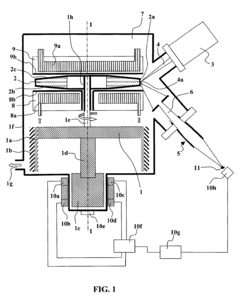
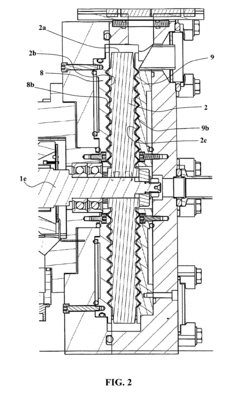
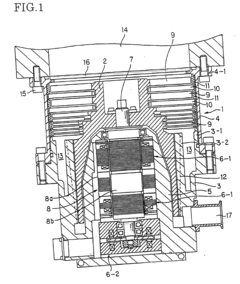
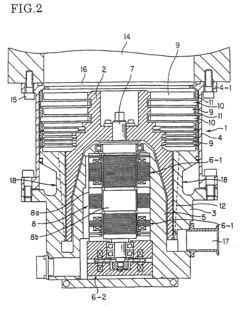
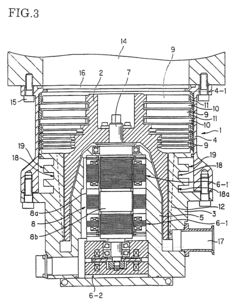
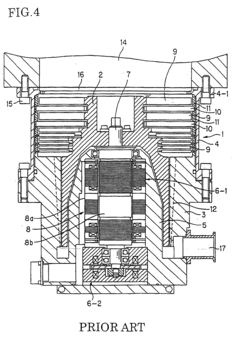
Exploring Vacuum Pump Use in High-Energy X-ray Instrumentation
JUL 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
X-ray Vacuum Tech Evolution
The evolution of vacuum technology in X-ray instrumentation has been a critical factor in advancing high-energy physics research and applications. The journey began in the early 20th century with the development of basic vacuum tubes, which were essential for generating and controlling X-rays. As the demand for higher energy and more precise X-ray beams grew, so did the need for more sophisticated vacuum systems.
In the 1950s and 1960s, the introduction of turbomolecular pumps marked a significant milestone in X-ray vacuum technology. These pumps allowed for the creation of cleaner, higher-quality vacuums, which were crucial for reducing beam scattering and improving overall system performance. This advancement enabled researchers to achieve higher X-ray energies and better resolution in their experiments.
The 1970s and 1980s saw the integration of ion pumps and cryopumps into X-ray systems. These technologies offered even higher vacuum levels and cleaner environments, further enhancing the capabilities of X-ray instrumentation. Ion pumps, in particular, became popular due to their ability to maintain ultra-high vacuums without mechanical moving parts, reducing vibration and increasing reliability.
As synchrotron radiation sources became more prevalent in the 1990s and 2000s, vacuum technology had to evolve to meet the demands of these powerful X-ray generators. The need for extremely low pressures and contamination-free environments led to the development of specialized vacuum chambers and pumping systems. Non-evaporable getter (NEG) pumps emerged as a crucial technology, capable of maintaining ultra-high vacuums in the complex geometries of synchrotron beamlines.
Recent years have seen a focus on improving the energy efficiency and reliability of vacuum systems in X-ray instrumentation. The development of more compact and efficient turbomolecular pumps, along with advanced control systems, has allowed for better integration of vacuum technology into increasingly sophisticated X-ray devices. Additionally, the use of computational fluid dynamics and vacuum modeling software has enabled more precise design and optimization of vacuum systems for specific X-ray applications.
The ongoing evolution of vacuum technology continues to push the boundaries of what is possible in high-energy X-ray instrumentation. Current research is exploring novel materials and pump designs to achieve even higher vacuum levels and improved stability. As X-ray technologies advance towards higher energies and more precise measurements, vacuum technology remains a critical enabler, constantly adapting to meet the evolving needs of the field.
In the 1950s and 1960s, the introduction of turbomolecular pumps marked a significant milestone in X-ray vacuum technology. These pumps allowed for the creation of cleaner, higher-quality vacuums, which were crucial for reducing beam scattering and improving overall system performance. This advancement enabled researchers to achieve higher X-ray energies and better resolution in their experiments.
The 1970s and 1980s saw the integration of ion pumps and cryopumps into X-ray systems. These technologies offered even higher vacuum levels and cleaner environments, further enhancing the capabilities of X-ray instrumentation. Ion pumps, in particular, became popular due to their ability to maintain ultra-high vacuums without mechanical moving parts, reducing vibration and increasing reliability.
As synchrotron radiation sources became more prevalent in the 1990s and 2000s, vacuum technology had to evolve to meet the demands of these powerful X-ray generators. The need for extremely low pressures and contamination-free environments led to the development of specialized vacuum chambers and pumping systems. Non-evaporable getter (NEG) pumps emerged as a crucial technology, capable of maintaining ultra-high vacuums in the complex geometries of synchrotron beamlines.
Recent years have seen a focus on improving the energy efficiency and reliability of vacuum systems in X-ray instrumentation. The development of more compact and efficient turbomolecular pumps, along with advanced control systems, has allowed for better integration of vacuum technology into increasingly sophisticated X-ray devices. Additionally, the use of computational fluid dynamics and vacuum modeling software has enabled more precise design and optimization of vacuum systems for specific X-ray applications.
The ongoing evolution of vacuum technology continues to push the boundaries of what is possible in high-energy X-ray instrumentation. Current research is exploring novel materials and pump designs to achieve even higher vacuum levels and improved stability. As X-ray technologies advance towards higher energies and more precise measurements, vacuum technology remains a critical enabler, constantly adapting to meet the evolving needs of the field.
High-Energy X-ray Market Trends
The high-energy X-ray market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand across various industries and applications. This trend is expected to continue, with the market projected to expand at a robust rate over the next decade. The primary factors contributing to this growth include advancements in medical imaging technologies, rising investments in industrial non-destructive testing, and growing applications in scientific research and material analysis.
In the medical sector, high-energy X-ray systems are becoming increasingly crucial for advanced diagnostic imaging and radiation therapy. The global push for early disease detection and more precise treatment methods has led to a surge in demand for high-resolution imaging equipment. Hospitals and diagnostic centers are upgrading their facilities with state-of-the-art X-ray systems, driving market growth.
The industrial sector is another key driver of the high-energy X-ray market. Non-destructive testing (NDT) applications in aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing industries are expanding rapidly. These industries rely on high-energy X-ray systems for quality control, structural integrity assessments, and defect detection in complex components. As manufacturing processes become more sophisticated, the need for advanced inspection technologies continues to grow.
Scientific research institutions and material analysis laboratories are also contributing to the market's upward trajectory. High-energy X-ray instrumentation is essential for cutting-edge research in fields such as materials science, nanotechnology, and particle physics. Government and private sector investments in research and development activities are fueling the demand for more powerful and precise X-ray systems.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the high-energy X-ray market, owing to their well-established healthcare infrastructure and strong industrial base. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure, industrial growth, and rising investments in research and development activities in countries like China, Japan, and India.
Technological advancements are playing a crucial role in shaping market trends. Innovations in detector technology, image processing algorithms, and system integration are enhancing the capabilities of high-energy X-ray systems. The development of more compact, energy-efficient, and user-friendly systems is expanding the potential applications and market reach of these instruments.
The market is also witnessing a shift towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions. Manufacturers are focusing on developing X-ray systems with reduced radiation exposure and improved energy efficiency. This trend aligns with global efforts to minimize environmental impact and enhance safety in various industries.
In the medical sector, high-energy X-ray systems are becoming increasingly crucial for advanced diagnostic imaging and radiation therapy. The global push for early disease detection and more precise treatment methods has led to a surge in demand for high-resolution imaging equipment. Hospitals and diagnostic centers are upgrading their facilities with state-of-the-art X-ray systems, driving market growth.
The industrial sector is another key driver of the high-energy X-ray market. Non-destructive testing (NDT) applications in aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing industries are expanding rapidly. These industries rely on high-energy X-ray systems for quality control, structural integrity assessments, and defect detection in complex components. As manufacturing processes become more sophisticated, the need for advanced inspection technologies continues to grow.
Scientific research institutions and material analysis laboratories are also contributing to the market's upward trajectory. High-energy X-ray instrumentation is essential for cutting-edge research in fields such as materials science, nanotechnology, and particle physics. Government and private sector investments in research and development activities are fueling the demand for more powerful and precise X-ray systems.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the high-energy X-ray market, owing to their well-established healthcare infrastructure and strong industrial base. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure, industrial growth, and rising investments in research and development activities in countries like China, Japan, and India.
Technological advancements are playing a crucial role in shaping market trends. Innovations in detector technology, image processing algorithms, and system integration are enhancing the capabilities of high-energy X-ray systems. The development of more compact, energy-efficient, and user-friendly systems is expanding the potential applications and market reach of these instruments.
The market is also witnessing a shift towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions. Manufacturers are focusing on developing X-ray systems with reduced radiation exposure and improved energy efficiency. This trend aligns with global efforts to minimize environmental impact and enhance safety in various industries.
Vacuum Pump Challenges in X-ray
Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in high-energy X-ray instrumentation, ensuring optimal performance and precision in various scientific and industrial applications. However, their use in this context presents several significant challenges that researchers and engineers must address to maintain the integrity and efficiency of X-ray systems.
One of the primary challenges is maintaining ultra-high vacuum conditions necessary for X-ray generation and propagation. High-energy X-ray systems often require vacuum levels in the range of 10^-6 to 10^-9 torr. Achieving and sustaining such low pressures demands sophisticated vacuum pump technologies and meticulous system design. Contamination from outgassing materials or minute leaks can significantly impact vacuum quality, necessitating stringent material selection and leak detection protocols.
The integration of vacuum pumps with X-ray instrumentation poses another set of challenges. Space constraints within X-ray systems often limit the size and placement of vacuum pumps, requiring compact yet powerful solutions. Additionally, the pumps must be carefully isolated to prevent vibrations from affecting sensitive X-ray detectors and optics. This isolation is critical for maintaining the high spatial resolution and image quality demanded in advanced X-ray applications.
Heat management is a significant concern in high-energy X-ray systems. Vacuum pumps generate heat during operation, which can affect the thermal stability of X-ray components. Efficient cooling mechanisms must be implemented to dissipate this heat without compromising the vacuum integrity or introducing additional vibrations to the system.
The choice of vacuum pump technology is crucial and presents its own challenges. While turbomolecular pumps offer high pumping speeds and can achieve very low pressures, they are sensitive to mechanical shocks and require careful handling. Ion pumps, on the other hand, provide vibration-free operation but may struggle with high gas loads and have limited pumping speeds for certain gases.
Reliability and maintenance of vacuum pumps in X-ray systems present ongoing challenges. Continuous operation in high-radiation environments can degrade pump components over time, potentially leading to performance issues or failures. Developing pumps with radiation-resistant materials and designs is essential for long-term reliability. Moreover, the need for minimal downtime in many X-ray applications requires pump systems with predictive maintenance capabilities and quick serviceability.
Lastly, the cost-effectiveness of vacuum pump solutions in high-energy X-ray instrumentation remains a challenge. Balancing the need for high-performance, reliable vacuum systems with budget constraints requires innovative approaches in pump design and system integration. This challenge extends to the development of energy-efficient pump technologies that can reduce operational costs without compromising vacuum quality.
One of the primary challenges is maintaining ultra-high vacuum conditions necessary for X-ray generation and propagation. High-energy X-ray systems often require vacuum levels in the range of 10^-6 to 10^-9 torr. Achieving and sustaining such low pressures demands sophisticated vacuum pump technologies and meticulous system design. Contamination from outgassing materials or minute leaks can significantly impact vacuum quality, necessitating stringent material selection and leak detection protocols.
The integration of vacuum pumps with X-ray instrumentation poses another set of challenges. Space constraints within X-ray systems often limit the size and placement of vacuum pumps, requiring compact yet powerful solutions. Additionally, the pumps must be carefully isolated to prevent vibrations from affecting sensitive X-ray detectors and optics. This isolation is critical for maintaining the high spatial resolution and image quality demanded in advanced X-ray applications.
Heat management is a significant concern in high-energy X-ray systems. Vacuum pumps generate heat during operation, which can affect the thermal stability of X-ray components. Efficient cooling mechanisms must be implemented to dissipate this heat without compromising the vacuum integrity or introducing additional vibrations to the system.
The choice of vacuum pump technology is crucial and presents its own challenges. While turbomolecular pumps offer high pumping speeds and can achieve very low pressures, they are sensitive to mechanical shocks and require careful handling. Ion pumps, on the other hand, provide vibration-free operation but may struggle with high gas loads and have limited pumping speeds for certain gases.
Reliability and maintenance of vacuum pumps in X-ray systems present ongoing challenges. Continuous operation in high-radiation environments can degrade pump components over time, potentially leading to performance issues or failures. Developing pumps with radiation-resistant materials and designs is essential for long-term reliability. Moreover, the need for minimal downtime in many X-ray applications requires pump systems with predictive maintenance capabilities and quick serviceability.
Lastly, the cost-effectiveness of vacuum pump solutions in high-energy X-ray instrumentation remains a challenge. Balancing the need for high-performance, reliable vacuum systems with budget constraints requires innovative approaches in pump design and system integration. This challenge extends to the development of energy-efficient pump technologies that can reduce operational costs without compromising vacuum quality.
Current Vacuum Solutions
01 Improved vacuum pump designs
Various innovations in vacuum pump designs aim to enhance efficiency, reduce noise, and improve overall performance. These designs may include modifications to rotor configurations, sealing mechanisms, or the integration of advanced materials to optimize pump operation.- Improved vacuum pump designs: Various innovations in vacuum pump designs aim to enhance efficiency, reduce noise, and improve overall performance. These designs may include modifications to rotor configurations, sealing mechanisms, or the integration of advanced materials to optimize pump operation.
- Energy-efficient vacuum pump systems: Developments in energy-efficient vacuum pump systems focus on reducing power consumption while maintaining high performance. These systems may incorporate advanced control algorithms, variable speed drives, or heat recovery mechanisms to optimize energy usage.
- Vacuum pump cooling and lubrication: Innovations in cooling and lubrication systems for vacuum pumps aim to improve reliability and extend operational life. These may include advanced cooling techniques, self-lubricating materials, or intelligent lubrication systems that adapt to pump conditions.
- Multi-stage vacuum pump configurations: Multi-stage vacuum pump designs combine different pump types or stages to achieve higher vacuum levels or improved pumping speeds. These configurations may integrate various pump technologies to optimize performance across a wide range of pressure conditions.
- Smart vacuum pump control systems: Advanced control systems for vacuum pumps incorporate sensors, data analytics, and connectivity features to optimize pump operation, enable predictive maintenance, and integrate with broader industrial automation systems. These smart systems can adapt to changing process requirements and improve overall system efficiency.
02 Energy-efficient vacuum pump systems
Development of energy-efficient vacuum pump systems focuses on reducing power consumption while maintaining high performance. These systems may incorporate advanced control algorithms, variable speed drives, or heat recovery mechanisms to optimize energy usage.Expand Specific Solutions03 Vacuum pump cooling and lubrication
Innovations in cooling and lubrication systems for vacuum pumps aim to improve reliability and extend operational life. These may include advanced cooling techniques, self-lubricating materials, or intelligent lubrication systems that adapt to pump conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Multi-stage vacuum pump configurations
Multi-stage vacuum pump designs combine different pump types or stages to achieve higher vacuum levels or improved pumping speeds. These configurations may integrate various pump technologies to optimize performance across a wide range of pressure conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Smart vacuum pump control systems
Integration of smart control systems in vacuum pumps enables advanced monitoring, diagnostics, and optimization. These systems may incorporate sensors, IoT connectivity, and machine learning algorithms to enhance pump performance, predict maintenance needs, and optimize energy consumption.Expand Specific Solutions
X-ray Vacuum Pump Manufacturers
The exploration of vacuum pump use in high-energy X-ray instrumentation is currently in a growth phase, with increasing market demand driven by advancements in scientific research and industrial applications. The global market for vacuum pumps in this sector is expanding, with key players like Edwards Ltd., LEYBOLD AG, and Siemens Healthineers AG leading the way. These companies are investing heavily in R&D to improve pump efficiency and reliability for high-energy X-ray systems. The technology is maturing rapidly, with innovations focusing on enhancing vacuum quality, reducing pump size, and increasing energy efficiency. Collaborations between academic institutions like Tsinghua University and industry leaders are accelerating technological progress, positioning vacuum pump technology as a critical component in the evolution of high-energy X-ray instrumentation.
Edwards Ltd.
Technical Solution: Edwards Ltd. has developed advanced vacuum pump technologies specifically tailored for high-energy X-ray instrumentation. Their innovative approach includes the use of dry pumping technology, which eliminates the need for oil in the pumping mechanism. This results in a cleaner vacuum environment, crucial for sensitive X-ray equipment. The company's GXS dry screw pump series offers high pumping speeds of up to 3400 m³/h [1], making it suitable for large-scale X-ray facilities. Additionally, Edwards has implemented intelligent control systems that optimize pump performance based on the specific requirements of X-ray instrumentation, ensuring stable vacuum levels and reducing energy consumption [2].
Strengths: Oil-free operation reduces contamination risks; high pumping speeds suitable for large-scale facilities; intelligent control systems for optimized performance. Weaknesses: Higher initial cost compared to traditional oil-sealed pumps; may require specialized maintenance.
LEYBOLD AG
Technical Solution: LEYBOLD AG has pioneered the development of turbomolecular pumps specifically designed for high-energy X-ray applications. Their TURBOVAC i/iX series integrates advanced rotor designs with magnetic bearings, allowing for vibration-free operation critical in precision X-ray instrumentation. These pumps achieve ultimate pressures below 1 × 10⁻¹⁰ mbar [3], essential for maintaining the high vacuum required in X-ray beam paths. LEYBOLD's pumps also feature adaptive drive technology that adjusts rotor speed based on gas load, optimizing efficiency and extending the pump's lifespan. Furthermore, they have implemented a unique hybrid bearing system that combines ceramic ball bearings with magnetic bearings, enhancing reliability and reducing maintenance needs [4].
Strengths: Extremely low ultimate pressure capabilities; vibration-free operation ideal for sensitive X-ray equipment; adaptive drive technology for efficiency. Weaknesses: Higher complexity may lead to increased costs; specialized expertise required for maintenance and repairs.
Key Vacuum Pump Innovations
Compact source of a high-brightness X-ray beam
PatentInactiveEP1804271A2
Innovation
- Integration of a high-speed vacuum pump to both generate and maintain vacuum and drive the rotating anode, combined with advanced cooling and thermal insulation to reduce size, cost, and vibrations, and enhance X-ray brilliance.
Vacuum pump
PatentInactiveEP1344939B1
Innovation
- A vacuum pump design featuring a groove spacing or recess on the base member that allows for plastic deformation to absorb rotational collision energy, reducing the transmission of damaging torque to the outer casing without additional components.
Radiation Safety Regulations
Radiation safety regulations play a crucial role in the development and implementation of high-energy X-ray instrumentation, particularly when incorporating vacuum pump technology. These regulations are designed to protect workers, the public, and the environment from the potential harmful effects of ionizing radiation.
In the context of high-energy X-ray instrumentation, regulatory bodies such as the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) and national radiation protection agencies establish guidelines and standards for safe operation. These regulations typically cover aspects such as shielding requirements, dose limits, and operational procedures.
For vacuum pump applications in X-ray systems, specific considerations must be addressed to ensure compliance with radiation safety regulations. The vacuum environment can potentially alter the behavior of X-rays, necessitating additional safety measures. Regulations often require the implementation of interlocks and fail-safe mechanisms to prevent accidental exposure during maintenance or operation of the vacuum system.
Radiation monitoring is another critical aspect governed by safety regulations. Continuous monitoring of radiation levels in and around the X-ray instrumentation is mandatory, with specific attention given to potential leak points in the vacuum system. Regular calibration and maintenance of radiation detection equipment are typically required to ensure accurate measurements and timely response to any anomalies.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements for personnel working with high-energy X-ray instrumentation and associated vacuum systems are also outlined in radiation safety regulations. This may include specialized clothing, dosimeters, and training on proper use of safety equipment.
Disposal of potentially contaminated materials, including vacuum pump oil and components exposed to radiation, is subject to strict regulatory guidelines. Proper documentation and tracking of radiation exposure levels for both personnel and equipment are essential components of compliance with these regulations.
Regulatory bodies often require periodic safety assessments and audits of facilities using high-energy X-ray instrumentation with vacuum pump technology. These assessments evaluate the effectiveness of radiation protection measures, identify potential hazards, and ensure ongoing compliance with evolving safety standards.
As technology advances, radiation safety regulations are continually updated to address new challenges and incorporate improved safety practices. Researchers and engineers working on vacuum pump applications in high-energy X-ray instrumentation must stay informed about these regulatory changes and adapt their designs and operational procedures accordingly.
In the context of high-energy X-ray instrumentation, regulatory bodies such as the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) and national radiation protection agencies establish guidelines and standards for safe operation. These regulations typically cover aspects such as shielding requirements, dose limits, and operational procedures.
For vacuum pump applications in X-ray systems, specific considerations must be addressed to ensure compliance with radiation safety regulations. The vacuum environment can potentially alter the behavior of X-rays, necessitating additional safety measures. Regulations often require the implementation of interlocks and fail-safe mechanisms to prevent accidental exposure during maintenance or operation of the vacuum system.
Radiation monitoring is another critical aspect governed by safety regulations. Continuous monitoring of radiation levels in and around the X-ray instrumentation is mandatory, with specific attention given to potential leak points in the vacuum system. Regular calibration and maintenance of radiation detection equipment are typically required to ensure accurate measurements and timely response to any anomalies.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements for personnel working with high-energy X-ray instrumentation and associated vacuum systems are also outlined in radiation safety regulations. This may include specialized clothing, dosimeters, and training on proper use of safety equipment.
Disposal of potentially contaminated materials, including vacuum pump oil and components exposed to radiation, is subject to strict regulatory guidelines. Proper documentation and tracking of radiation exposure levels for both personnel and equipment are essential components of compliance with these regulations.
Regulatory bodies often require periodic safety assessments and audits of facilities using high-energy X-ray instrumentation with vacuum pump technology. These assessments evaluate the effectiveness of radiation protection measures, identify potential hazards, and ensure ongoing compliance with evolving safety standards.
As technology advances, radiation safety regulations are continually updated to address new challenges and incorporate improved safety practices. Researchers and engineers working on vacuum pump applications in high-energy X-ray instrumentation must stay informed about these regulatory changes and adapt their designs and operational procedures accordingly.
Energy Efficiency in Vacuum Pumps
Energy efficiency in vacuum pumps is a critical consideration in high-energy X-ray instrumentation. As these systems often require continuous operation, optimizing energy consumption can lead to significant cost savings and reduced environmental impact. Modern vacuum pump designs focus on improving efficiency through various technological advancements.
One key approach to enhancing energy efficiency is the implementation of variable speed drives (VSDs). These allow pumps to adjust their operating speed based on the required vacuum level, reducing energy waste during periods of lower demand. VSDs can result in energy savings of up to 50% compared to traditional fixed-speed pumps.
Advanced motor technologies also play a crucial role in improving pump efficiency. The adoption of permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs) has shown promising results, offering higher efficiency across a wide range of operating conditions compared to conventional induction motors. PMSMs can achieve efficiency ratings of up to 96%, contributing to overall system performance.
Heat recovery systems represent another avenue for energy optimization in vacuum pumps. By capturing and repurposing the heat generated during pump operation, facilities can reduce their overall energy consumption. This recovered heat can be utilized for space heating or integrated into other industrial processes, further enhancing the overall energy efficiency of the system.
Innovative pump designs, such as dry screw pumps, have also emerged as energy-efficient alternatives to traditional oil-sealed rotary vane pumps. These pumps operate without oil, reducing friction and minimizing energy losses associated with oil circulation and cooling. Dry screw pumps can offer energy savings of up to 30% compared to their oil-sealed counterparts.
The integration of smart control systems and IoT technologies has further revolutionized vacuum pump energy management. These systems enable real-time monitoring and optimization of pump performance, allowing for predictive maintenance and energy-efficient operation. By analyzing operational data, these smart systems can identify inefficiencies and automatically adjust pump parameters to maximize energy savings.
Advancements in materials science have also contributed to improved pump efficiency. The use of low-friction coatings and advanced composite materials in pump components reduces wear and energy losses due to friction. These materials can extend pump lifespan while maintaining optimal performance and energy efficiency over time.
As the demand for high-energy X-ray instrumentation continues to grow, the focus on energy-efficient vacuum pump solutions will remain paramount. Ongoing research and development efforts are likely to yield further improvements in pump design, control strategies, and materials, driving the industry towards ever-higher standards of energy efficiency and sustainability.
One key approach to enhancing energy efficiency is the implementation of variable speed drives (VSDs). These allow pumps to adjust their operating speed based on the required vacuum level, reducing energy waste during periods of lower demand. VSDs can result in energy savings of up to 50% compared to traditional fixed-speed pumps.
Advanced motor technologies also play a crucial role in improving pump efficiency. The adoption of permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs) has shown promising results, offering higher efficiency across a wide range of operating conditions compared to conventional induction motors. PMSMs can achieve efficiency ratings of up to 96%, contributing to overall system performance.
Heat recovery systems represent another avenue for energy optimization in vacuum pumps. By capturing and repurposing the heat generated during pump operation, facilities can reduce their overall energy consumption. This recovered heat can be utilized for space heating or integrated into other industrial processes, further enhancing the overall energy efficiency of the system.
Innovative pump designs, such as dry screw pumps, have also emerged as energy-efficient alternatives to traditional oil-sealed rotary vane pumps. These pumps operate without oil, reducing friction and minimizing energy losses associated with oil circulation and cooling. Dry screw pumps can offer energy savings of up to 30% compared to their oil-sealed counterparts.
The integration of smart control systems and IoT technologies has further revolutionized vacuum pump energy management. These systems enable real-time monitoring and optimization of pump performance, allowing for predictive maintenance and energy-efficient operation. By analyzing operational data, these smart systems can identify inefficiencies and automatically adjust pump parameters to maximize energy savings.
Advancements in materials science have also contributed to improved pump efficiency. The use of low-friction coatings and advanced composite materials in pump components reduces wear and energy losses due to friction. These materials can extend pump lifespan while maintaining optimal performance and energy efficiency over time.
As the demand for high-energy X-ray instrumentation continues to grow, the focus on energy-efficient vacuum pump solutions will remain paramount. Ongoing research and development efforts are likely to yield further improvements in pump design, control strategies, and materials, driving the industry towards ever-higher standards of energy efficiency and sustainability.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!