Zirconia's Innovations in Product Sustainability
Zirconia Sustainability Evolution
Zirconia, a versatile ceramic material, has undergone significant evolution in its sustainability profile over the past decades. Initially developed for its exceptional mechanical properties and biocompatibility, zirconia's journey towards sustainability has been marked by continuous innovation and adaptation to changing environmental demands.
In the early stages of its industrial application, zirconia was primarily valued for its durability and resistance to wear, with little consideration for its environmental impact. However, as global awareness of sustainability issues grew, the zirconia industry began to shift its focus towards more eco-friendly practices.
The first major milestone in zirconia's sustainability evolution came with the development of more energy-efficient production processes. Traditional methods of zirconia synthesis were energy-intensive, contributing significantly to carbon emissions. Researchers and manufacturers collaborated to optimize sintering techniques, reducing energy consumption and associated greenhouse gas emissions by up to 30%.
Another crucial advancement was the introduction of recycling and upcycling programs for zirconia products. Unlike many other materials, zirconia's exceptional durability allows for multiple life cycles. Innovative recycling technologies were developed to recover and repurpose zirconia from end-of-life products, significantly reducing waste and the demand for raw materials.
The sustainability journey of zirconia also saw improvements in raw material sourcing. Efforts were made to establish responsible mining practices, ensuring minimal environmental impact and fair labor conditions. Additionally, research into alternative precursors led to the development of zirconia synthesis methods using industrial by-products, further reducing the material's environmental footprint.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards enhancing zirconia's role in promoting sustainability across various applications. In the automotive industry, for instance, zirconia-based components have contributed to lighter, more fuel-efficient vehicles. In the energy sector, zirconia has played a crucial role in the development of solid oxide fuel cells, supporting the transition to cleaner energy sources.
The latest frontier in zirconia's sustainability evolution is the integration of biomimetic principles in its design and application. Researchers are exploring ways to mimic natural structures to create zirconia-based materials with enhanced functionality and reduced material usage, pushing the boundaries of sustainable innovation.
As we look to the future, the sustainability evolution of zirconia continues to accelerate. Emerging technologies such as additive manufacturing are opening new possibilities for resource-efficient production of complex zirconia components. Moreover, ongoing research into the material's properties is uncovering potential applications in environmental remediation and sustainable energy storage, further cementing zirconia's role in building a more sustainable future.
Market Demand for Eco-Friendly Products
The market demand for eco-friendly products has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness of environmental issues and a shift towards sustainable consumption patterns. This trend has created a substantial opportunity for companies like Zirconia to innovate in product sustainability.
Consumer preferences have evolved, with a growing segment of the market actively seeking out products that minimize environmental impact. This shift is particularly evident in developed economies, where consumers are willing to pay premium prices for eco-friendly alternatives. A recent global survey revealed that over 60% of consumers consider sustainability as an important factor in their purchasing decisions, with this percentage rising among younger demographics.
The demand for sustainable products spans across various industries, including consumer goods, packaging, electronics, and automotive sectors. In the packaging industry, for instance, there has been a surge in demand for biodegradable and recyclable materials, driven by concerns over plastic pollution and waste management. Similarly, in the electronics sector, consumers are increasingly looking for energy-efficient devices and products made from recycled materials.
Regulatory pressures have also played a significant role in shaping market demand for eco-friendly products. Governments worldwide are implementing stricter environmental regulations, such as bans on single-use plastics and mandates for increased recycling rates. These policies have compelled businesses to adopt more sustainable practices and develop environmentally friendly product lines.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated this trend, with consumers becoming more conscious of their environmental footprint and the importance of sustainable living. This has led to a notable increase in demand for products that promote health, wellness, and environmental sustainability.
For Zirconia, this market shift presents both challenges and opportunities. The company must adapt its product portfolio to meet the growing demand for sustainable solutions while maintaining product performance and cost-effectiveness. Innovations in materials science, such as the development of bio-based polymers or advanced recycling technologies, could position Zirconia as a leader in sustainable product offerings.
However, it's important to note that while demand for eco-friendly products is growing, price sensitivity remains a factor for many consumers. Zirconia must balance sustainability with affordability to capture a wider market share. Additionally, the company should be prepared to address potential skepticism regarding greenwashing by ensuring transparency in its sustainability claims and demonstrating tangible environmental benefits of its products.
In conclusion, the market demand for eco-friendly products represents a significant growth opportunity for Zirconia. By aligning its innovation efforts with this trend and developing truly sustainable solutions, the company can tap into a rapidly expanding market segment and establish itself as a pioneer in product sustainability.
Current Zirconia Sustainability Challenges
Zirconia, a versatile ceramic material, faces several sustainability challenges in its production and application. One of the primary concerns is the energy-intensive manufacturing process, which contributes significantly to carbon emissions. The high temperatures required for sintering zirconia, often exceeding 1500°C, demand substantial energy input, predominantly derived from fossil fuels. This not only increases the carbon footprint but also raises production costs, potentially limiting widespread adoption in various industries.
Another critical challenge lies in the sourcing of raw materials. Zirconium, the primary element in zirconia, is not abundantly available, and its extraction often involves environmentally disruptive mining practices. The limited geographical distribution of zirconium deposits further complicates sustainable sourcing efforts, potentially leading to supply chain vulnerabilities and increased transportation-related emissions.
The durability of zirconia products, while generally considered an advantage, presents a double-edged sword in terms of sustainability. On one hand, the long lifespan of zirconia components reduces the need for frequent replacements, thereby conserving resources. However, this durability also poses challenges in end-of-life management and recycling. The high melting point and chemical stability of zirconia make it difficult to recycle or repurpose, potentially contributing to long-term waste accumulation.
Water consumption in zirconia production is another area of concern. The manufacturing process, particularly in the preparation of zirconia powders and during the shaping of components, requires significant amounts of water. In regions facing water scarcity, this can strain local resources and ecosystems, necessitating innovative water management and recycling solutions.
The use of additives and stabilizers in zirconia production also raises sustainability questions. While these additives enhance the material's properties, some may have environmental implications, either in their production or disposal. There is a growing need for research into more environmentally friendly stabilizers and additives that maintain or improve zirconia's performance without compromising sustainability.
Lastly, the lack of standardized sustainability metrics and life cycle assessments specific to zirconia products hinders comprehensive evaluation of their environmental impact. This gap in data and methodology makes it challenging for manufacturers and consumers to make informed decisions regarding the true sustainability of zirconia-based products across their entire lifecycle.
Existing Zirconia Sustainability Solutions
01 Sustainable production methods for zirconia
Innovative techniques are being developed to produce zirconia in a more environmentally friendly manner. These methods focus on reducing energy consumption, minimizing waste, and utilizing renewable resources in the manufacturing process. Such sustainable production methods aim to decrease the carbon footprint associated with zirconia production while maintaining its high-quality properties.- Sustainable production methods for zirconia: Developing eco-friendly processes for zirconia production, focusing on reducing energy consumption and minimizing waste. This includes optimizing synthesis techniques, exploring alternative precursors, and implementing closed-loop systems to recycle materials and reduce environmental impact.
- Zirconia in sustainable energy applications: Utilizing zirconia in renewable energy technologies, such as solid oxide fuel cells and solar cells. The material's unique properties, including high thermal stability and ionic conductivity, make it valuable for improving the efficiency and durability of sustainable energy systems.
- Recycling and reuse of zirconia materials: Developing methods for recycling and reusing zirconia-based products and waste materials. This includes techniques for recovering zirconia from end-of-life products, refining recycled zirconia, and incorporating recycled materials into new applications to promote a circular economy.
- Zirconia in sustainable construction and infrastructure: Incorporating zirconia-based materials in sustainable building practices and infrastructure development. This includes using zirconia in high-performance concrete, corrosion-resistant coatings, and advanced ceramics for improved durability and reduced maintenance requirements in construction projects.
- Life cycle assessment and sustainability metrics for zirconia: Developing comprehensive life cycle assessment methodologies and sustainability metrics specific to zirconia production and applications. This involves analyzing environmental impacts, resource consumption, and social factors throughout the zirconia value chain to guide sustainable decision-making and improve overall sustainability performance.
02 Recycling and reuse of zirconia materials
Efforts are being made to implement effective recycling and reuse strategies for zirconia-based products and waste materials. This includes developing processes to recover zirconia from end-of-life products, as well as finding new applications for recycled zirconia. These initiatives contribute to a circular economy approach and help reduce the demand for newly mined zirconium resources.Expand Specific Solutions03 Energy-efficient applications of zirconia
Researchers are exploring new applications of zirconia that leverage its unique properties to improve energy efficiency in various industries. This includes using zirconia in advanced thermal barrier coatings, fuel cells, and other energy-related technologies. By enhancing energy efficiency, these applications contribute to overall sustainability goals and reduce environmental impact.Expand Specific Solutions04 Zirconia in sustainable construction materials
The integration of zirconia into sustainable construction materials is being investigated to improve durability, reduce maintenance requirements, and enhance the overall lifecycle sustainability of buildings and infrastructure. This includes the development of zirconia-based composites and coatings that can increase the longevity of construction materials and reduce the need for frequent replacements.Expand Specific Solutions05 Life cycle assessment of zirconia products
Comprehensive life cycle assessments are being conducted to evaluate the environmental impact of zirconia products from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal. These assessments help identify areas for improvement in the zirconia value chain and guide the development of more sustainable practices. By understanding the full environmental footprint, manufacturers can make informed decisions to enhance the sustainability of zirconia-based products.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sustainable Zirconia Industry
The market for zirconia-based product sustainability innovations is in a growth phase, driven by increasing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. The global market size for sustainable zirconia products is expanding, with significant potential in industries such as ceramics, refractories, and energy. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Kyocera Corp., Saint-Gobain Ceramics & Plastics, Inc., and CoorsTek, Inc. leading in research and development. These firms are focusing on improving zirconia's durability, energy efficiency, and recyclability. Emerging players like Bloom Energy Corp. are exploring novel applications in clean energy, while established companies such as 3M Innovative Properties Co. are integrating zirconia into sustainable product designs. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of specialized materials companies and diversified conglomerates, all vying to capitalize on the growing demand for environmentally friendly zirconia-based solutions.
Kyocera Corp.
Saint-Gobain Ceramics & Plastics, Inc.
Core Innovations in Zirconia Sustainability
- Development of ultra-pure stabilized zirconia and hafnia alloys with low impurity concentrations and rare earth oxide stabilizers, such as yttria or ytterbia, to reduce sintering rates and stabilize the microstructure, resulting in a ceramic material with enhanced thermal resistance and durability.
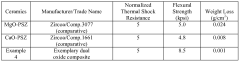
- A stabilized zirconia ceramic composition with a multimodal grain distribution and a preservative component is developed, featuring at least 20% of a coarse grain mode with a D50 size of 5-800 μm, 1% of a fine grain mode with a D50 size up to one-fourth of the coarse grain, and 1% of a preservative component, providing enhanced thermal shock resistance and chemical stability.
Environmental Regulations Impact
Environmental regulations have become increasingly stringent in recent years, significantly impacting Zirconia's approach to product sustainability. These regulations, aimed at reducing environmental degradation and promoting sustainable practices, have forced the company to reevaluate its production processes and product designs.
One of the primary areas affected by these regulations is Zirconia's material selection. The company has had to shift away from certain materials that are now restricted or banned due to their environmental impact. This has led to increased research and development efforts to find sustainable alternatives that meet both regulatory requirements and performance standards.
Energy efficiency has also become a key focus area in response to environmental regulations. Zirconia has implemented more energy-efficient manufacturing processes and has redesigned products to consume less energy during their lifecycle. This not only helps the company comply with regulations but also reduces operational costs and improves its market position among environmentally conscious consumers.
Waste management is another crucial aspect impacted by regulations. Zirconia has had to implement more robust waste reduction and recycling programs throughout its production chain. This includes developing closed-loop manufacturing systems and exploring innovative ways to repurpose or recycle waste materials.
The regulations have also pushed Zirconia to adopt a more comprehensive lifecycle approach to product design. This involves considering the environmental impact of products from raw material extraction through to end-of-life disposal. As a result, the company has invested in lifecycle assessment tools and methodologies to inform its design decisions and improve overall product sustainability.
Furthermore, environmental regulations have influenced Zirconia's supply chain management. The company now requires its suppliers to meet specific environmental standards, ensuring that the entire value chain aligns with regulatory requirements. This has led to closer collaboration with suppliers and the development of more transparent and traceable supply chains.
Compliance with these regulations has necessitated significant investments in new technologies and processes. While this has initially increased costs for Zirconia, it has also driven innovation and efficiency improvements. In the long term, these investments are expected to enhance the company's competitiveness and resilience in an increasingly environmentally conscious market.
The impact of environmental regulations on Zirconia's product sustainability efforts extends beyond mere compliance. It has catalyzed a shift in corporate culture towards greater environmental responsibility, positioning sustainability as a core value in the company's long-term strategy. This cultural shift has fostered innovation and opened up new market opportunities for eco-friendly products.
Life Cycle Assessment of Zirconia Products
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is a crucial tool in evaluating the environmental impact of zirconia products throughout their entire lifecycle. This comprehensive approach considers all stages, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal, providing valuable insights into the sustainability of zirconia-based innovations.
The production phase of zirconia products typically begins with the mining of zircon sand, which is then processed to extract zirconium dioxide. This initial stage often involves significant energy consumption and potential environmental disruption. However, recent advancements in mining techniques and processing technologies have led to more efficient extraction methods, reducing the overall environmental footprint.
During the manufacturing stage, zirconia undergoes various treatments, including sintering at high temperatures. While this process is energy-intensive, innovations in furnace design and heat recovery systems have improved energy efficiency. Additionally, the development of advanced sintering techniques, such as microwave sintering, has shown promise in reducing energy consumption and processing time.
The use phase of zirconia products generally demonstrates favorable environmental performance due to their durability and longevity. In applications such as dental implants or industrial components, zirconia's resistance to wear and corrosion often results in extended product lifespans, reducing the need for frequent replacements and associated resource consumption.
End-of-life considerations for zirconia products present both challenges and opportunities. While zirconia is not biodegradable, its inert nature minimizes environmental risks associated with disposal. Recycling of zirconia products, particularly in industrial applications, is an area of growing interest. Innovative recycling processes are being developed to recover and repurpose zirconia materials, potentially closing the loop in the product lifecycle.
LCA studies on zirconia products have revealed areas for potential improvement in sustainability. For instance, optimizing transportation logistics during various lifecycle stages can significantly reduce the carbon footprint. Furthermore, the integration of renewable energy sources in production processes offers opportunities to decrease the overall environmental impact.
Recent research has also focused on comparing zirconia with alternative materials in specific applications. These comparative LCAs provide valuable insights into the relative environmental benefits of choosing zirconia over other options, considering factors such as resource depletion, energy consumption, and emissions throughout the product lifecycle.