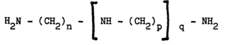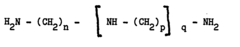How to Design Insulation for Neodymium Magnets in High-Voltage Circuits
SEP 15, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Neodymium Magnet Insulation Background and Objectives
Neodymium magnets have revolutionized numerous industries since their commercial introduction in the 1980s, offering unprecedented magnetic strength in compact form factors. These rare-earth magnets, primarily composed of neodymium, iron, and boron (NdFeB), provide magnetic field strengths up to ten times greater than traditional ferrite magnets, making them invaluable in applications requiring powerful magnetic fields within limited spaces.
The evolution of neodymium magnet technology has been marked by continuous improvements in magnetic properties, temperature stability, and corrosion resistance. Initially developed by Sumitomo Special Metals and General Motors, these magnets have seen their maximum energy product (BHmax) increase from approximately 30 MGOe to over 60 MGOe in specialized grades, representing significant technological advancement in magnetic materials science.
In high-voltage circuit applications, neodymium magnets have become increasingly prevalent in transformers, motors, generators, and sensing devices. However, their electrical conductivity presents unique challenges when integrated into systems operating at elevated voltages. The combination of conductive properties and strong magnetic fields can lead to eddy current formation, potential electrical arcing, and compromised system integrity without proper insulation.
The primary objective of neodymium magnet insulation research is to develop reliable, durable insulation systems that maintain electrical isolation while preserving magnetic performance across diverse operating conditions. This includes withstanding voltage potentials exceeding 1000V, operating temperatures ranging from -40°C to +180°C, and maintaining integrity despite mechanical stresses from magnetic forces and thermal cycling.
Current insulation approaches vary widely, including conformal coatings, encapsulation methods, specialized tapes, and composite materials. Each solution presents distinct advantages and limitations regarding dielectric strength, thermal conductivity, mechanical resilience, and manufacturing complexity. The technological trajectory indicates movement toward multi-functional insulation systems that simultaneously address electrical isolation, thermal management, and mechanical protection.
Emerging trends in this field include the development of nano-engineered insulation materials with enhanced dielectric properties, advanced polymer composites offering superior thermal stability, and automated precision application techniques for consistent insulation layer formation. These innovations aim to extend the operational envelope of neodymium magnets in high-voltage environments while minimizing performance compromises.
The strategic importance of this technology extends beyond immediate applications, as efficient high-voltage magnetic systems are critical components in renewable energy infrastructure, electric transportation, advanced manufacturing, and next-generation power distribution networks. Mastering neodymium magnet insulation represents a key enabling technology for numerous high-growth industries aligned with global electrification and energy efficiency initiatives.
The evolution of neodymium magnet technology has been marked by continuous improvements in magnetic properties, temperature stability, and corrosion resistance. Initially developed by Sumitomo Special Metals and General Motors, these magnets have seen their maximum energy product (BHmax) increase from approximately 30 MGOe to over 60 MGOe in specialized grades, representing significant technological advancement in magnetic materials science.
In high-voltage circuit applications, neodymium magnets have become increasingly prevalent in transformers, motors, generators, and sensing devices. However, their electrical conductivity presents unique challenges when integrated into systems operating at elevated voltages. The combination of conductive properties and strong magnetic fields can lead to eddy current formation, potential electrical arcing, and compromised system integrity without proper insulation.
The primary objective of neodymium magnet insulation research is to develop reliable, durable insulation systems that maintain electrical isolation while preserving magnetic performance across diverse operating conditions. This includes withstanding voltage potentials exceeding 1000V, operating temperatures ranging from -40°C to +180°C, and maintaining integrity despite mechanical stresses from magnetic forces and thermal cycling.
Current insulation approaches vary widely, including conformal coatings, encapsulation methods, specialized tapes, and composite materials. Each solution presents distinct advantages and limitations regarding dielectric strength, thermal conductivity, mechanical resilience, and manufacturing complexity. The technological trajectory indicates movement toward multi-functional insulation systems that simultaneously address electrical isolation, thermal management, and mechanical protection.
Emerging trends in this field include the development of nano-engineered insulation materials with enhanced dielectric properties, advanced polymer composites offering superior thermal stability, and automated precision application techniques for consistent insulation layer formation. These innovations aim to extend the operational envelope of neodymium magnets in high-voltage environments while minimizing performance compromises.
The strategic importance of this technology extends beyond immediate applications, as efficient high-voltage magnetic systems are critical components in renewable energy infrastructure, electric transportation, advanced manufacturing, and next-generation power distribution networks. Mastering neodymium magnet insulation represents a key enabling technology for numerous high-growth industries aligned with global electrification and energy efficiency initiatives.
Market Demand Analysis for Insulated Magnets in HV Applications
The global market for insulated neodymium magnets in high-voltage applications has experienced significant growth over the past decade, driven primarily by the rapid expansion of electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy systems, and advanced power electronics. The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for this specialized segment reached approximately 8.7% between 2018 and 2023, outpacing the broader permanent magnet market.
Electric vehicle manufacturers represent the largest demand sector, accounting for nearly 42% of the total market share. This dominance stems from the critical role that properly insulated neodymium magnets play in EV powertrains, where they must operate reliably under high voltage conditions while maintaining magnetic performance. Industry forecasts suggest that as EV production continues to accelerate globally, demand for specialized insulated magnets will grow by 12-15% annually through 2028.
The renewable energy sector, particularly wind turbine generators, constitutes the second-largest market segment at 27%. These applications require magnets capable of withstanding both high voltage and challenging environmental conditions. As countries worldwide increase renewable energy capacity to meet climate goals, this segment is projected to expand substantially, with offshore wind installations driving particularly strong demand for advanced insulation solutions.
Industrial motor applications represent another significant market at 18%, with particular growth in high-efficiency motors for manufacturing and HVAC systems. These applications increasingly require magnets with superior insulation properties to prevent eddy current losses and ensure operational safety in high-voltage environments.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates production and consumption, with China accounting for 65% of global manufacturing capacity. However, recent supply chain concerns have accelerated efforts to develop alternative production hubs in North America and Europe, where demand is growing at 10-11% annually.
Customer requirements are increasingly stringent, with specifications demanding insulation materials that can withstand operating temperatures above 180°C while maintaining dielectric strength exceeding 20 kV/mm. Additionally, there is growing demand for insulation solutions that can resist thermal cycling, vibration, and chemical exposure without degradation over 15+ year service lifespans.
The price premium for properly insulated neodymium magnets versus standard variants ranges from 15-30% depending on application requirements, with customers demonstrating willingness to pay higher premiums for solutions offering verified reliability data and performance guarantees. This pricing dynamic has created attractive profit margins for manufacturers with proprietary insulation technologies and robust testing capabilities.
Electric vehicle manufacturers represent the largest demand sector, accounting for nearly 42% of the total market share. This dominance stems from the critical role that properly insulated neodymium magnets play in EV powertrains, where they must operate reliably under high voltage conditions while maintaining magnetic performance. Industry forecasts suggest that as EV production continues to accelerate globally, demand for specialized insulated magnets will grow by 12-15% annually through 2028.
The renewable energy sector, particularly wind turbine generators, constitutes the second-largest market segment at 27%. These applications require magnets capable of withstanding both high voltage and challenging environmental conditions. As countries worldwide increase renewable energy capacity to meet climate goals, this segment is projected to expand substantially, with offshore wind installations driving particularly strong demand for advanced insulation solutions.
Industrial motor applications represent another significant market at 18%, with particular growth in high-efficiency motors for manufacturing and HVAC systems. These applications increasingly require magnets with superior insulation properties to prevent eddy current losses and ensure operational safety in high-voltage environments.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates production and consumption, with China accounting for 65% of global manufacturing capacity. However, recent supply chain concerns have accelerated efforts to develop alternative production hubs in North America and Europe, where demand is growing at 10-11% annually.
Customer requirements are increasingly stringent, with specifications demanding insulation materials that can withstand operating temperatures above 180°C while maintaining dielectric strength exceeding 20 kV/mm. Additionally, there is growing demand for insulation solutions that can resist thermal cycling, vibration, and chemical exposure without degradation over 15+ year service lifespans.
The price premium for properly insulated neodymium magnets versus standard variants ranges from 15-30% depending on application requirements, with customers demonstrating willingness to pay higher premiums for solutions offering verified reliability data and performance guarantees. This pricing dynamic has created attractive profit margins for manufacturers with proprietary insulation technologies and robust testing capabilities.
Technical Challenges in Magnet Insulation for High-Voltage Environments
The insulation of neodymium magnets in high-voltage circuits presents several significant technical challenges that must be addressed to ensure system reliability and safety. The primary difficulty stems from the dual requirements of electrical isolation and thermal management, as neodymium magnets are both electrically conductive and sensitive to temperature fluctuations.
Electrical breakdown represents the most critical challenge, with voltage gradients in high-voltage environments potentially exceeding the dielectric strength of conventional insulation materials. This is particularly problematic at sharp edges and corners of magnets where electric field concentration occurs, creating localized stress points that can lead to premature insulation failure.
Thermal management poses another substantial hurdle. Neodymium magnets have relatively low Curie temperatures (310-400°C) and can experience irreversible demagnetization at even lower temperatures (80-200°C depending on grade). Insulation materials must therefore balance excellent electrical isolation properties with sufficient thermal conductivity to prevent heat buildup that could compromise magnet performance.
Material compatibility issues further complicate insulation design. Many high-performance insulating materials may react chemically with the neodymium-iron-boron alloy or its protective coatings, particularly in the presence of moisture or under thermal cycling conditions. This can lead to degradation of both the insulation and the magnet itself over time.
Mechanical stress management presents additional challenges, as differential thermal expansion between magnets and insulation materials can create mechanical stresses during operation. These stresses may cause cracking in brittle insulation materials or delamination at interfaces, compromising the insulation integrity.
Manufacturing and assembly considerations also impose constraints on insulation design. The strong magnetic forces of neodymium magnets complicate handling during the insulation application process, while achieving uniform insulation thickness around complex magnet geometries requires specialized techniques.
Environmental factors introduce further complications, with humidity, chemical exposure, and radiation potentially degrading insulation performance over time. High-voltage applications often operate in harsh environments where these factors can accelerate aging and deterioration of insulation systems.
Corona discharge and partial discharge phenomena represent subtle but persistent threats to insulation longevity. These localized electrical breakdowns occur at voltages below the insulation's rated breakdown strength but can cause cumulative damage through ion bombardment, ozone generation, and localized heating.
Electrical breakdown represents the most critical challenge, with voltage gradients in high-voltage environments potentially exceeding the dielectric strength of conventional insulation materials. This is particularly problematic at sharp edges and corners of magnets where electric field concentration occurs, creating localized stress points that can lead to premature insulation failure.
Thermal management poses another substantial hurdle. Neodymium magnets have relatively low Curie temperatures (310-400°C) and can experience irreversible demagnetization at even lower temperatures (80-200°C depending on grade). Insulation materials must therefore balance excellent electrical isolation properties with sufficient thermal conductivity to prevent heat buildup that could compromise magnet performance.
Material compatibility issues further complicate insulation design. Many high-performance insulating materials may react chemically with the neodymium-iron-boron alloy or its protective coatings, particularly in the presence of moisture or under thermal cycling conditions. This can lead to degradation of both the insulation and the magnet itself over time.
Mechanical stress management presents additional challenges, as differential thermal expansion between magnets and insulation materials can create mechanical stresses during operation. These stresses may cause cracking in brittle insulation materials or delamination at interfaces, compromising the insulation integrity.
Manufacturing and assembly considerations also impose constraints on insulation design. The strong magnetic forces of neodymium magnets complicate handling during the insulation application process, while achieving uniform insulation thickness around complex magnet geometries requires specialized techniques.
Environmental factors introduce further complications, with humidity, chemical exposure, and radiation potentially degrading insulation performance over time. High-voltage applications often operate in harsh environments where these factors can accelerate aging and deterioration of insulation systems.
Corona discharge and partial discharge phenomena represent subtle but persistent threats to insulation longevity. These localized electrical breakdowns occur at voltages below the insulation's rated breakdown strength but can cause cumulative damage through ion bombardment, ozone generation, and localized heating.
Current Insulation Solutions for Neodymium Magnets
01 Thermal insulation materials for neodymium magnets
Various thermal insulation materials can be used to protect neodymium magnets from temperature fluctuations that could affect their magnetic properties. These materials include ceramic coatings, polymer composites, and specialized insulating foams that provide effective thermal barriers while maintaining the magnetic performance. The insulation helps prevent demagnetization that can occur when neodymium magnets are exposed to high temperatures.- Thermal insulation materials for neodymium magnets: Various thermal insulation materials can be used to protect neodymium magnets from temperature fluctuations that could degrade their magnetic properties. These materials include ceramic coatings, polymer-based insulators, and composite materials that provide effective thermal barriers while maintaining the magnetic functionality. Proper thermal insulation helps prevent demagnetization at high temperatures and extends the operational life of the magnets in applications where temperature control is critical.
- Electrical insulation coatings for neodymium magnets: Specialized electrical insulation coatings can be applied to neodymium magnets to prevent electrical conductivity issues while preserving magnetic properties. These coatings include epoxy resins, parylene films, and specialized varnishes that create a dielectric barrier around the magnet. Such insulation is particularly important in electric motors, generators, and other applications where the magnets are exposed to electrical fields or where eddy current losses need to be minimized.
- Corrosion-resistant insulation for neodymium magnets: Corrosion-resistant insulation techniques protect neodymium magnets from environmental degradation, particularly in humid or corrosive environments. These include nickel-copper-nickel triple layer coatings, epoxy encapsulation, and specialized polymer coatings that seal the magnet surface from moisture and corrosive agents. Such protective insulation significantly extends the lifespan of neodymium magnets in outdoor applications, marine environments, or industrial settings with corrosive atmospheres.
- Mechanical protection and insulation systems: Mechanical protection systems provide both insulation and physical protection for neodymium magnets in high-stress applications. These include reinforced housings, shock-absorbing mounting systems, and composite enclosures that protect against impacts, vibrations, and mechanical stresses. Such systems are particularly important in automotive applications, industrial machinery, and consumer electronics where magnets may be subjected to physical shocks or mechanical wear.
- Advanced composite insulation materials: Advanced composite materials combine multiple insulation properties for neodymium magnets, offering thermal, electrical, and mechanical protection simultaneously. These include nano-enhanced polymers, ceramic-polymer hybrids, and multi-layer insulation systems that provide comprehensive protection while minimizing space requirements. Such advanced materials are particularly valuable in aerospace applications, medical devices, and other high-performance settings where multiple forms of protection are required within strict space and weight constraints.
02 Electrical insulation coatings for neodymium magnets
Specialized electrical insulation coatings can be applied to neodymium magnets to prevent electrical conductivity issues in applications where the magnets are used in electrical systems. These coatings include epoxy resins, specialized polymers, and oxide layers that provide electrical isolation while maintaining the magnetic strength. The electrical insulation is particularly important in motor and generator applications to prevent eddy current losses.Expand Specific Solutions03 Corrosion-resistant insulation for neodymium magnets
Corrosion-resistant insulation methods protect neodymium magnets from environmental factors that can cause degradation. These include specialized coatings such as nickel-copper-nickel layers, epoxy sealants, and passivation treatments that create a protective barrier against moisture, oxygen, and corrosive chemicals. These protective layers extend the lifespan of the magnets while maintaining their magnetic properties in harsh environments.Expand Specific Solutions04 Mechanical protection and insulation systems
Mechanical protection systems for neodymium magnets include encapsulation methods, protective housings, and shock-absorbing materials that shield the brittle magnets from physical damage. These systems often incorporate multiple layers of protection including rubber compounds, specialized polymers, and metal casings that provide both insulation and structural support. The mechanical protection is crucial for applications where magnets may be subjected to impacts or vibrations.Expand Specific Solutions05 Composite insulation materials for specialized applications
Advanced composite materials combine multiple insulation properties for specialized neodymium magnet applications. These composites may incorporate nanomaterials, ceramic-polymer hybrids, and multi-functional coatings that simultaneously provide thermal, electrical, and corrosion protection. These sophisticated insulation systems are designed for extreme environments such as aerospace, medical devices, or high-performance motors where magnets must maintain stability under challenging conditions.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Suppliers in Magnetic Insulation Industry
The insulation design for neodymium magnets in high-voltage circuits is currently in a growth phase, with the market expanding due to increasing applications in renewable energy, electric vehicles, and advanced electronics. The global market is estimated to reach several billion dollars by 2025, driven by demand for efficient power systems. Technologically, the field is moderately mature but evolving rapidly, with companies like Siemens AG, TDK Corp., and Murata Manufacturing leading innovation through advanced materials and designs. Sumitomo Electric and Texas Instruments are developing specialized insulation solutions, while research institutions like MIT and CNRS contribute fundamental breakthroughs. Emerging players like Yantai Zhenghai Magnetic Material and Commonwealth Fusion Systems are introducing novel approaches to high-voltage magnetic insulation challenges.
Murata Manufacturing Co. Ltd.
Technical Solution: Murata has developed specialized insulation technology for neodymium magnets used in high-frequency power conversion circuits. Their approach utilizes proprietary ceramic-based coatings with nanoscale engineering to achieve exceptional dielectric strength (>20kV/mm) while maintaining thermal conductivity above 1.5 W/m·K. The company's insulation system incorporates gradient-structured materials that distribute electric field stress more evenly across the insulation layer, reducing the risk of partial discharge and electrical breakdown. Murata's process includes precision plasma-assisted deposition techniques that ensure uniform coverage on complex magnet geometries with thickness variations less than 3μm. Their insulation design is particularly effective in applications with rapid voltage transients, providing protection against dV/dt rates exceeding 10kV/μs while maintaining magnetic performance.
Strengths: Excellent thermal conductivity allows efficient heat dissipation from the magnet while maintaining electrical isolation. Superior performance under high dV/dt conditions makes it ideal for power electronics applications. Weaknesses: The specialized ceramic materials and deposition processes result in higher manufacturing costs compared to polymer-based alternatives.
Siemens AG
Technical Solution: Siemens has developed advanced multi-layer insulation systems specifically designed for neodymium magnets in high-voltage applications. Their approach combines nano-composite materials with specialized epoxy resins that maintain dielectric strength at temperatures up to 180°C. The company's patented vacuum pressure impregnation (VPI) technique creates void-free insulation layers that prevent partial discharge and electrical breakdown in high-voltage environments. Siemens' solution incorporates fluoropolymer coatings with ceramic additives that enhance thermal conductivity while maintaining excellent electrical isolation properties. Their insulation systems are designed to withstand voltage transients up to 20kV while protecting the neodymium magnets from corrosion and demagnetization effects that can occur in high-voltage circuits.
Strengths: Superior thermal management capabilities allow operation in extreme temperature environments while maintaining insulation integrity. The multi-layer approach provides redundancy against insulation failure. Weaknesses: The complex manufacturing process increases production costs and time compared to simpler insulation methods, making it less suitable for low-cost applications.
Key Patents and Research in High-Voltage Magnet Insulation
High-voltage insulation power supply circuit, high-voltage insulation rod, and high-voltage insulation power supply method
PatentWO2011109969A1
Innovation
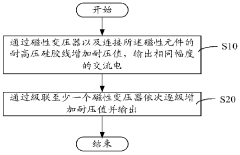
- Using high-voltage insulated power supply circuits and rods including magnetic transformers and high-voltage resistant silicone wires, the magnetic transformer gradually increases the withstand voltage value, outputs alternating current of the same amplitude, replaces high-frequency transformers, and achieves high magnetic permeability and low-loss power mutual inductance.
Insulator for high and medium voltage windings and process for manufacturing such an insulator
PatentInactiveEP0031555A1
Innovation
- A solid condensation product with primary amine endings is used, which is soluble in epoxy impregnating resin at gelation temperature, accelerating the epoxy-acid anhydride reaction and minimizing resin loss, while bonding mica-based tape to a fabric or felt support with a minimal solvent-free adhesive quantity, ensuring good cohesion without forming a continuous film.
Thermal Management Considerations for Insulated Magnets
Thermal management represents a critical aspect of insulation design for neodymium magnets in high-voltage circuits. These powerful permanent magnets exhibit temperature-dependent performance characteristics that must be carefully considered when designing insulation systems. The maximum operating temperature for neodymium magnets typically ranges between 80°C and 200°C, depending on their specific grade and composition, with higher-grade magnets generally having lower maximum operating temperatures.
Insulation materials themselves contribute to thermal challenges by potentially creating heat traps around the magnets. Materials with poor thermal conductivity may protect against electrical breakdown but can simultaneously prevent efficient heat dissipation, leading to accelerated demagnetization. This trade-off necessitates careful material selection that balances electrical insulation properties with thermal conductivity characteristics.
Heat generation in high-voltage circuits occurs through multiple mechanisms, including resistive losses in conductors, eddy current losses in magnetic materials, and hysteresis losses. When neodymium magnets are exposed to these heat sources without adequate thermal management, they risk irreversible demagnetization, particularly if temperatures exceed their maximum operating threshold.
Effective thermal management strategies include incorporating heat sinks or thermal pathways that direct heat away from the magnets while maintaining electrical isolation. Aluminum nitride and beryllium oxide ceramic insulators offer excellent thermal conductivity combined with electrical insulation properties, though cost and manufacturing complexity must be considered. Thermally conductive epoxies and potting compounds can also provide dual functionality as both insulators and heat transfer media.
Active cooling solutions may be necessary for high-power applications. These can include forced air cooling, liquid cooling systems, or thermoelectric cooling elements integrated into the insulation design. The selection depends on the specific application requirements, space constraints, and operational environment.
Thermal expansion differentials between magnets, insulation materials, and surrounding components must be addressed to prevent mechanical stress during thermal cycling. This is particularly important in applications experiencing wide temperature variations, where differential expansion can compromise insulation integrity or create mechanical failures over time.
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and finite element analysis (FEA) have become essential tools for optimizing thermal management in insulated magnet designs. These simulation techniques allow engineers to predict temperature distributions, identify potential hotspots, and evaluate various cooling strategies before physical prototyping, significantly reducing development time and costs.
Insulation materials themselves contribute to thermal challenges by potentially creating heat traps around the magnets. Materials with poor thermal conductivity may protect against electrical breakdown but can simultaneously prevent efficient heat dissipation, leading to accelerated demagnetization. This trade-off necessitates careful material selection that balances electrical insulation properties with thermal conductivity characteristics.
Heat generation in high-voltage circuits occurs through multiple mechanisms, including resistive losses in conductors, eddy current losses in magnetic materials, and hysteresis losses. When neodymium magnets are exposed to these heat sources without adequate thermal management, they risk irreversible demagnetization, particularly if temperatures exceed their maximum operating threshold.
Effective thermal management strategies include incorporating heat sinks or thermal pathways that direct heat away from the magnets while maintaining electrical isolation. Aluminum nitride and beryllium oxide ceramic insulators offer excellent thermal conductivity combined with electrical insulation properties, though cost and manufacturing complexity must be considered. Thermally conductive epoxies and potting compounds can also provide dual functionality as both insulators and heat transfer media.
Active cooling solutions may be necessary for high-power applications. These can include forced air cooling, liquid cooling systems, or thermoelectric cooling elements integrated into the insulation design. The selection depends on the specific application requirements, space constraints, and operational environment.
Thermal expansion differentials between magnets, insulation materials, and surrounding components must be addressed to prevent mechanical stress during thermal cycling. This is particularly important in applications experiencing wide temperature variations, where differential expansion can compromise insulation integrity or create mechanical failures over time.
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and finite element analysis (FEA) have become essential tools for optimizing thermal management in insulated magnet designs. These simulation techniques allow engineers to predict temperature distributions, identify potential hotspots, and evaluate various cooling strategies before physical prototyping, significantly reducing development time and costs.
Safety Standards and Compliance for High-Voltage Magnetic Components
Compliance with safety standards is paramount when designing insulation for neodymium magnets in high-voltage circuits. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) provides comprehensive guidelines through standards such as IEC 60664 for insulation coordination and IEC 61010 for measurement equipment safety. These standards establish minimum clearance and creepage distances based on operating voltage, pollution degree, and altitude considerations.
The UL 1446 standard specifically addresses electrical insulation systems in magnetic components, defining temperature ratings and aging test protocols. For applications exceeding 1000V, adherence to IEC 60071 becomes essential, as it outlines insulation coordination principles for high-voltage electrical equipment.
Regional variations in safety requirements must be considered during design phases. European markets follow EN 60950 and the Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU, while North American applications must comply with UL 840 for insulation coordination and NFPA 70E for electrical safety in workplaces.
Testing and certification procedures represent a critical compliance pathway. Dielectric strength testing (hipot testing) verifies insulation integrity under voltage stress conditions, typically requiring withstand capabilities of 2-3 times the rated operating voltage plus 1000V for one minute without breakdown. Partial discharge testing becomes mandatory for components operating above 3kV to detect insulation defects before catastrophic failure.
Thermal classification compliance according to IEC 60085 ensures insulation materials maintain their properties throughout the component's operational life. Class H (180°C) or Class N (200°C) insulation systems are typically required for neodymium magnet applications due to their temperature sensitivity and the heat generated in high-voltage environments.
Environmental considerations introduce additional compliance requirements. RoHS and REACH regulations restrict hazardous substances in insulation materials, while IP ratings (IEC 60529) specify protection levels against environmental factors. For applications in explosive atmospheres, ATEX Directive 2014/34/EU compliance becomes necessary, requiring specialized insulation designs that prevent spark generation.
Documentation requirements include detailed insulation coordination plans, material safety data sheets, test reports, and risk assessments. Maintaining comprehensive compliance documentation facilitates certification processes and provides evidence of due diligence in addressing safety concerns, which is particularly important for liability protection in high-voltage applications involving powerful neodymium magnets.
The UL 1446 standard specifically addresses electrical insulation systems in magnetic components, defining temperature ratings and aging test protocols. For applications exceeding 1000V, adherence to IEC 60071 becomes essential, as it outlines insulation coordination principles for high-voltage electrical equipment.
Regional variations in safety requirements must be considered during design phases. European markets follow EN 60950 and the Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU, while North American applications must comply with UL 840 for insulation coordination and NFPA 70E for electrical safety in workplaces.
Testing and certification procedures represent a critical compliance pathway. Dielectric strength testing (hipot testing) verifies insulation integrity under voltage stress conditions, typically requiring withstand capabilities of 2-3 times the rated operating voltage plus 1000V for one minute without breakdown. Partial discharge testing becomes mandatory for components operating above 3kV to detect insulation defects before catastrophic failure.
Thermal classification compliance according to IEC 60085 ensures insulation materials maintain their properties throughout the component's operational life. Class H (180°C) or Class N (200°C) insulation systems are typically required for neodymium magnet applications due to their temperature sensitivity and the heat generated in high-voltage environments.
Environmental considerations introduce additional compliance requirements. RoHS and REACH regulations restrict hazardous substances in insulation materials, while IP ratings (IEC 60529) specify protection levels against environmental factors. For applications in explosive atmospheres, ATEX Directive 2014/34/EU compliance becomes necessary, requiring specialized insulation designs that prevent spark generation.
Documentation requirements include detailed insulation coordination plans, material safety data sheets, test reports, and risk assessments. Maintaining comprehensive compliance documentation facilitates certification processes and provides evidence of due diligence in addressing safety concerns, which is particularly important for liability protection in high-voltage applications involving powerful neodymium magnets.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!