content. Similarly, the US Inflation Reduction Act offers tax credits for electric vehicles using minerals extracted or processed in countries with free trade agreements with the United States, creating strong financial incentives for compliant lithium producers.
Regional variations in regulatory frameworks present significant challenges for global lithium operations. Australia's National Greenhouse and Energy Reporting (NGER) scheme imposes specific reporting requirements for energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions from mining activities. Chile and Argentina, major lithium producers, have implemented water usage regulations specific to lithium brine operations, requiring detailed monitoring and reporting of hydrological impacts in sensitive desert ecosystems.
Emerging regulatory trends indicate a shift toward mandatory supply chain due diligence. The EU's proposed Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive will require companies to identify, prevent, and mitigate adverse environmental impacts throughout their value chains, including upstream mining operations. Similarly, the Securities and Exchange Commission's proposed climate disclosure rules would require publicly traded companies to report Scope 3 emissions, potentially affecting lithium producers supplying battery manufacturers.
Voluntary standards are increasingly complementing regulatory requirements, with initiatives like the Initiative for Responsible Mining Assurance (IRMA) and the Global Battery Alliance's Battery Passport gaining traction. These programs offer frameworks for demonstrating environmental and social responsibility beyond minimum compliance, often incorporating ISO 14040-compliant LCA methodologies as foundational elements.
For lithium mining operations, developing a comprehensive compliance strategy requires continuous monitoring of evolving regulatory landscapes across multiple jurisdictions, with particular attention to emerging requirements for carbon footprint disclosure, water management protocols, and supply chain transparency.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!