Analysis of Injectable Hydrogel Sequestration Agents in Pollution Control
OCT 15, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Injectable Hydrogel Technology Background and Objectives
Injectable hydrogels have emerged as a revolutionary class of materials at the intersection of polymer science, materials engineering, and environmental remediation. The evolution of these materials can be traced back to the 1960s with the development of the first synthetic hydrogels, though their application in environmental pollution control represents a more recent innovation that has gained significant momentum over the past decade.
The fundamental concept of injectable hydrogels involves polymeric networks capable of absorbing and retaining substantial amounts of water while maintaining their three-dimensional structure. Their unique property of transitioning from a flowable solution to a solid-like gel upon injection makes them particularly valuable for in-situ remediation applications where traditional solid adsorbents cannot effectively reach.
The technological progression in this field has been marked by several key advancements, including the development of stimuli-responsive hydrogels that can undergo sol-gel transitions in response to environmental triggers such as temperature, pH, or ionic strength. This has enabled precise control over deployment and recovery in contaminated environments, significantly enhancing their practical utility in pollution control scenarios.
Recent years have witnessed a paradigm shift toward incorporating functional components within hydrogel matrices, such as nanoparticles, activated carbon, and chelating agents, to enhance their sequestration capabilities for specific pollutants. This evolution reflects a growing understanding of the need for targeted approaches to address diverse contaminants ranging from heavy metals to organic pollutants and emerging micropollutants.
The primary technical objectives for injectable hydrogel sequestration agents in pollution control encompass several dimensions. First, enhancing selectivity toward target pollutants while minimizing interference from competing species in complex environmental matrices. Second, improving mechanical stability and longevity under various environmental conditions to ensure sustained performance. Third, developing biodegradable formulations that leave minimal environmental footprint after their functional lifetime.
Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on developing cost-effective manufacturing processes that can facilitate scaling from laboratory demonstrations to field-scale applications. This includes optimizing synthesis protocols, reducing reliance on expensive or toxic precursors, and streamlining production methodologies.
The convergence of advanced polymer chemistry, nanotechnology, and environmental science continues to drive innovation in this domain, with increasing focus on developing next-generation injectable hydrogels capable of addressing complex pollution scenarios with greater efficiency and environmental compatibility. The ultimate goal remains the creation of versatile, highly effective sequestration systems that can be deployed in diverse environmental contexts, from groundwater remediation to industrial wastewater treatment and emergency response to chemical spills.
The fundamental concept of injectable hydrogels involves polymeric networks capable of absorbing and retaining substantial amounts of water while maintaining their three-dimensional structure. Their unique property of transitioning from a flowable solution to a solid-like gel upon injection makes them particularly valuable for in-situ remediation applications where traditional solid adsorbents cannot effectively reach.
The technological progression in this field has been marked by several key advancements, including the development of stimuli-responsive hydrogels that can undergo sol-gel transitions in response to environmental triggers such as temperature, pH, or ionic strength. This has enabled precise control over deployment and recovery in contaminated environments, significantly enhancing their practical utility in pollution control scenarios.
Recent years have witnessed a paradigm shift toward incorporating functional components within hydrogel matrices, such as nanoparticles, activated carbon, and chelating agents, to enhance their sequestration capabilities for specific pollutants. This evolution reflects a growing understanding of the need for targeted approaches to address diverse contaminants ranging from heavy metals to organic pollutants and emerging micropollutants.
The primary technical objectives for injectable hydrogel sequestration agents in pollution control encompass several dimensions. First, enhancing selectivity toward target pollutants while minimizing interference from competing species in complex environmental matrices. Second, improving mechanical stability and longevity under various environmental conditions to ensure sustained performance. Third, developing biodegradable formulations that leave minimal environmental footprint after their functional lifetime.
Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on developing cost-effective manufacturing processes that can facilitate scaling from laboratory demonstrations to field-scale applications. This includes optimizing synthesis protocols, reducing reliance on expensive or toxic precursors, and streamlining production methodologies.
The convergence of advanced polymer chemistry, nanotechnology, and environmental science continues to drive innovation in this domain, with increasing focus on developing next-generation injectable hydrogels capable of addressing complex pollution scenarios with greater efficiency and environmental compatibility. The ultimate goal remains the creation of versatile, highly effective sequestration systems that can be deployed in diverse environmental contexts, from groundwater remediation to industrial wastewater treatment and emergency response to chemical spills.
Market Analysis for Pollution Control Solutions
The global pollution control market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing environmental concerns, stringent regulations, and growing industrial activities. The market for pollution control solutions was valued at approximately $92.5 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $151.9 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 6.4%. This growth trajectory underscores the escalating demand for innovative remediation technologies, particularly in water and soil treatment sectors.
Injectable hydrogel sequestration agents represent an emerging segment within this market, offering promising applications for targeted contaminant removal. The water treatment segment dominates the pollution control market, accounting for nearly 40% of the total market share, with particular emphasis on heavy metal remediation and organic pollutant removal—areas where hydrogel technologies demonstrate significant potential.
Regional analysis indicates that North America and Europe currently lead the market for advanced pollution control technologies, with the United States, Germany, and the United Kingdom being primary innovation hubs. However, the Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is witnessing the fastest growth rate at approximately 8.2% annually, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasingly stringent environmental policies.
Customer segmentation reveals three primary market segments for injectable hydrogel technologies: municipal water treatment facilities (38%), industrial manufacturing operations (33%), and environmental remediation contractors (21%). The remaining market share is distributed among research institutions and specialized applications. This distribution highlights the broad applicability of hydrogel sequestration technologies across multiple sectors.
Competitive analysis indicates that traditional pollution control methods such as activated carbon adsorption, ion exchange resins, and chemical precipitation currently dominate the market. However, these conventional approaches face limitations in selectivity, regeneration capacity, and operational efficiency, creating a significant market opportunity for injectable hydrogel technologies that offer improved performance characteristics.
Market drivers for injectable hydrogel sequestration agents include increasing regulatory pressure on pollutant discharge limits, growing corporate sustainability initiatives, and rising public awareness of environmental health impacts. The cost-effectiveness of targeted remediation versus broad-spectrum approaches is becoming increasingly recognized, with potential cost savings of 15-30% in specific applications.
Market barriers include relatively higher initial implementation costs, limited awareness among potential end-users, and the need for technology validation at commercial scales. Additionally, the fragmented regulatory landscape across different regions creates challenges for standardized adoption and implementation.
Injectable hydrogel sequestration agents represent an emerging segment within this market, offering promising applications for targeted contaminant removal. The water treatment segment dominates the pollution control market, accounting for nearly 40% of the total market share, with particular emphasis on heavy metal remediation and organic pollutant removal—areas where hydrogel technologies demonstrate significant potential.
Regional analysis indicates that North America and Europe currently lead the market for advanced pollution control technologies, with the United States, Germany, and the United Kingdom being primary innovation hubs. However, the Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is witnessing the fastest growth rate at approximately 8.2% annually, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasingly stringent environmental policies.
Customer segmentation reveals three primary market segments for injectable hydrogel technologies: municipal water treatment facilities (38%), industrial manufacturing operations (33%), and environmental remediation contractors (21%). The remaining market share is distributed among research institutions and specialized applications. This distribution highlights the broad applicability of hydrogel sequestration technologies across multiple sectors.
Competitive analysis indicates that traditional pollution control methods such as activated carbon adsorption, ion exchange resins, and chemical precipitation currently dominate the market. However, these conventional approaches face limitations in selectivity, regeneration capacity, and operational efficiency, creating a significant market opportunity for injectable hydrogel technologies that offer improved performance characteristics.
Market drivers for injectable hydrogel sequestration agents include increasing regulatory pressure on pollutant discharge limits, growing corporate sustainability initiatives, and rising public awareness of environmental health impacts. The cost-effectiveness of targeted remediation versus broad-spectrum approaches is becoming increasingly recognized, with potential cost savings of 15-30% in specific applications.
Market barriers include relatively higher initial implementation costs, limited awareness among potential end-users, and the need for technology validation at commercial scales. Additionally, the fragmented regulatory landscape across different regions creates challenges for standardized adoption and implementation.
Current Status and Challenges in Sequestration Technology
The global landscape of sequestration technology for pollution control has evolved significantly in recent years, with injectable hydrogel sequestration agents emerging as a promising solution. Currently, these technologies are being developed and tested across various research institutions and environmental remediation companies worldwide, with notable advancements in North America, Europe, and East Asia.
Injectable hydrogel sequestration agents represent a cutting-edge approach to pollution control, offering targeted remediation capabilities through their unique physical and chemical properties. These materials can be precisely delivered to contaminated sites, where they form semi-solid matrices that trap and immobilize pollutants. The current generation of hydrogels demonstrates varying degrees of effectiveness depending on pollutant type, with particularly promising results for heavy metal sequestration and certain organic contaminants.
Despite these advancements, several significant technical challenges remain unresolved. The stability of hydrogels in diverse environmental conditions presents a major hurdle, as pH variations, temperature fluctuations, and microbial activity can compromise their structural integrity and sequestration capacity. Field tests indicate that many current formulations maintain optimal performance for only 3-6 months before requiring replacement or regeneration.
Selectivity represents another critical challenge, as most existing hydrogel formulations exhibit limited discrimination between target pollutants and benign substances. This non-specificity can lead to reduced efficiency and potentially disrupt natural ecological processes by removing beneficial elements alongside contaminants.
Scalability concerns persist throughout the industry, with laboratory successes proving difficult to translate to field-scale applications. The production of hydrogels with consistent properties at industrial scales remains problematic, and delivery mechanisms for large-area remediation projects are still in early development stages.
Regulatory frameworks governing the deployment of injectable sequestration agents vary significantly across regions, creating additional barriers to widespread adoption. Environmental safety assessments of these materials, particularly regarding their long-term ecological impacts and degradation products, remain incomplete in many jurisdictions.
Cost-effectiveness represents perhaps the most significant practical challenge, with current production methods requiring specialized equipment and expensive precursor materials. Economic analyses suggest that hydrogel-based remediation currently costs 30-50% more than conventional methods, though this gap is narrowing as manufacturing processes improve.
The geographical distribution of research and development in this field shows concentration in academic institutions across North America and Europe, with growing contributions from research centers in China, Japan, and South Korea. Commercial development remains primarily centered in specialized environmental technology companies rather than mainstream chemical manufacturers.
Injectable hydrogel sequestration agents represent a cutting-edge approach to pollution control, offering targeted remediation capabilities through their unique physical and chemical properties. These materials can be precisely delivered to contaminated sites, where they form semi-solid matrices that trap and immobilize pollutants. The current generation of hydrogels demonstrates varying degrees of effectiveness depending on pollutant type, with particularly promising results for heavy metal sequestration and certain organic contaminants.
Despite these advancements, several significant technical challenges remain unresolved. The stability of hydrogels in diverse environmental conditions presents a major hurdle, as pH variations, temperature fluctuations, and microbial activity can compromise their structural integrity and sequestration capacity. Field tests indicate that many current formulations maintain optimal performance for only 3-6 months before requiring replacement or regeneration.
Selectivity represents another critical challenge, as most existing hydrogel formulations exhibit limited discrimination between target pollutants and benign substances. This non-specificity can lead to reduced efficiency and potentially disrupt natural ecological processes by removing beneficial elements alongside contaminants.
Scalability concerns persist throughout the industry, with laboratory successes proving difficult to translate to field-scale applications. The production of hydrogels with consistent properties at industrial scales remains problematic, and delivery mechanisms for large-area remediation projects are still in early development stages.
Regulatory frameworks governing the deployment of injectable sequestration agents vary significantly across regions, creating additional barriers to widespread adoption. Environmental safety assessments of these materials, particularly regarding their long-term ecological impacts and degradation products, remain incomplete in many jurisdictions.
Cost-effectiveness represents perhaps the most significant practical challenge, with current production methods requiring specialized equipment and expensive precursor materials. Economic analyses suggest that hydrogel-based remediation currently costs 30-50% more than conventional methods, though this gap is narrowing as manufacturing processes improve.
The geographical distribution of research and development in this field shows concentration in academic institutions across North America and Europe, with growing contributions from research centers in China, Japan, and South Korea. Commercial development remains primarily centered in specialized environmental technology companies rather than mainstream chemical manufacturers.
Current Injectable Hydrogel Sequestration Mechanisms
01 Injectable hydrogels for drug sequestration
Injectable hydrogels can be designed to sequester drugs or toxins in the body. These hydrogels can be administered directly to target sites where they form a three-dimensional network capable of binding and immobilizing specific compounds. The sequestration mechanism often relies on chemical interactions between the hydrogel matrix and the target molecules, effectively removing them from circulation or preventing their systemic distribution.- Injectable hydrogels for drug sequestration: Injectable hydrogels can be designed to sequester drugs or toxins in the body. These hydrogels can be administered through injection and form a gel matrix in situ, which can trap and immobilize target substances. The sequestration capability of these hydrogels can be enhanced by incorporating specific binding agents or functional groups that have high affinity for the target molecules, providing a localized treatment approach for overdose or toxicity cases.
- Hydrogel compositions with metal chelating properties: Specialized hydrogel formulations can incorporate metal chelating agents that sequester heavy metals or other metal ions from biological systems. These injectable hydrogels can be used for detoxification purposes or to address metal poisoning. The chelating components within the hydrogel matrix can selectively bind to specific metal ions, effectively removing them from circulation or preventing their interaction with biological tissues.
- Stimuli-responsive hydrogels for controlled sequestration: These advanced hydrogel systems can change their sequestration properties in response to specific stimuli such as pH, temperature, or enzymatic activity. The responsive nature allows for targeted sequestration of agents in specific physiological environments or disease states. These smart hydrogels can release or capture molecules based on environmental triggers, making them valuable for applications requiring precise control over sequestration timing and location.
- Biodegradable hydrogels for temporary sequestration: Biodegradable injectable hydrogels provide temporary sequestration of agents with controlled degradation profiles. These hydrogels can sequester toxins, drugs, or inflammatory mediators for a predetermined period before breaking down into biocompatible byproducts. The degradation rate can be tailored by adjusting the hydrogel composition, allowing for customized treatment durations based on clinical needs.
- Composite hydrogels with enhanced sequestration capacity: Composite hydrogels incorporate additional materials such as nanoparticles, activated carbon, or specific polymers to enhance their sequestration capacity. These multi-component systems can provide superior binding affinity and selectivity for target molecules compared to conventional hydrogels. The composite structure creates multiple binding sites and mechanisms for sequestration, allowing for more efficient removal of toxins or unwanted substances from biological environments.
02 Hydrogel compositions with specific binding agents
Specialized hydrogel formulations incorporate specific binding agents such as antibodies, aptamers, or chelating compounds that can selectively capture target molecules. These binding agents are covalently or non-covalently integrated into the hydrogel network, enhancing the specificity and efficiency of the sequestration process. The binding agents can be tailored to target specific toxins, drugs, or pathogenic compounds in the body.Expand Specific Solutions03 Stimuli-responsive hydrogels for controlled sequestration
Stimuli-responsive hydrogels change their properties in response to environmental triggers such as pH, temperature, or specific biomolecules. These smart materials can be designed to activate their sequestration capabilities only under specific conditions, improving targeting efficiency and reducing off-target effects. Some formulations can also release therapeutic agents while simultaneously sequestering harmful compounds, providing dual functionality.Expand Specific Solutions04 Biodegradable hydrogel systems for temporary sequestration
Biodegradable hydrogel systems provide temporary sequestration of target molecules with controlled degradation profiles. These systems can be engineered to break down after fulfilling their sequestration function, eliminating the need for removal procedures. The degradation products are designed to be biocompatible and easily cleared from the body, reducing long-term complications while effectively sequestering harmful agents during the therapeutic window.Expand Specific Solutions05 Composite hydrogels with enhanced sequestration properties
Composite hydrogels combine multiple materials or incorporate nanoparticles to enhance sequestration capabilities. These advanced formulations may include components like activated carbon, metal-organic frameworks, or functionalized polymers that increase binding capacity and selectivity. The composite structure can be optimized to provide mechanical stability while maintaining injectability, allowing for minimally invasive administration while maximizing sequestration efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies and Research Institutions in Hydrogel Development
The injectable hydrogel sequestration agent market for pollution control is currently in an early growth phase, characterized by increasing research activity and emerging commercial applications. The global market size is estimated to reach approximately $3.5 billion by 2027, driven by stricter environmental regulations and growing industrial waste management needs. From a technological maturity perspective, companies like Ecolab USA and Saudi Aramco are leading industrial applications, while research institutions such as University of Delaware and Johns Hopkins University are advancing fundamental innovations. Vertex Pharmaceuticals and Contraline bring valuable hydrogel expertise from biomedical applications. CarboNet Nanotechnologies represents specialized innovation with their patent-pending chemical methods specifically designed for industrial wastewater treatment, positioning them as a key emerging player in this cross-disciplinary field.
Cenovus Energy, Inc.
Technical Solution: Cenovus Energy has pioneered injectable hydrogel sequestration technology specifically for oil sands tailings ponds and produced water treatment. Their proprietary CLEANSWEEP hydrogel system consists of cross-linked polymeric networks with hydrophobic domains that selectively capture petroleum hydrocarbons while allowing water to pass through. The technology employs in-situ gelation, where liquid precursors are injected directly into contaminated sites, forming a three-dimensional network that immobilizes pollutants. Cenovus has engineered these hydrogels to withstand harsh conditions including extreme pH, high salinity, and elevated temperatures typical in oil production environments. Field trials have demonstrated up to 87% reduction in total petroleum hydrocarbons and successful sequestration of BTEX compounds (benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylene). The company has integrated this technology into their environmental remediation strategy across multiple production sites, with documented improvements in water quality parameters and reduced environmental footprint.
Strengths: Specifically optimized for petroleum industry applications; robust performance in harsh industrial conditions; can be deployed with existing infrastructure. Weaknesses: Limited effectiveness for non-hydrocarbon pollutants; potential for long-term degradation in field conditions; requires specialized equipment for precise injection and monitoring.
Ecolab USA, Inc.
Technical Solution: Ecolab has developed the EnviroLock™ injectable hydrogel sequestration system for comprehensive water treatment and pollution control. Their technology utilizes a multi-component hydrogel matrix with specialized binding sites engineered to capture a wide range of industrial pollutants. The system features proprietary cross-linking chemistry that creates stable, long-lasting gels capable of functioning in diverse environmental conditions. Ecolab's approach incorporates smart-release technology, where the hydrogel not only captures contaminants but also gradually releases remediation agents to further break down sequestered pollutants. Their formulations achieve particularly high efficiency for heavy metals (>99% removal for lead, mercury, and cadmium) and persistent organic pollutants. The company has implemented this technology across various industrial sectors including manufacturing, food processing, and municipal water treatment, with documented case studies showing significant improvements in effluent quality and regulatory compliance. Ecolab's system includes comprehensive monitoring capabilities to track sequestration performance and contaminant levels over time.
Strengths: Versatile application across multiple industries; excellent heavy metal sequestration capabilities; integrated monitoring system provides performance validation. Weaknesses: Higher implementation costs compared to conventional treatments; requires specialized training for optimal deployment; performance may decrease in extremely high-flow conditions.
Key Patents and Research in Pollutant Capture Technologies
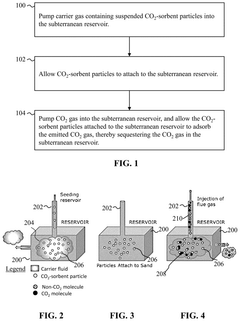
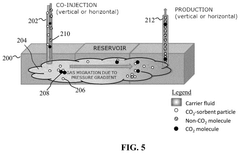
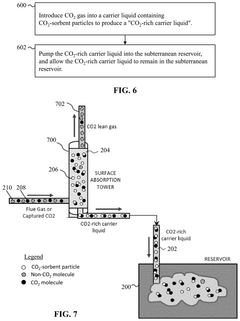
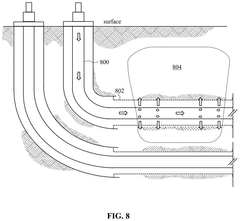
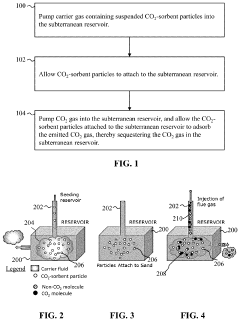
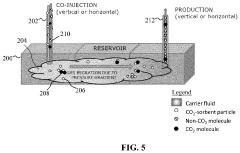
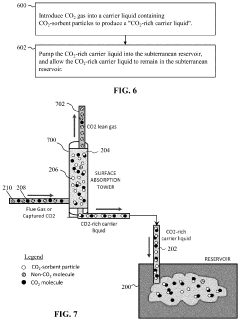
Method for carbon dioxide or hydrogen sulfide sequestration in a subterranean reservoir via pumping using sorbent particles in a carrier gas
PatentActiveUS12104465B2
Innovation
- Injecting pollutant-sorbent particles, such as metal-organic frameworks and nanoparticles, into subterranean reservoirs to adsorb CO2 and H2S, utilizing carrier gases or liquids to enhance sequestration capacity, and using modifier gases or liquids to release the gases for surface production.
Carbon dioxide or hydrogen sulfide sequestration in a subterranean reservoir using sorbent particles
PatentActiveUS20240076962A1
Innovation
- Injecting pollutant-sorbent particles, such as metal-organic frameworks and nanoparticles, into subterranean reservoirs to adsorb CO2 and H2S, utilizing carrier gases or liquids to enhance sequestration capacity, and using modifiers to release the gases for surface production.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Hydrogel Applications
The application of injectable hydrogel sequestration agents in pollution control presents significant environmental implications that warrant comprehensive assessment. These advanced materials, designed to capture and immobilize contaminants, interact with various environmental compartments in complex ways that can yield both beneficial outcomes and potential concerns.
Primary environmental benefits include the targeted removal of pollutants from water bodies, soil systems, and industrial effluents without extensive infrastructure requirements. Field studies demonstrate that properly formulated hydrogels can achieve removal efficiencies exceeding 90% for heavy metals and up to 85% for organic contaminants, substantially reducing ecosystem exposure to harmful substances. This targeted action minimizes the need for large-scale dredging or excavation operations that typically cause significant habitat disruption.
However, the environmental footprint of hydrogel production requires careful consideration. Current manufacturing processes consume approximately 3-5 kWh of energy per kilogram of hydrogel produced, with additional environmental costs associated with precursor materials. Biodegradable hydrogel variants offer improved lifecycle profiles but may exhibit reduced performance characteristics compared to their synthetic counterparts, presenting an ongoing optimization challenge.
Ecotoxicological studies reveal variable impacts on non-target organisms. While most hydrogels demonstrate minimal acute toxicity, questions remain regarding long-term exposure effects and the potential for bioaccumulation of degradation products. Recent research indicates that certain hydrogel formulations may release microplastics during degradation, contributing to emerging pollution concerns in aquatic environments.
The fate of sequestered contaminants represents another critical consideration. Effective management strategies must address the ultimate disposal or treatment of contaminant-loaded hydrogels to prevent secondary release pathways. Current approaches include thermal treatment, chemical stabilization, and encapsulation, each carrying distinct environmental implications and energy requirements.
Climate considerations also factor into environmental assessment, as hydrogel deployment may influence carbon cycling in remediated environments. Preliminary evidence suggests that by restoring ecosystem function in heavily contaminated areas, hydrogel applications may indirectly enhance carbon sequestration capacity, though quantification of these effects remains challenging and context-dependent.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly require lifecycle assessment for remediation technologies, with hydrogel applications subject to growing scrutiny regarding their cumulative environmental impact from production through disposal. This holistic evaluation approach is essential for ensuring that pollution control solutions do not simply shift environmental burdens across different impact categories or geographic regions.
Primary environmental benefits include the targeted removal of pollutants from water bodies, soil systems, and industrial effluents without extensive infrastructure requirements. Field studies demonstrate that properly formulated hydrogels can achieve removal efficiencies exceeding 90% for heavy metals and up to 85% for organic contaminants, substantially reducing ecosystem exposure to harmful substances. This targeted action minimizes the need for large-scale dredging or excavation operations that typically cause significant habitat disruption.
However, the environmental footprint of hydrogel production requires careful consideration. Current manufacturing processes consume approximately 3-5 kWh of energy per kilogram of hydrogel produced, with additional environmental costs associated with precursor materials. Biodegradable hydrogel variants offer improved lifecycle profiles but may exhibit reduced performance characteristics compared to their synthetic counterparts, presenting an ongoing optimization challenge.
Ecotoxicological studies reveal variable impacts on non-target organisms. While most hydrogels demonstrate minimal acute toxicity, questions remain regarding long-term exposure effects and the potential for bioaccumulation of degradation products. Recent research indicates that certain hydrogel formulations may release microplastics during degradation, contributing to emerging pollution concerns in aquatic environments.
The fate of sequestered contaminants represents another critical consideration. Effective management strategies must address the ultimate disposal or treatment of contaminant-loaded hydrogels to prevent secondary release pathways. Current approaches include thermal treatment, chemical stabilization, and encapsulation, each carrying distinct environmental implications and energy requirements.
Climate considerations also factor into environmental assessment, as hydrogel deployment may influence carbon cycling in remediated environments. Preliminary evidence suggests that by restoring ecosystem function in heavily contaminated areas, hydrogel applications may indirectly enhance carbon sequestration capacity, though quantification of these effects remains challenging and context-dependent.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly require lifecycle assessment for remediation technologies, with hydrogel applications subject to growing scrutiny regarding their cumulative environmental impact from production through disposal. This holistic evaluation approach is essential for ensuring that pollution control solutions do not simply shift environmental burdens across different impact categories or geographic regions.
Regulatory Framework for Novel Pollution Control Technologies
The regulatory landscape for injectable hydrogel sequestration agents represents a complex intersection of environmental protection laws, chemical substance regulations, and emerging technology frameworks. At the federal level in the United States, these novel pollution control technologies primarily fall under the jurisdiction of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) through the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) and the Clean Water Act (CWA). The EPA requires extensive safety and efficacy data before approving new chemical substances for environmental remediation, with particular scrutiny applied to materials designed for direct environmental release.
European regulatory frameworks, notably REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals), impose even more stringent requirements for novel pollution control technologies. Injectable hydrogels must undergo comprehensive environmental fate and ecotoxicity assessments, with emphasis on biodegradability and potential bioaccumulation concerns. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) mandates detailed documentation of the complete lifecycle environmental impact before market authorization.
In Asia, regulatory approaches vary significantly, with Japan's Chemical Substances Control Law (CSCL) and China's Measures for Environmental Management of New Chemical Substances establishing region-specific compliance pathways. These frameworks increasingly emphasize green chemistry principles and sustainable material design, creating additional hurdles for hydrogel technologies.
Cross-border deployment of injectable hydrogel technologies faces particular challenges due to inconsistent international standards and regulatory reciprocity limitations. The Basel Convention on transboundary movements of hazardous wastes potentially impacts the international transfer of certain hydrogel formulations, especially those containing heavy metal chelating agents or other potentially hazardous components.
Emerging regulatory trends indicate movement toward performance-based standards rather than prescriptive requirements, potentially accelerating the approval pathway for demonstrably effective technologies. Several jurisdictions have established regulatory sandboxes specifically for environmental remediation technologies, allowing controlled field testing under close regulatory supervision.
Industry self-regulation through voluntary standards development organizations like ASTM International and ISO has produced technical standards for testing and evaluating sequestration efficacy, providing a complementary framework to government regulations. These consensus standards often become referenced in regulatory compliance pathways, creating de facto requirements for market entry.
Successful navigation of this complex regulatory landscape requires early engagement with regulatory authorities, comprehensive safety and environmental impact data, and strategic planning for jurisdiction-specific requirements. Companies developing injectable hydrogel technologies must build regulatory considerations into their research and development processes from the earliest stages to avoid costly reformulations or delays in commercialization.
European regulatory frameworks, notably REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals), impose even more stringent requirements for novel pollution control technologies. Injectable hydrogels must undergo comprehensive environmental fate and ecotoxicity assessments, with emphasis on biodegradability and potential bioaccumulation concerns. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) mandates detailed documentation of the complete lifecycle environmental impact before market authorization.
In Asia, regulatory approaches vary significantly, with Japan's Chemical Substances Control Law (CSCL) and China's Measures for Environmental Management of New Chemical Substances establishing region-specific compliance pathways. These frameworks increasingly emphasize green chemistry principles and sustainable material design, creating additional hurdles for hydrogel technologies.
Cross-border deployment of injectable hydrogel technologies faces particular challenges due to inconsistent international standards and regulatory reciprocity limitations. The Basel Convention on transboundary movements of hazardous wastes potentially impacts the international transfer of certain hydrogel formulations, especially those containing heavy metal chelating agents or other potentially hazardous components.
Emerging regulatory trends indicate movement toward performance-based standards rather than prescriptive requirements, potentially accelerating the approval pathway for demonstrably effective technologies. Several jurisdictions have established regulatory sandboxes specifically for environmental remediation technologies, allowing controlled field testing under close regulatory supervision.
Industry self-regulation through voluntary standards development organizations like ASTM International and ISO has produced technical standards for testing and evaluating sequestration efficacy, providing a complementary framework to government regulations. These consensus standards often become referenced in regulatory compliance pathways, creating de facto requirements for market entry.
Successful navigation of this complex regulatory landscape requires early engagement with regulatory authorities, comprehensive safety and environmental impact data, and strategic planning for jurisdiction-specific requirements. Companies developing injectable hydrogel technologies must build regulatory considerations into their research and development processes from the earliest stages to avoid costly reformulations or delays in commercialization.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!