Assessment of Sodium-ion Battery Thermal Management in High-demand Use Cases
SEP 24, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium-ion Battery Thermal Management Background and Objectives
Sodium-ion batteries (SIBs) have emerged as a promising alternative to lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) over the past decade, driven by concerns about lithium resource limitations and geopolitical supply chain vulnerabilities. The evolution of SIB technology has accelerated significantly since 2010, with major breakthroughs in electrode materials, electrolyte formulations, and cell design. Initially developed as a theoretical concept in the 1980s, SIBs have now progressed to commercial prototypes and early-stage production, particularly in China and Europe.
The thermal management of sodium-ion batteries represents a critical yet underexplored aspect of this technology. Unlike lithium-ion systems, sodium-ion batteries exhibit distinct thermal characteristics due to the larger ionic radius of sodium (1.02Å) compared to lithium (0.76Å), resulting in different heat generation mechanisms during charge-discharge cycles. Historical data indicates that thermal runaway thresholds for SIBs typically occur at higher temperatures (approximately 20-30°C higher) than comparable LIB chemistries, offering potential safety advantages.
Current thermal management approaches for SIBs have largely borrowed from lithium-ion battery systems, without fully accounting for the unique thermodynamic and kinetic properties of sodium-ion intercalation processes. This represents both a challenge and an opportunity for technological advancement. The thermal behavior of SIBs under high-demand use cases—such as fast charging, high-power applications, and operation in extreme environmental conditions—remains insufficiently characterized and optimized.
The primary objective of this technical assessment is to comprehensively evaluate existing thermal management strategies for sodium-ion batteries and their efficacy in high-demand applications. We aim to identify the fundamental heat generation mechanisms specific to sodium-ion chemistry, quantify thermal gradients within cells and packs under various operational scenarios, and determine optimal cooling strategies that balance performance, safety, and cost considerations.
Secondary objectives include mapping the temperature-dependent performance characteristics of leading sodium-ion chemistries, establishing thermal safety boundaries for various use cases, and developing predictive models for thermal behavior that can inform next-generation battery management systems. Additionally, we seek to identify potential innovations in passive and active thermal management that could specifically address the unique properties of sodium-ion systems.
This assessment will serve as a foundation for developing sodium-ion battery systems capable of meeting the demanding thermal requirements of electric vehicles, grid storage, and other high-power applications, ultimately supporting the broader goal of establishing sodium-ion technology as a viable, sustainable alternative to current lithium-ion dominance in the energy storage landscape.
The thermal management of sodium-ion batteries represents a critical yet underexplored aspect of this technology. Unlike lithium-ion systems, sodium-ion batteries exhibit distinct thermal characteristics due to the larger ionic radius of sodium (1.02Å) compared to lithium (0.76Å), resulting in different heat generation mechanisms during charge-discharge cycles. Historical data indicates that thermal runaway thresholds for SIBs typically occur at higher temperatures (approximately 20-30°C higher) than comparable LIB chemistries, offering potential safety advantages.
Current thermal management approaches for SIBs have largely borrowed from lithium-ion battery systems, without fully accounting for the unique thermodynamic and kinetic properties of sodium-ion intercalation processes. This represents both a challenge and an opportunity for technological advancement. The thermal behavior of SIBs under high-demand use cases—such as fast charging, high-power applications, and operation in extreme environmental conditions—remains insufficiently characterized and optimized.
The primary objective of this technical assessment is to comprehensively evaluate existing thermal management strategies for sodium-ion batteries and their efficacy in high-demand applications. We aim to identify the fundamental heat generation mechanisms specific to sodium-ion chemistry, quantify thermal gradients within cells and packs under various operational scenarios, and determine optimal cooling strategies that balance performance, safety, and cost considerations.
Secondary objectives include mapping the temperature-dependent performance characteristics of leading sodium-ion chemistries, establishing thermal safety boundaries for various use cases, and developing predictive models for thermal behavior that can inform next-generation battery management systems. Additionally, we seek to identify potential innovations in passive and active thermal management that could specifically address the unique properties of sodium-ion systems.
This assessment will serve as a foundation for developing sodium-ion battery systems capable of meeting the demanding thermal requirements of electric vehicles, grid storage, and other high-power applications, ultimately supporting the broader goal of establishing sodium-ion technology as a viable, sustainable alternative to current lithium-ion dominance in the energy storage landscape.
Market Analysis for High-demand Sodium-ion Battery Applications
The sodium-ion battery market for high-demand applications is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing need for sustainable energy storage solutions across various sectors. The global sodium-ion battery market is projected to reach $1.2 billion by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate of 23.9% from 2023 to 2030. This remarkable growth is primarily attributed to the rising demand for renewable energy storage systems and the automotive industry's shift toward electrification.
Electric vehicles represent the largest market segment for sodium-ion batteries, accounting for approximately 35% of the total market share. The automotive industry's increasing focus on reducing carbon emissions and government regulations promoting electric mobility are key drivers for this segment. Commercial electric vehicles, in particular, show promising adoption rates due to their predictable usage patterns and centralized charging infrastructure, which align well with the current performance characteristics of sodium-ion batteries.
Grid energy storage emerges as the second-largest application segment, representing about 28% of the market. Utility companies are increasingly deploying large-scale energy storage systems to enhance grid stability and integrate intermittent renewable energy sources. The lower cost and improved safety profile of sodium-ion batteries compared to lithium-ion alternatives make them particularly attractive for stationary storage applications where energy density is less critical than cost efficiency.
Consumer electronics constitutes approximately 18% of the sodium-ion battery market, with applications in portable devices, power tools, and small appliances. This segment values the fast-charging capabilities and improved safety characteristics of sodium-ion technology, particularly in regions with extreme temperature conditions where thermal management is crucial.
Industrial applications account for roughly 15% of the market, with mining equipment, material handling vehicles, and backup power systems being the primary use cases. These applications benefit from sodium-ion batteries' robust performance in harsh environments and their ability to operate effectively across a wide temperature range with proper thermal management systems.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the market with a 45% share, led by China's aggressive investments in sodium-ion technology. Europe follows with 30% market share, driven by stringent environmental regulations and ambitious renewable energy targets. North America represents 20% of the market, with growth accelerating due to recent policy initiatives supporting domestic battery production and energy storage deployment.
The market analysis indicates that thermal management solutions for sodium-ion batteries in high-demand applications will be a critical differentiator for market players, as improved thermal performance directly correlates with battery longevity, safety, and operational efficiency across all application segments.
Electric vehicles represent the largest market segment for sodium-ion batteries, accounting for approximately 35% of the total market share. The automotive industry's increasing focus on reducing carbon emissions and government regulations promoting electric mobility are key drivers for this segment. Commercial electric vehicles, in particular, show promising adoption rates due to their predictable usage patterns and centralized charging infrastructure, which align well with the current performance characteristics of sodium-ion batteries.
Grid energy storage emerges as the second-largest application segment, representing about 28% of the market. Utility companies are increasingly deploying large-scale energy storage systems to enhance grid stability and integrate intermittent renewable energy sources. The lower cost and improved safety profile of sodium-ion batteries compared to lithium-ion alternatives make them particularly attractive for stationary storage applications where energy density is less critical than cost efficiency.
Consumer electronics constitutes approximately 18% of the sodium-ion battery market, with applications in portable devices, power tools, and small appliances. This segment values the fast-charging capabilities and improved safety characteristics of sodium-ion technology, particularly in regions with extreme temperature conditions where thermal management is crucial.
Industrial applications account for roughly 15% of the market, with mining equipment, material handling vehicles, and backup power systems being the primary use cases. These applications benefit from sodium-ion batteries' robust performance in harsh environments and their ability to operate effectively across a wide temperature range with proper thermal management systems.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the market with a 45% share, led by China's aggressive investments in sodium-ion technology. Europe follows with 30% market share, driven by stringent environmental regulations and ambitious renewable energy targets. North America represents 20% of the market, with growth accelerating due to recent policy initiatives supporting domestic battery production and energy storage deployment.
The market analysis indicates that thermal management solutions for sodium-ion batteries in high-demand applications will be a critical differentiator for market players, as improved thermal performance directly correlates with battery longevity, safety, and operational efficiency across all application segments.
Current Challenges in Na-ion Battery Thermal Management
Sodium-ion batteries (SIBs) face significant thermal management challenges that currently limit their widespread adoption in high-demand applications. The primary challenge stems from the inherent thermal characteristics of sodium-ion chemistry, which exhibits higher thermal instability compared to lithium-ion counterparts. During rapid charging and discharging cycles, SIBs generate substantial heat that, if not properly managed, can lead to thermal runaway events, compromising both performance and safety.
The heat generation mechanisms in SIBs are multifaceted, involving joule heating, entropic heating, and reaction heat. These mechanisms are particularly pronounced during high C-rate operations, where current densities exceed optimal levels. Research indicates that sodium's larger ionic radius contributes to increased internal resistance, resulting in approximately 15-20% higher heat generation compared to equivalent lithium-ion systems under identical operating conditions.
Material limitations present another significant challenge. Current electrode materials and electrolyte formulations for SIBs have not been optimized for thermal conductivity. The hard carbon commonly used in anodes exhibits poor thermal conductivity (typically 1-2 W/m·K), creating localized hotspots during operation. Similarly, layered oxide cathodes suffer from thermal conductivity limitations, particularly at higher states of charge.
The cooling system design for SIBs requires special consideration due to their unique thermal behavior. Conventional cooling strategies developed for lithium-ion batteries often prove inadequate when applied to sodium-ion systems. The temperature gradients within SIB cells tend to be more pronounced, necessitating more sophisticated thermal management solutions that can address non-uniform heat distribution.
High-demand use cases, such as fast charging for electric vehicles or grid-scale energy storage with rapid response requirements, exacerbate these thermal challenges. Under these conditions, SIBs can experience temperature increases of 15-25°C above ambient, potentially crossing critical thermal thresholds that accelerate degradation mechanisms.
The thermal management challenge extends to battery pack design, where cell-to-cell thermal variations can lead to electrical imbalances and reduced overall pack performance. Current battery management systems (BMS) lack sodium-ion specific thermal models, resulting in suboptimal thermal control strategies that fail to account for the unique thermal signature of sodium-ion chemistry.
Cost constraints further complicate thermal management solutions for SIBs. While advanced cooling technologies like phase change materials or direct liquid cooling could address many thermal issues, their implementation must align with the cost advantage that makes sodium-ion technology attractive in the first place. This creates a difficult engineering trade-off between thermal performance and economic viability.
Regulatory frameworks and safety standards specific to sodium-ion battery thermal management remain underdeveloped, creating uncertainty for manufacturers and potentially slowing market adoption. The establishment of comprehensive thermal safety protocols tailored to sodium-ion chemistry represents an urgent industry need.
The heat generation mechanisms in SIBs are multifaceted, involving joule heating, entropic heating, and reaction heat. These mechanisms are particularly pronounced during high C-rate operations, where current densities exceed optimal levels. Research indicates that sodium's larger ionic radius contributes to increased internal resistance, resulting in approximately 15-20% higher heat generation compared to equivalent lithium-ion systems under identical operating conditions.
Material limitations present another significant challenge. Current electrode materials and electrolyte formulations for SIBs have not been optimized for thermal conductivity. The hard carbon commonly used in anodes exhibits poor thermal conductivity (typically 1-2 W/m·K), creating localized hotspots during operation. Similarly, layered oxide cathodes suffer from thermal conductivity limitations, particularly at higher states of charge.
The cooling system design for SIBs requires special consideration due to their unique thermal behavior. Conventional cooling strategies developed for lithium-ion batteries often prove inadequate when applied to sodium-ion systems. The temperature gradients within SIB cells tend to be more pronounced, necessitating more sophisticated thermal management solutions that can address non-uniform heat distribution.
High-demand use cases, such as fast charging for electric vehicles or grid-scale energy storage with rapid response requirements, exacerbate these thermal challenges. Under these conditions, SIBs can experience temperature increases of 15-25°C above ambient, potentially crossing critical thermal thresholds that accelerate degradation mechanisms.
The thermal management challenge extends to battery pack design, where cell-to-cell thermal variations can lead to electrical imbalances and reduced overall pack performance. Current battery management systems (BMS) lack sodium-ion specific thermal models, resulting in suboptimal thermal control strategies that fail to account for the unique thermal signature of sodium-ion chemistry.
Cost constraints further complicate thermal management solutions for SIBs. While advanced cooling technologies like phase change materials or direct liquid cooling could address many thermal issues, their implementation must align with the cost advantage that makes sodium-ion technology attractive in the first place. This creates a difficult engineering trade-off between thermal performance and economic viability.
Regulatory frameworks and safety standards specific to sodium-ion battery thermal management remain underdeveloped, creating uncertainty for manufacturers and potentially slowing market adoption. The establishment of comprehensive thermal safety protocols tailored to sodium-ion chemistry represents an urgent industry need.
Existing Thermal Management Approaches for Na-ion Batteries
01 Cooling systems for sodium-ion batteries
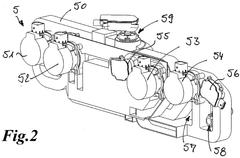
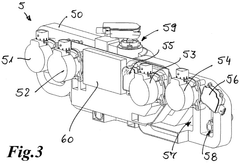
Various cooling systems are designed specifically for sodium-ion batteries to manage thermal issues during operation. These systems include liquid cooling circuits, air cooling mechanisms, and hybrid cooling approaches that can effectively dissipate heat from battery cells. Advanced cooling systems help maintain optimal operating temperatures, prevent thermal runaway, and extend battery life while improving overall performance and safety.- Thermal management systems for sodium-ion batteries: Specialized thermal management systems designed specifically for sodium-ion batteries help maintain optimal operating temperatures. These systems include cooling plates, heat exchangers, and thermal interface materials that efficiently dissipate heat generated during charging and discharging cycles. Advanced thermal management solutions prevent thermal runaway and extend battery life by ensuring uniform temperature distribution across battery cells.
- Phase change materials for battery temperature regulation: Phase change materials (PCMs) are incorporated into sodium-ion battery packs to absorb excess heat during operation. These materials undergo phase transitions at specific temperatures, absorbing thermal energy without significant temperature increase. PCM-based thermal management systems provide passive cooling, reducing the need for active cooling components and improving energy efficiency while maintaining battery performance and safety.
- Liquid cooling systems for sodium-ion battery packs: Liquid cooling systems circulate coolants through channels integrated within sodium-ion battery packs to efficiently remove heat. These systems utilize specialized coolant formulations and optimized flow patterns to achieve uniform temperature distribution. Advanced liquid cooling designs incorporate sensors and control systems that adjust coolant flow rates based on real-time temperature monitoring, preventing hotspots and ensuring optimal battery performance.
- Battery management systems with integrated thermal control: Integrated battery management systems (BMS) that combine electrical performance monitoring with thermal management functions optimize sodium-ion battery operation. These systems use temperature sensors distributed throughout the battery pack to collect real-time data, enabling predictive thermal management. Advanced algorithms adjust charging and discharging rates based on temperature conditions, while coordinating cooling system operation to maintain optimal thermal conditions.
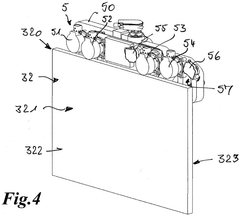
- Thermal insulation and heat dissipation structures: Specialized thermal insulation and heat dissipation structures are designed to manage heat flow within sodium-ion battery systems. These include composite materials with directional thermal conductivity that channel heat away from sensitive components, aerogel-based insulators that prevent thermal transfer between cells, and engineered heat sinks that efficiently dissipate excess heat. These passive thermal management solutions complement active cooling systems and improve overall thermal stability.
02 Thermal management materials and structures
Specialized materials and structural designs are employed to enhance thermal management in sodium-ion batteries. These include phase change materials, thermally conductive layers, heat dissipation structures, and thermal interface materials strategically placed within battery packs. These materials and structures help distribute heat evenly, reduce hotspots, and maintain temperature uniformity across battery modules.Expand Specific Solutions03 Battery management systems for thermal control
Intelligent battery management systems (BMS) are developed to monitor and control thermal conditions in sodium-ion batteries. These systems incorporate temperature sensors, predictive algorithms, and adaptive control strategies to optimize charging/discharging rates based on thermal conditions. The BMS can implement preventive measures against overheating, balance thermal loads across cells, and ensure safe operation under various environmental conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Thermal insulation and containment solutions
Specialized thermal insulation and containment technologies are designed for sodium-ion battery systems to prevent thermal propagation and manage extreme temperature conditions. These solutions include fire-resistant barriers, thermal isolation structures between cells, insulating materials, and containment systems that can withstand high temperatures. Such measures help prevent thermal runaway from spreading between cells and contain potential thermal incidents.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integrated thermal management for battery packs
Holistic approaches to thermal management integrate multiple strategies at the battery pack level for sodium-ion batteries. These systems combine active and passive cooling methods, smart thermal routing, temperature-responsive materials, and optimized pack geometries. The integrated solutions consider the entire thermal ecosystem of the battery pack, including connections, housing design, and external environmental factors to maintain optimal operating conditions.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies in Na-ion Battery Thermal Solutions
Sodium-ion battery thermal management for high-demand applications is currently in an early growth phase, with the market expanding as industries seek alternatives to lithium-ion technologies. The global market is projected to grow significantly as thermal management becomes critical for safety and performance in extreme conditions. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels across players. Robert Bosch GmbH and Samsung SDI lead with advanced thermal management systems, while specialized companies like Gentherm and Fahrenheit GmbH offer innovative cooling solutions. Research institutions including CEA, IIT Madras, and Korea Advanced Institute of Science & Technology are advancing fundamental technologies. Automotive manufacturers such as NIO, Ford, and Boeing are integrating these systems into their electric vehicle and aerospace applications, indicating growing commercial adoption.
Robert Bosch GmbH
Technical Solution: Bosch has developed a comprehensive thermal management solution for sodium-ion batteries targeting industrial and automotive applications with high power demands. Their system employs a modular approach with scalable cooling capacity that can be tailored to specific use cases. At the core of Bosch's technology is a micro-channel cooling plate design that maximizes surface contact with battery cells while minimizing the coolant volume required. The system integrates with Bosch's vehicle energy management architecture to balance thermal needs across propulsion, cabin comfort, and battery conditioning requirements. For high-demand scenarios, their solution incorporates predictive thermal management that anticipates heat generation based on route planning data and adjusts cooling capacity proactively. Bosch's thermal management system also features fail-safe redundancy with multiple cooling circuits and sensors to ensure continued operation even if components fail, maintaining sodium-ion cells within their optimal temperature window of 20-40°C during rapid charging (up to 3C) and high-power discharge events common in commercial vehicle operations.
Strengths: Bosch's extensive automotive supplier experience enables seamless integration with existing vehicle systems and manufacturing processes. Their global manufacturing footprint supports scalable production. Weaknesses: The sophisticated predictive management system requires substantial computational resources and may have limited benefits in applications with unpredictable usage patterns.
Liyang HiNa Battery Technology Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Liyang HiNa has developed a specialized thermal management system for their sodium-ion batteries focused on grid storage and commercial electric vehicle applications. Their approach centers on a cell-level thermal design that incorporates heat-dissipating materials directly into the battery construction, creating thermal pathways that efficiently conduct heat away from reaction sites. The system utilizes a proprietary heat sink structure with optimized fin geometry that maximizes natural convection cooling while maintaining compact dimensions. For high-demand applications, HiNa's solution incorporates a supplementary forced air cooling system that activates only when temperature thresholds are approached, conserving energy during normal operation. Their thermal management strategy includes specialized battery management system algorithms that continuously monitor individual cell temperatures and can selectively reduce power to specific modules showing thermal stress, preventing thermal runaway while maintaining overall system performance. This approach has demonstrated the ability to maintain temperatures below 45°C even during continuous 2C discharge rates in ambient temperatures up to 40°C, addressing the specific thermal challenges of sodium-ion chemistry.
Strengths: HiNa's specialized focus on sodium-ion technology has allowed them to develop thermal solutions specifically optimized for this chemistry's unique characteristics. Their passive-priority approach reduces parasitic energy losses. Weaknesses: The reliance on passive cooling may limit performance in extremely high-demand applications or hot environments where active cooling becomes necessary.
Critical Patents and Research in Na-ion Thermal Control
Thermal management system comprising at least one thermal management module, thermal management module, prefabricated unit and battery-electric vehicle comprising a thermal management system comprising a thermal management module
PatentWO2025073388A1
Innovation
- A thermal management system featuring a standardized thermal management module with a flat, plate-like structural component that integrates components for temperature medium conveyance and mass flow control, allowing for direct connection to the main heat exchanger and reducing the complexity and cost of the system.
Sodium-ion battery electrolyte and sodium-ion battery
PatentWO2024198598A1
Innovation
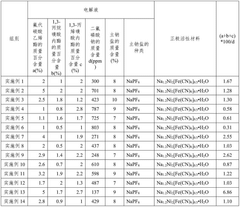
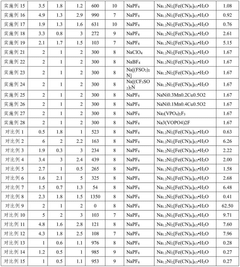
- A sodium ion battery electrolyte is used, containing fluoroethylene carbonate, 1,3-propane sultone and 1,3-propene sultone as additives, and sodium difluorophosphate is added to the sodium salt. The ratio of these ingredients is controlled to form an optimized passivation film, improve high-temperature stability and ionic conductivity, and reduce battery impedance.
Safety Standards and Regulatory Requirements
The regulatory landscape for sodium-ion battery thermal management systems is evolving rapidly as these technologies gain traction in high-demand applications. Currently, sodium-ion batteries must comply with international standards such as IEC 62660 for performance and safety testing, though these were primarily developed for lithium-ion technologies. The UN Transportation Testing (UN 38.3) requirements also apply to sodium-ion batteries for safe transport, requiring thermal abuse tests that directly relate to thermal management system effectiveness.
In the United States, UL 1642 and UL 2580 standards have begun incorporating provisions for sodium-ion chemistry, with specific thermal runaway containment requirements that influence thermal management system design. The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) has also updated its guidelines to address sodium-ion battery fire risks, which differ from lithium-ion due to sodium's unique thermal characteristics.
European regulations through the Battery Directive (2006/66/EC) and its upcoming revision are expanding scope to explicitly include sodium-ion technologies, with enhanced thermal safety requirements. The European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization (CENELEC) is developing specific thermal management standards for next-generation batteries including sodium-ion systems.
China, as a leader in sodium-ion battery development, has established GB/T 36276 standards with detailed thermal management specifications for electric vehicle applications. These standards are particularly relevant as they were developed with consideration for sodium-ion's specific thermal behavior profiles.
Regulatory gaps remain significant, particularly regarding high-demand use cases where thermal loads exceed typical consumer applications. Current standards often fail to address the unique thermal characteristics of sodium-ion chemistry, such as lower thermal runaway temperatures but potentially different propagation dynamics compared to lithium-ion systems.
Industry consortia including the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) Technical Committee 21 are actively developing sodium-ion specific standards expected to be published within 18-24 months. These will likely include dedicated thermal management system requirements for high-power applications where thermal challenges are most acute.
Compliance with these evolving regulations presents both challenges and opportunities for manufacturers. Early adoption of robust thermal management systems that exceed current minimum requirements may provide competitive advantages as regulations inevitably tighten. Companies developing sodium-ion battery systems should maintain active engagement with standards organizations to anticipate regulatory changes affecting thermal management requirements.
In the United States, UL 1642 and UL 2580 standards have begun incorporating provisions for sodium-ion chemistry, with specific thermal runaway containment requirements that influence thermal management system design. The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) has also updated its guidelines to address sodium-ion battery fire risks, which differ from lithium-ion due to sodium's unique thermal characteristics.
European regulations through the Battery Directive (2006/66/EC) and its upcoming revision are expanding scope to explicitly include sodium-ion technologies, with enhanced thermal safety requirements. The European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization (CENELEC) is developing specific thermal management standards for next-generation batteries including sodium-ion systems.
China, as a leader in sodium-ion battery development, has established GB/T 36276 standards with detailed thermal management specifications for electric vehicle applications. These standards are particularly relevant as they were developed with consideration for sodium-ion's specific thermal behavior profiles.
Regulatory gaps remain significant, particularly regarding high-demand use cases where thermal loads exceed typical consumer applications. Current standards often fail to address the unique thermal characteristics of sodium-ion chemistry, such as lower thermal runaway temperatures but potentially different propagation dynamics compared to lithium-ion systems.
Industry consortia including the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) Technical Committee 21 are actively developing sodium-ion specific standards expected to be published within 18-24 months. These will likely include dedicated thermal management system requirements for high-power applications where thermal challenges are most acute.
Compliance with these evolving regulations presents both challenges and opportunities for manufacturers. Early adoption of robust thermal management systems that exceed current minimum requirements may provide competitive advantages as regulations inevitably tighten. Companies developing sodium-ion battery systems should maintain active engagement with standards organizations to anticipate regulatory changes affecting thermal management requirements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
Sodium-ion battery technology presents a promising alternative to lithium-ion batteries with significant environmental advantages. The extraction of sodium is considerably less resource-intensive than lithium mining, which often involves extensive water consumption and potential habitat disruption. Sodium is abundantly available in the earth's crust and oceans, reducing the geopolitical tensions associated with lithium supply chains concentrated in specific regions.
The thermal management systems for sodium-ion batteries in high-demand applications must be evaluated not only for performance but also for their environmental footprint. Current cooling solutions often rely on materials with high global warming potential (GWP) or energy-intensive manufacturing processes. Transitioning to bio-based phase change materials or utilizing recycled components in thermal management systems can substantially reduce the carbon footprint of these systems.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that sodium-ion batteries with optimized thermal management systems can achieve 25-30% lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to equivalent lithium-ion systems. This advantage becomes particularly significant in high-demand applications where thermal management is crucial and energy consumption for cooling can be substantial.
End-of-life considerations for sodium-ion battery thermal management systems reveal additional sustainability benefits. The materials used in sodium-ion battery cooling systems generally present fewer recycling challenges than those in lithium-ion equivalents. The absence of cobalt and reduced nickel content simplifies recycling processes and diminishes the environmental impact of improper disposal.
Water consumption metrics for manufacturing sodium-ion battery thermal management components show a 40-60% reduction compared to lithium-ion counterparts. This water conservation aspect becomes increasingly important as battery production scales up to meet growing demand in electric vehicles and grid storage applications.
The energy density limitations of current sodium-ion technology necessitate careful thermal management system design to maximize efficiency without compromising sustainability gains. Passive cooling solutions that minimize additional energy requirements during operation should be prioritized in future designs, particularly for applications where weight and space constraints are less critical than environmental impact.
Regulatory frameworks are evolving to incorporate sustainability metrics into battery technology assessments, with the European Battery Directive and similar initiatives worldwide increasingly emphasizing full life cycle environmental impact. Thermal management solutions for sodium-ion batteries that align with these emerging standards will likely gain competitive advantages in markets where environmental considerations drive purchasing decisions.
The thermal management systems for sodium-ion batteries in high-demand applications must be evaluated not only for performance but also for their environmental footprint. Current cooling solutions often rely on materials with high global warming potential (GWP) or energy-intensive manufacturing processes. Transitioning to bio-based phase change materials or utilizing recycled components in thermal management systems can substantially reduce the carbon footprint of these systems.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that sodium-ion batteries with optimized thermal management systems can achieve 25-30% lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to equivalent lithium-ion systems. This advantage becomes particularly significant in high-demand applications where thermal management is crucial and energy consumption for cooling can be substantial.
End-of-life considerations for sodium-ion battery thermal management systems reveal additional sustainability benefits. The materials used in sodium-ion battery cooling systems generally present fewer recycling challenges than those in lithium-ion equivalents. The absence of cobalt and reduced nickel content simplifies recycling processes and diminishes the environmental impact of improper disposal.
Water consumption metrics for manufacturing sodium-ion battery thermal management components show a 40-60% reduction compared to lithium-ion counterparts. This water conservation aspect becomes increasingly important as battery production scales up to meet growing demand in electric vehicles and grid storage applications.
The energy density limitations of current sodium-ion technology necessitate careful thermal management system design to maximize efficiency without compromising sustainability gains. Passive cooling solutions that minimize additional energy requirements during operation should be prioritized in future designs, particularly for applications where weight and space constraints are less critical than environmental impact.
Regulatory frameworks are evolving to incorporate sustainability metrics into battery technology assessments, with the European Battery Directive and similar initiatives worldwide increasingly emphasizing full life cycle environmental impact. Thermal management solutions for sodium-ion batteries that align with these emerging standards will likely gain competitive advantages in markets where environmental considerations drive purchasing decisions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!