Ethylene Vinyl Acetate: Benefits in Advanced Packaging Solutions
EVA in Packaging: Evolution and Objectives
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) has emerged as a pivotal material in the packaging industry, revolutionizing the way products are protected and presented. The evolution of EVA in packaging solutions can be traced back to the mid-20th century when it was first synthesized. Initially, its applications were limited, but as researchers and manufacturers recognized its unique properties, EVA's role in packaging began to expand rapidly.
The journey of EVA in packaging has been marked by continuous innovation and adaptation to meet evolving market demands. In its early days, EVA was primarily used as a sealant and adhesive in packaging materials. However, as manufacturing processes improved and the material's versatility became more apparent, it found its way into more sophisticated packaging applications.
One of the key milestones in EVA's evolution was its integration into flexible packaging solutions. The material's excellent flexibility, toughness, and barrier properties made it an ideal component in multi-layer films and pouches. This development opened up new possibilities for food packaging, extending shelf life and improving product protection.
The objectives of incorporating EVA into advanced packaging solutions have been multifaceted. Primarily, the goal has been to enhance the performance and functionality of packaging materials. EVA's low-temperature sealing capabilities, for instance, have been crucial in developing efficient and energy-saving packaging processes. Additionally, its compatibility with various other polymers has allowed for the creation of customized packaging solutions tailored to specific product requirements.
Another significant objective has been to improve the sustainability profile of packaging materials. As environmental concerns have gained prominence, the packaging industry has sought materials that can reduce overall material usage while maintaining or improving performance. EVA's contribution to lightweight packaging solutions aligns well with this goal, offering potential reductions in transportation costs and carbon footprint.
The evolution of EVA in packaging has also been driven by the objective of enhancing user experience. Its soft and flexible nature has enabled the development of easy-to-open packages and squeezable containers, improving convenience for consumers. Furthermore, EVA's clarity and gloss have made it valuable in creating visually appealing packaging that can effectively showcase products on retail shelves.
Looking ahead, the objectives for EVA in packaging continue to evolve. There is a growing focus on developing EVA formulations with improved recyclability and biodegradability, addressing the increasing demand for more environmentally friendly packaging solutions. Additionally, research is ongoing to further enhance EVA's barrier properties, potentially expanding its use in high-performance packaging for sensitive products such as electronics and pharmaceuticals.
Market Demand Analysis for EVA Packaging
The market demand for Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) in advanced packaging solutions has been experiencing significant growth in recent years. This surge is primarily driven by the increasing need for high-performance, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly packaging materials across various industries. EVA's unique properties, including flexibility, durability, and excellent barrier characteristics, make it an ideal choice for many packaging applications.
In the food and beverage industry, EVA packaging solutions have gained substantial traction due to their ability to extend shelf life and maintain product freshness. The material's low-temperature sealing properties and resistance to moisture and oxygen permeation have led to its widespread adoption in flexible packaging for perishable goods. This trend is expected to continue as consumers demand longer-lasting and better-preserved food products.
The pharmaceutical and healthcare sectors have also contributed significantly to the growing demand for EVA packaging. The material's compatibility with medical-grade applications, coupled with its ability to provide protection against light, moisture, and contaminants, has made it a preferred choice for drug packaging and medical device enclosures. As the global healthcare industry expands, the demand for EVA in this sector is projected to increase substantially.
In the electronics industry, EVA has found applications in protective packaging for sensitive components and devices. Its shock-absorbing properties and ability to conform to irregular shapes make it ideal for safeguarding delicate electronic products during transportation and storage. With the rapid growth of e-commerce and the increasing complexity of electronic devices, the demand for EVA packaging in this sector is expected to rise significantly.
The automotive industry has also recognized the benefits of EVA in packaging solutions for spare parts and components. The material's resistance to vibration and impact, combined with its lightweight nature, makes it suitable for protecting automotive parts during shipping and handling. As the automotive aftermarket continues to grow, the demand for EVA packaging in this sector is likely to increase.
Sustainability concerns have further boosted the market demand for EVA packaging. The material's recyclability and potential for bio-based formulations align with the growing emphasis on environmentally friendly packaging solutions. Many companies are actively seeking alternatives to traditional plastic packaging, and EVA's eco-friendly characteristics position it as a viable option in this context.
EVA Technology: Current State and Challenges
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) has emerged as a key material in advanced packaging solutions, offering a unique combination of properties that address many challenges in the packaging industry. Currently, EVA technology is widely used in various sectors, including food packaging, medical devices, and electronics, due to its excellent flexibility, transparency, and barrier properties.
The current state of EVA technology showcases significant advancements in polymer science and material engineering. Manufacturers have successfully developed EVA copolymers with varying vinyl acetate content, allowing for customization of properties such as flexibility, clarity, and adhesion strength. This versatility has led to the widespread adoption of EVA in multi-layer packaging structures, where it serves as an effective tie layer or sealant.
One of the primary challenges facing EVA technology is its limited heat resistance compared to some other packaging materials. While EVA offers excellent low-temperature performance, its relatively low melting point can restrict its use in high-temperature applications. Researchers are actively working on improving the thermal stability of EVA through various methods, including crosslinking and the incorporation of nanofillers.
Another significant challenge is the balance between oxygen barrier properties and flexibility. While EVA provides good barrier properties against moisture, its oxygen barrier performance is not as robust as some competing materials. This limitation has spurred research into EVA-based nanocomposites and multi-layer structures to enhance gas barrier properties without compromising flexibility.
Environmental concerns present both challenges and opportunities for EVA technology. As the packaging industry moves towards more sustainable solutions, there is a growing demand for biodegradable or easily recyclable materials. While EVA is not inherently biodegradable, efforts are underway to develop EVA blends with biodegradable polymers and to improve its recyclability.
The geographical distribution of EVA technology development is primarily concentrated in regions with strong polymer and packaging industries, such as North America, Europe, and East Asia. These areas are at the forefront of research and innovation in EVA technology, driving advancements in material properties and processing techniques.
In conclusion, EVA technology in advanced packaging solutions is characterized by its versatility and ongoing innovation. While it faces challenges in heat resistance, gas barrier properties, and sustainability, these issues are actively being addressed through research and development efforts. The future of EVA in packaging looks promising, with potential breakthroughs in material science and processing technologies poised to overcome current limitations and expand its applications in the packaging industry.
Current EVA Packaging Solutions
01 Improved flexibility and durability
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) offers enhanced flexibility and durability in various applications. Its elastic properties allow for better shock absorption and resistance to cracking, making it ideal for use in footwear, sports equipment, and packaging materials.- Improved flexibility and durability: Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) offers enhanced flexibility and durability in various applications. Its elastic properties allow for better shock absorption and resistance to cracking, making it ideal for use in footwear, sports equipment, and packaging materials.
- Enhanced thermal insulation: EVA provides excellent thermal insulation properties, making it suitable for use in construction materials, automotive components, and cold storage applications. It helps maintain temperature stability and reduces energy consumption in various products.
- Chemical resistance and barrier properties: EVA exhibits good resistance to chemicals and acts as an effective barrier against moisture and gases. These properties make it valuable in packaging, agricultural films, and protective coatings for various industries.
- Improved adhesion and compatibility: EVA's unique chemical structure allows for excellent adhesion to various substrates and compatibility with other materials. This makes it useful in adhesives, sealants, and as a polymer modifier in blends and composites.
- Low-temperature performance: EVA maintains its flexibility and impact resistance at low temperatures, making it suitable for cold weather applications such as winter sports equipment, automotive parts, and outdoor gear.
02 Enhanced thermal insulation
EVA provides excellent thermal insulation properties, making it suitable for use in construction materials, automotive components, and cold storage applications. It helps maintain temperature stability and reduces energy consumption in various products.Expand Specific Solutions03 Chemical resistance and barrier properties
EVA exhibits good resistance to chemicals and acts as an effective barrier against moisture and gases. These properties make it valuable in packaging, agricultural films, and protective coatings for various industries.Expand Specific Solutions04 Improved adhesion and compatibility
EVA's unique chemical structure allows for excellent adhesion to various substrates and compatibility with other materials. This makes it useful in adhesives, sealants, and as a polymer modifier in blends and composites.Expand Specific Solutions05 Low-temperature performance
EVA maintains its flexibility and impact resistance at low temperatures, making it suitable for cold weather applications such as winter sports equipment, automotive parts, and outdoor products.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in EVA Packaging Industry
The Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) market in advanced packaging solutions is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for flexible and sustainable packaging materials. The global market size is expanding, with projections indicating significant growth in the coming years. Technologically, EVA is relatively mature, but ongoing innovations are enhancing its properties and applications. Key players like DuPont de Nemours, Celanese, and Kuraray are at the forefront of EVA development, focusing on improving performance characteristics such as barrier properties and thermal stability. Companies like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. and LG Chem are also making significant contributions, particularly in expanding production capacities and developing specialized grades for advanced packaging applications.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Kuraray Co., Ltd.
Core EVA Innovations for Packaging
- Incorporating a polymer seed, such as vinyl acetate, ethylene vinyl acetate, acrylic, or styrene acrylic polymers, into the ethylene/vinyl acetate emulsion process with a specific polyvinyl alcohol and nonionic emulsifier system to achieve broader particle size distribution and higher solids levels while maintaining low viscosity.
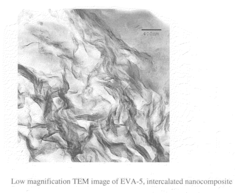
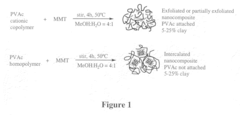
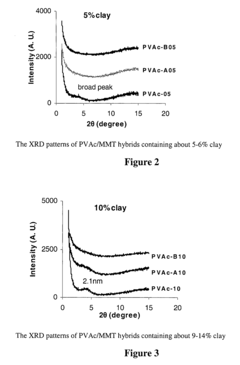
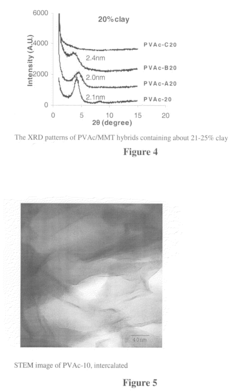
- Solution blending of EVA with a masterbatch of cationic poly(vinyl acetate)/silicate nanocomposite, where the silicate is substantially exfoliated, maintains mechanical properties and prevents loss of exfoliation during heat processing.
Environmental Impact of EVA Packaging
The environmental impact of EVA packaging is a crucial consideration in the adoption of this advanced packaging solution. EVA's versatility and durability contribute to its widespread use, but also raise concerns about its ecological footprint throughout its lifecycle.
One of the primary environmental advantages of EVA packaging is its potential for recyclability. When properly sorted and processed, EVA can be recycled and repurposed, reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills. However, the recycling process for EVA is not as straightforward as for some other materials, and it requires specialized facilities and techniques to ensure effective recycling.
The production of EVA packaging involves the use of petrochemical resources, which can have negative environmental implications. The extraction and processing of these raw materials contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption. However, compared to some alternative packaging materials, EVA's lightweight nature can lead to reduced transportation-related emissions when distributing packaged products.
EVA's durability and resistance to degradation, while beneficial for product protection, can pose challenges in terms of biodegradability. Unlike some biodegradable packaging materials, EVA does not readily break down in natural environments, potentially contributing to long-term pollution if not properly disposed of or recycled.
The use of EVA in packaging applications can have positive environmental impacts in terms of food waste reduction. Its excellent barrier properties help extend the shelf life of perishable goods, potentially decreasing food spoilage and the associated environmental costs of food production and disposal.
Efforts are being made to improve the environmental profile of EVA packaging. Research into bio-based EVA alternatives, derived from renewable resources, shows promise in reducing the reliance on fossil fuels. Additionally, advancements in EVA formulations are focusing on enhancing its recyclability and compatibility with existing recycling streams.
The end-of-life management of EVA packaging remains a significant environmental concern. Improper disposal can lead to accumulation in landfills or marine environments. However, initiatives to improve collection and recycling infrastructure for flexible packaging materials, including EVA, are gaining traction globally.
In conclusion, while EVA packaging offers numerous benefits in advanced packaging solutions, its environmental impact is complex and multifaceted. Balancing its performance advantages with ecological considerations requires ongoing research, innovation, and improvements in recycling technologies and waste management practices.
Regulatory Landscape for EVA in Packaging
The regulatory landscape for Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) in packaging is complex and multifaceted, reflecting the material's widespread use and potential impact on food safety and environmental concerns. At the forefront of regulatory considerations is the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which has approved EVA for food contact applications under specific conditions. The FDA's regulations, outlined in 21 CFR 177.1350, stipulate the permissible composition and manufacturing processes for EVA resins used in food packaging.
In the European Union, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) oversees the use of EVA in food contact materials. The EU's Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 provides the overarching framework for materials intended to come into contact with food, while specific measures for plastic materials are detailed in Regulation (EU) No 10/2011. These regulations set migration limits for substances that may transfer from packaging materials to food, ensuring consumer safety.
Global harmonization efforts, such as those led by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), aim to establish international standards for food packaging materials, including EVA. The Codex Alimentarius Commission, a joint WHO/FAO initiative, provides guidelines that influence national regulations worldwide.
Environmental regulations also play a crucial role in shaping the use of EVA in packaging. Many countries have implemented or are developing extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes, which hold manufacturers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their packaging materials. These regulations often incentivize the use of recyclable or biodegradable materials, potentially impacting the adoption of EVA in certain applications.
The circular economy concept has gained traction in recent years, leading to regulations that promote the recycling and reuse of packaging materials. While EVA offers excellent recyclability, regulations may vary regarding the specific recycling processes and end-of-life management for EVA-based packaging.
Emerging concerns about microplastics and their environmental impact have prompted some regulatory bodies to scrutinize polymer-based packaging materials more closely. Although EVA is not typically associated with microplastic pollution to the same extent as some other plastics, future regulations may address its potential environmental impact more comprehensively.
As sustainability becomes an increasingly important factor in packaging design, regulations are evolving to encourage the use of bio-based and renewable materials. This trend may influence the regulatory landscape for EVA, potentially favoring formulations that incorporate renewable content or demonstrate improved environmental performance.