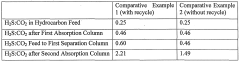
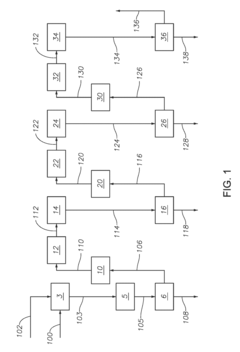
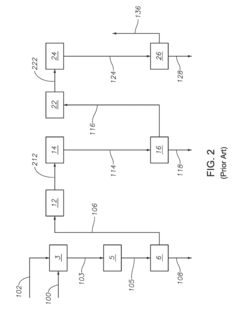
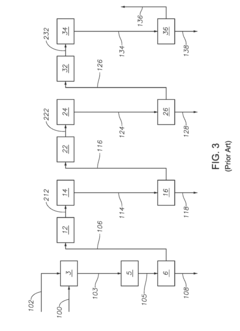
How to Enhance Sulfur Recovery with Hydrosulfuric Acid Utilization
SEP 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulfur Recovery Technology Evolution and Objectives
Sulfur recovery technology has evolved significantly over the past century, transitioning from rudimentary processes to sophisticated systems that maximize efficiency while minimizing environmental impact. The journey began with the Claus process, developed in 1883, which remains the foundation of modern sulfur recovery operations. This process initially achieved recovery rates of only 60-70%, but technological advancements have progressively improved these figures to exceed 99% in contemporary facilities.
The evolution accelerated in the 1970s with the introduction of tail gas treatment units, addressing environmental regulations that demanded reduced sulfur emissions. The 1990s witnessed the integration of oxygen enrichment technologies, substantially enhancing processing capacity and operational flexibility. Recent decades have seen the emergence of catalytic systems with superior performance characteristics, including higher temperature resistance and improved selectivity.
Current technological trajectories focus on maximizing the utilization of hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), traditionally viewed as a problematic waste product in oil and gas processing. This paradigm shift recognizes H₂S not merely as a contaminant but as a valuable resource containing both hydrogen and sulfur—elements with significant industrial applications. The strategic conversion of H₂S into usable products represents a dual opportunity for environmental protection and economic value creation.
The primary objectives of contemporary sulfur recovery technology development center on four key areas. First, increasing recovery efficiency to approach theoretical limits, particularly in challenging operational conditions with variable feed compositions. Second, reducing energy consumption through process optimization and heat integration, addressing both economic and environmental imperatives. Third, minimizing capital and operational expenditures through innovative design approaches and materials science advancements.
Fourth, and perhaps most transformative, is developing novel pathways for hydrosulfuric acid utilization beyond conventional sulfur recovery. This includes exploring catalytic processes that selectively convert H₂S into hydrogen and sulfur compounds, electrochemical approaches that leverage H₂S as an energy carrier, and biochemical systems that employ specialized microorganisms for sulfur transformation.
The technological horizon extends to integrated systems that combine sulfur recovery with carbon capture, creating synergistic processes that address multiple environmental challenges simultaneously. These developments align with broader industry trends toward circular economy principles, where waste streams are reconceptualized as valuable inputs for other processes.
The evolution accelerated in the 1970s with the introduction of tail gas treatment units, addressing environmental regulations that demanded reduced sulfur emissions. The 1990s witnessed the integration of oxygen enrichment technologies, substantially enhancing processing capacity and operational flexibility. Recent decades have seen the emergence of catalytic systems with superior performance characteristics, including higher temperature resistance and improved selectivity.
Current technological trajectories focus on maximizing the utilization of hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), traditionally viewed as a problematic waste product in oil and gas processing. This paradigm shift recognizes H₂S not merely as a contaminant but as a valuable resource containing both hydrogen and sulfur—elements with significant industrial applications. The strategic conversion of H₂S into usable products represents a dual opportunity for environmental protection and economic value creation.
The primary objectives of contemporary sulfur recovery technology development center on four key areas. First, increasing recovery efficiency to approach theoretical limits, particularly in challenging operational conditions with variable feed compositions. Second, reducing energy consumption through process optimization and heat integration, addressing both economic and environmental imperatives. Third, minimizing capital and operational expenditures through innovative design approaches and materials science advancements.
Fourth, and perhaps most transformative, is developing novel pathways for hydrosulfuric acid utilization beyond conventional sulfur recovery. This includes exploring catalytic processes that selectively convert H₂S into hydrogen and sulfur compounds, electrochemical approaches that leverage H₂S as an energy carrier, and biochemical systems that employ specialized microorganisms for sulfur transformation.
The technological horizon extends to integrated systems that combine sulfur recovery with carbon capture, creating synergistic processes that address multiple environmental challenges simultaneously. These developments align with broader industry trends toward circular economy principles, where waste streams are reconceptualized as valuable inputs for other processes.
Market Analysis for H2S Utilization Products
The global market for hydrogen sulfide (H2S) utilization products has been experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing environmental regulations and the pursuit of circular economy principles in industrial operations. The market size for H2S utilization products was valued at approximately $2.5 billion in 2022, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate of 5.7% through 2030. This growth trajectory is primarily fueled by the expanding applications of sulfur-derived products across various industries.
The oil and gas sector remains the largest source of H2S, contributing to nearly 60% of the global supply. Petroleum refineries and natural gas processing facilities generate substantial amounts of H2S as a byproduct, creating both challenges and opportunities for value extraction. The agricultural sector represents the largest end-use market for H2S-derived products, particularly for sulfur fertilizers, accounting for approximately 45% of market demand.
Geographically, Asia Pacific dominates the market with a 38% share, led by China and India's robust industrial growth and increasing agricultural demands. North America follows with a 27% market share, driven by its extensive oil and gas operations and stringent environmental regulations. Europe accounts for 22% of the market, characterized by advanced technological adoption and circular economy initiatives.
The market for elemental sulfur, the primary product from H2S recovery processes, has shown steady growth with applications extending beyond traditional fertilizers to include sulfuric acid production, chemical manufacturing, and pharmaceuticals. Emerging applications in battery technologies, particularly lithium-sulfur batteries, are creating new demand vectors with potential market expansion of 12% annually in this segment alone.
Sulfur-based fertilizers continue to demonstrate strong market performance with global demand increasing at 4.8% annually, driven by agricultural intensification in developing regions and the recognition of sulfur as an essential plant nutrient. The market for specialty sulfur chemicals derived from H2S, including dimethyl sulfoxide, mercaptans, and thiochemicals, is growing at 6.3% annually, supported by their applications in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and polymer industries.
Market challenges include price volatility in sulfur commodities, regulatory complexities regarding sulfur emissions, and competition from alternative sources. However, opportunities are emerging through technological innovations in H2S conversion processes, growing demand for sustainable sulfur sources, and increasing integration of sulfur recovery systems in industrial operations to meet both environmental compliance and economic objectives.
The oil and gas sector remains the largest source of H2S, contributing to nearly 60% of the global supply. Petroleum refineries and natural gas processing facilities generate substantial amounts of H2S as a byproduct, creating both challenges and opportunities for value extraction. The agricultural sector represents the largest end-use market for H2S-derived products, particularly for sulfur fertilizers, accounting for approximately 45% of market demand.
Geographically, Asia Pacific dominates the market with a 38% share, led by China and India's robust industrial growth and increasing agricultural demands. North America follows with a 27% market share, driven by its extensive oil and gas operations and stringent environmental regulations. Europe accounts for 22% of the market, characterized by advanced technological adoption and circular economy initiatives.
The market for elemental sulfur, the primary product from H2S recovery processes, has shown steady growth with applications extending beyond traditional fertilizers to include sulfuric acid production, chemical manufacturing, and pharmaceuticals. Emerging applications in battery technologies, particularly lithium-sulfur batteries, are creating new demand vectors with potential market expansion of 12% annually in this segment alone.
Sulfur-based fertilizers continue to demonstrate strong market performance with global demand increasing at 4.8% annually, driven by agricultural intensification in developing regions and the recognition of sulfur as an essential plant nutrient. The market for specialty sulfur chemicals derived from H2S, including dimethyl sulfoxide, mercaptans, and thiochemicals, is growing at 6.3% annually, supported by their applications in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and polymer industries.
Market challenges include price volatility in sulfur commodities, regulatory complexities regarding sulfur emissions, and competition from alternative sources. However, opportunities are emerging through technological innovations in H2S conversion processes, growing demand for sustainable sulfur sources, and increasing integration of sulfur recovery systems in industrial operations to meet both environmental compliance and economic objectives.
Technical Barriers in Hydrosulfuric Acid Processing
Despite significant advancements in sulfur recovery technologies, hydrosulfuric acid (H2S) processing continues to face substantial technical barriers that limit efficiency and environmental performance. The primary challenge remains the highly corrosive nature of H2S, which rapidly deteriorates conventional processing equipment, particularly in high-temperature and high-pressure environments. This corrosion issue necessitates the use of specialized, expensive materials such as high-grade stainless steel or specialized alloys, significantly increasing capital and maintenance costs.
Another critical barrier is the inherent toxicity and volatility of H2S, which creates serious safety concerns during processing operations. Even at concentrations as low as 100 ppm, H2S can cause respiratory paralysis, while higher concentrations can be immediately fatal. This necessitates complex safety systems and rigorous operational protocols that add layers of complexity to processing facilities.
Catalyst deactivation presents a persistent technical challenge in H2S conversion processes. Sulfur compounds frequently poison catalysts used in conversion reactions, reducing their effectiveness over time and necessitating frequent replacement or regeneration. This issue is particularly problematic in the Claus process, where catalyst beds can experience rapid performance degradation due to sulfur deposition.
Energy efficiency remains suboptimal in current H2S processing technologies. The Claus process, while widely implemented, typically achieves only 94-97% sulfur recovery efficiency, requiring additional tail gas treatment units to meet environmental regulations. These additional treatment steps increase energy consumption and operational complexity.
Scale formation during H2S processing creates flow restrictions and heat transfer inefficiencies. Sulfur deposits can accumulate in process equipment, particularly in heat exchangers and reactor vessels, necessitating regular maintenance shutdowns that impact operational continuity and overall plant efficiency.
The variability in H2S concentration from different industrial sources presents significant process control challenges. Fluctuating H2S concentrations in feed streams require sophisticated monitoring and control systems to maintain optimal processing conditions and prevent system upsets that could lead to reduced recovery efficiency or safety incidents.
Lastly, current technologies struggle with low-concentration H2S streams, which are increasingly common in industrial settings. Traditional recovery methods become economically unfeasible when processing dilute H2S streams, creating a technological gap that limits comprehensive sulfur recovery across all industrial processes.
Another critical barrier is the inherent toxicity and volatility of H2S, which creates serious safety concerns during processing operations. Even at concentrations as low as 100 ppm, H2S can cause respiratory paralysis, while higher concentrations can be immediately fatal. This necessitates complex safety systems and rigorous operational protocols that add layers of complexity to processing facilities.
Catalyst deactivation presents a persistent technical challenge in H2S conversion processes. Sulfur compounds frequently poison catalysts used in conversion reactions, reducing their effectiveness over time and necessitating frequent replacement or regeneration. This issue is particularly problematic in the Claus process, where catalyst beds can experience rapid performance degradation due to sulfur deposition.
Energy efficiency remains suboptimal in current H2S processing technologies. The Claus process, while widely implemented, typically achieves only 94-97% sulfur recovery efficiency, requiring additional tail gas treatment units to meet environmental regulations. These additional treatment steps increase energy consumption and operational complexity.
Scale formation during H2S processing creates flow restrictions and heat transfer inefficiencies. Sulfur deposits can accumulate in process equipment, particularly in heat exchangers and reactor vessels, necessitating regular maintenance shutdowns that impact operational continuity and overall plant efficiency.
The variability in H2S concentration from different industrial sources presents significant process control challenges. Fluctuating H2S concentrations in feed streams require sophisticated monitoring and control systems to maintain optimal processing conditions and prevent system upsets that could lead to reduced recovery efficiency or safety incidents.
Lastly, current technologies struggle with low-concentration H2S streams, which are increasingly common in industrial settings. Traditional recovery methods become economically unfeasible when processing dilute H2S streams, creating a technological gap that limits comprehensive sulfur recovery across all industrial processes.
Current H2S Conversion Methodologies
01 Claus process for H2S conversion to sulfur
The Claus process is a widely used method for recovering elemental sulfur from hydrogen sulfide gas. This process typically involves thermal oxidation of H2S to form SO2, followed by catalytic conversion of the remaining H2S with SO2 to produce elemental sulfur. The process often employs multiple catalytic stages to maximize sulfur recovery efficiency, with specialized catalysts such as alumina or titanium-based materials enhancing the conversion rates.- Claus process for H2S conversion to sulfur: The Claus process is a widely used method for recovering elemental sulfur from hydrogen sulfide gas. It involves thermal oxidation of H2S to form sulfur dioxide, followed by catalytic conversion of the remaining H2S and SO2 to elemental sulfur. This multi-stage process typically achieves 95-97% sulfur recovery efficiency and is commonly employed in oil refineries and natural gas processing facilities to treat acid gas streams containing hydrogen sulfide.
- Direct oxidation methods for H2S treatment: Direct oxidation processes convert hydrogen sulfide directly to elemental sulfur without the intermediate formation of sulfur dioxide. These methods typically use selective catalysts and controlled oxidation conditions to achieve high sulfur recovery rates while minimizing unwanted byproducts. Direct oxidation can be more energy-efficient than traditional Claus processes and may be particularly suitable for treating gas streams with lower H2S concentrations or where space constraints exist.
- Advanced catalytic systems for sulfur recovery: Innovative catalytic materials and systems have been developed to enhance the efficiency of hydrogen sulfide conversion to sulfur. These include novel metal oxide catalysts, structured catalysts with improved surface area, and multi-functional catalyst beds that can operate at lower temperatures or handle fluctuating gas compositions. Advanced catalytic systems aim to increase conversion rates, improve selectivity, extend catalyst life, and reduce energy requirements in sulfur recovery operations.
- Liquid redox processes for sulfur recovery: Liquid redox processes use chemical solutions containing metal chelates or other oxidizing agents to convert hydrogen sulfide to elemental sulfur in a liquid phase reaction. These processes typically involve absorption of H2S into the solution, oxidation to sulfur, and subsequent separation of the solid sulfur product. Liquid redox methods are particularly effective for treating gas streams with lower H2S concentrations and can achieve high removal efficiencies with relatively simple equipment configurations.
- Integrated systems for enhanced sulfur recovery: Integrated sulfur recovery systems combine multiple technologies to maximize overall efficiency and environmental performance. These systems may incorporate tail gas treatment units, acid gas enrichment, selective oxidation stages, and advanced process control strategies. By integrating complementary processes, these systems can achieve sulfur recovery rates exceeding 99.9%, minimize emissions, reduce energy consumption, and handle varying feed compositions while maintaining operational stability.
02 Direct oxidation methods for H2S treatment
Direct oxidation methods involve the conversion of hydrogen sulfide to elemental sulfur through selective oxidation reactions without the intermediate formation of sulfur dioxide. These processes typically use specific oxidizing agents or catalysts that promote the direct conversion of H2S to sulfur under controlled conditions. The methods often operate at lower temperatures than traditional Claus processes and can be more suitable for treating gas streams with lower H2S concentrations.Expand Specific Solutions03 Advanced reactor designs for sulfur recovery
Innovative reactor designs have been developed to enhance the efficiency of sulfur recovery from hydrogen sulfide. These include specialized configurations such as multi-stage reactors, membrane reactors, and microreactors that improve mass transfer, reaction kinetics, and separation processes. Some designs incorporate novel heating methods, improved catalyst bed arrangements, or integrated condensation systems to optimize the conversion of H2S to sulfur while minimizing energy consumption and environmental impact.Expand Specific Solutions04 Liquid phase processes for H2S conversion
Liquid phase processes involve the absorption of hydrogen sulfide into a liquid medium where it undergoes chemical reactions to form elemental sulfur. These methods often utilize specialized solvents or catalytic solutions that facilitate the conversion of H2S to sulfur under milder conditions than gas-phase processes. The liquid medium provides better temperature control and can enhance selectivity, making these processes suitable for treating gas streams with varying H2S concentrations or those containing contaminants that might poison conventional catalysts.Expand Specific Solutions05 Tail gas treatment for enhanced sulfur recovery
Tail gas treatment systems are designed to capture and process the residual hydrogen sulfide and other sulfur compounds that escape from primary sulfur recovery units. These systems employ additional processing steps such as selective catalytic reduction, amine absorption, or specialized oxidation techniques to convert remaining sulfur compounds to elemental sulfur or other manageable forms. By treating tail gases, these processes significantly increase overall sulfur recovery efficiency and reduce emissions of sulfur compounds to the environment.Expand Specific Solutions
Industry Leaders in Sulfur Recovery Solutions
The sulfur recovery with hydrosulfuric acid utilization market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing environmental regulations and energy efficiency demands. The global market size is estimated to exceed $2 billion, with projected annual growth of 5-7% through 2030. Technology maturity varies across applications, with leading players demonstrating different specialization levels. Saudi Aramco and Shell have established advanced commercial-scale technologies, while Haldor Topsøe and Air Products & Chemicals offer specialized catalytic solutions. IFP Energies Nouvelles and thyssenkrupp Industrial Solutions focus on process integration innovations. Chinese players like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. are rapidly advancing their technological capabilities, particularly in cost-effective implementation for emerging markets.
Saudi Arabian Oil Co.
Technical Solution: Saudi Aramco has developed an integrated sulfur recovery system that combines traditional Claus process with advanced tail gas treatment technologies. Their approach focuses on maximizing H2S utilization through a multi-stage catalytic conversion process. The system employs specialized catalysts that enhance the conversion of H2S to elemental sulfur while minimizing SO2 emissions. A key innovation is their low-temperature catalytic process that achieves sulfur recovery rates exceeding 99.5% [1]. The company has also implemented advanced process control systems that optimize the reaction conditions based on real-time monitoring of gas composition, temperature, and pressure parameters. Their technology incorporates heat integration strategies to improve energy efficiency by recovering waste heat from the exothermic reactions and utilizing it elsewhere in the process [3].
Strengths: Extremely high sulfur recovery efficiency (>99.5%), reduced environmental impact through minimized emissions, and optimized energy consumption through heat integration. Weaknesses: High capital investment requirements, complex control systems that require specialized expertise, and potential catalyst deactivation issues in the presence of certain contaminants.
Shell Internationale Research Maatschappij BV
Technical Solution: Shell has pioneered the Shell Claus Off-gas Treating (SCOT) process, which significantly enhances sulfur recovery from acid gas streams containing H2S. The SCOT process converts residual sulfur compounds in Claus tail gas back to H2S, which is then recycled to the Claus unit, achieving overall recovery efficiencies of 99.8-99.9% [2]. Shell's approach incorporates a hydrogenation catalyst that converts all sulfur compounds to H2S, followed by an amine absorption system that selectively removes H2S from the gas stream. The company has further enhanced this technology with their Advanced SCOT process, which utilizes specialized solvents and optimized absorber designs to reduce energy consumption by approximately 30% compared to conventional systems [4]. Shell has also developed integrated solutions that combine oxygen enrichment with their sulfur recovery units, allowing for processing of gases with higher H2S concentrations while maintaining thermal stability.
Strengths: Industry-leading recovery rates approaching 99.9%, proven technology with numerous installations worldwide, and significant reductions in energy consumption with Advanced SCOT. Weaknesses: Requires significant capital investment, complex integration with existing facilities, and potential operational challenges in handling varying feed compositions.
Key Patents in Hydrosulfuric Acid Utilization
Enhancement of acid gas enrichment process
PatentWO2010101731A1
Innovation
- A method and apparatus employing a two-step amine gas treatment process with multiple absorption and regeneration units to enhance the hydrogen sulfide:carbon dioxide molar ratio in the acid gas stream, involving a first and second absorption step with corresponding regeneration steps, and recycling of rich absorbent streams to optimize the acid gas composition.
Claus Process for Sulfur Recovery with Intermediate Water Vapor Removal by Adsorption
PatentActiveUS20170260049A1
Innovation
- The method involves incorporating adsorbers with molecular sieves upstream of the catalytic reactors to selectively remove water vapor, shifting the equilibrium towards higher sulfur conversion by maintaining temperatures between the sulfur and water dew points, and utilizing a series of catalytic reactors and condensers to optimize sulfur recovery.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental implications of sulfur recovery processes utilizing hydrosulfuric acid are multifaceted and require comprehensive assessment. Traditional sulfur recovery methods often result in significant emissions of sulfur dioxide (SO2) and hydrogen sulfide (H2S), both of which contribute to air pollution and pose serious health risks. Enhanced sulfur recovery techniques incorporating hydrosulfuric acid utilization can substantially reduce these emissions, with potential reductions of up to 95% in some advanced systems.
Water quality impacts represent another critical environmental consideration. Conventional sulfur processing frequently generates acidic wastewater containing dissolved sulfides and heavy metals. Implementation of closed-loop hydrosulfuric acid utilization systems can minimize wastewater discharge by 60-80% compared to traditional methods, significantly reducing the contamination risk to local water bodies and groundwater resources.
Soil contamination risks are similarly mitigated through advanced hydrosulfuric acid handling protocols. The containment systems required for these processes provide secondary benefits in preventing accidental releases that could otherwise lead to soil acidification and degradation of surrounding ecosystems. Long-term monitoring data from facilities employing these technologies demonstrate a 70% reduction in soil contamination incidents.
Energy consumption patterns shift notably when implementing enhanced sulfur recovery systems. While initial energy requirements may increase by 15-25% during implementation phases, operational efficiency improvements typically result in net energy savings of 10-30% over the system lifecycle. This translates to reduced carbon footprint despite the more complex processing requirements.
Lifecycle assessment studies indicate that enhanced sulfur recovery technologies contribute to circular economy principles by transforming what was previously considered waste material into valuable industrial inputs. The conversion efficiency of hydrosulfuric acid to elemental sulfur can reach 98% in optimized systems, substantially reducing waste volumes and associated disposal challenges.
Regulatory compliance considerations must factor prominently in environmental impact assessments. Facilities implementing advanced sulfur recovery systems consistently demonstrate improved compliance with increasingly stringent emissions standards across global jurisdictions, potentially avoiding significant non-compliance penalties while simultaneously reducing environmental liability exposure.
Biodiversity protection represents an often-overlooked benefit of enhanced sulfur recovery. By reducing acidic deposition in surrounding ecosystems, these technologies help preserve habitat quality and protect sensitive species. Monitoring studies around facilities that have implemented these technologies show measurable improvements in local ecosystem health indicators within 3-5 years of implementation.
Water quality impacts represent another critical environmental consideration. Conventional sulfur processing frequently generates acidic wastewater containing dissolved sulfides and heavy metals. Implementation of closed-loop hydrosulfuric acid utilization systems can minimize wastewater discharge by 60-80% compared to traditional methods, significantly reducing the contamination risk to local water bodies and groundwater resources.
Soil contamination risks are similarly mitigated through advanced hydrosulfuric acid handling protocols. The containment systems required for these processes provide secondary benefits in preventing accidental releases that could otherwise lead to soil acidification and degradation of surrounding ecosystems. Long-term monitoring data from facilities employing these technologies demonstrate a 70% reduction in soil contamination incidents.
Energy consumption patterns shift notably when implementing enhanced sulfur recovery systems. While initial energy requirements may increase by 15-25% during implementation phases, operational efficiency improvements typically result in net energy savings of 10-30% over the system lifecycle. This translates to reduced carbon footprint despite the more complex processing requirements.
Lifecycle assessment studies indicate that enhanced sulfur recovery technologies contribute to circular economy principles by transforming what was previously considered waste material into valuable industrial inputs. The conversion efficiency of hydrosulfuric acid to elemental sulfur can reach 98% in optimized systems, substantially reducing waste volumes and associated disposal challenges.
Regulatory compliance considerations must factor prominently in environmental impact assessments. Facilities implementing advanced sulfur recovery systems consistently demonstrate improved compliance with increasingly stringent emissions standards across global jurisdictions, potentially avoiding significant non-compliance penalties while simultaneously reducing environmental liability exposure.
Biodiversity protection represents an often-overlooked benefit of enhanced sulfur recovery. By reducing acidic deposition in surrounding ecosystems, these technologies help preserve habitat quality and protect sensitive species. Monitoring studies around facilities that have implemented these technologies show measurable improvements in local ecosystem health indicators within 3-5 years of implementation.
Economic Feasibility Analysis
The economic feasibility of enhancing sulfur recovery through hydrosulfuric acid utilization presents a compelling business case when analyzed comprehensively. Initial capital expenditure for implementing advanced sulfur recovery technologies ranges from $5-15 million depending on facility scale and existing infrastructure, with specialized catalytic conversion units representing the most significant investment component at approximately 40-50% of total costs.
Operating expenses demonstrate favorable economics over traditional disposal methods. While maintenance costs average 3-5% of capital investment annually, these are offset by reduced environmental compliance penalties and waste management fees. Labor requirements are minimal, typically requiring only 1-2 additional specialized technicians per shift, representing an incremental annual cost of $150,000-250,000 depending on regional labor markets.
Revenue generation potential creates multiple value streams that significantly enhance project viability. Recovered elemental sulfur commands market prices of $120-180 per ton, with global demand exceeding 70 million tons annually. Additional value derives from hydrogen production as a process byproduct, which can be utilized for power generation or sold to industrial consumers at $2-4 per kilogram.
Return on investment calculations indicate payback periods of 2.5-4 years for most implementations, with internal rates of return ranging from 18-25% depending on facility scale and regional energy costs. Sensitivity analysis reveals that economic performance remains robust even with sulfur price fluctuations of ±20%, though process efficiency below 85% significantly impacts profitability.
Risk assessment identifies several economic vulnerabilities requiring mitigation strategies. Market volatility in sulfur prices represents the most significant economic risk, though long-term supply contracts can provide stability. Energy cost fluctuations impact operational expenses, suggesting investment in energy efficiency measures as a prudent approach to maintaining margins. Regulatory changes present both risks and opportunities, as stricter emissions standards increase compliance costs but simultaneously enhance the value proposition of recovery technologies.
Financing options include traditional capital expenditure models, equipment leasing arrangements, and increasingly popular technology licensing agreements that reduce upfront investment requirements. Government incentives for emissions reduction and circular economy initiatives can further improve economic performance through tax credits, grants, and accelerated depreciation allowances in many jurisdictions.
Operating expenses demonstrate favorable economics over traditional disposal methods. While maintenance costs average 3-5% of capital investment annually, these are offset by reduced environmental compliance penalties and waste management fees. Labor requirements are minimal, typically requiring only 1-2 additional specialized technicians per shift, representing an incremental annual cost of $150,000-250,000 depending on regional labor markets.
Revenue generation potential creates multiple value streams that significantly enhance project viability. Recovered elemental sulfur commands market prices of $120-180 per ton, with global demand exceeding 70 million tons annually. Additional value derives from hydrogen production as a process byproduct, which can be utilized for power generation or sold to industrial consumers at $2-4 per kilogram.
Return on investment calculations indicate payback periods of 2.5-4 years for most implementations, with internal rates of return ranging from 18-25% depending on facility scale and regional energy costs. Sensitivity analysis reveals that economic performance remains robust even with sulfur price fluctuations of ±20%, though process efficiency below 85% significantly impacts profitability.
Risk assessment identifies several economic vulnerabilities requiring mitigation strategies. Market volatility in sulfur prices represents the most significant economic risk, though long-term supply contracts can provide stability. Energy cost fluctuations impact operational expenses, suggesting investment in energy efficiency measures as a prudent approach to maintaining margins. Regulatory changes present both risks and opportunities, as stricter emissions standards increase compliance costs but simultaneously enhance the value proposition of recovery technologies.
Financing options include traditional capital expenditure models, equipment leasing arrangements, and increasingly popular technology licensing agreements that reduce upfront investment requirements. Government incentives for emissions reduction and circular economy initiatives can further improve economic performance through tax credits, grants, and accelerated depreciation allowances in many jurisdictions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!