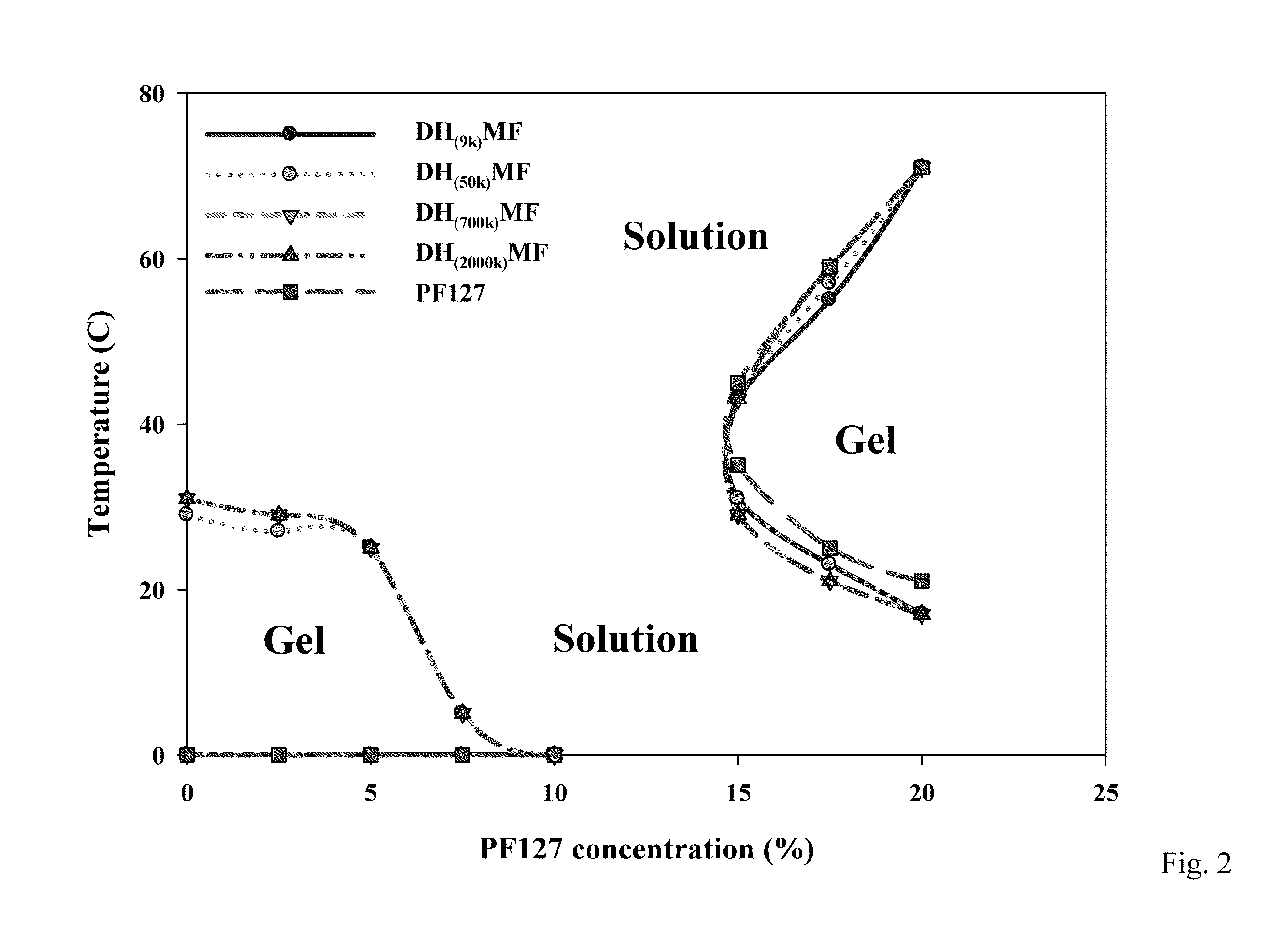
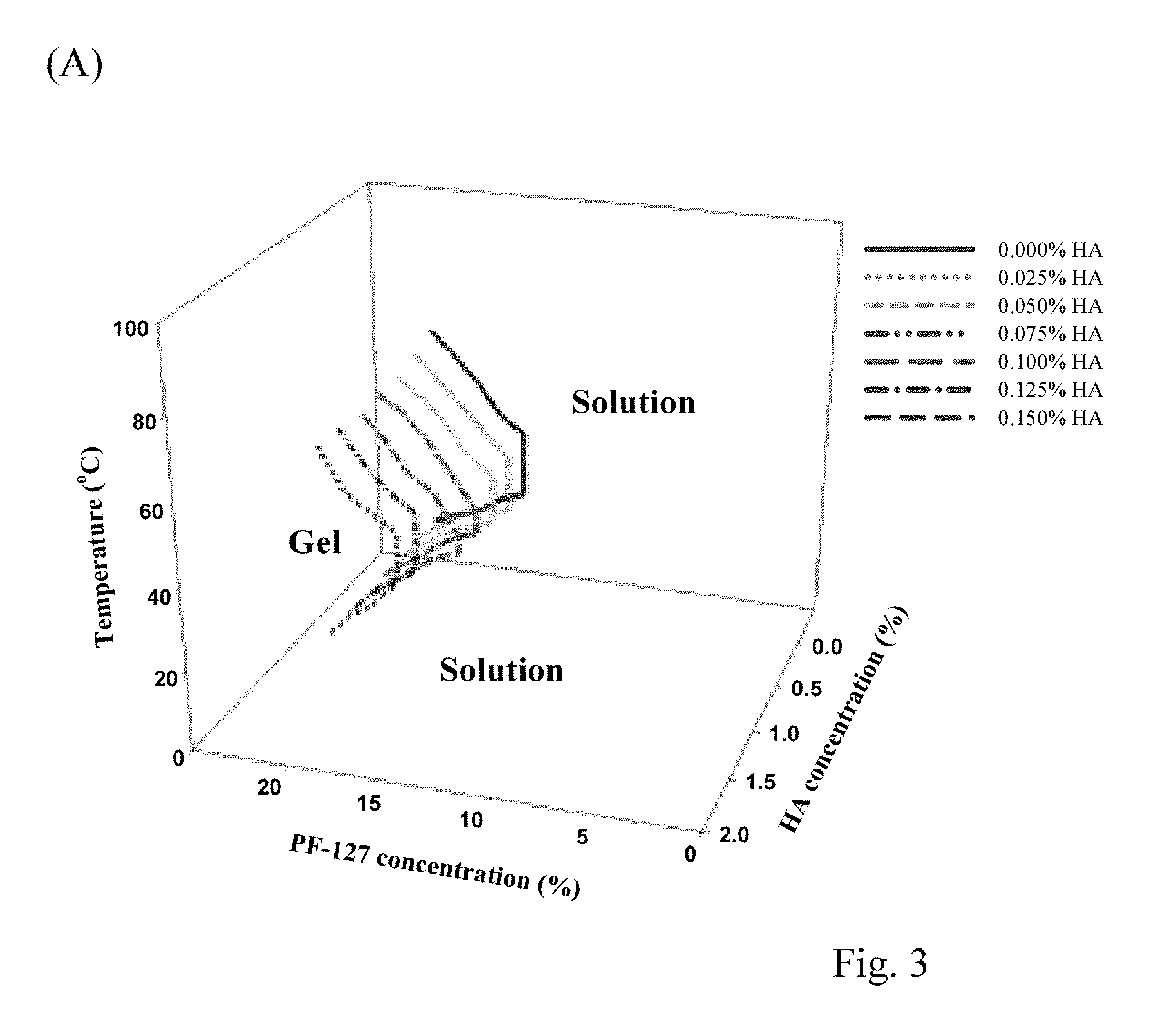
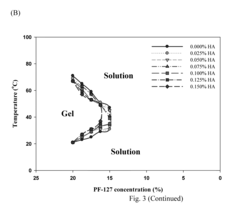
Injectable Hydrogel Assays in Drug Sensitivity and Resistance Testing
OCT 15, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Injectable Hydrogel Technology Background and Objectives
Injectable hydrogels have emerged as a revolutionary platform in biomedical research, particularly in the field of drug sensitivity and resistance testing. The evolution of this technology can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring three-dimensional cell culture systems to better mimic the in vivo tumor microenvironment. Traditional two-dimensional cell culture methods failed to recapitulate the complex interactions between cancer cells and their surrounding matrix, leading to significant discrepancies between laboratory findings and clinical outcomes.
The development trajectory of injectable hydrogels has been marked by significant advancements in biomaterial science, particularly in creating materials with tunable mechanical properties, biodegradability, and biocompatibility. Early hydrogel systems were primarily composed of natural polymers such as collagen and Matrigel, which provided basic structural support but lacked consistency and customizability. The field has since progressed toward synthetic and semi-synthetic hydrogel systems that offer precise control over mechanical properties, degradation rates, and biochemical functionalities.
A pivotal shift occurred around 2010-2015 with the integration of patient-derived cells into hydrogel platforms, enabling personalized drug testing approaches. This innovation addressed the critical need for predictive preclinical models that account for patient-specific tumor characteristics and drug response patterns. The technology has continued to evolve with the incorporation of advanced imaging techniques, high-throughput screening capabilities, and computational modeling.
The primary objective of injectable hydrogel technology in drug sensitivity testing is to establish physiologically relevant three-dimensional models that accurately predict patient-specific responses to anticancer therapies. These platforms aim to bridge the gap between conventional laboratory testing and clinical outcomes by replicating key aspects of the tumor microenvironment, including cell-cell interactions, extracellular matrix composition, and mechanical forces.
Additional technical goals include developing hydrogel systems with enhanced reproducibility, scalability for high-throughput applications, and compatibility with existing clinical workflows. Researchers are working toward creating standardized protocols that can be readily implemented in clinical settings, potentially revolutionizing the approach to personalized cancer treatment.
The technology also aims to address the critical challenge of drug resistance by providing platforms to study resistance mechanisms in real-time and identify effective combination therapies. By enabling the systematic evaluation of drug efficacy against patient-derived tumor cells in a physiologically relevant context, injectable hydrogels hold promise for improving treatment outcomes and reducing the trial-and-error approach currently dominating cancer therapy selection.
The development trajectory of injectable hydrogels has been marked by significant advancements in biomaterial science, particularly in creating materials with tunable mechanical properties, biodegradability, and biocompatibility. Early hydrogel systems were primarily composed of natural polymers such as collagen and Matrigel, which provided basic structural support but lacked consistency and customizability. The field has since progressed toward synthetic and semi-synthetic hydrogel systems that offer precise control over mechanical properties, degradation rates, and biochemical functionalities.
A pivotal shift occurred around 2010-2015 with the integration of patient-derived cells into hydrogel platforms, enabling personalized drug testing approaches. This innovation addressed the critical need for predictive preclinical models that account for patient-specific tumor characteristics and drug response patterns. The technology has continued to evolve with the incorporation of advanced imaging techniques, high-throughput screening capabilities, and computational modeling.
The primary objective of injectable hydrogel technology in drug sensitivity testing is to establish physiologically relevant three-dimensional models that accurately predict patient-specific responses to anticancer therapies. These platforms aim to bridge the gap between conventional laboratory testing and clinical outcomes by replicating key aspects of the tumor microenvironment, including cell-cell interactions, extracellular matrix composition, and mechanical forces.
Additional technical goals include developing hydrogel systems with enhanced reproducibility, scalability for high-throughput applications, and compatibility with existing clinical workflows. Researchers are working toward creating standardized protocols that can be readily implemented in clinical settings, potentially revolutionizing the approach to personalized cancer treatment.
The technology also aims to address the critical challenge of drug resistance by providing platforms to study resistance mechanisms in real-time and identify effective combination therapies. By enabling the systematic evaluation of drug efficacy against patient-derived tumor cells in a physiologically relevant context, injectable hydrogels hold promise for improving treatment outcomes and reducing the trial-and-error approach currently dominating cancer therapy selection.
Market Analysis for Drug Sensitivity Testing Solutions
The global market for drug sensitivity and resistance testing solutions has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing prevalence of cancer and infectious diseases, coupled with the rising demand for personalized medicine. The market for injectable hydrogel-based assays represents a particularly innovative segment within this broader landscape, offering unique advantages for three-dimensional cell culture and drug response evaluation.
Current market estimates value the global drug sensitivity testing market at approximately $8.5 billion, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2% through 2028. Injectable hydrogel technologies specifically are experiencing even more rapid adoption, with some analysts suggesting growth rates exceeding 12% annually as these platforms demonstrate superior predictive capabilities compared to traditional 2D cell culture methods.
North America currently dominates the market share, accounting for roughly 40% of global revenue, followed by Europe at 30% and Asia-Pacific at 20%. The remaining 10% is distributed across other regions. This geographic distribution reflects both research infrastructure investment and cancer treatment expenditures globally.
Key market segments include oncology applications (representing approximately 65% of the market), infectious disease testing (20%), and other applications including autoimmune disorders (15%). Within oncology, breast, lung, and colorectal cancer testing comprise the largest application areas, reflecting both disease prevalence and treatment complexity.
End-user analysis reveals that hospital-associated laboratories and academic research institutions currently represent the largest market segments (40% and 30% respectively), while pharmaceutical R&D departments (20%) and independent clinical laboratories (10%) constitute smaller but growing segments. The pharmaceutical sector's interest is particularly noteworthy, as injectable hydrogel platforms increasingly serve as critical tools in drug development pipelines.
Market drivers include the growing emphasis on precision medicine approaches, increasing cancer incidence rates, technological advancements in 3D cell culture systems, and rising healthcare expenditures globally. Regulatory support for companion diagnostics has further accelerated market growth, particularly in developed economies.
Challenges limiting market expansion include high costs associated with advanced testing platforms, technical complexity requiring specialized expertise, and reimbursement uncertainties in some regions. Additionally, standardization issues across different hydrogel formulations present obstacles to widespread clinical implementation.
Emerging market opportunities exist in developing economies where cancer rates are rising rapidly but testing infrastructure remains underdeveloped. Furthermore, the integration of injectable hydrogel assays with artificial intelligence and machine learning for improved predictive analytics represents a significant growth avenue for market participants.
Current market estimates value the global drug sensitivity testing market at approximately $8.5 billion, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2% through 2028. Injectable hydrogel technologies specifically are experiencing even more rapid adoption, with some analysts suggesting growth rates exceeding 12% annually as these platforms demonstrate superior predictive capabilities compared to traditional 2D cell culture methods.
North America currently dominates the market share, accounting for roughly 40% of global revenue, followed by Europe at 30% and Asia-Pacific at 20%. The remaining 10% is distributed across other regions. This geographic distribution reflects both research infrastructure investment and cancer treatment expenditures globally.
Key market segments include oncology applications (representing approximately 65% of the market), infectious disease testing (20%), and other applications including autoimmune disorders (15%). Within oncology, breast, lung, and colorectal cancer testing comprise the largest application areas, reflecting both disease prevalence and treatment complexity.
End-user analysis reveals that hospital-associated laboratories and academic research institutions currently represent the largest market segments (40% and 30% respectively), while pharmaceutical R&D departments (20%) and independent clinical laboratories (10%) constitute smaller but growing segments. The pharmaceutical sector's interest is particularly noteworthy, as injectable hydrogel platforms increasingly serve as critical tools in drug development pipelines.
Market drivers include the growing emphasis on precision medicine approaches, increasing cancer incidence rates, technological advancements in 3D cell culture systems, and rising healthcare expenditures globally. Regulatory support for companion diagnostics has further accelerated market growth, particularly in developed economies.
Challenges limiting market expansion include high costs associated with advanced testing platforms, technical complexity requiring specialized expertise, and reimbursement uncertainties in some regions. Additionally, standardization issues across different hydrogel formulations present obstacles to widespread clinical implementation.
Emerging market opportunities exist in developing economies where cancer rates are rising rapidly but testing infrastructure remains underdeveloped. Furthermore, the integration of injectable hydrogel assays with artificial intelligence and machine learning for improved predictive analytics represents a significant growth avenue for market participants.
Current Challenges in Hydrogel-Based Drug Testing
Despite the promising potential of injectable hydrogels for drug sensitivity and resistance testing, several significant challenges currently impede their widespread adoption and clinical translation. The primary technical hurdle involves achieving consistent mechanical properties across hydrogel batches. Variations in stiffness, porosity, and degradation rates can significantly affect drug diffusion kinetics and cellular responses, leading to inconsistent test results and poor reproducibility between experiments.
Another major challenge lies in the accurate recreation of the tumor microenvironment (TME). While hydrogels provide a three-dimensional structure, they often fail to fully recapitulate the complex extracellular matrix composition, stromal cell interactions, and biochemical gradients present in native tumors. This simplification may lead to drug response profiles that do not accurately predict in vivo outcomes, limiting clinical relevance.
The integration of vasculature-mimicking structures represents a persistent technical obstacle. The absence of functional blood vessels in most hydrogel systems prevents proper modeling of drug delivery dynamics and hypoxic gradients that significantly influence tumor drug resistance mechanisms. Current approaches using microfluidic channels or sacrificial templates show promise but remain technically challenging to implement consistently.
Standardization issues plague the field, with diverse protocols for hydrogel preparation, cell encapsulation, drug administration, and response assessment making cross-laboratory comparisons difficult. The lack of validated benchmarks against which to compare hydrogel-based assay results further complicates the establishment of reliable testing platforms.
Scaling limitations present significant barriers to high-throughput applications. Many hydrogel preparation techniques are labor-intensive and difficult to automate, restricting their utility in pharmaceutical screening programs that require rapid testing of numerous compounds across multiple conditions.
Real-time monitoring capabilities remain underdeveloped, with most current systems requiring endpoint analysis that fails to capture the dynamic nature of drug responses. Non-invasive imaging and sensing technologies compatible with hydrogel matrices are needed to enable continuous assessment of cellular responses without disrupting the 3D architecture.
Regulatory and validation challenges further complicate clinical implementation. The complex nature of hydrogel-based assays makes them difficult to validate against established gold standards, and regulatory frameworks for their use in personalized medicine applications remain underdeveloped, creating uncertainty around their eventual clinical adoption.
Another major challenge lies in the accurate recreation of the tumor microenvironment (TME). While hydrogels provide a three-dimensional structure, they often fail to fully recapitulate the complex extracellular matrix composition, stromal cell interactions, and biochemical gradients present in native tumors. This simplification may lead to drug response profiles that do not accurately predict in vivo outcomes, limiting clinical relevance.
The integration of vasculature-mimicking structures represents a persistent technical obstacle. The absence of functional blood vessels in most hydrogel systems prevents proper modeling of drug delivery dynamics and hypoxic gradients that significantly influence tumor drug resistance mechanisms. Current approaches using microfluidic channels or sacrificial templates show promise but remain technically challenging to implement consistently.
Standardization issues plague the field, with diverse protocols for hydrogel preparation, cell encapsulation, drug administration, and response assessment making cross-laboratory comparisons difficult. The lack of validated benchmarks against which to compare hydrogel-based assay results further complicates the establishment of reliable testing platforms.
Scaling limitations present significant barriers to high-throughput applications. Many hydrogel preparation techniques are labor-intensive and difficult to automate, restricting their utility in pharmaceutical screening programs that require rapid testing of numerous compounds across multiple conditions.
Real-time monitoring capabilities remain underdeveloped, with most current systems requiring endpoint analysis that fails to capture the dynamic nature of drug responses. Non-invasive imaging and sensing technologies compatible with hydrogel matrices are needed to enable continuous assessment of cellular responses without disrupting the 3D architecture.
Regulatory and validation challenges further complicate clinical implementation. The complex nature of hydrogel-based assays makes them difficult to validate against established gold standards, and regulatory frameworks for their use in personalized medicine applications remain underdeveloped, creating uncertainty around their eventual clinical adoption.
Current Injectable Hydrogel Assay Methodologies
01 3D hydrogel platforms for drug sensitivity testing
Three-dimensional hydrogel platforms provide a physiologically relevant environment for testing drug sensitivity and resistance. These platforms mimic the extracellular matrix and allow for the culture of patient-derived cells or organoids, enabling more accurate prediction of drug responses compared to traditional 2D cultures. The hydrogels can be formulated with various biomaterials to match the mechanical and biochemical properties of specific tissues, enhancing the clinical relevance of drug sensitivity assays.- 3D hydrogel platforms for drug sensitivity testing: Three-dimensional hydrogel platforms provide a more physiologically relevant environment for testing drug sensitivity and resistance compared to traditional 2D cell cultures. These platforms mimic the extracellular matrix and allow for better prediction of in vivo drug responses. The 3D structure enables more accurate assessment of how cancer cells respond to various treatments, helping to identify effective therapeutic strategies and mechanisms of drug resistance.
- Injectable hydrogels for personalized medicine applications: Injectable hydrogels can be used for personalized medicine by incorporating patient-derived cells or tissues to create patient-specific drug sensitivity assays. These hydrogels allow for the testing of multiple drug candidates simultaneously on patient samples, enabling the selection of the most effective treatment regimen. The injectable nature of these hydrogels makes them particularly suitable for minimally invasive applications and real-time monitoring of drug responses.
- Stimuli-responsive hydrogels for controlled drug release and testing: Stimuli-responsive hydrogels can change their properties in response to external stimuli such as temperature, pH, or light. These smart materials can be used to create drug sensitivity assays that more accurately mimic the dynamic in vivo environment. By controlling the release of drugs within the hydrogel, researchers can better understand how drug concentration and exposure time affect cellular responses, providing insights into mechanisms of drug resistance.
- Hydrogel-based high-throughput screening systems: Hydrogel-based high-throughput screening systems enable the rapid testing of numerous drug candidates against patient-derived cells or tissues. These systems incorporate advanced imaging and analysis techniques to quantify drug responses in real-time. The high-throughput nature of these assays allows for comprehensive drug sensitivity profiling, helping to identify effective drug combinations and overcome resistance mechanisms.
- Biomarker identification in hydrogel drug sensitivity assays: Hydrogel-based drug sensitivity assays can be used to identify biomarkers associated with drug response or resistance. By analyzing cellular behavior and molecular changes within the hydrogel environment before and after drug exposure, researchers can identify predictive biomarkers for treatment outcomes. This approach enables the development of companion diagnostics that can guide treatment selection and monitor the emergence of resistance during therapy.
02 Injectable hydrogels for personalized medicine applications
Injectable hydrogels can be used for personalized medicine approaches by incorporating patient-derived cells or tissues to test drug sensitivity and resistance patterns. These systems allow for rapid screening of multiple therapeutic agents simultaneously, helping clinicians select the most effective treatment regimens for individual patients. The injectable nature of these hydrogels facilitates minimally invasive sampling and testing procedures, making them suitable for clinical applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Stimuli-responsive hydrogels for controlled drug release and testing
Stimuli-responsive hydrogels can change their properties in response to external stimuli such as pH, temperature, or light, allowing for controlled release of drugs and precise testing of drug sensitivity. These smart hydrogels enable the evaluation of drug efficacy under various physiological conditions and can simulate the dynamic microenvironment of tissues. The responsive nature of these hydrogels also facilitates the study of drug resistance mechanisms that may develop over time or under specific conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Hydrogel-based high-throughput screening systems
Hydrogel-based high-throughput screening systems enable rapid testing of multiple drugs or drug combinations against patient-derived cells or organoids. These systems incorporate advanced imaging and analysis technologies to quantify drug responses in real-time. The high-throughput nature of these platforms allows for comprehensive evaluation of drug sensitivity and resistance patterns, facilitating the identification of effective therapeutic strategies and potential resistance mechanisms.Expand Specific Solutions05 Composite hydrogels with enhanced functionality for drug testing
Composite hydrogels incorporating multiple components such as nanoparticles, growth factors, or extracellular matrix proteins provide enhanced functionality for drug sensitivity testing. These advanced hydrogel systems can better recapitulate the complexity of native tissues and tumor microenvironments, leading to more accurate prediction of drug responses. The composite nature of these hydrogels allows for the simultaneous evaluation of multiple parameters affecting drug sensitivity and resistance, including cell-matrix interactions and paracrine signaling.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies in Hydrogel Drug Testing Industry
Injectable hydrogel assays for drug sensitivity and resistance testing represent an emerging field at the intersection of biomaterials and precision medicine. The market is in its early growth phase, with an estimated global market size of $300-500 million and projected annual growth of 15-20%. The technology demonstrates moderate maturity, with key players advancing different aspects of the ecosystem. Koninklijke Philips NV and F. Hoffmann-La Roche are leveraging their established healthcare infrastructure to commercialize these platforms, while specialized companies like Contraline and Incept LLC focus on innovative hydrogel formulations. Academic institutions, particularly Chinese Academy of Sciences and Johns Hopkins University, are driving fundamental research. The competitive landscape is characterized by strategic partnerships between research institutions and pharmaceutical companies, with increasing interest from medical device manufacturers seeking to expand their diagnostic portfolios.
Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Technical Solution: The Changchun Institute has developed innovative injectable hydrogel systems based on self-assembling peptides and polysaccharide derivatives specifically designed for drug sensitivity testing. Their technology features temperature-responsive hydrogels that undergo sol-gel transition at physiological temperatures, allowing for minimally invasive delivery and formation of 3D cellular microenvironments. The institute's platform incorporates multiple extracellular matrix components (collagen, laminin, fibronectin) at physiologically relevant concentrations to recreate tissue-specific niches. Their hydrogels feature controlled degradation profiles (2-30 days) that can be tailored to specific testing requirements. The system has been extensively validated for testing traditional chemotherapeutics, targeted therapies, and immunomodulatory agents, with particular success in predicting resistance mechanisms in solid tumors. Recent advancements include the incorporation of gradient-generating capabilities to study drug penetration dynamics and hypoxia-induced resistance.
Strengths: Excellent biocompatibility with minimal batch-to-batch variation; versatile formulation options for different tissue types; cost-effective production methods. Weaknesses: Limited commercial availability outside China; requires specialized expertise for optimal implementation; moderate throughput compared to some competing technologies.
Institute of Process Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Technical Solution: The Institute of Process Engineering has developed a comprehensive injectable hydrogel platform called "HydroTest" specifically for drug sensitivity and resistance testing. Their technology utilizes a composite hydrogel system combining synthetic and natural polymers with precisely controlled mechanical properties (stiffness range 0.5-40 kPa) and degradation kinetics. The platform features microfluidic integration for high-throughput formation of uniform hydrogel microspheres containing patient-derived cells, enabling parallel testing of multiple drug candidates. Their system incorporates advanced imaging capabilities for real-time monitoring of cellular responses, including confocal microscopy compatibility and fluorescent reporter systems. The institute has developed specialized analytical algorithms to quantify drug response parameters including IC50 values, cell death mechanisms, and resistance marker expression. Their technology has been validated in clinical studies for multiple cancer types, showing significant improvement in predicting therapeutic outcomes compared to conventional 2D assays.
Strengths: Excellent scalability from research to clinical applications; comprehensive analytical tools for quantitative assessment; robust performance across diverse tissue types. Weaknesses: Complex setup requiring specialized training; moderate cost for initial implementation; requires integration with advanced imaging systems for optimal performance.
Key Patents in Hydrogel-Based Drug Resistance Testing
Thermosensitive injectable hydrogel for drug delivery
PatentInactiveUS20150366975A1
Innovation
- A thermosensitive injectable hydrogel composed of hyaluronan and a copolymer of polyethylene oxide (PEO) and polypropylene oxide (PPO), with a gel formation temperature between 30° C. and 37° C., is developed, allowing for in situ formation and sustained drug release at the tumor site, enhancing therapeutic efficacy.
Dynamically crosslinked injectable hydrogels with chemically stabilized multilamellar vesicles
PatentPendingUS20250295584A1
Innovation
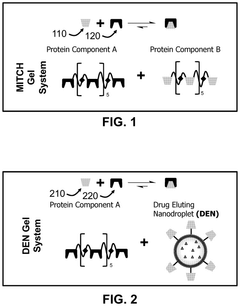
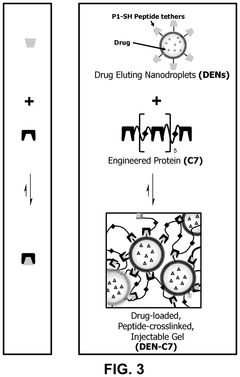
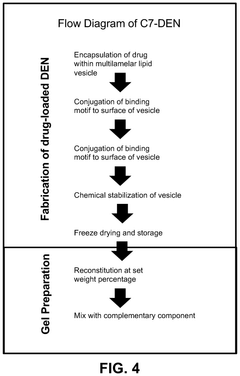
- The development of chemically stabilized multilamellar vesicles within a physically crosslinked hydrogel system, using a C7 protein and P1-functionalized lipids, allows for rapid mixing and injection without external stimuli, providing tunable drug release and mechanical protection during delivery.
Regulatory Pathway for Clinical Implementation
The regulatory landscape for injectable hydrogel assays in drug sensitivity and resistance testing presents a complex pathway toward clinical implementation. These innovative platforms must navigate through multiple regulatory frameworks, primarily overseen by the FDA in the United States through its Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) or the Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER), depending on the specific classification of the hydrogel system.
For clinical implementation, injectable hydrogel assays would likely be classified as combination products, incorporating both device and biological components. This classification necessitates comprehensive preclinical validation studies demonstrating safety, reproducibility, and correlation with established clinical outcomes. Manufacturers must address biocompatibility concerns, stability of the hydrogel matrix, and potential immunological responses when implanted in patients.
The regulatory pathway typically begins with Investigational Device Exemption (IDE) applications to conduct initial clinical trials. These trials must establish not only the safety profile but also demonstrate clinical utility in predicting drug responses with statistical significance compared to standard methods. The FDA's breakthrough device designation could potentially accelerate this process for hydrogel assays that show substantial advantages over current diagnostic approaches in oncology.
Quality control measures represent another critical regulatory consideration. Manufacturers must implement robust quality management systems compliant with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and ISO 13485 standards. This includes validation of production processes, sterilization methods, and shelf-life stability of the hydrogel components to ensure consistent performance across batches.
Reimbursement pathways present additional challenges beyond regulatory approval. Clinical utility studies must demonstrate cost-effectiveness and improved patient outcomes to secure coverage from Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurers. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) may require additional evidence through coverage with evidence development (CED) programs before granting routine reimbursement.
International regulatory harmonization efforts, including through the International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF), are increasingly important for global implementation. While the European Union's Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR) provide pathways in Europe, significant differences remain in regulatory requirements across major markets, necessitating tailored submission strategies.
Data privacy and ethical considerations also factor into regulatory compliance, particularly regarding patient sample handling, genetic information storage, and long-term follow-up requirements. Manufacturers must develop comprehensive consent procedures and data management protocols that comply with HIPAA in the US and GDPR in Europe.
For clinical implementation, injectable hydrogel assays would likely be classified as combination products, incorporating both device and biological components. This classification necessitates comprehensive preclinical validation studies demonstrating safety, reproducibility, and correlation with established clinical outcomes. Manufacturers must address biocompatibility concerns, stability of the hydrogel matrix, and potential immunological responses when implanted in patients.
The regulatory pathway typically begins with Investigational Device Exemption (IDE) applications to conduct initial clinical trials. These trials must establish not only the safety profile but also demonstrate clinical utility in predicting drug responses with statistical significance compared to standard methods. The FDA's breakthrough device designation could potentially accelerate this process for hydrogel assays that show substantial advantages over current diagnostic approaches in oncology.
Quality control measures represent another critical regulatory consideration. Manufacturers must implement robust quality management systems compliant with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and ISO 13485 standards. This includes validation of production processes, sterilization methods, and shelf-life stability of the hydrogel components to ensure consistent performance across batches.
Reimbursement pathways present additional challenges beyond regulatory approval. Clinical utility studies must demonstrate cost-effectiveness and improved patient outcomes to secure coverage from Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurers. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) may require additional evidence through coverage with evidence development (CED) programs before granting routine reimbursement.
International regulatory harmonization efforts, including through the International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF), are increasingly important for global implementation. While the European Union's Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR) provide pathways in Europe, significant differences remain in regulatory requirements across major markets, necessitating tailored submission strategies.
Data privacy and ethical considerations also factor into regulatory compliance, particularly regarding patient sample handling, genetic information storage, and long-term follow-up requirements. Manufacturers must develop comprehensive consent procedures and data management protocols that comply with HIPAA in the US and GDPR in Europe.
Personalized Medicine Applications and Integration
Injectable hydrogel assays represent a transformative approach in personalized medicine, offering unprecedented capabilities for tailoring treatment regimens to individual patient profiles. These three-dimensional microenvironments closely mimic native tissue conditions, allowing for more accurate prediction of patient-specific drug responses than traditional two-dimensional cell culture systems. The integration of these assays into clinical decision-making workflows enables physicians to select optimal therapeutic agents based on ex vivo testing of patient-derived cells within customized hydrogel matrices.
The personalization potential extends beyond simple drug selection to comprehensive treatment strategy development. By incorporating patient-specific tumor cells or organoids into injectable hydrogels, clinicians can simultaneously test multiple drug candidates and combinations, identifying not only effective agents but also potential resistance mechanisms. This approach significantly reduces the trial-and-error nature of conventional treatment protocols, particularly beneficial for patients with rare cancers or those who have developed resistance to standard therapies.
Real-time monitoring capabilities further enhance the personalized medicine value proposition. Advanced hydrogel formulations incorporating biosensors or imaging-compatible components allow for continuous assessment of drug effects, providing dynamic information about treatment efficacy rather than single-timepoint measurements. This temporal dimension of data collection enables more nuanced understanding of drug response kinetics, critical for optimizing dosing schedules and combination sequencing.
Integration with existing healthcare infrastructure represents both a challenge and opportunity. Current efforts focus on standardizing hydrogel assay protocols to ensure reproducibility across different clinical settings while maintaining sufficient flexibility to accommodate patient-specific requirements. Several academic medical centers have established specialized laboratories that bridge research capabilities with clinical applications, creating pipelines for patient sample processing, hydrogel-based testing, and results interpretation.
Electronic health record (EHR) integration pathways are being developed to seamlessly incorporate hydrogel assay results into clinical decision support systems. These interfaces translate complex experimental data into actionable clinical recommendations, often utilizing machine learning algorithms to identify patterns across patient cohorts while preserving individual response characteristics. Such systems enable continuous learning from accumulated patient outcomes, progressively refining predictive models.
Cost-effectiveness analyses demonstrate that while injectable hydrogel assays require initial investment in specialized equipment and expertise, they potentially generate substantial downstream savings by avoiding ineffective treatments and associated complications. Several insurance providers have initiated pilot programs covering these tests for specific cancer types, recognizing their potential to optimize therapeutic outcomes and resource utilization.
The personalization potential extends beyond simple drug selection to comprehensive treatment strategy development. By incorporating patient-specific tumor cells or organoids into injectable hydrogels, clinicians can simultaneously test multiple drug candidates and combinations, identifying not only effective agents but also potential resistance mechanisms. This approach significantly reduces the trial-and-error nature of conventional treatment protocols, particularly beneficial for patients with rare cancers or those who have developed resistance to standard therapies.
Real-time monitoring capabilities further enhance the personalized medicine value proposition. Advanced hydrogel formulations incorporating biosensors or imaging-compatible components allow for continuous assessment of drug effects, providing dynamic information about treatment efficacy rather than single-timepoint measurements. This temporal dimension of data collection enables more nuanced understanding of drug response kinetics, critical for optimizing dosing schedules and combination sequencing.
Integration with existing healthcare infrastructure represents both a challenge and opportunity. Current efforts focus on standardizing hydrogel assay protocols to ensure reproducibility across different clinical settings while maintaining sufficient flexibility to accommodate patient-specific requirements. Several academic medical centers have established specialized laboratories that bridge research capabilities with clinical applications, creating pipelines for patient sample processing, hydrogel-based testing, and results interpretation.
Electronic health record (EHR) integration pathways are being developed to seamlessly incorporate hydrogel assay results into clinical decision support systems. These interfaces translate complex experimental data into actionable clinical recommendations, often utilizing machine learning algorithms to identify patterns across patient cohorts while preserving individual response characteristics. Such systems enable continuous learning from accumulated patient outcomes, progressively refining predictive models.
Cost-effectiveness analyses demonstrate that while injectable hydrogel assays require initial investment in specialized equipment and expertise, they potentially generate substantial downstream savings by avoiding ineffective treatments and associated complications. Several insurance providers have initiated pilot programs covering these tests for specific cancer types, recognizing their potential to optimize therapeutic outcomes and resource utilization.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!