How to Capitalize on Zirconia's Market Potential?
Zirconia Market Overview
Zirconia, a versatile ceramic material, has been gaining significant traction in various industries due to its exceptional properties. The global zirconia market has experienced steady growth over the past decade, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 6.5% from 2015 to 2020. This growth trajectory is expected to continue, with projections indicating a market value of $2.5 billion by 2025.
The demand for zirconia is primarily driven by its widespread applications across multiple sectors. In the medical and dental industries, zirconia has become increasingly popular for prosthetics and implants due to its biocompatibility and aesthetic appeal. The automotive sector utilizes zirconia in oxygen sensors and catalytic converters, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. Additionally, the electronics industry has found zirconia invaluable in the production of solid oxide fuel cells and other advanced components.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the zirconia market, accounting for over 40% of the global share. This is largely attributed to the rapid industrialization and growing manufacturing sectors in countries like China and India. North America and Europe follow closely, with significant demand stemming from their advanced healthcare and automotive industries.
The market landscape is characterized by a mix of established players and emerging companies. Key market leaders include Saint-Gobain, Tosoh Corporation, and Daiichi Kigenso Kagaku Kogyo Co., Ltd. These companies have invested heavily in research and development to enhance product quality and expand their application range.
Despite the positive outlook, the zirconia market faces certain challenges. The volatility in raw material prices, particularly zircon sand, can impact production costs and market stability. Environmental concerns related to mining and processing of zirconia have also led to increased regulatory scrutiny in some regions.
Emerging trends in the zirconia market include the development of nano-zirconia particles for advanced applications and the increasing adoption of 3D printing technology for zirconia-based products. These innovations are opening up new avenues for market growth and product diversification.
To capitalize on zirconia's market potential, companies need to focus on product innovation, sustainable production methods, and strategic partnerships across the value chain. Exploring untapped applications in emerging industries and investing in advanced manufacturing technologies could provide significant competitive advantages in this evolving market landscape.
Demand Analysis
The global zirconia market has been experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand across various industries. The versatility and unique properties of zirconia have positioned it as a material of choice in sectors such as ceramics, electronics, healthcare, and automotive.
In the dental industry, zirconia has gained substantial traction due to its biocompatibility, durability, and aesthetic appeal. The rising prevalence of dental disorders and the growing emphasis on cosmetic dentistry have fueled the demand for zirconia-based dental implants and prosthetics. This trend is expected to continue as the global population ages and dental care awareness increases.
The electronics sector presents another substantial market for zirconia. With the ongoing miniaturization of electronic devices and the push for higher performance, zirconia's excellent thermal and electrical insulation properties make it an ideal material for components in smartphones, tablets, and other consumer electronics. The rapid pace of technological advancements and the increasing adoption of 5G technology are likely to further boost zirconia demand in this sector.
In the automotive industry, zirconia finds applications in oxygen sensors, catalytic converters, and thermal barrier coatings. The global shift towards electric vehicles and stricter emission regulations are driving the need for more efficient and durable components, creating opportunities for zirconia-based solutions.
The healthcare sector, beyond dentistry, also shows promising growth potential for zirconia. Its use in orthopedic implants, particularly hip replacements, is gaining traction due to its superior wear resistance and biocompatibility compared to traditional materials. As the global population ages and the incidence of osteoarthritis increases, the demand for zirconia in this application is expected to rise.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific is emerging as a key market for zirconia, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing disposable incomes. China and India, in particular, are expected to be major contributors to market growth, with their expanding manufacturing sectors and growing middle-class populations.
However, the zirconia market also faces challenges. The high cost of production and processing compared to some alternative materials can limit its adoption in price-sensitive applications. Additionally, the environmental impact of zirconia mining and processing is a growing concern, potentially leading to stricter regulations that could affect market dynamics.
In conclusion, the zirconia market shows strong growth potential across multiple industries, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer preferences. To capitalize on this potential, companies should focus on developing cost-effective production methods, exploring new applications, and addressing sustainability concerns to ensure long-term market viability.
Technical Challenges
Zirconia, a versatile ceramic material, faces several technical challenges that hinder its full market potential. One of the primary obstacles is the complexity of its manufacturing process. The production of high-quality zirconia requires precise control over temperature, pressure, and composition, which can be difficult to maintain consistently at scale. This complexity often leads to increased production costs and potential quality inconsistencies.
Another significant challenge lies in the material's inherent brittleness. While zirconia boasts impressive strength and hardness, its susceptibility to sudden fracture under certain conditions limits its application in high-stress environments. This characteristic necessitates careful design considerations and may restrict its use in certain industries where reliability is paramount.
The stabilization of zirconia's crystal structure presents an ongoing technical hurdle. Different phases of zirconia exhibit varying properties, and maintaining the desired phase throughout the product's lifecycle is crucial for performance. The transformation toughening mechanism, while beneficial for some applications, can lead to unpredictable behavior in others, requiring extensive research and development to optimize for specific use cases.
Surface finishing and machining of zirconia components pose additional challenges. The material's hardness, while advantageous in many applications, makes it difficult to achieve precise dimensions and smooth surfaces without specialized equipment and techniques. This can increase production time and costs, potentially limiting zirconia's competitiveness in certain market segments.
The biocompatibility of zirconia, particularly in medical and dental applications, requires ongoing research and validation. While generally considered safe, long-term studies on its performance and potential interactions with biological systems are necessary to expand its use in these high-value markets. Regulatory hurdles and the need for extensive clinical trials can slow down market penetration in these sectors.
Thermal management is another area of concern, especially in high-temperature applications. Zirconia's low thermal conductivity, while beneficial in some contexts, can lead to thermal stress and potential failure in others. Developing composite materials or innovative designs to mitigate these thermal issues is an active area of research that could unlock new market opportunities.
Lastly, the environmental impact of zirconia production and disposal presents both a challenge and an opportunity. As sustainability becomes increasingly important across industries, developing more eco-friendly production methods and exploring recycling possibilities for zirconia products could significantly enhance its market appeal and long-term viability.
Current Applications
01 Zirconia synthesis and processing methods
Various techniques for synthesizing and processing zirconia materials, including sol-gel methods, hydrothermal synthesis, and sintering processes. These methods aim to control the crystalline structure, particle size, and properties of zirconia for different applications.- Zirconia synthesis and processing methods: Various methods for synthesizing and processing zirconia are described, including techniques for controlling particle size, crystalline structure, and purity. These methods aim to produce zirconia with specific properties suitable for different applications in industries such as ceramics, electronics, and catalysis.
- Zirconia-based dental materials: Zirconia is widely used in dental applications due to its biocompatibility, strength, and aesthetic properties. Innovations in this field include improved formulations for dental prosthetics, crowns, and implants, as well as novel manufacturing techniques to enhance the material's performance and durability in oral environments.
- Zirconia in fuel cell technology: Zirconia plays a crucial role in solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) as an electrolyte material. Research focuses on improving the ionic conductivity, stability, and performance of zirconia-based electrolytes at various operating temperatures, aiming to enhance overall fuel cell efficiency and longevity.
- Zirconia coatings and thin films: Advancements in zirconia coating technologies are explored, including methods for depositing thin films on various substrates. These coatings offer improved wear resistance, thermal insulation, and corrosion protection in applications ranging from cutting tools to aerospace components.
- Zirconia-based composites and nanocomposites: Development of zirconia-based composite materials, including nanocomposites, aims to combine the beneficial properties of zirconia with other materials. These composites offer enhanced mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties, finding applications in advanced ceramics, sensors, and structural materials.
02 Zirconia-based dental materials
Development of zirconia-based materials for dental applications, such as crowns, bridges, and implants. These materials offer high strength, biocompatibility, and aesthetic properties suitable for dental restorations.Expand Specific Solutions03 Zirconia in catalysis and fuel cells
Utilization of zirconia as a catalyst support or component in various catalytic processes and as an electrolyte material in solid oxide fuel cells. Zirconia's stability and ionic conductivity make it valuable for these applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Zirconia coatings and thin films
Methods for depositing zirconia coatings and thin films on various substrates for applications such as thermal barrier coatings, optical coatings, and protective layers. These coatings enhance the durability and performance of materials in harsh environments.Expand Specific Solutions05 Zirconia composites and nanostructures
Development of zirconia-based composites and nanostructured materials with enhanced mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties. These materials combine zirconia with other components to create advanced materials for various industrial and technological applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Industry Leaders
The zirconia market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand across various industries. The market size is expanding, with projections indicating significant growth potential in the coming years. Technologically, zirconia applications are maturing, with companies like 3M Innovative Properties Co., Tosoh Corp., and Kyocera Corp. leading innovation. These firms, along with others like Daiichi Kigenso Kagaku Kogyo Co., Ltd. and Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd., are advancing zirconia's properties and applications. The competitive landscape is diverse, featuring both established players and emerging companies, particularly from China and Japan. This dynamic environment suggests opportunities for market expansion and technological breakthroughs in zirconia's applications across dental, ceramic, and advanced materials sectors.
Tosoh Corp.
Daiichi Kigenso Kagaku Kogyo Co., Ltd.
Key Innovations
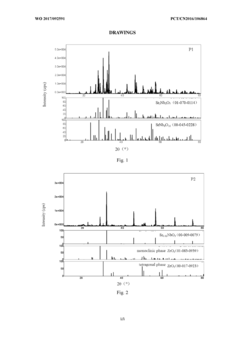
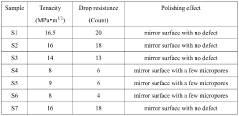
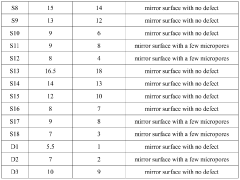
- Introduction of cubic SrxNbO3 stable phase dispersed within the zirconia matrix to enhance drop resistance performance.
- Novel preparation method involving mixing of zirconia, SrCO3, and Nb2O5 powders to create a composite ceramic material.
- Application of the composite ceramic material for manufacturing appearance parts with improved tenacity and drop resistance.
- A method involving wet mixing of silicon-containing zirconia powder with sodium carbonate and tetraethoxysilane, followed by calcination at reduced temperatures (900-1200°C) and subsequent sintering at 1415-1450°C to produce a silicon-containing zirconia calcined and sintered body with increased compactness and structural strength.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of zirconia production and utilization is a critical consideration in capitalizing on its market potential. Zirconia mining and processing can have significant effects on local ecosystems, including soil erosion, water pollution, and habitat disruption. However, compared to some other materials, zirconia extraction generally has a lower environmental footprint due to its relatively abundant nature and the efficiency of modern mining techniques.
In the manufacturing process, zirconia production requires high temperatures, which can lead to substantial energy consumption and associated greenhouse gas emissions. However, ongoing research and technological advancements are focusing on improving energy efficiency in zirconia production, potentially reducing its carbon footprint. Additionally, the durability and longevity of zirconia-based products contribute to their overall sustainability, as they often require less frequent replacement than alternative materials.
Zirconia's applications in various industries also present opportunities for environmental benefits. In the automotive sector, zirconia-based sensors and components can improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. In the energy industry, zirconia's use in solid oxide fuel cells and other clean energy technologies supports the transition to more sustainable power generation methods.
The recyclability of zirconia is an area of growing interest. While not as easily recyclable as some metals, research is ongoing to develop more effective recycling processes for zirconia-containing products. This could significantly enhance the material's lifecycle sustainability and reduce the need for new raw material extraction.
In the medical and dental fields, zirconia's biocompatibility and durability contribute to reduced waste from frequent replacements of medical devices and implants. However, the disposal of zirconia-based medical products requires careful management to prevent potential environmental contamination.
As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, companies looking to capitalize on zirconia's market potential must prioritize sustainable practices throughout the supply chain. This includes implementing responsible mining practices, optimizing manufacturing processes for energy efficiency, and investing in research for improved recycling and end-of-life management of zirconia products.
By addressing these environmental considerations proactively, businesses can not only mitigate potential risks but also create new market opportunities. Eco-friendly zirconia products and production methods could become significant differentiators in an increasingly environmentally conscious market, potentially opening up new avenues for growth and customer engagement.
Global Trade Dynamics
The global trade dynamics of zirconia have been significantly influenced by the material's unique properties and diverse applications across various industries. As a key component in advanced ceramics, zirconia has witnessed a steady increase in international trade flows over the past decade. The primary drivers of this growth include the expanding dental and medical sectors, the rising demand for high-performance materials in industrial applications, and the growing aerospace and automotive industries.
Major exporting countries for zirconia and zirconia-based products include China, Japan, Germany, and the United States, with emerging players like India and South Korea gaining market share. These nations have invested heavily in research and development, as well as manufacturing capabilities, to meet the global demand for high-quality zirconia materials.
The import landscape is equally diverse, with developed economies such as the United States and European Union countries being significant consumers of zirconia products. However, rapidly industrializing nations in Asia and South America are also becoming important markets, driven by their growing manufacturing sectors and increasing technological sophistication.
Trade policies and regulations play a crucial role in shaping the global zirconia market. Tariffs, non-tariff barriers, and trade agreements have a substantial impact on the flow of zirconia and related products across borders. For instance, recent trade tensions between major economies have led to shifts in supply chains and pricing structures, creating both challenges and opportunities for market participants.
The COVID-19 pandemic has introduced new dynamics to the global zirconia trade. While it initially disrupted supply chains and caused a temporary slowdown in demand, the subsequent economic recovery has led to a surge in orders, particularly in the medical and dental sectors. This has highlighted the importance of diversified supply chains and the need for localized production capabilities in key markets.
Looking ahead, the global trade dynamics for zirconia are expected to be shaped by several factors. These include the ongoing push for sustainable and environmentally friendly materials, the increasing adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies such as 3D printing, and the growing demand for high-performance materials in emerging applications like solid oxide fuel cells and sensors. As these trends evolve, companies looking to capitalize on zirconia's market potential must stay attuned to the shifting global trade landscape and position themselves strategically within international supply chains.