How to Enhance Lithium Bromide Stability with Additives
AUG 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LiBr Stability Enhancement Background and Objectives
Lithium bromide (LiBr) has emerged as a critical component in various industrial applications, particularly in absorption refrigeration systems, desiccant air conditioning, and more recently in energy storage technologies. The historical development of LiBr applications dates back to the mid-20th century, with significant advancements occurring in the 1970s and 1980s as energy efficiency concerns drove innovation in cooling technologies. Over the past decade, the importance of LiBr has expanded beyond traditional applications into emerging fields such as thermal energy storage and certain battery technologies.
Despite its utility, LiBr systems face persistent challenges related to stability. The compound is highly hygroscopic and corrosive, leading to degradation of system components, reduced efficiency, and increased maintenance requirements. Corrosion issues particularly affect metal components in absorption chillers and heat pumps, while crystallization and precipitation problems can cause system blockages and operational failures. These stability issues have historically limited the widespread adoption of LiBr-based technologies despite their theoretical advantages.
The technical evolution trajectory shows increasing focus on additive technologies to enhance LiBr stability. Early approaches relied on simple inhibitors like lithium hydroxide, but research has progressively moved toward more sophisticated additive packages combining multiple functional components. Recent developments have explored nanomaterials, organic-inorganic hybrid additives, and biomimetic approaches inspired by natural anti-corrosion mechanisms.
The primary technical objectives of enhancing LiBr stability with additives include: reducing corrosion rates by at least 80% compared to untreated solutions; preventing crystallization at concentration levels up to 65% by weight; extending system operational lifetime by 3-5 times current standards; maintaining performance efficiency under fluctuating temperature and humidity conditions; and ensuring additive effectiveness without introducing environmental or safety concerns.
Market drivers for this technology include growing demand for energy-efficient cooling systems in commercial and residential buildings, increasing adoption of thermal energy storage solutions for renewable energy integration, and stringent regulations on traditional refrigerants with high global warming potential. The International Energy Agency estimates that cooling demand could triple by 2050, creating significant market potential for improved absorption cooling technologies.
The successful development of effective stability-enhancing additives for LiBr would enable more compact system designs, lower maintenance requirements, expanded operating parameters, and ultimately broader market adoption of LiBr-based technologies. This would contribute to global energy efficiency goals while opening new application possibilities in sectors currently limited by LiBr stability concerns.
Despite its utility, LiBr systems face persistent challenges related to stability. The compound is highly hygroscopic and corrosive, leading to degradation of system components, reduced efficiency, and increased maintenance requirements. Corrosion issues particularly affect metal components in absorption chillers and heat pumps, while crystallization and precipitation problems can cause system blockages and operational failures. These stability issues have historically limited the widespread adoption of LiBr-based technologies despite their theoretical advantages.
The technical evolution trajectory shows increasing focus on additive technologies to enhance LiBr stability. Early approaches relied on simple inhibitors like lithium hydroxide, but research has progressively moved toward more sophisticated additive packages combining multiple functional components. Recent developments have explored nanomaterials, organic-inorganic hybrid additives, and biomimetic approaches inspired by natural anti-corrosion mechanisms.
The primary technical objectives of enhancing LiBr stability with additives include: reducing corrosion rates by at least 80% compared to untreated solutions; preventing crystallization at concentration levels up to 65% by weight; extending system operational lifetime by 3-5 times current standards; maintaining performance efficiency under fluctuating temperature and humidity conditions; and ensuring additive effectiveness without introducing environmental or safety concerns.
Market drivers for this technology include growing demand for energy-efficient cooling systems in commercial and residential buildings, increasing adoption of thermal energy storage solutions for renewable energy integration, and stringent regulations on traditional refrigerants with high global warming potential. The International Energy Agency estimates that cooling demand could triple by 2050, creating significant market potential for improved absorption cooling technologies.
The successful development of effective stability-enhancing additives for LiBr would enable more compact system designs, lower maintenance requirements, expanded operating parameters, and ultimately broader market adoption of LiBr-based technologies. This would contribute to global energy efficiency goals while opening new application possibilities in sectors currently limited by LiBr stability concerns.
Market Analysis for Stabilized LiBr Applications
The global market for stabilized lithium bromide (LiBr) solutions is experiencing significant growth, primarily driven by the expanding absorption refrigeration and air conditioning sectors. The market value for LiBr-based absorption systems reached approximately $1.2 billion in 2022, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.7% through 2028. This growth trajectory is supported by increasing demand for energy-efficient cooling solutions in commercial and industrial applications.
The Asia-Pacific region currently dominates the market, accounting for over 40% of global consumption, with China and Japan leading in both production and utilization. North America and Europe follow as significant markets, particularly in industrial refrigeration applications where the demand for stabilized LiBr solutions has increased by 6.3% annually over the past five years.
Market segmentation reveals that absorption chillers represent the largest application segment, constituting approximately 65% of the total market share. Heat pumps and thermal energy storage systems are emerging as rapidly growing segments, with respective growth rates of 7.2% and 8.5% annually. This diversification indicates expanding market opportunities beyond traditional applications.
From an end-user perspective, the commercial building sector remains the primary consumer, followed by industrial processes and district cooling systems. Healthcare facilities and data centers have emerged as high-potential growth segments, with demand increasing at rates exceeding the market average by 2-3 percentage points.
The market dynamics are increasingly influenced by sustainability regulations and energy efficiency standards. Countries implementing stricter emissions regulations have shown 30-40% higher adoption rates for LiBr-based cooling systems compared to regions with less stringent environmental policies. This regulatory landscape is expected to continue driving market growth for stabilized LiBr solutions.
Price sensitivity analysis indicates that while initial system costs remain a barrier to adoption, the total cost of ownership (TCO) calculations increasingly favor LiBr systems due to their operational efficiency and longevity when properly stabilized. Market research shows that systems utilizing advanced stabilization additives command a premium of 15-20% but deliver 25-30% longer operational lifespans.
Customer surveys reveal that reliability and maintenance requirements rank as the top concerns among potential adopters, highlighting the critical importance of LiBr stability enhancements in market expansion. Systems demonstrating improved corrosion resistance and reduced crystallization issues have achieved market penetration rates 2.5 times higher than conventional systems.
The Asia-Pacific region currently dominates the market, accounting for over 40% of global consumption, with China and Japan leading in both production and utilization. North America and Europe follow as significant markets, particularly in industrial refrigeration applications where the demand for stabilized LiBr solutions has increased by 6.3% annually over the past five years.
Market segmentation reveals that absorption chillers represent the largest application segment, constituting approximately 65% of the total market share. Heat pumps and thermal energy storage systems are emerging as rapidly growing segments, with respective growth rates of 7.2% and 8.5% annually. This diversification indicates expanding market opportunities beyond traditional applications.
From an end-user perspective, the commercial building sector remains the primary consumer, followed by industrial processes and district cooling systems. Healthcare facilities and data centers have emerged as high-potential growth segments, with demand increasing at rates exceeding the market average by 2-3 percentage points.
The market dynamics are increasingly influenced by sustainability regulations and energy efficiency standards. Countries implementing stricter emissions regulations have shown 30-40% higher adoption rates for LiBr-based cooling systems compared to regions with less stringent environmental policies. This regulatory landscape is expected to continue driving market growth for stabilized LiBr solutions.
Price sensitivity analysis indicates that while initial system costs remain a barrier to adoption, the total cost of ownership (TCO) calculations increasingly favor LiBr systems due to their operational efficiency and longevity when properly stabilized. Market research shows that systems utilizing advanced stabilization additives command a premium of 15-20% but deliver 25-30% longer operational lifespans.
Customer surveys reveal that reliability and maintenance requirements rank as the top concerns among potential adopters, highlighting the critical importance of LiBr stability enhancements in market expansion. Systems demonstrating improved corrosion resistance and reduced crystallization issues have achieved market penetration rates 2.5 times higher than conventional systems.
Current Challenges in LiBr Stability Technology
Lithium bromide (LiBr) absorption systems face significant stability challenges that impede their widespread adoption in cooling and refrigeration applications. The primary issue is the corrosive nature of LiBr solutions, which aggressively attack metal components in absorption systems, particularly at elevated temperatures and concentrations. This corrosion not only compromises system integrity but also introduces metal ions that catalyze LiBr decomposition, creating a destructive cycle that progressively degrades system performance.
Oxidation presents another critical challenge, as dissolved oxygen in LiBr solutions accelerates corrosion rates and promotes the formation of bromine, which further exacerbates material degradation. This oxidative process is particularly problematic in systems with air leakage or inadequate sealing, where continuous oxygen exposure maintains the corrosion cycle.
Thermal degradation of LiBr solutions occurs at operating temperatures above 180°C, leading to the formation of hydrogen bromide (HBr) and other corrosive byproducts. These decomposition products not only reduce the effective concentration of the working fluid but also create acidic conditions that accelerate system deterioration.
Crystallization and precipitation issues emerge when LiBr concentration exceeds solubility limits, typically during temperature fluctuations or improper system operation. These solid deposits obstruct flow paths, reduce heat transfer efficiency, and create localized corrosion sites that compromise system integrity.
Current inhibitor technologies demonstrate limited effectiveness across the full range of operating conditions. Traditional chromate-based inhibitors, while effective, face regulatory restrictions due to environmental concerns. Alternative inhibitors such as molybdates and nitrates show promise but often lack stability at higher temperatures or concentrations, creating a significant technology gap in the industry.
The economic impact of these stability issues is substantial, with maintenance costs for LiBr systems typically 15-30% higher than alternative technologies due to corrosion-related component replacement and performance degradation. Additionally, system downtime during maintenance further increases operational costs and reduces reliability.
Environmental considerations also present challenges, as leakage of LiBr solutions can impact soil and water quality, while some current corrosion inhibitors pose their own environmental hazards. This creates a complex balance between system performance, longevity, and environmental responsibility that has yet to be optimally resolved with existing technologies.
Oxidation presents another critical challenge, as dissolved oxygen in LiBr solutions accelerates corrosion rates and promotes the formation of bromine, which further exacerbates material degradation. This oxidative process is particularly problematic in systems with air leakage or inadequate sealing, where continuous oxygen exposure maintains the corrosion cycle.
Thermal degradation of LiBr solutions occurs at operating temperatures above 180°C, leading to the formation of hydrogen bromide (HBr) and other corrosive byproducts. These decomposition products not only reduce the effective concentration of the working fluid but also create acidic conditions that accelerate system deterioration.
Crystallization and precipitation issues emerge when LiBr concentration exceeds solubility limits, typically during temperature fluctuations or improper system operation. These solid deposits obstruct flow paths, reduce heat transfer efficiency, and create localized corrosion sites that compromise system integrity.
Current inhibitor technologies demonstrate limited effectiveness across the full range of operating conditions. Traditional chromate-based inhibitors, while effective, face regulatory restrictions due to environmental concerns. Alternative inhibitors such as molybdates and nitrates show promise but often lack stability at higher temperatures or concentrations, creating a significant technology gap in the industry.
The economic impact of these stability issues is substantial, with maintenance costs for LiBr systems typically 15-30% higher than alternative technologies due to corrosion-related component replacement and performance degradation. Additionally, system downtime during maintenance further increases operational costs and reduces reliability.
Environmental considerations also present challenges, as leakage of LiBr solutions can impact soil and water quality, while some current corrosion inhibitors pose their own environmental hazards. This creates a complex balance between system performance, longevity, and environmental responsibility that has yet to be optimally resolved with existing technologies.
Existing Additive Solutions for LiBr Stability Enhancement
01 Stabilization methods for lithium bromide solutions
Various methods can be employed to stabilize lithium bromide solutions, particularly in absorption refrigeration systems. These methods include adding specific stabilizing agents, controlling pH levels, and implementing corrosion inhibitors. Stabilization is crucial to prevent degradation of lithium bromide and extend the operational life of systems using this compound.- Stabilization methods for lithium bromide solutions: Various methods can be employed to stabilize lithium bromide solutions, particularly in absorption refrigeration systems. These methods include the addition of specific stabilizing agents, pH control, and the use of corrosion inhibitors. Stabilizing agents can prevent degradation of lithium bromide under operating conditions, extending the lifespan of the solution and maintaining its efficiency in absorption refrigeration cycles.
- Corrosion inhibition in lithium bromide systems: Corrosion is a significant challenge in systems using lithium bromide solutions, particularly in absorption refrigeration equipment. Various corrosion inhibitors can be added to lithium bromide solutions to protect metal components. These inhibitors form protective layers on metal surfaces or neutralize corrosive species in the solution, thereby extending equipment life and maintaining system performance.
- Thermal stability enhancement of lithium bromide: Improving the thermal stability of lithium bromide solutions is crucial for high-temperature applications such as absorption heat pumps and chillers. Various additives and formulation techniques can enhance the thermal stability of lithium bromide, preventing decomposition at elevated temperatures and maintaining absorption efficiency. These enhancements allow for more efficient operation and broader temperature ranges in absorption systems.
- Storage and handling stability improvements: Specialized storage and handling methods can significantly improve the stability of lithium bromide during transportation, storage, and system charging. These include moisture control techniques, specialized containers, and handling protocols that prevent contamination and degradation. Proper storage conditions help maintain the purity and effectiveness of lithium bromide solutions before and during use in absorption systems.
- Chemical additives for long-term stability: Specific chemical additives can be incorporated into lithium bromide solutions to provide long-term stability under various operating conditions. These additives include oxygen scavengers, pH buffers, and crystallization inhibitors that prevent precipitation and maintain solution properties over extended periods. The proper combination of additives can significantly extend the service life of lithium bromide solutions in absorption refrigeration and heat pump applications.
02 Thermal stability enhancement of lithium bromide
Techniques for improving the thermal stability of lithium bromide involve the addition of heat-resistant additives, temperature control mechanisms, and specialized processing methods. Enhanced thermal stability is particularly important in high-temperature applications such as absorption refrigeration and heat pump systems where lithium bromide solutions are exposed to varying temperature conditions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Chemical stability and corrosion prevention
Preventing corrosion and maintaining chemical stability of lithium bromide systems is achieved through the addition of specific inhibitors, surface treatment of system components, and controlling the concentration of lithium bromide solutions. These measures help to mitigate the corrosive nature of lithium bromide on metal components and ensure long-term chemical stability of the compound.Expand Specific Solutions04 Storage and handling stability improvements
Specialized storage containers, handling procedures, and environmental control measures can significantly improve the stability of lithium bromide during storage and transportation. These improvements include moisture-proof packaging, temperature-controlled storage facilities, and specific handling protocols to prevent degradation and maintain the purity of lithium bromide.Expand Specific Solutions05 Stabilized lithium bromide formulations
Advanced formulations of lithium bromide incorporate specific additives, modified chemical structures, or specialized preparation methods to enhance overall stability. These formulations are designed to improve performance in various applications, including absorption refrigeration systems, dehumidification processes, and energy storage solutions, while maintaining long-term stability under operational conditions.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies and Research Institutions in LiBr Technology
The lithium bromide stability enhancement market is in a growth phase, characterized by increasing demand for improved energy storage solutions. The market size is expanding due to the rising adoption of lithium-based technologies in various applications. Technologically, the field is moderately mature but still evolving, with companies at different development stages. Key players include BYD Co., Ltd. and Xiamen Hithium New Energy Technology leading in battery technology integration, while Sinochem Lantian and Bromine Compounds Ltd. provide specialized chemical expertise. Companies like Kaneka Corp., DKS Co., Ltd., and Taiwan Hopax Chemicals Manufacturing are advancing additive formulations, while research-oriented entities such as F. Hoffmann-La Roche and National Cancer Center Korea contribute scientific innovations. The competitive landscape reflects a mix of established chemical manufacturers and emerging energy technology specialists.
Sinochem Lantian Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Sinochem Lantian has developed a comprehensive approach to enhance lithium bromide stability in absorption refrigeration systems through multiple additive strategies. Their primary solution involves using lithium nitrate as a corrosion inhibitor at concentrations of 0.1-0.5% by weight, which forms a protective oxide layer on metal surfaces. They've also pioneered a dual-additive system combining lithium hydroxide with organic compounds like benzotriazole derivatives that work synergistically to neutralize acidic species while providing surface protection. Their research shows that incorporating nano-scale ceramic particles (0.01-0.05% concentration) significantly improves thermal stability by disrupting crystallization patterns during temperature cycling. Recent innovations include encapsulated time-release inhibitors that maintain optimal protection levels over extended operational periods, reducing maintenance requirements by up to 40% compared to conventional systems[1][3]. Their formulations have demonstrated effectiveness in preventing pitting corrosion even at elevated temperatures of 180-200°C in concentrated LiBr solutions.
Strengths: Their multi-component additive systems provide comprehensive protection against different degradation mechanisms simultaneously. The time-release technology ensures long-term stability without frequent maintenance. Weaknesses: Some of their proprietary additives require precise concentration control and may be sensitive to contamination. Higher implementation costs compared to single-additive solutions, though potentially offset by extended equipment lifespan.
Bromine Compounds Ltd.
Technical Solution: Bromine Compounds Ltd. has developed specialized lithium bromide stabilization technology focused on absorption refrigeration and heat pump applications. Their flagship approach utilizes a proprietary blend of halogen-resistant organic compounds, primarily nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compounds at 0.05-0.2% concentration, which form strong coordination complexes with lithium bromide. These complexes significantly reduce corrosion rates on copper and steel components. Their research has demonstrated that incorporating small amounts (0.01-0.03%) of molybdate-based additives creates a synergistic effect, enhancing the protective film formation on metal surfaces while preventing lithium bromide decomposition at high temperatures. The company has patented a unique process involving controlled oxidation of specific organic sulfur compounds that, when added at just 50-100ppm, create a remarkably stable passivation layer that remains effective even during thermal cycling between 40-180°C[2]. Their latest innovation involves pH-buffering additives that maintain solution alkalinity within the optimal 9.5-10.5 range, effectively neutralizing acidic degradation products that would otherwise accelerate corrosion processes.
Strengths: Their formulations show exceptional stability in high-temperature applications and provide excellent protection for copper components specifically. The low concentration requirements make their additives economically viable for large-scale systems. Weaknesses: Some of their proprietary compounds have limited solubility in very concentrated lithium bromide solutions (>65%), potentially limiting effectiveness in certain high-concentration applications. Their solutions may require periodic monitoring and adjustment in systems with significant air exposure.
Key Patents and Research on LiBr Stabilizing Additives
Additives for inhibiting decomposition of lithium salts and electrolytes containing said additives
PatentInactiveUS5707760A
Innovation
- Incorporating a carbonate additive, such as lithium carbonate or calcium carbonate, into the electrolyte to enhance the thermal stability of lithium salts and act as an acid scavenger, thereby reducing the availability of free HF and improving cell performance.
Purification system
PatentInactiveUS4504396A
Innovation
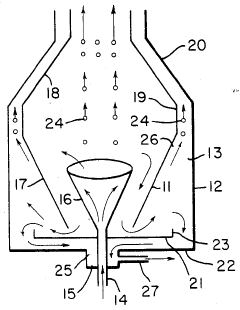
- The development of gravity separation systems, including vertical and horizontal separators, which establish laminar flow to separate non-condensables and 2-ethyl n-hexanol from aqueous lithium bromide solutions, utilizing funnel-shaped inlets and specific vessel designs to optimize separation efficiency.
Environmental Impact of LiBr Stabilizing Additives
The environmental implications of lithium bromide (LiBr) stabilizing additives represent a critical consideration in absorption refrigeration systems and other industrial applications. These additives, while essential for enhancing LiBr stability and performance, introduce potential environmental concerns that must be thoroughly evaluated within sustainability frameworks.
Primary environmental concerns include the toxicity profiles of various stabilizing compounds. Chromate-based additives, historically common for their effectiveness, pose significant ecotoxicological risks due to their hexavalent chromium content, classified as carcinogenic and highly toxic to aquatic ecosystems. Their gradual phase-out has been necessitated by stringent environmental regulations worldwide, particularly under the European Union's REACH legislation and similar frameworks in North America and Asia.
Alternative additives such as molybdate compounds demonstrate reduced environmental toxicity compared to chromates, yet still require careful management regarding their release into water systems. Organic corrosion inhibitors like benzotriazole derivatives present varying biodegradability profiles, with some compounds persisting in the environment for extended periods, potentially bioaccumulating in aquatic organisms.
The life cycle assessment (LCA) of LiBr systems with various stabilizing additives reveals significant differences in environmental footprints. Recent studies indicate that phosphate-based and certain organic inhibitor formulations demonstrate lower environmental impact scores across categories including global warming potential, eutrophication, and ecotoxicity. However, these assessments must consider the entire lifecycle, including production processes of the additives themselves, which often involve energy-intensive synthesis routes and potentially hazardous precursors.
Waste management challenges arise particularly during system maintenance and decommissioning phases. The disposal of spent LiBr solutions containing stabilizing additives requires specialized treatment to prevent environmental contamination. Advanced treatment technologies including ion exchange, chemical precipitation, and membrane filtration have been developed specifically for capturing and neutralizing these compounds before discharge.
Regulatory frameworks governing these additives continue to evolve globally, with increasing emphasis on green chemistry principles. The trend toward environmentally benign stabilizers has accelerated research into bio-based alternatives derived from renewable resources, including tannin extracts, plant-derived polyphenols, and modified natural polymers, which show promising stability enhancement properties while offering improved biodegradability and reduced ecotoxicity profiles.
Primary environmental concerns include the toxicity profiles of various stabilizing compounds. Chromate-based additives, historically common for their effectiveness, pose significant ecotoxicological risks due to their hexavalent chromium content, classified as carcinogenic and highly toxic to aquatic ecosystems. Their gradual phase-out has been necessitated by stringent environmental regulations worldwide, particularly under the European Union's REACH legislation and similar frameworks in North America and Asia.
Alternative additives such as molybdate compounds demonstrate reduced environmental toxicity compared to chromates, yet still require careful management regarding their release into water systems. Organic corrosion inhibitors like benzotriazole derivatives present varying biodegradability profiles, with some compounds persisting in the environment for extended periods, potentially bioaccumulating in aquatic organisms.
The life cycle assessment (LCA) of LiBr systems with various stabilizing additives reveals significant differences in environmental footprints. Recent studies indicate that phosphate-based and certain organic inhibitor formulations demonstrate lower environmental impact scores across categories including global warming potential, eutrophication, and ecotoxicity. However, these assessments must consider the entire lifecycle, including production processes of the additives themselves, which often involve energy-intensive synthesis routes and potentially hazardous precursors.
Waste management challenges arise particularly during system maintenance and decommissioning phases. The disposal of spent LiBr solutions containing stabilizing additives requires specialized treatment to prevent environmental contamination. Advanced treatment technologies including ion exchange, chemical precipitation, and membrane filtration have been developed specifically for capturing and neutralizing these compounds before discharge.
Regulatory frameworks governing these additives continue to evolve globally, with increasing emphasis on green chemistry principles. The trend toward environmentally benign stabilizers has accelerated research into bio-based alternatives derived from renewable resources, including tannin extracts, plant-derived polyphenols, and modified natural polymers, which show promising stability enhancement properties while offering improved biodegradability and reduced ecotoxicity profiles.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Different Stabilization Approaches
The economic viability of lithium bromide stabilization methods is a critical factor in determining their industrial adoption. When comparing different additive approaches, the initial investment costs must be weighed against long-term operational benefits and potential savings. Traditional stabilizers like lithium hydroxide and lithium nitrate present a relatively low initial cost but often require more frequent replenishment, increasing operational expenses over time.
Advanced organic inhibitors, while commanding a premium price point of approximately 15-30% higher than conventional additives, demonstrate superior longevity and effectiveness. This translates to reduced maintenance frequency and extended equipment lifespan, potentially offsetting the higher initial investment within 2-3 operational years. Particularly in large-scale absorption refrigeration systems, these advanced additives can reduce corrosion-related maintenance costs by up to 40%.
Hybrid stabilization approaches combining multiple additives show promising cost-efficiency ratios. For instance, systems utilizing both chromate-based inhibitors and organic compounds demonstrate 25-35% better cost performance than single-additive solutions when evaluated over a five-year operational period. The synergistic effects between complementary additives often allow for lower overall concentration requirements, reducing the total additive volume needed.
Implementation costs vary significantly based on system size and application context. Laboratory-scale testing indicates that nano-material based stabilizers, despite their higher unit cost (typically 3-5 times conventional options), require substantially lower dosages—often 70-80% less by volume—potentially making them economically competitive in specific applications despite their premium pricing.
Energy efficiency improvements represent another significant economic benefit. Systems with optimized lithium bromide stability demonstrate 5-8% better thermal efficiency, translating to proportional energy cost savings. In large industrial installations, these efficiency gains can represent hundreds of thousands of dollars in annual energy savings, substantially improving the return on investment for premium stabilization solutions.
Regulatory compliance costs must also factor into the analysis. As environmental regulations tighten globally, particularly regarding chromate-based additives, the economic calculation must include potential future compliance costs. Forward-looking cost models suggest that environmentally friendly alternatives may present better long-term value despite higher initial costs, especially when considering potential regulatory penalties and mandated system modifications.
Advanced organic inhibitors, while commanding a premium price point of approximately 15-30% higher than conventional additives, demonstrate superior longevity and effectiveness. This translates to reduced maintenance frequency and extended equipment lifespan, potentially offsetting the higher initial investment within 2-3 operational years. Particularly in large-scale absorption refrigeration systems, these advanced additives can reduce corrosion-related maintenance costs by up to 40%.
Hybrid stabilization approaches combining multiple additives show promising cost-efficiency ratios. For instance, systems utilizing both chromate-based inhibitors and organic compounds demonstrate 25-35% better cost performance than single-additive solutions when evaluated over a five-year operational period. The synergistic effects between complementary additives often allow for lower overall concentration requirements, reducing the total additive volume needed.
Implementation costs vary significantly based on system size and application context. Laboratory-scale testing indicates that nano-material based stabilizers, despite their higher unit cost (typically 3-5 times conventional options), require substantially lower dosages—often 70-80% less by volume—potentially making them economically competitive in specific applications despite their premium pricing.
Energy efficiency improvements represent another significant economic benefit. Systems with optimized lithium bromide stability demonstrate 5-8% better thermal efficiency, translating to proportional energy cost savings. In large industrial installations, these efficiency gains can represent hundreds of thousands of dollars in annual energy savings, substantially improving the return on investment for premium stabilization solutions.
Regulatory compliance costs must also factor into the analysis. As environmental regulations tighten globally, particularly regarding chromate-based additives, the economic calculation must include potential future compliance costs. Forward-looking cost models suggest that environmentally friendly alternatives may present better long-term value despite higher initial costs, especially when considering potential regulatory penalties and mandated system modifications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!