Global Regulation of Sodium-ion Battery Thermal Management Approaches
SEP 24, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium-ion Battery Thermal Management Background and Objectives
Sodium-ion batteries (SIBs) have emerged as a promising alternative to lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) due to the abundance and wide geographical distribution of sodium resources. The development of SIBs can be traced back to the 1970s, but significant research momentum has only been gained in the past decade as concerns about lithium supply constraints have intensified. The evolution of SIB technology has been characterized by continuous improvements in electrode materials, electrolytes, and battery architecture to enhance energy density, cycling stability, and safety performance.
Thermal management represents a critical aspect of battery technology development, as temperature significantly impacts battery performance, safety, and lifespan. Historically, thermal management approaches for batteries have evolved from simple passive cooling systems to sophisticated active thermal management solutions incorporating liquid cooling, phase change materials, and intelligent control algorithms. For sodium-ion batteries specifically, thermal management presents unique challenges due to the distinct electrochemical properties and thermal behaviors compared to lithium-ion counterparts.
The global regulatory landscape for battery thermal management has been shaped by safety incidents in various applications, particularly in electric vehicles and energy storage systems. Major regulatory frameworks such as UN 38.3, IEC 62133, and UL 1642 have established testing protocols for battery safety, including thermal abuse tests. However, these regulations were primarily developed for lithium-ion batteries, creating a need for sodium-ion specific thermal management standards as the technology advances toward commercialization.
The primary objectives of sodium-ion battery thermal management are to maintain optimal operating temperature ranges (typically between 15-35°C), prevent thermal runaway events, ensure uniform temperature distribution across battery packs, and maximize battery lifespan while minimizing energy consumption of the thermal management system itself. These objectives must be achieved while considering cost constraints, as one of the key value propositions of sodium-ion technology is its potential cost advantage over lithium-ion batteries.
Current technological trends in SIB thermal management include the development of electrolytes with improved thermal stability, advanced battery management systems with predictive thermal modeling capabilities, and innovative cooling strategies optimized for the specific heat generation patterns of sodium-ion chemistry. Research is increasingly focused on understanding the fundamental thermal behaviors of sodium-ion cells under various operating conditions and developing tailored thermal management solutions that address the unique characteristics of this emerging battery technology.
Thermal management represents a critical aspect of battery technology development, as temperature significantly impacts battery performance, safety, and lifespan. Historically, thermal management approaches for batteries have evolved from simple passive cooling systems to sophisticated active thermal management solutions incorporating liquid cooling, phase change materials, and intelligent control algorithms. For sodium-ion batteries specifically, thermal management presents unique challenges due to the distinct electrochemical properties and thermal behaviors compared to lithium-ion counterparts.
The global regulatory landscape for battery thermal management has been shaped by safety incidents in various applications, particularly in electric vehicles and energy storage systems. Major regulatory frameworks such as UN 38.3, IEC 62133, and UL 1642 have established testing protocols for battery safety, including thermal abuse tests. However, these regulations were primarily developed for lithium-ion batteries, creating a need for sodium-ion specific thermal management standards as the technology advances toward commercialization.
The primary objectives of sodium-ion battery thermal management are to maintain optimal operating temperature ranges (typically between 15-35°C), prevent thermal runaway events, ensure uniform temperature distribution across battery packs, and maximize battery lifespan while minimizing energy consumption of the thermal management system itself. These objectives must be achieved while considering cost constraints, as one of the key value propositions of sodium-ion technology is its potential cost advantage over lithium-ion batteries.
Current technological trends in SIB thermal management include the development of electrolytes with improved thermal stability, advanced battery management systems with predictive thermal modeling capabilities, and innovative cooling strategies optimized for the specific heat generation patterns of sodium-ion chemistry. Research is increasingly focused on understanding the fundamental thermal behaviors of sodium-ion cells under various operating conditions and developing tailored thermal management solutions that address the unique characteristics of this emerging battery technology.
Market Analysis for Sodium-ion Battery Applications
The sodium-ion battery market is experiencing significant growth as an alternative to traditional lithium-ion batteries, driven by several key factors. The global market value for sodium-ion batteries is projected to reach $500 million by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate exceeding 20% over the next decade. This growth trajectory is supported by increasing demand for sustainable energy storage solutions and concerns about lithium supply chain vulnerabilities.
The automotive sector represents the largest potential application market for sodium-ion batteries, particularly in regions with established electric vehicle infrastructure. Countries like China, which has already deployed sodium-ion batteries in commercial vehicles, are leading adoption rates. The European market is following closely, with several manufacturers announcing integration plans for sodium-ion technology in their upcoming electric vehicle models.
Grid-scale energy storage presents another substantial market opportunity, valued at approximately $300 million currently. Sodium-ion batteries offer compelling advantages in this sector due to their safety profile and thermal stability characteristics, which reduce thermal management complexity compared to lithium-ion alternatives. This application segment is expected to grow at 25% annually through 2030.
Consumer electronics represents a developing market segment, though currently limited by energy density constraints of sodium-ion technology. However, as thermal management innovations improve energy density metrics, this segment could expand significantly, particularly for applications where safety is prioritized over maximum energy density.
Regional market distribution shows Asia-Pacific dominating with 65% market share, followed by Europe at 20% and North America at 12%. China specifically accounts for nearly 40% of the global market, with substantial government backing through its 14th Five-Year Plan which explicitly supports sodium-ion battery development.
Market barriers include competition from established lithium-ion technology, which benefits from decades of optimization and manufacturing scale. However, recent supply chain disruptions and price volatility in lithium markets have accelerated interest in sodium-ion alternatives. The cost differential between the technologies has narrowed to approximately 15%, with projections suggesting price parity could be achieved by 2028.
Customer adoption analysis indicates that thermal management advantages of sodium-ion batteries are increasingly recognized as a value proposition, particularly in applications where operating temperature ranges are challenging or where active cooling systems add significant complexity and cost to battery systems.
The automotive sector represents the largest potential application market for sodium-ion batteries, particularly in regions with established electric vehicle infrastructure. Countries like China, which has already deployed sodium-ion batteries in commercial vehicles, are leading adoption rates. The European market is following closely, with several manufacturers announcing integration plans for sodium-ion technology in their upcoming electric vehicle models.
Grid-scale energy storage presents another substantial market opportunity, valued at approximately $300 million currently. Sodium-ion batteries offer compelling advantages in this sector due to their safety profile and thermal stability characteristics, which reduce thermal management complexity compared to lithium-ion alternatives. This application segment is expected to grow at 25% annually through 2030.
Consumer electronics represents a developing market segment, though currently limited by energy density constraints of sodium-ion technology. However, as thermal management innovations improve energy density metrics, this segment could expand significantly, particularly for applications where safety is prioritized over maximum energy density.
Regional market distribution shows Asia-Pacific dominating with 65% market share, followed by Europe at 20% and North America at 12%. China specifically accounts for nearly 40% of the global market, with substantial government backing through its 14th Five-Year Plan which explicitly supports sodium-ion battery development.
Market barriers include competition from established lithium-ion technology, which benefits from decades of optimization and manufacturing scale. However, recent supply chain disruptions and price volatility in lithium markets have accelerated interest in sodium-ion alternatives. The cost differential between the technologies has narrowed to approximately 15%, with projections suggesting price parity could be achieved by 2028.
Customer adoption analysis indicates that thermal management advantages of sodium-ion batteries are increasingly recognized as a value proposition, particularly in applications where operating temperature ranges are challenging or where active cooling systems add significant complexity and cost to battery systems.
Global Thermal Management Challenges and Regulatory Landscape
Sodium-ion battery technology has emerged as a promising alternative to lithium-ion batteries, particularly due to the abundance and lower cost of sodium resources. However, the thermal management of these batteries presents significant challenges that vary across global regions, influenced by diverse climatic conditions, regulatory frameworks, and safety standards.
The thermal behavior of sodium-ion batteries differs from their lithium counterparts, exhibiting unique characteristics during charging, discharging, and storage. These differences necessitate specialized thermal management approaches that must comply with regional regulations while ensuring optimal performance and safety. In extreme temperature environments, from arctic cold to tropical heat, sodium-ion batteries face distinct thermal challenges that impact their efficiency, lifespan, and safety profiles.
Regulatory frameworks governing battery thermal management vary significantly worldwide. The European Union has implemented stringent requirements through regulations such as the Battery Directive and UN ECE R100, which mandate specific thermal runaway prevention measures and thermal management system specifications. These regulations emphasize the importance of thermal stability during normal operation and fault conditions, requiring manufacturers to demonstrate compliance through rigorous testing protocols.
In North America, the regulatory landscape is shaped by standards from organizations like UL, IEEE, and NFPA, alongside federal regulations from agencies such as the Department of Transportation. These frameworks focus on thermal event prevention, detection, and containment, with particular emphasis on large-scale energy storage applications where thermal runaway risks are magnified.
Asian markets present a complex regulatory environment, with China's GB standards imposing strict thermal management requirements for batteries in electric vehicles and energy storage systems. Japan and South Korea have developed their own thermal safety standards, often incorporating elements from international frameworks while addressing specific regional concerns.
Emerging economies face unique challenges in regulating sodium-ion battery thermal management, often adopting modified versions of international standards while building indigenous regulatory capacity. This regulatory diversity creates significant compliance challenges for global manufacturers seeking to deploy sodium-ion battery technologies across multiple markets.
Climate considerations further complicate the regulatory landscape, with regions experiencing extreme temperatures requiring specialized thermal management approaches. Arctic regions demand effective battery heating systems to maintain performance in sub-zero conditions, while tropical regions necessitate enhanced cooling capabilities to prevent thermal runaway in high ambient temperatures.
The global regulatory framework continues to evolve as sodium-ion battery technology matures, with increasing emphasis on harmonization of standards to facilitate international trade while maintaining rigorous safety requirements. This evolution presents both challenges and opportunities for technology developers seeking to optimize thermal management approaches for diverse global markets.
The thermal behavior of sodium-ion batteries differs from their lithium counterparts, exhibiting unique characteristics during charging, discharging, and storage. These differences necessitate specialized thermal management approaches that must comply with regional regulations while ensuring optimal performance and safety. In extreme temperature environments, from arctic cold to tropical heat, sodium-ion batteries face distinct thermal challenges that impact their efficiency, lifespan, and safety profiles.
Regulatory frameworks governing battery thermal management vary significantly worldwide. The European Union has implemented stringent requirements through regulations such as the Battery Directive and UN ECE R100, which mandate specific thermal runaway prevention measures and thermal management system specifications. These regulations emphasize the importance of thermal stability during normal operation and fault conditions, requiring manufacturers to demonstrate compliance through rigorous testing protocols.
In North America, the regulatory landscape is shaped by standards from organizations like UL, IEEE, and NFPA, alongside federal regulations from agencies such as the Department of Transportation. These frameworks focus on thermal event prevention, detection, and containment, with particular emphasis on large-scale energy storage applications where thermal runaway risks are magnified.
Asian markets present a complex regulatory environment, with China's GB standards imposing strict thermal management requirements for batteries in electric vehicles and energy storage systems. Japan and South Korea have developed their own thermal safety standards, often incorporating elements from international frameworks while addressing specific regional concerns.
Emerging economies face unique challenges in regulating sodium-ion battery thermal management, often adopting modified versions of international standards while building indigenous regulatory capacity. This regulatory diversity creates significant compliance challenges for global manufacturers seeking to deploy sodium-ion battery technologies across multiple markets.
Climate considerations further complicate the regulatory landscape, with regions experiencing extreme temperatures requiring specialized thermal management approaches. Arctic regions demand effective battery heating systems to maintain performance in sub-zero conditions, while tropical regions necessitate enhanced cooling capabilities to prevent thermal runaway in high ambient temperatures.
The global regulatory framework continues to evolve as sodium-ion battery technology matures, with increasing emphasis on harmonization of standards to facilitate international trade while maintaining rigorous safety requirements. This evolution presents both challenges and opportunities for technology developers seeking to optimize thermal management approaches for diverse global markets.
Current Thermal Management Solutions for Sodium-ion Batteries
01 Cooling systems for sodium-ion batteries
Various cooling systems are designed specifically for sodium-ion batteries to manage thermal issues during operation. These include liquid cooling circuits, air cooling systems, and heat exchangers that efficiently dissipate heat generated during charging and discharging cycles. These cooling mechanisms help maintain optimal operating temperature ranges, prevent thermal runaway, and extend battery life while ensuring safety during high-power applications.- Cooling systems for sodium-ion batteries: Various cooling systems are designed specifically for sodium-ion batteries to manage thermal issues during operation. These systems include liquid cooling channels, heat pipes, and phase change materials that efficiently dissipate heat from battery cells. Advanced cooling architectures ensure uniform temperature distribution across battery packs, preventing hotspots and extending battery life while maintaining optimal performance under various operating conditions.
- Thermal management control strategies: Intelligent control strategies are implemented to actively manage the thermal behavior of sodium-ion batteries. These include predictive algorithms that anticipate temperature changes based on usage patterns, adaptive control systems that adjust cooling intensity according to real-time thermal measurements, and battery management systems that optimize charging and discharging rates to minimize heat generation. These strategies help maintain batteries within safe operating temperature ranges while maximizing energy efficiency.
- Battery pack design for improved thermal management: Innovative battery pack designs incorporate thermal considerations from the ground up. These designs feature optimized cell spacing, strategic placement of thermal interfaces, and integrated cooling pathways. Some designs include thermally conductive materials between cells, insulation layers to prevent thermal runaway propagation, and modular structures that facilitate heat dissipation. These design approaches help manage temperature gradients across the battery pack and improve overall thermal stability.
- Thermal interface materials and heat transfer enhancement: Specialized thermal interface materials are developed to improve heat transfer from sodium-ion battery cells to cooling systems. These materials include high thermal conductivity composites, phase change materials with tailored melting points, and thermally conductive adhesives. Advanced heat transfer enhancement techniques such as micro-channel heat sinks, enhanced surface structures, and thermally conductive coatings are also employed to maximize cooling efficiency while minimizing the thermal management system's weight and volume.
- Safety mechanisms for thermal runaway prevention: Comprehensive safety mechanisms are integrated into sodium-ion battery systems to prevent thermal runaway incidents. These include temperature monitoring sensors distributed throughout the battery pack, automatic shutdown systems that activate when critical temperature thresholds are exceeded, thermal fuses, and pressure relief mechanisms. Some designs incorporate fire-resistant materials and thermal isolation barriers between cells to contain potential thermal events and prevent propagation throughout the battery system.
02 Thermal management materials and structures
Advanced materials and structural designs are employed to enhance thermal conductivity and heat dissipation in sodium-ion batteries. These include phase change materials, thermally conductive layers between cells, and specialized battery pack architectures that facilitate efficient heat transfer. The integration of these materials and structures helps to distribute heat evenly throughout the battery system, preventing hotspots and temperature gradients that could lead to performance degradation.Expand Specific Solutions03 Battery management systems for thermal control
Intelligent battery management systems (BMS) are developed to monitor and control the thermal conditions of sodium-ion batteries in real-time. These systems utilize temperature sensors, predictive algorithms, and adaptive control strategies to optimize charging/discharging rates based on thermal conditions. The BMS can preemptively adjust operating parameters to prevent overheating and ensure balanced temperature distribution across battery modules.Expand Specific Solutions04 Thermal insulation and containment solutions
Specialized thermal insulation and containment technologies are designed to isolate sodium-ion batteries from external temperature fluctuations and contain heat within safe boundaries. These solutions include multi-layer insulation materials, thermal barriers, and compartmentalized designs that prevent thermal propagation between cells. Such approaches are particularly important for applications in extreme environments or where thermal stability is critical for safety and performance.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integrated thermal management for battery packs and systems
Holistic approaches to thermal management consider the entire sodium-ion battery system, including integration with vehicle or grid storage thermal management. These solutions combine multiple cooling/heating methods, smart thermal routing, and energy-efficient temperature regulation strategies. The integrated systems optimize overall energy consumption while maintaining ideal operating temperatures across various usage scenarios and environmental conditions.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies and Research Institutions in Na-ion Battery Sector
The global sodium-ion battery thermal management market is currently in an early growth phase, characterized by increasing research activities and emerging commercial applications. Market size remains relatively modest compared to lithium-ion technologies but is expanding rapidly due to sodium-ion's cost advantages and sustainability benefits. From a technical maturity perspective, the field is evolving with key players developing diverse approaches. Companies like LG Energy Solution, Faradion, and Beijing Zhongke Haina Technology lead in core battery technology development, while established automotive manufacturers such as Renault, Stellantis, and Robert Bosch are integrating thermal management solutions. Research institutions including CEA, Lawrence Livermore National Security, and various technical universities are advancing fundamental thermal regulation technologies, creating a competitive landscape balanced between commercial deployment and continued innovation.
Liyang HiNa Battery Technology Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Liyang HiNa has developed an innovative thermal management approach for sodium-ion batteries that combines passive and active cooling strategies. Their system features a proprietary immersion cooling technology where cells are partially submerged in a non-conductive, thermally efficient fluid that directly absorbs and distributes heat. This is complemented by a network of micro-channels that circulate coolant through critical hotspots identified through thermal mapping. HiNa's approach incorporates thin graphene heat spreaders between cells to enhance lateral heat distribution and minimize thermal gradients. Their thermal management system is designed to operate efficiently across a wide temperature range (-20°C to 60°C), with adaptive control mechanisms that optimize cooling based on ambient conditions and usage patterns. The company has reported that this integrated approach reduces maximum temperature differences across cell arrays by up to 70% compared to conventional cooling methods.
Strengths: Their immersion cooling technology provides superior thermal uniformity across the entire battery pack, eliminating hotspots that typically accelerate degradation. The system requires minimal external power for operation, making it highly efficient for mobile applications. Weaknesses: The liquid cooling medium requires periodic maintenance and replacement, potentially increasing long-term operational costs and complexity.
Robert Bosch GmbH
Technical Solution: Bosch has engineered a comprehensive thermal management system for sodium-ion batteries that integrates with their broader vehicle thermal architecture. Their approach utilizes a sophisticated liquid cooling system with variable flow control that dynamically adjusts coolant circulation based on real-time thermal modeling. The system incorporates thin cooling plates with optimized flow channels positioned between battery cells, ensuring uniform temperature distribution. Bosch's thermal management solution features advanced sensors that monitor not only temperature but also thermal gradients across the battery pack, enabling predictive cooling adjustments before hotspots can form. Their system integrates with vehicle HVAC systems to recover waste heat during cold conditions, improving battery efficiency in low-temperature environments. Bosch has demonstrated that their thermal management approach can maintain sodium-ion batteries within optimal temperature ranges (15-35°C) even under extreme ambient conditions ranging from -30°C to 50°C.
Strengths: Bosch's extensive automotive integration experience enables seamless incorporation of battery thermal management with existing vehicle systems, optimizing overall energy efficiency. Their established global manufacturing infrastructure facilitates standardized production and quality control. Weaknesses: The system's complexity requires sophisticated control algorithms and multiple sensors, potentially increasing cost and creating more potential failure points compared to simpler thermal management approaches.
Key Patents and Technical Literature on Na-ion Battery Cooling
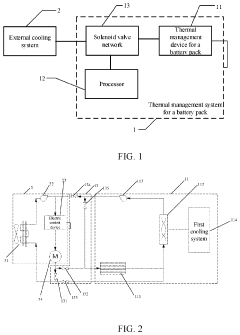
Thermal management system for battery pack and thermal management system for electric vehicle
PatentActiveUS11904728B2
Innovation
- A thermal management system that integrates a thermal management device for the battery pack with a processor and solenoid valve network connected to an external cooling system, allowing for efficient heat transfer and energy recycling by utilizing waste heat from the electric motor and control cooling system.
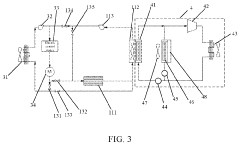
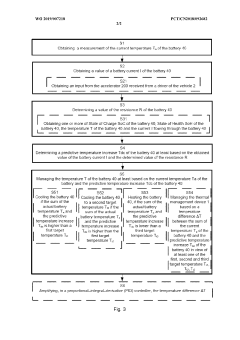
Thermal Management System
PatentWO2019007218A1
Innovation
- Proactive thermal management approach that predicts temperature increases based on battery current and resistance measurements rather than relying solely on reactive temperature control.
- Integration of real-time battery resistance determination into the thermal management system to enable more accurate temperature rise predictions.
- Combined use of actual measured temperature and predicted temperature increase for more effective thermal management decision-making.
International Safety Standards and Compliance Requirements
The regulatory landscape for sodium-ion battery thermal management systems varies significantly across different regions, with international bodies establishing baseline standards that individual countries often adapt or enhance. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has developed several standards applicable to sodium-ion batteries, including IEC 62660 for performance and endurance testing and IEC 62619 for safety requirements of large-format secondary lithium cells and batteries. While these standards were initially designed for lithium-ion technologies, they are increasingly being referenced for sodium-ion applications due to similar thermal management concerns.
UN Transportation Testing (UN 38.3) represents another critical regulatory framework that addresses the safe transport of batteries, including specific provisions for thermal management during shipping and handling. These regulations require batteries to withstand altitude simulation, thermal testing, vibration, shock, external short circuit, impact, overcharge, and forced discharge without dangerous effects. For sodium-ion batteries, the thermal runaway characteristics differ from lithium-ion counterparts, potentially requiring modified testing protocols.
Regional variations in compliance requirements present significant challenges for global manufacturers. The European Union's Battery Directive and the upcoming Battery Regulation incorporate specific thermal safety provisions, while China's GB/T standards include GB/T 36276-2018 which addresses thermal management systems for new energy vehicles. In North America, UL 1973 and UL 9540A standards provide testing methodologies for battery systems that include thermal management considerations.
Emerging economies are developing their regulatory frameworks, often adopting international standards while adding region-specific requirements. India's Automotive Research Association of India (ARAI) has begun developing standards specifically addressing thermal management in battery systems for electric vehicles, including provisions for sodium-ion technologies.
Compliance testing methodologies for thermal management systems typically include temperature cycling, thermal shock resistance, thermal runaway propagation prevention, and heat dissipation efficiency. These tests evaluate the system's ability to maintain optimal operating temperatures under various conditions and prevent catastrophic thermal events.
Industry stakeholders must navigate this complex regulatory environment while the technology continues to evolve. Harmonization efforts are underway through organizations like the Global Battery Alliance and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) to develop consistent standards specifically addressing sodium-ion battery thermal management approaches, potentially reducing compliance costs and accelerating market adoption.
UN Transportation Testing (UN 38.3) represents another critical regulatory framework that addresses the safe transport of batteries, including specific provisions for thermal management during shipping and handling. These regulations require batteries to withstand altitude simulation, thermal testing, vibration, shock, external short circuit, impact, overcharge, and forced discharge without dangerous effects. For sodium-ion batteries, the thermal runaway characteristics differ from lithium-ion counterparts, potentially requiring modified testing protocols.
Regional variations in compliance requirements present significant challenges for global manufacturers. The European Union's Battery Directive and the upcoming Battery Regulation incorporate specific thermal safety provisions, while China's GB/T standards include GB/T 36276-2018 which addresses thermal management systems for new energy vehicles. In North America, UL 1973 and UL 9540A standards provide testing methodologies for battery systems that include thermal management considerations.
Emerging economies are developing their regulatory frameworks, often adopting international standards while adding region-specific requirements. India's Automotive Research Association of India (ARAI) has begun developing standards specifically addressing thermal management in battery systems for electric vehicles, including provisions for sodium-ion technologies.
Compliance testing methodologies for thermal management systems typically include temperature cycling, thermal shock resistance, thermal runaway propagation prevention, and heat dissipation efficiency. These tests evaluate the system's ability to maintain optimal operating temperatures under various conditions and prevent catastrophic thermal events.
Industry stakeholders must navigate this complex regulatory environment while the technology continues to evolve. Harmonization efforts are underway through organizations like the Global Battery Alliance and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) to develop consistent standards specifically addressing sodium-ion battery thermal management approaches, potentially reducing compliance costs and accelerating market adoption.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The environmental impact of sodium-ion battery thermal management systems represents a critical consideration in the global regulatory landscape. Unlike lithium-ion batteries, sodium-ion technologies utilize more abundant and less environmentally problematic raw materials, potentially reducing the ecological footprint associated with resource extraction. However, thermal management approaches themselves carry significant environmental implications that regulators worldwide are increasingly addressing through policy frameworks.
Current regulatory trends emphasize life cycle assessment (LCA) methodologies to evaluate the environmental impact of thermal management systems. The European Union's Battery Directive, currently under revision, is expected to incorporate specific provisions for sodium-ion batteries, including requirements for thermal management systems that minimize energy consumption and waste generation. Similarly, China's evolving battery regulations are beginning to address the carbon footprint of thermal management technologies as part of broader sustainability initiatives.
Material selection for thermal management components faces increasing scrutiny under global chemical regulations. Coolants, phase change materials, and insulation components must comply with restrictions on hazardous substances, such as those outlined in the EU's REACH regulation and similar frameworks in North America and Asia. This regulatory pressure is driving innovation toward bio-based thermal interface materials and recyclable heat dissipation components.
End-of-life considerations represent another significant regulatory focus area. The recyclability of thermal management systems, particularly those utilizing liquid cooling or specialized phase change materials, presents unique challenges. Emerging regulations in Japan and South Korea specifically address the recoverability of thermal management components from battery systems, establishing minimum recycling efficiency thresholds and mandating design-for-disassembly approaches.
Energy efficiency requirements for thermal management systems are becoming more stringent globally. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) is developing standards that will likely establish maximum energy consumption parameters for battery thermal management, with sodium-ion specific provisions under consideration. These standards are expected to influence regulatory frameworks across multiple jurisdictions, potentially creating harmonized efficiency requirements.
Water usage and contamination risks associated with liquid cooling systems are attracting regulatory attention, particularly in water-stressed regions. Regulations in California and Australia have begun to address water conservation in industrial cooling applications, with implications for battery thermal management. These frameworks may establish precedents for water-efficient design requirements that could eventually extend to sodium-ion battery applications globally.
Current regulatory trends emphasize life cycle assessment (LCA) methodologies to evaluate the environmental impact of thermal management systems. The European Union's Battery Directive, currently under revision, is expected to incorporate specific provisions for sodium-ion batteries, including requirements for thermal management systems that minimize energy consumption and waste generation. Similarly, China's evolving battery regulations are beginning to address the carbon footprint of thermal management technologies as part of broader sustainability initiatives.
Material selection for thermal management components faces increasing scrutiny under global chemical regulations. Coolants, phase change materials, and insulation components must comply with restrictions on hazardous substances, such as those outlined in the EU's REACH regulation and similar frameworks in North America and Asia. This regulatory pressure is driving innovation toward bio-based thermal interface materials and recyclable heat dissipation components.
End-of-life considerations represent another significant regulatory focus area. The recyclability of thermal management systems, particularly those utilizing liquid cooling or specialized phase change materials, presents unique challenges. Emerging regulations in Japan and South Korea specifically address the recoverability of thermal management components from battery systems, establishing minimum recycling efficiency thresholds and mandating design-for-disassembly approaches.
Energy efficiency requirements for thermal management systems are becoming more stringent globally. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) is developing standards that will likely establish maximum energy consumption parameters for battery thermal management, with sodium-ion specific provisions under consideration. These standards are expected to influence regulatory frameworks across multiple jurisdictions, potentially creating harmonized efficiency requirements.
Water usage and contamination risks associated with liquid cooling systems are attracting regulatory attention, particularly in water-stressed regions. Regulations in California and Australia have begun to address water conservation in industrial cooling applications, with implications for battery thermal management. These frameworks may establish precedents for water-efficient design requirements that could eventually extend to sodium-ion battery applications globally.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!