How Injectable Hydrogel Facilitates Non-Invasive Surgical Techniques
OCT 15, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Injectable Hydrogel Evolution and Objectives
Injectable hydrogels have emerged as a revolutionary biomaterial in the medical field, evolving significantly since their initial development in the late 1970s. The journey began with simple cross-linked polymer networks designed for controlled drug release, progressing through several generations of increasingly sophisticated formulations. Early hydrogels faced challenges with biocompatibility and mechanical stability, limiting their clinical applications. The 1990s marked a turning point with the introduction of naturally derived hydrogels from collagen, alginate, and hyaluronic acid, which demonstrated superior biocompatibility and tissue integration.
The 2000s witnessed the development of stimuli-responsive hydrogels capable of changing their properties in response to environmental cues such as temperature, pH, or enzymatic activity. This innovation expanded their potential applications in targeted drug delivery and tissue engineering. By the 2010s, injectable hydrogels specifically designed for minimally invasive surgical applications began gaining significant attention, with researchers focusing on optimizing gelation kinetics, mechanical properties, and bioactive functionalities.
Current technological objectives for injectable hydrogels in non-invasive surgical techniques center around several key areas. Primary among these is achieving precise control over gelation timing, allowing surgeons to administer the material in liquid form that solidifies rapidly once in position. This capability is crucial for applications such as targeted drug delivery, tissue adhesion, and void filling during minimally invasive procedures.
Another critical objective involves enhancing the mechanical properties of hydrogels to match those of native tissues while maintaining injectability through fine-gauge needles. This balance between flowability during delivery and structural integrity post-implantation represents a significant engineering challenge that continues to drive innovation in polymer chemistry and formulation science.
Biocompatibility remains a paramount concern, with ongoing efforts to develop hydrogels that not only avoid adverse immune responses but actively promote healing through controlled release of bioactive molecules or by serving as scaffolds for cell growth and tissue regeneration. The integration of imaging agents into hydrogel formulations represents another important objective, enabling real-time visualization during placement procedures and subsequent monitoring of degradation and therapeutic effects.
Looking forward, the field is moving toward personalized hydrogel systems that can be tailored to individual patient needs, potentially incorporating patient-derived cells or growth factors. Additionally, researchers are exploring "smart" hydrogels capable of responding to pathological conditions, releasing therapeutics on-demand, or adapting their properties over time to match the changing needs of healing tissues.
The 2000s witnessed the development of stimuli-responsive hydrogels capable of changing their properties in response to environmental cues such as temperature, pH, or enzymatic activity. This innovation expanded their potential applications in targeted drug delivery and tissue engineering. By the 2010s, injectable hydrogels specifically designed for minimally invasive surgical applications began gaining significant attention, with researchers focusing on optimizing gelation kinetics, mechanical properties, and bioactive functionalities.
Current technological objectives for injectable hydrogels in non-invasive surgical techniques center around several key areas. Primary among these is achieving precise control over gelation timing, allowing surgeons to administer the material in liquid form that solidifies rapidly once in position. This capability is crucial for applications such as targeted drug delivery, tissue adhesion, and void filling during minimally invasive procedures.
Another critical objective involves enhancing the mechanical properties of hydrogels to match those of native tissues while maintaining injectability through fine-gauge needles. This balance between flowability during delivery and structural integrity post-implantation represents a significant engineering challenge that continues to drive innovation in polymer chemistry and formulation science.
Biocompatibility remains a paramount concern, with ongoing efforts to develop hydrogels that not only avoid adverse immune responses but actively promote healing through controlled release of bioactive molecules or by serving as scaffolds for cell growth and tissue regeneration. The integration of imaging agents into hydrogel formulations represents another important objective, enabling real-time visualization during placement procedures and subsequent monitoring of degradation and therapeutic effects.
Looking forward, the field is moving toward personalized hydrogel systems that can be tailored to individual patient needs, potentially incorporating patient-derived cells or growth factors. Additionally, researchers are exploring "smart" hydrogels capable of responding to pathological conditions, releasing therapeutics on-demand, or adapting their properties over time to match the changing needs of healing tissues.
Market Analysis for Minimally Invasive Surgical Solutions
The minimally invasive surgical solutions market has experienced substantial growth over the past decade, driven by increasing patient demand for reduced recovery times and lower complication rates. Currently valued at approximately $20.5 billion globally, this market is projected to reach $32.7 billion by 2026, representing a compound annual growth rate of 9.8%. Injectable hydrogels represent a particularly promising segment within this expanding market, with specialized medical hydrogels growing at an even faster rate of 12.3% annually.
Healthcare providers are increasingly prioritizing minimally invasive approaches due to their demonstrable benefits in patient outcomes and cost efficiency. Hospital administrators report average cost savings of 30-40% per procedure when utilizing minimally invasive techniques compared to traditional open surgeries, primarily due to shorter hospital stays and reduced complication rates. Patient satisfaction scores for minimally invasive procedures consistently exceed 85%, compared to 62% for conventional surgical approaches.
Regional market analysis reveals North America currently dominates with 42% market share, followed by Europe (28%) and Asia-Pacific (21%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing the fastest growth rate at 14.2% annually, driven by improving healthcare infrastructure and increasing adoption of advanced surgical technologies in countries like China, India, and South Korea.
Injectable hydrogel applications are particularly well-positioned within several high-growth surgical specialties. Orthopedic applications lead with 31% market share, followed by cardiovascular (24%), neurological (18%), and general surgery (15%). The remaining 12% encompasses emerging applications across various specialties including ophthalmology and plastic surgery.
Demographic trends further support market expansion, with the global aging population driving increased demand for minimally invasive interventions. Patients aged 65+ represent the fastest-growing demographic segment requiring surgical interventions, with a 4.2% annual increase in procedure volume. This population particularly benefits from the reduced recovery times and lower complication rates associated with hydrogel-facilitated minimally invasive techniques.
Reimbursement landscapes are increasingly favorable, with major insurance providers expanding coverage for minimally invasive procedures. Medicare and private insurers have increased reimbursement rates by an average of 15% for qualifying minimally invasive procedures over the past three years, recognizing their long-term cost benefits and improved outcomes.
Market challenges include initial technology adoption costs, with specialized equipment for hydrogel-based procedures averaging $75,000-150,000 per surgical suite. However, return on investment analyses indicate these costs are typically recovered within 14-18 months through increased procedure volumes and improved efficiency.
Healthcare providers are increasingly prioritizing minimally invasive approaches due to their demonstrable benefits in patient outcomes and cost efficiency. Hospital administrators report average cost savings of 30-40% per procedure when utilizing minimally invasive techniques compared to traditional open surgeries, primarily due to shorter hospital stays and reduced complication rates. Patient satisfaction scores for minimally invasive procedures consistently exceed 85%, compared to 62% for conventional surgical approaches.
Regional market analysis reveals North America currently dominates with 42% market share, followed by Europe (28%) and Asia-Pacific (21%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing the fastest growth rate at 14.2% annually, driven by improving healthcare infrastructure and increasing adoption of advanced surgical technologies in countries like China, India, and South Korea.
Injectable hydrogel applications are particularly well-positioned within several high-growth surgical specialties. Orthopedic applications lead with 31% market share, followed by cardiovascular (24%), neurological (18%), and general surgery (15%). The remaining 12% encompasses emerging applications across various specialties including ophthalmology and plastic surgery.
Demographic trends further support market expansion, with the global aging population driving increased demand for minimally invasive interventions. Patients aged 65+ represent the fastest-growing demographic segment requiring surgical interventions, with a 4.2% annual increase in procedure volume. This population particularly benefits from the reduced recovery times and lower complication rates associated with hydrogel-facilitated minimally invasive techniques.
Reimbursement landscapes are increasingly favorable, with major insurance providers expanding coverage for minimally invasive procedures. Medicare and private insurers have increased reimbursement rates by an average of 15% for qualifying minimally invasive procedures over the past three years, recognizing their long-term cost benefits and improved outcomes.
Market challenges include initial technology adoption costs, with specialized equipment for hydrogel-based procedures averaging $75,000-150,000 per surgical suite. However, return on investment analyses indicate these costs are typically recovered within 14-18 months through increased procedure volumes and improved efficiency.
Injectable Hydrogel Technology Landscape and Barriers
Injectable hydrogel technology represents a significant advancement in minimally invasive surgical procedures, offering a versatile platform for drug delivery, tissue engineering, and wound healing. The current global landscape shows varying levels of development and implementation across regions. North America, particularly the United States, leads in research and commercialization efforts, with numerous academic institutions and biotech companies actively developing novel formulations. Europe follows closely, with strong contributions from countries like Germany, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom, where regulatory frameworks have been relatively accommodating for clinical trials.
In Asia, Japan and South Korea have emerged as innovation hubs for injectable hydrogel technologies, while China is rapidly expanding its research capabilities in this domain. The Middle East and Africa remain relatively underrepresented in this technological space, though some research initiatives are beginning to emerge in countries like Israel and South Africa.
Despite promising advancements, several significant barriers impede the widespread adoption of injectable hydrogels in non-invasive surgical applications. Technical challenges include achieving optimal mechanical properties that balance injectability with structural integrity post-injection. Many hydrogels exhibit syneresis (water expulsion) over time, compromising their long-term stability in vivo. Additionally, controlling gelation kinetics remains problematic—too rapid gelation can cause needle clogging during injection, while slow gelation may result in material dispersion before proper positioning.
Biocompatibility presents another major hurdle. While many hydrogels demonstrate acceptable short-term biocompatibility, long-term host responses remain inadequately characterized. Immunogenicity concerns persist, particularly with naturally derived polymers that may contain residual cellular components or endotoxins. Furthermore, degradation products from synthetic hydrogels might accumulate in tissues, potentially causing inflammatory responses or toxicity.
Regulatory challenges constitute a significant barrier to clinical translation. The complex nature of injectable hydrogels—often combining device and drug characteristics—creates regulatory ambiguity. Different jurisdictions apply varying classification schemes, complicating multinational development strategies. The FDA's regulatory pathway for combination products remains particularly demanding, requiring extensive preclinical and clinical data.
Manufacturing scalability presents additional obstacles. Many laboratory-developed formulations utilize processes difficult to scale industrially while maintaining batch-to-batch consistency. Sterilization methods may compromise hydrogel properties, and shelf-life stability remains suboptimal for many formulations, limiting commercial viability.
In Asia, Japan and South Korea have emerged as innovation hubs for injectable hydrogel technologies, while China is rapidly expanding its research capabilities in this domain. The Middle East and Africa remain relatively underrepresented in this technological space, though some research initiatives are beginning to emerge in countries like Israel and South Africa.
Despite promising advancements, several significant barriers impede the widespread adoption of injectable hydrogels in non-invasive surgical applications. Technical challenges include achieving optimal mechanical properties that balance injectability with structural integrity post-injection. Many hydrogels exhibit syneresis (water expulsion) over time, compromising their long-term stability in vivo. Additionally, controlling gelation kinetics remains problematic—too rapid gelation can cause needle clogging during injection, while slow gelation may result in material dispersion before proper positioning.
Biocompatibility presents another major hurdle. While many hydrogels demonstrate acceptable short-term biocompatibility, long-term host responses remain inadequately characterized. Immunogenicity concerns persist, particularly with naturally derived polymers that may contain residual cellular components or endotoxins. Furthermore, degradation products from synthetic hydrogels might accumulate in tissues, potentially causing inflammatory responses or toxicity.
Regulatory challenges constitute a significant barrier to clinical translation. The complex nature of injectable hydrogels—often combining device and drug characteristics—creates regulatory ambiguity. Different jurisdictions apply varying classification schemes, complicating multinational development strategies. The FDA's regulatory pathway for combination products remains particularly demanding, requiring extensive preclinical and clinical data.
Manufacturing scalability presents additional obstacles. Many laboratory-developed formulations utilize processes difficult to scale industrially while maintaining batch-to-batch consistency. Sterilization methods may compromise hydrogel properties, and shelf-life stability remains suboptimal for many formulations, limiting commercial viability.
Current Injectable Hydrogel Formulations and Applications
01 Injectable hydrogels for minimally invasive drug delivery
Injectable hydrogels can be formulated to deliver therapeutic agents in a minimally invasive manner. These hydrogels can be injected as liquids that subsequently form gels in situ, allowing for controlled release of drugs, proteins, or other bioactive molecules. The hydrogels can be designed with specific degradation profiles to optimize drug release kinetics and therapeutic efficacy while minimizing patient discomfort and recovery time.- Injectable hydrogels for minimally invasive drug delivery: Injectable hydrogels can be formulated to deliver therapeutic agents in a minimally invasive manner. These hydrogels can be injected as liquids that subsequently form gels in situ, allowing for controlled release of drugs, proteins, or other bioactive compounds. The gelation can be triggered by various mechanisms including temperature, pH, or ionic interactions. This approach reduces the need for surgical implantation while providing sustained release of therapeutic agents at the target site.
- Biodegradable hydrogels for tissue engineering applications: Biodegradable injectable hydrogels can serve as scaffolds for tissue engineering and regeneration. These hydrogels provide a three-dimensional environment that supports cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation. The biodegradable nature of these hydrogels allows for gradual replacement by native tissue as healing progresses. Various natural and synthetic polymers can be used to create these biodegradable matrices, which can be tailored to match the mechanical properties of the target tissue.
- Stimuli-responsive injectable hydrogels: Stimuli-responsive injectable hydrogels can undergo reversible sol-gel transitions in response to external stimuli such as temperature, pH, light, or electrical signals. These smart materials can be designed to form gels under physiological conditions after injection, enabling precise control over their properties and behavior in vivo. Applications include controlled drug release systems where the release rate can be modulated by applying specific stimuli, as well as injectable materials for tissue repair that can adapt to changing physiological environments.
- Injectable hydrogels for cosmetic and aesthetic applications: Injectable hydrogels can be used for various cosmetic and aesthetic applications, including wrinkle filling, soft tissue augmentation, and facial contouring. These hydrogels provide a non-surgical alternative to traditional cosmetic procedures, offering immediate results with minimal downtime. The hydrogels can be formulated to mimic the mechanical properties of natural tissues, providing natural-looking and feeling results. Some formulations also incorporate bioactive components that can improve skin quality over time.
- Composite injectable hydrogels with enhanced functionality: Composite injectable hydrogels incorporate additional components such as nanoparticles, microspheres, or bioactive molecules to enhance their functionality. These composite systems can combine the benefits of different materials to achieve superior mechanical properties, improved biocompatibility, or enhanced therapeutic effects. For example, hydrogels containing nanoparticles may offer improved mechanical strength or additional functionalities such as antimicrobial properties or imaging capabilities. These advanced formulations expand the potential applications of injectable hydrogels in both medical and cosmetic fields.
02 Temperature-responsive injectable hydrogels
Temperature-responsive hydrogels undergo sol-gel transition at physiological temperatures, making them ideal for injectable non-invasive applications. These smart materials remain liquid at room temperature for easy injection and solidify upon reaching body temperature, forming a stable gel matrix. This property enables precise placement of the hydrogel through minimally invasive procedures for various applications including tissue engineering, wound healing, and localized drug delivery.Expand Specific Solutions03 Injectable hydrogels for tissue engineering and regeneration
Injectable hydrogels provide scaffolds for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications through minimally invasive procedures. These biomaterials can be loaded with cells, growth factors, and other bioactive molecules to promote tissue repair and regeneration. The three-dimensional network of the hydrogel mimics the extracellular matrix, supporting cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation while maintaining the desired shape and mechanical properties of the regenerating tissue.Expand Specific Solutions04 Shear-thinning injectable hydrogels
Shear-thinning hydrogels exhibit decreased viscosity under applied shear stress during injection and rapidly recover their gel structure once the stress is removed. This property enables easy injectability through fine needles while maintaining structural integrity post-injection. These hydrogels can be engineered with self-healing properties and tunable mechanical characteristics to match specific tissue requirements, making them ideal for minimally invasive delivery of therapeutic agents or cells to target sites.Expand Specific Solutions05 Biocompatible and biodegradable injectable hydrogels
Biocompatible and biodegradable injectable hydrogels are designed to integrate with host tissues without causing adverse immune responses and degrade at controlled rates that match tissue regeneration timelines. These hydrogels are typically composed of natural polymers like hyaluronic acid, collagen, or alginate, or synthetic polymers such as poly(ethylene glycol) or poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid). The biodegradation products are non-toxic and can be metabolized or excreted by the body, eliminating the need for surgical removal and making these hydrogels ideal for non-invasive therapeutic applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies and Research Institutions in Hydrogel Innovation
Injectable hydrogel technology for non-invasive surgical techniques is currently in a growth phase, with the market expected to expand significantly due to increasing demand for minimally invasive procedures. The global market size is projected to reach several billion dollars by 2028, driven by applications in drug delivery, tissue engineering, and wound healing. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels across different applications. Leading research institutions like University of Strasbourg, Harvard College, and CNRS are advancing fundamental science, while companies including Boston Scientific Scimed, Covalon Technologies, and Ruining Bio are commercializing applications. Chinese entities such as Sichuan University and Jiangsu Jicui are rapidly gaining ground in this space. The competitive landscape features collaboration between academic institutions and industry players, with increasing patent activity indicating accelerating innovation in biocompatible materials and delivery systems.
Sichuan University
Technical Solution: Sichuan University has pioneered injectable hydrogels based on modified natural polymers including chitosan, alginate, and cellulose derivatives. Their technology employs a multi-component mixing approach where separate precursor solutions combine during injection to form hydrogels in situ. A key innovation is their development of self-healing hydrogels containing dynamic covalent bonds that allow the material to recover after deformation, making them ideal for tissues subjected to mechanical stress[6]. Their hydrogels incorporate nano-silicate particles that enhance mechanical properties and provide binding sites for therapeutic proteins, enabling sustained drug release profiles over weeks to months. Sichuan researchers have demonstrated particular success in wound healing applications, where their hydrogels create moist environments that accelerate epithelialization while delivering antimicrobial agents[7]. The technology includes thermo-responsive hydrogels that transition from solution to gel state at body temperature, enabling precise localization at injection sites. Recent advances include conductive hydrogels incorporating graphene oxide nanoparticles that support electrical signaling in neural tissue engineering applications, showing promise for spinal cord injury repair[8].
Strengths: Excellent biocompatibility due to natural polymer base; strong adhesion to tissue surfaces even in wet environments; cost-effective manufacturing potential compared to synthetic alternatives. Weaknesses: Batch-to-batch variability of natural polymers may affect performance consistency; limited mechanical strength compared to some synthetic systems; potential immunogenicity concerns with certain natural polymer sources.
President & Fellows of Harvard College
Technical Solution: Harvard's injectable hydrogel technology utilizes shear-thinning biomaterials that exhibit solid-like behavior at rest but flow under applied stress, enabling minimally invasive delivery through small-gauge needles. Their platform combines hyaluronic acid with peptide crosslinkers to create a dual-network hydrogel system that rapidly self-heals post-injection. This technology has been engineered to deliver therapeutic agents including cells, growth factors, and small molecules with controlled release profiles. Harvard researchers have demonstrated successful applications in cardiac tissue repair, where hydrogels deliver stem cells and promote vascularization in damaged heart tissue[1]. Their hydrogels incorporate bioactive components that mimic extracellular matrix properties, promoting cell adhesion and tissue integration. Recent advances include stimuli-responsive hydrogels that can change properties in response to temperature, pH, or enzymatic activity at the target site, allowing for precise control over therapeutic delivery and gel degradation rates[2].
Strengths: Superior mechanical tunability allowing customization for different tissue environments; excellent biocompatibility with minimal inflammatory response; versatile delivery platform for multiple therapeutic agents. Weaknesses: Potential challenges with long-term stability in certain physiological environments; some formulations may require specialized storage conditions; scaling manufacturing while maintaining batch-to-batch consistency remains challenging.
Key Patents and Breakthroughs in Hydrogel Technology
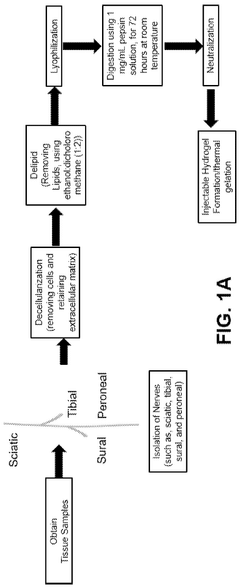
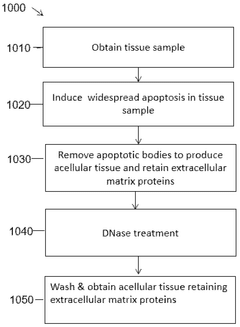
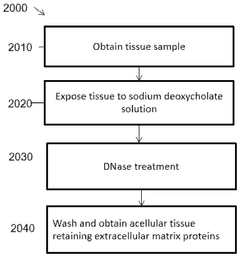
Decellularized, delipidated tissues, hydrogels thereof, and uses thereof
PatentWO2024220395A1
Innovation
- Development of decellularized, delipidated tissue hydrogels that retain native extracellular matrix proteins and undergo thermal gelation at body temperature, using methods such as apoptosis-based and chemical decellularization followed by delipidation to enhance gelation kinetics and mechanical properties.
Biocompatibility and Safety Considerations
Biocompatibility represents a critical factor in the development and application of injectable hydrogels for non-invasive surgical techniques. These biomaterials must demonstrate minimal immunogenicity and toxicity when introduced into the human body. Current research indicates that natural polymer-based hydrogels, such as those derived from hyaluronic acid, alginate, and collagen, generally exhibit superior biocompatibility compared to their synthetic counterparts. However, even natural polymers require extensive modification and testing to ensure they do not trigger adverse immune responses.
Safety considerations extend beyond mere biocompatibility to encompass degradation profiles and byproduct toxicity. Injectable hydrogels must degrade at predictable rates that align with tissue regeneration timelines, releasing non-toxic byproducts that can be metabolized or excreted through normal physiological pathways. Recent studies have shown that controlling crosslinking density and incorporating enzymatically degradable linkages can significantly improve degradation profiles, enhancing overall safety profiles.
Sterilization presents another crucial challenge in hydrogel development. Traditional sterilization methods such as autoclaving often compromise the structural integrity and functional properties of hydrogels. Alternative approaches including gamma irradiation, ethylene oxide treatment, and sterile filtration each present unique advantages and limitations. The selection of appropriate sterilization techniques must balance efficacy against preservation of the hydrogel's mechanical and biological properties.
Long-term safety monitoring remains an underexplored area requiring further investigation. While acute inflammatory responses to injectable hydrogels are well-documented, the potential for delayed hypersensitivity reactions or chronic inflammation requires longitudinal studies. Regulatory frameworks increasingly demand comprehensive safety data packages that include both short-term biocompatibility testing and extended monitoring protocols.
The integration of bioactive components, such as growth factors or therapeutic cells, introduces additional safety considerations. These components must maintain stability within the hydrogel matrix without leaching uncontrollably into surrounding tissues. Controlled release systems that respond to specific physiological triggers represent a promising approach to enhancing safety while maximizing therapeutic efficacy.
Batch-to-batch consistency represents a significant manufacturing challenge that directly impacts safety profiles. Variations in molecular weight, crosslinking density, or impurity levels can dramatically alter in vivo performance. Advanced analytical techniques including rheological characterization, spectroscopic analysis, and high-throughput screening methods are increasingly employed to ensure consistent safety profiles across production batches.
Safety considerations extend beyond mere biocompatibility to encompass degradation profiles and byproduct toxicity. Injectable hydrogels must degrade at predictable rates that align with tissue regeneration timelines, releasing non-toxic byproducts that can be metabolized or excreted through normal physiological pathways. Recent studies have shown that controlling crosslinking density and incorporating enzymatically degradable linkages can significantly improve degradation profiles, enhancing overall safety profiles.
Sterilization presents another crucial challenge in hydrogel development. Traditional sterilization methods such as autoclaving often compromise the structural integrity and functional properties of hydrogels. Alternative approaches including gamma irradiation, ethylene oxide treatment, and sterile filtration each present unique advantages and limitations. The selection of appropriate sterilization techniques must balance efficacy against preservation of the hydrogel's mechanical and biological properties.
Long-term safety monitoring remains an underexplored area requiring further investigation. While acute inflammatory responses to injectable hydrogels are well-documented, the potential for delayed hypersensitivity reactions or chronic inflammation requires longitudinal studies. Regulatory frameworks increasingly demand comprehensive safety data packages that include both short-term biocompatibility testing and extended monitoring protocols.
The integration of bioactive components, such as growth factors or therapeutic cells, introduces additional safety considerations. These components must maintain stability within the hydrogel matrix without leaching uncontrollably into surrounding tissues. Controlled release systems that respond to specific physiological triggers represent a promising approach to enhancing safety while maximizing therapeutic efficacy.
Batch-to-batch consistency represents a significant manufacturing challenge that directly impacts safety profiles. Variations in molecular weight, crosslinking density, or impurity levels can dramatically alter in vivo performance. Advanced analytical techniques including rheological characterization, spectroscopic analysis, and high-throughput screening methods are increasingly employed to ensure consistent safety profiles across production batches.
Regulatory Pathway for Injectable Biomaterials
The regulatory landscape for injectable biomaterials, particularly hydrogels used in non-invasive surgical techniques, presents a complex pathway that varies significantly across global jurisdictions. In the United States, the FDA typically classifies injectable hydrogels as combination products, requiring evaluation through either the Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) or the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER), depending on the primary mode of action. Most injectable hydrogels for surgical applications fall under Class III medical devices or drug-device combinations, necessitating a Premarket Approval (PMA) pathway that demands comprehensive clinical trials demonstrating both safety and efficacy.
European regulatory frameworks approach injectable biomaterials through the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), with most surgical hydrogels classified as Class III devices. The conformity assessment procedure requires involvement of a Notified Body and the compilation of extensive technical documentation, including clinical evaluation reports that demonstrate positive benefit-risk profiles. The CE marking process has become increasingly stringent since the implementation of the new MDR in 2021, particularly regarding clinical evidence requirements.
In Asian markets, particularly Japan and China, regulatory pathways have distinct characteristics. Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) has established the Sakigake designation system for innovative medical technologies, potentially expediting approval for novel injectable hydrogels. China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) requires extensive local clinical trials, even for products approved elsewhere, though recent reforms have introduced accelerated pathways for innovative medical technologies.
Quality management systems compliant with ISO 13485 standards are universally required across major markets, with particular emphasis on manufacturing controls, sterilization validation, and stability testing for injectable biomaterials. Biocompatibility testing according to ISO 10993 series is mandatory, with special attention to cytotoxicity, sensitization, irritation, and systemic toxicity for injectable hydrogels that remain in the body for extended periods.
Post-market surveillance requirements have intensified globally, with regulatory bodies demanding robust systems for adverse event reporting and long-term follow-up studies. This is particularly relevant for injectable hydrogels, as their long-term in vivo behavior may reveal safety concerns not evident during pre-market clinical trials. Manufacturers must implement comprehensive risk management plans that address potential degradation products, migration issues, and long-term tissue interactions.
Harmonization efforts through the International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF) are gradually streamlining global requirements, though significant regional differences persist. Companies developing injectable hydrogels must adopt strategic regulatory planning early in development, considering potential parallel submissions to multiple authorities to optimize global market access timelines.
European regulatory frameworks approach injectable biomaterials through the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), with most surgical hydrogels classified as Class III devices. The conformity assessment procedure requires involvement of a Notified Body and the compilation of extensive technical documentation, including clinical evaluation reports that demonstrate positive benefit-risk profiles. The CE marking process has become increasingly stringent since the implementation of the new MDR in 2021, particularly regarding clinical evidence requirements.
In Asian markets, particularly Japan and China, regulatory pathways have distinct characteristics. Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) has established the Sakigake designation system for innovative medical technologies, potentially expediting approval for novel injectable hydrogels. China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) requires extensive local clinical trials, even for products approved elsewhere, though recent reforms have introduced accelerated pathways for innovative medical technologies.
Quality management systems compliant with ISO 13485 standards are universally required across major markets, with particular emphasis on manufacturing controls, sterilization validation, and stability testing for injectable biomaterials. Biocompatibility testing according to ISO 10993 series is mandatory, with special attention to cytotoxicity, sensitization, irritation, and systemic toxicity for injectable hydrogels that remain in the body for extended periods.
Post-market surveillance requirements have intensified globally, with regulatory bodies demanding robust systems for adverse event reporting and long-term follow-up studies. This is particularly relevant for injectable hydrogels, as their long-term in vivo behavior may reveal safety concerns not evident during pre-market clinical trials. Manufacturers must implement comprehensive risk management plans that address potential degradation products, migration issues, and long-term tissue interactions.
Harmonization efforts through the International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF) are gradually streamlining global requirements, though significant regional differences persist. Companies developing injectable hydrogels must adopt strategic regulatory planning early in development, considering potential parallel submissions to multiple authorities to optimize global market access timelines.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!