Benchmarking Electrochemical Cell Design in Wireless Technology
AUG 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Electrochemical Cell Evolution and Objectives
Electrochemical cell technology has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the late 18th century with Alessandro Volta's pioneering work. The trajectory of development has been marked by incremental improvements in materials, electrolytes, and design configurations, leading to today's sophisticated cells that power wireless technologies. The historical progression from simple galvanic cells to modern lithium-ion and beyond represents a continuous quest for higher energy density, longer cycle life, and enhanced safety profiles.
In the wireless technology domain, electrochemical cells have evolved from bulky power sources with limited capacity to compact, high-performance energy storage solutions. The 1990s marked a pivotal shift with the commercial introduction of lithium-ion batteries, which revolutionized portable electronics and subsequently wireless communications. This technological leap enabled the miniaturization and extended operational time of wireless devices, fundamentally changing consumer expectations and industry standards.
Current technological trends indicate a focus on several key objectives for electrochemical cell design in wireless applications. Primary among these is the pursuit of higher energy density to support increasingly power-hungry wireless technologies while maintaining or reducing physical dimensions. Concurrently, there is an emphasis on improving power density to accommodate peak load demands characteristic of modern wireless transmission protocols.
Cycle life extension represents another critical objective, with research directed toward cell chemistries and architectures that can withstand thousands of charge-discharge cycles without significant capacity degradation. This is particularly relevant for embedded wireless systems where battery replacement is impractical or impossible. Safety enhancements remain paramount, especially as energy densities increase, necessitating advanced thermal management and protective circuitry.
Sustainability has emerged as a defining objective in recent years, driving research into materials that are abundant, environmentally benign, and recyclable. This includes exploration of alternatives to cobalt and other critical materials with supply chain vulnerabilities. Fast-charging capabilities have also become increasingly important, with targets of achieving 80% charge in under 15 minutes without compromising cell longevity.
The integration of smart functionality represents the frontier of electrochemical cell evolution, with objectives centered on embedding sensors and communication capabilities directly into cells. This enables real-time monitoring of cell health, predictive maintenance, and adaptive charging protocols that optimize performance based on usage patterns and environmental conditions. Such intelligence is particularly valuable in wireless networks where system reliability is paramount.
In the wireless technology domain, electrochemical cells have evolved from bulky power sources with limited capacity to compact, high-performance energy storage solutions. The 1990s marked a pivotal shift with the commercial introduction of lithium-ion batteries, which revolutionized portable electronics and subsequently wireless communications. This technological leap enabled the miniaturization and extended operational time of wireless devices, fundamentally changing consumer expectations and industry standards.
Current technological trends indicate a focus on several key objectives for electrochemical cell design in wireless applications. Primary among these is the pursuit of higher energy density to support increasingly power-hungry wireless technologies while maintaining or reducing physical dimensions. Concurrently, there is an emphasis on improving power density to accommodate peak load demands characteristic of modern wireless transmission protocols.
Cycle life extension represents another critical objective, with research directed toward cell chemistries and architectures that can withstand thousands of charge-discharge cycles without significant capacity degradation. This is particularly relevant for embedded wireless systems where battery replacement is impractical or impossible. Safety enhancements remain paramount, especially as energy densities increase, necessitating advanced thermal management and protective circuitry.
Sustainability has emerged as a defining objective in recent years, driving research into materials that are abundant, environmentally benign, and recyclable. This includes exploration of alternatives to cobalt and other critical materials with supply chain vulnerabilities. Fast-charging capabilities have also become increasingly important, with targets of achieving 80% charge in under 15 minutes without compromising cell longevity.
The integration of smart functionality represents the frontier of electrochemical cell evolution, with objectives centered on embedding sensors and communication capabilities directly into cells. This enables real-time monitoring of cell health, predictive maintenance, and adaptive charging protocols that optimize performance based on usage patterns and environmental conditions. Such intelligence is particularly valuable in wireless networks where system reliability is paramount.
Wireless Technology Market Demand Analysis
The wireless technology market has experienced unprecedented growth over the past decade, with electrochemical cell design playing a crucial role in this expansion. Current market analysis indicates that the global wireless technology market is projected to reach $3.9 trillion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate of 10.5%. Electrochemical cell innovations are directly contributing to this growth by enabling longer device operation times and supporting more power-intensive wireless applications.
Consumer demand for wireless devices with extended battery life continues to be a primary market driver. Research shows that 78% of smartphone users identify battery performance as a critical factor in purchasing decisions. This consumer preference has created significant market pressure for improved electrochemical cell designs that can deliver higher energy density while maintaining safety standards.
The enterprise sector represents another substantial market segment, with businesses increasingly adopting wireless solutions for operational efficiency. Corporate spending on wireless technology infrastructure reached $189 billion in 2022, with approximately 35% of this investment directed toward power management solutions. Organizations are particularly focused on reducing maintenance costs associated with battery replacement in distributed wireless sensor networks and IoT deployments.
Healthcare applications present a rapidly expanding market opportunity for advanced electrochemical cell designs. The medical wearables segment alone is growing at 24.7% annually, with patients and healthcare providers demanding devices that can operate reliably for extended periods without recharging. Implantable medical devices represent an especially demanding application, requiring electrochemical cells with exceptional longevity and biocompatibility.
Emerging markets are showing accelerated adoption rates for wireless technologies, creating new demand for cost-effective yet high-performance electrochemical solutions. Countries across Southeast Asia and Africa are experiencing wireless technology growth rates exceeding 15% annually, often leapfrogging traditional wired infrastructure entirely. These markets are particularly sensitive to device affordability, creating demand for electrochemical designs that balance performance with cost-effectiveness.
Environmental considerations are increasingly influencing market dynamics, with 67% of consumers expressing preference for eco-friendly battery solutions. This trend is driving demand for electrochemical cells with reduced environmental impact, including designs that minimize toxic materials and facilitate end-of-life recycling. Regulatory frameworks in Europe and parts of Asia are accelerating this shift through mandates on battery composition and recycling requirements.
Consumer demand for wireless devices with extended battery life continues to be a primary market driver. Research shows that 78% of smartphone users identify battery performance as a critical factor in purchasing decisions. This consumer preference has created significant market pressure for improved electrochemical cell designs that can deliver higher energy density while maintaining safety standards.
The enterprise sector represents another substantial market segment, with businesses increasingly adopting wireless solutions for operational efficiency. Corporate spending on wireless technology infrastructure reached $189 billion in 2022, with approximately 35% of this investment directed toward power management solutions. Organizations are particularly focused on reducing maintenance costs associated with battery replacement in distributed wireless sensor networks and IoT deployments.
Healthcare applications present a rapidly expanding market opportunity for advanced electrochemical cell designs. The medical wearables segment alone is growing at 24.7% annually, with patients and healthcare providers demanding devices that can operate reliably for extended periods without recharging. Implantable medical devices represent an especially demanding application, requiring electrochemical cells with exceptional longevity and biocompatibility.
Emerging markets are showing accelerated adoption rates for wireless technologies, creating new demand for cost-effective yet high-performance electrochemical solutions. Countries across Southeast Asia and Africa are experiencing wireless technology growth rates exceeding 15% annually, often leapfrogging traditional wired infrastructure entirely. These markets are particularly sensitive to device affordability, creating demand for electrochemical designs that balance performance with cost-effectiveness.
Environmental considerations are increasingly influencing market dynamics, with 67% of consumers expressing preference for eco-friendly battery solutions. This trend is driving demand for electrochemical cells with reduced environmental impact, including designs that minimize toxic materials and facilitate end-of-life recycling. Regulatory frameworks in Europe and parts of Asia are accelerating this shift through mandates on battery composition and recycling requirements.
Current Challenges in Electrochemical Cell Design
Despite significant advancements in electrochemical cell technology for wireless applications, several critical challenges persist that impede optimal performance and widespread adoption. The miniaturization requirements for modern wireless devices create substantial constraints on cell design, forcing engineers to balance power density with physical dimensions. This trade-off frequently results in compromised performance metrics, particularly in applications requiring sustained high-power output.
Material limitations represent another significant hurdle in electrochemical cell development. Current electrode materials exhibit degradation under repeated charge-discharge cycles, leading to capacity fade and shortened operational lifespans. Additionally, electrolyte stability remains problematic, especially at elevated temperatures or during rapid charging scenarios common in wireless technology applications.
Thermal management presents a persistent challenge, as heat generation during operation can trigger cascading failure mechanisms. The proximity of electrochemical cells to sensitive electronic components in wireless devices exacerbates this issue, necessitating sophisticated thermal regulation systems that add complexity and cost to overall designs.
Interface engineering between cell components continues to be problematic, with contact resistance and interfacial stability affecting both performance and longevity. The formation of solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) layers, while necessary for cell function, often occurs unpredictably and can lead to impedance growth over time.
Safety concerns remain paramount, particularly regarding thermal runaway risks in lithium-based systems. The drive toward higher energy densities inherently increases safety risks, creating a challenging design paradox for wireless applications where user safety cannot be compromised.
Manufacturing scalability presents additional complications, as precision assembly requirements for advanced cell designs often conflict with mass production needs. Techniques that work effectively in laboratory settings frequently encounter translation difficulties when implemented in high-volume manufacturing environments.
Standardization gaps across the industry further complicate benchmarking efforts. The absence of universally accepted testing protocols makes performance comparisons between different cell designs problematic, hindering objective evaluation and slowing innovation cycles.
Environmental considerations add another layer of complexity, with regulatory pressures driving the need for more sustainable materials and manufacturing processes. The environmental footprint of electrochemical cells, from raw material extraction through end-of-life disposal, requires substantial improvement to align with global sustainability goals.
These multifaceted challenges necessitate integrated research approaches that address electrochemical, mechanical, thermal, and manufacturing aspects simultaneously rather than in isolation. The interdisciplinary nature of these challenges demands collaborative efforts across traditionally separate domains of expertise.
Material limitations represent another significant hurdle in electrochemical cell development. Current electrode materials exhibit degradation under repeated charge-discharge cycles, leading to capacity fade and shortened operational lifespans. Additionally, electrolyte stability remains problematic, especially at elevated temperatures or during rapid charging scenarios common in wireless technology applications.
Thermal management presents a persistent challenge, as heat generation during operation can trigger cascading failure mechanisms. The proximity of electrochemical cells to sensitive electronic components in wireless devices exacerbates this issue, necessitating sophisticated thermal regulation systems that add complexity and cost to overall designs.
Interface engineering between cell components continues to be problematic, with contact resistance and interfacial stability affecting both performance and longevity. The formation of solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) layers, while necessary for cell function, often occurs unpredictably and can lead to impedance growth over time.
Safety concerns remain paramount, particularly regarding thermal runaway risks in lithium-based systems. The drive toward higher energy densities inherently increases safety risks, creating a challenging design paradox for wireless applications where user safety cannot be compromised.
Manufacturing scalability presents additional complications, as precision assembly requirements for advanced cell designs often conflict with mass production needs. Techniques that work effectively in laboratory settings frequently encounter translation difficulties when implemented in high-volume manufacturing environments.
Standardization gaps across the industry further complicate benchmarking efforts. The absence of universally accepted testing protocols makes performance comparisons between different cell designs problematic, hindering objective evaluation and slowing innovation cycles.
Environmental considerations add another layer of complexity, with regulatory pressures driving the need for more sustainable materials and manufacturing processes. The environmental footprint of electrochemical cells, from raw material extraction through end-of-life disposal, requires substantial improvement to align with global sustainability goals.
These multifaceted challenges necessitate integrated research approaches that address electrochemical, mechanical, thermal, and manufacturing aspects simultaneously rather than in isolation. The interdisciplinary nature of these challenges demands collaborative efforts across traditionally separate domains of expertise.
Benchmarking Methodologies for Cell Performance
01 Electrode material optimization for electrochemical cells
The selection and optimization of electrode materials significantly impact electrochemical cell performance. Advanced materials such as novel alloys, composites, and nanostructured materials can enhance conductivity, stability, and electrochemical activity. Benchmarking studies compare different electrode compositions to identify optimal materials that balance performance metrics like power density, energy efficiency, and cycle life while considering factors such as cost-effectiveness and environmental impact.- Electrode Material Selection and Optimization: The selection and optimization of electrode materials significantly impact electrochemical cell performance. Advanced materials such as high-capacity alloys, composite structures, and novel carbon-based materials can enhance energy density, cycling stability, and rate capability. Benchmarking different electrode materials involves evaluating their electrochemical properties, structural stability during cycling, and compatibility with electrolytes to identify optimal compositions for specific applications.
- Electrolyte Formulation and Performance Evaluation: Electrolyte formulation plays a crucial role in electrochemical cell design benchmarking. The composition, concentration, and additives in electrolytes directly affect ionic conductivity, interfacial stability, and overall cell performance. Benchmarking studies compare different electrolyte systems to evaluate their impact on cell efficiency, safety characteristics, and long-term stability under various operating conditions, helping to identify optimal formulations for specific cell designs.
- Cell Architecture and Component Integration: The physical design and integration of cell components significantly influence electrochemical performance. Benchmarking different cell architectures involves comparing various designs such as cylindrical, prismatic, pouch, and flow cell configurations. Evaluation metrics include energy density, thermal management efficiency, mechanical stability, and manufacturing scalability. Optimized component integration and novel structural designs can lead to improved performance, longer cycle life, and enhanced safety characteristics.
- Performance Testing Protocols and Standards: Standardized testing protocols are essential for meaningful benchmarking of electrochemical cell designs. These protocols define specific testing conditions, measurement techniques, and performance metrics to ensure comparable results across different cell designs. Key benchmarking parameters include capacity retention, rate capability, temperature performance, cycle life, and safety characteristics. Advanced diagnostic techniques such as impedance spectroscopy, post-mortem analysis, and in-situ characterization methods provide deeper insights into cell behavior and failure mechanisms.
- Computational Modeling and Simulation Techniques: Computational modeling and simulation techniques have become invaluable tools for electrochemical cell design benchmarking. These approaches enable prediction of cell performance under various conditions without extensive physical testing. Models range from molecular-level simulations of electrode-electrolyte interfaces to system-level models of complete cells and battery packs. Benchmarking different modeling approaches helps identify the most accurate and efficient methods for predicting cell behavior, optimizing designs, and accelerating the development of next-generation electrochemical systems.
02 Electrolyte composition and formulation benchmarking
Electrolyte formulation plays a crucial role in electrochemical cell performance. Benchmarking studies evaluate various electrolyte compositions, additives, and concentrations to optimize ionic conductivity, electrochemical stability, and compatibility with electrode materials. Advanced electrolyte systems may incorporate ionic liquids, polymer electrolytes, or specialized additives to enhance cell performance, safety, and longevity across different operating conditions and temperature ranges.Expand Specific Solutions03 Cell architecture and component integration benchmarking
The physical design and integration of electrochemical cell components significantly impact overall performance. Benchmarking studies compare different cell architectures, including planar, tubular, and novel geometries, evaluating factors such as internal resistance, thermal management, and space utilization. Advanced designs optimize the spatial arrangement of electrodes, separators, current collectors, and sealing mechanisms to enhance energy density, power output, and operational reliability while minimizing manufacturing complexity.Expand Specific Solutions04 Performance metrics and standardized testing protocols
Standardized benchmarking methodologies are essential for meaningful comparison of electrochemical cell designs. These protocols establish consistent metrics for evaluating key performance indicators such as energy density, power density, cycle life, coulombic efficiency, and self-discharge rates. Advanced benchmarking approaches incorporate accelerated testing procedures, in-situ characterization techniques, and computational modeling to predict long-term performance and identify potential failure mechanisms under various operating conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Thermal management and safety benchmarking
Thermal management is critical for electrochemical cell safety and performance optimization. Benchmarking studies evaluate various cooling strategies, heat dissipation mechanisms, and safety features to prevent thermal runaway and ensure stable operation across different temperature ranges. Advanced designs incorporate innovative thermal management solutions such as phase change materials, specialized cooling channels, or intelligent thermal control systems to maintain optimal operating temperatures while enhancing safety and reliability.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies in Wireless Power Solutions
The electrochemical cell design benchmarking in wireless technology market is currently in a growth phase, with an estimated market size exceeding $5 billion and projected to expand at a CAGR of 12-15% through 2028. The competitive landscape features established telecommunications giants like QUALCOMM and Samsung Electronics driving innovation alongside specialized battery technology companies such as Contemporary Amperex Technology, StoreDot, and CAMX Power. Technical maturity varies significantly across applications, with consumer electronics implementations being most advanced. Qualcomm leads in integration technologies, while Samsung and LG Electronics excel in commercial deployment. Research institutions like Huazhong University and CNRS are advancing fundamental electrochemical innovations, creating a dynamic ecosystem where cross-industry collaboration is increasingly critical for market leadership.
QUALCOMM, Inc.
Technical Solution: Qualcomm has developed a comprehensive electrochemical cell benchmarking framework specifically designed for wireless technology integration. Their approach focuses on evaluating battery performance under the unique power demands of cellular communication systems. Qualcomm's benchmarking methodology incorporates real-time power profiling during various wireless transmission scenarios (5G, LTE, Wi-Fi) to identify optimal cell chemistries and form factors. Their testing protocols include specialized metrics for measuring battery performance during high-frequency power draws characteristic of wireless signal transmission and reception. Qualcomm has also pioneered benchmarking techniques for evaluating battery performance during wireless charging, with particular attention to efficiency losses and thermal management. Their system includes comparative analysis of different cell designs across multiple parameters including energy density, power capability, thermal behavior, and cycle life under wireless operation conditions.
Strengths: Unparalleled expertise in wireless communication systems allows for highly relevant benchmarking scenarios; extensive ecosystem partnerships enable comprehensive real-world validation. Weaknesses: Benchmarking may prioritize performance in mobile devices over other wireless technology applications; focus on semiconductor aspects may sometimes overshadow electrochemical considerations.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has established a sophisticated electrochemical cell benchmarking system specifically tailored for wireless technology applications. Their approach integrates hardware and software evaluation methodologies to assess battery performance across their diverse product ecosystem. Samsung's benchmarking framework includes comprehensive testing protocols that simulate real-world usage scenarios for wireless devices, with particular emphasis on fast charging capabilities and wireless charging efficiency. Their methodology incorporates advanced thermal imaging to map heat distribution during wireless charging, identifying potential design optimizations. Samsung has developed proprietary metrics for evaluating the impact of different cell designs on wireless signal transmission and reception quality. Their benchmarking system also includes accelerated aging tests that simulate years of wireless device usage patterns, enabling long-term performance prediction. Samsung's approach emphasizes comparative analysis across different cell chemistries, form factors, and manufacturing techniques to identify optimal designs for specific wireless applications.
Strengths: Vertical integration across device manufacturing and battery production enables holistic benchmarking approach; extensive consumer product experience provides valuable real-world performance data. Weaknesses: Benchmarking may be overly focused on consumer electronics applications rather than industrial or specialized wireless technologies; proprietary nature of some testing methodologies limits industry-wide standardization.
Key Patents in Electrochemical Cell Design
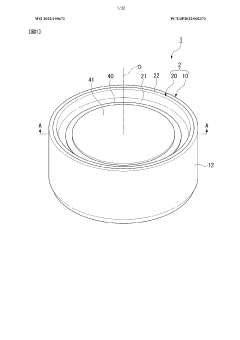
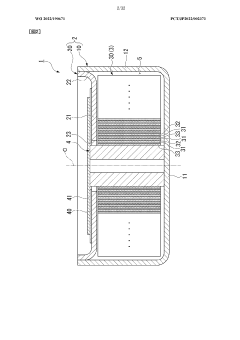
Electrochemical cell, electrochemical cell stack, and manufacturing methods for same
PatentWO2025094906A1
Innovation
- The electrochemical cell design incorporates a cell body with a cathode, electrolyte layer, and fuel electrode, along with inclined welds between metal members to enhance bonding strength and airtightness, while maintaining a shallow melting depth to prevent warping.
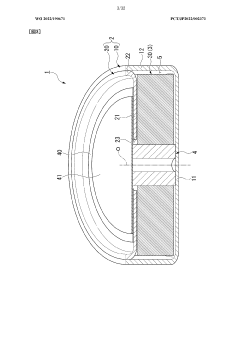
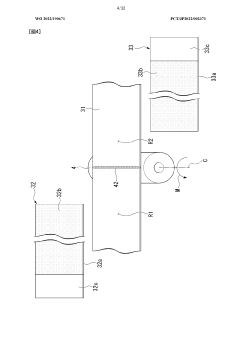
Electrochemical cell
PatentWO2022190671A1
Innovation
- The electrochemical cell design incorporates a support column that houses the electrode body, allowing for accurate alignment and welding of thin exterior components, with options for the support column to be either insulating or conductive, and featuring a current collector plate for improved electrical connection and assembly efficiency.
Sustainability Factors in Cell Manufacturing
Sustainability in electrochemical cell manufacturing has become a critical consideration as wireless technology continues to expand globally. The environmental impact of cell production processes demands immediate attention from manufacturers and researchers alike. Current manufacturing methods often involve energy-intensive processes and the use of toxic materials that pose significant environmental risks throughout the product lifecycle.
Material sourcing represents one of the primary sustainability challenges in cell manufacturing. Traditional electrochemical cells rely heavily on rare earth elements and precious metals with limited global reserves. The extraction of these materials frequently results in habitat destruction, water pollution, and substantial carbon emissions. Forward-thinking manufacturers are increasingly exploring alternative materials with lower environmental footprints, including organic compounds and abundant elements that can deliver comparable performance specifications.
Energy consumption during production constitutes another major sustainability concern. The manufacturing of electrochemical cells typically requires high-temperature processes and precision equipment operating continuously. Industry leaders are implementing renewable energy sources to power production facilities, with some achieving up to 40% reduction in carbon emissions through solar and wind integration. Advanced energy recovery systems are being deployed to capture and reuse waste heat from manufacturing processes, further improving overall efficiency.
Waste management practices significantly impact the sustainability profile of cell manufacturing operations. Chemical byproducts, metal scraps, and defective units create substantial waste streams that require responsible handling. Closed-loop manufacturing systems that recapture and reprocess materials are gaining traction, with recovery rates for certain metals now exceeding 85% in state-of-the-art facilities. Water recycling technologies have reduced freshwater consumption by up to 60% in modern production plants.
The longevity and end-of-life considerations of electrochemical cells also factor into sustainability assessments. Designing cells with extended operational lifespans reduces replacement frequency and associated resource demands. Modular designs that facilitate repair rather than replacement are emerging as best practices. Additionally, manufacturers are developing standardized recycling protocols to ensure valuable materials can be efficiently recovered when cells eventually reach end-of-life status.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly influence sustainability practices in cell manufacturing. International standards like ISO 14001 provide guidelines for environmental management systems, while region-specific regulations impose varying requirements for chemical use, emissions control, and waste disposal. Companies leading in sustainability metrics often exceed compliance requirements, recognizing that proactive environmental stewardship delivers both ecological benefits and competitive advantages in increasingly conscious markets.
Material sourcing represents one of the primary sustainability challenges in cell manufacturing. Traditional electrochemical cells rely heavily on rare earth elements and precious metals with limited global reserves. The extraction of these materials frequently results in habitat destruction, water pollution, and substantial carbon emissions. Forward-thinking manufacturers are increasingly exploring alternative materials with lower environmental footprints, including organic compounds and abundant elements that can deliver comparable performance specifications.
Energy consumption during production constitutes another major sustainability concern. The manufacturing of electrochemical cells typically requires high-temperature processes and precision equipment operating continuously. Industry leaders are implementing renewable energy sources to power production facilities, with some achieving up to 40% reduction in carbon emissions through solar and wind integration. Advanced energy recovery systems are being deployed to capture and reuse waste heat from manufacturing processes, further improving overall efficiency.
Waste management practices significantly impact the sustainability profile of cell manufacturing operations. Chemical byproducts, metal scraps, and defective units create substantial waste streams that require responsible handling. Closed-loop manufacturing systems that recapture and reprocess materials are gaining traction, with recovery rates for certain metals now exceeding 85% in state-of-the-art facilities. Water recycling technologies have reduced freshwater consumption by up to 60% in modern production plants.
The longevity and end-of-life considerations of electrochemical cells also factor into sustainability assessments. Designing cells with extended operational lifespans reduces replacement frequency and associated resource demands. Modular designs that facilitate repair rather than replacement are emerging as best practices. Additionally, manufacturers are developing standardized recycling protocols to ensure valuable materials can be efficiently recovered when cells eventually reach end-of-life status.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly influence sustainability practices in cell manufacturing. International standards like ISO 14001 provide guidelines for environmental management systems, while region-specific regulations impose varying requirements for chemical use, emissions control, and waste disposal. Companies leading in sustainability metrics often exceed compliance requirements, recognizing that proactive environmental stewardship delivers both ecological benefits and competitive advantages in increasingly conscious markets.
Standardization Efforts in Wireless Power Cells
The standardization of wireless power cells represents a critical development in the evolution of wireless technology infrastructure. Currently, several international bodies are actively working to establish unified standards for electrochemical cell design in wireless applications. The IEEE Power Electronics Society has formed a dedicated working group (P2100.1) specifically addressing standardization of power cell performance metrics and testing protocols for wireless devices.
These standardization efforts primarily focus on establishing consistent benchmarking methodologies that enable fair comparison between different electrochemical cell designs. Key parameters being standardized include energy density measurements, charge-discharge cycle definitions, temperature performance ranges, and safety compliance requirements specific to wireless power applications.
The Wireless Power Consortium (WPC) has expanded its scope beyond Qi charging to include standardized testing procedures for electrochemical cells used in conjunction with wireless charging systems. Their latest framework introduces standardized metrics for evaluating how different cell chemistries respond to the unique charging profiles of wireless power transfer.
Industry collaboration has accelerated through the formation of the Wireless Battery Alliance (WBA), where major manufacturers including Samsung, LG Energy Solution, and Tesla are working alongside technology integrators to develop interoperability standards. This alliance has published draft specifications for next-generation wireless power cells that define minimum performance thresholds and standardized form factors.
Regulatory bodies have also recognized the importance of standardization in this domain. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has established Technical Committee 21 to develop international standards for electrochemical cells in wireless applications, with particular emphasis on safety protocols and performance verification methodologies.
The GSMA, representing mobile network operators worldwide, has incorporated electrochemical cell standardization into its certification programs, ensuring that wireless devices meet minimum battery performance requirements before receiving network approval. This approach has created de facto standards that manufacturers must adhere to for market access.
Regional differences in standardization approaches present challenges, with European standards bodies emphasizing sustainability metrics and recyclability requirements, while North American standards focus more heavily on performance benchmarking. The harmonization of these regional approaches represents a significant ongoing effort within the international standards community.
These standardization efforts primarily focus on establishing consistent benchmarking methodologies that enable fair comparison between different electrochemical cell designs. Key parameters being standardized include energy density measurements, charge-discharge cycle definitions, temperature performance ranges, and safety compliance requirements specific to wireless power applications.
The Wireless Power Consortium (WPC) has expanded its scope beyond Qi charging to include standardized testing procedures for electrochemical cells used in conjunction with wireless charging systems. Their latest framework introduces standardized metrics for evaluating how different cell chemistries respond to the unique charging profiles of wireless power transfer.
Industry collaboration has accelerated through the formation of the Wireless Battery Alliance (WBA), where major manufacturers including Samsung, LG Energy Solution, and Tesla are working alongside technology integrators to develop interoperability standards. This alliance has published draft specifications for next-generation wireless power cells that define minimum performance thresholds and standardized form factors.
Regulatory bodies have also recognized the importance of standardization in this domain. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has established Technical Committee 21 to develop international standards for electrochemical cells in wireless applications, with particular emphasis on safety protocols and performance verification methodologies.
The GSMA, representing mobile network operators worldwide, has incorporated electrochemical cell standardization into its certification programs, ensuring that wireless devices meet minimum battery performance requirements before receiving network approval. This approach has created de facto standards that manufacturers must adhere to for market access.
Regional differences in standardization approaches present challenges, with European standards bodies emphasizing sustainability metrics and recyclability requirements, while North American standards focus more heavily on performance benchmarking. The harmonization of these regional approaches represents a significant ongoing effort within the international standards community.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!