Laser Welding vs Resistance: Cost Effectiveness Analysis
SEP 15, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Welding Technologies Background and Objectives
Welding technology has evolved significantly over the past century, transforming from rudimentary joining methods to sophisticated processes that enable modern manufacturing. The two predominant welding technologies—resistance welding and laser welding—represent different eras in this evolution. Resistance welding, developed in the late 19th century, relies on electrical resistance to generate heat at the junction of materials, while laser welding, emerging in the 1960s, utilizes concentrated light energy to create precise fusion zones.
The global welding market has experienced steady growth, reaching approximately $20 billion in 2022, with automotive, aerospace, and electronics manufacturing driving significant demand. Within this landscape, resistance welding has traditionally dominated industrial applications due to its established infrastructure and relatively lower initial investment costs. However, laser welding has gained substantial market share over the past two decades, particularly in high-precision industries.
Recent technological advancements have dramatically improved the efficiency and capabilities of both welding methods. Resistance welding has seen innovations in control systems and electrode materials, while laser welding has benefited from fiber laser technology, which offers higher energy efficiency and beam quality. These developments have blurred the once-clear cost distinctions between these technologies, necessitating a comprehensive reassessment of their economic viability across different applications.
The primary objective of this technical research is to conduct a detailed cost-effectiveness analysis comparing laser welding and resistance welding across various industrial applications. This analysis aims to establish quantifiable metrics for evaluating total ownership costs, including initial investment, operational expenses, maintenance requirements, and production outcomes such as quality, speed, and material versatility.
Additionally, this research seeks to identify specific application thresholds where each technology demonstrates superior economic performance. By establishing these thresholds, manufacturers can make more informed decisions about welding technology investments based on their specific production requirements, volume expectations, and quality standards.
The analysis will also explore emerging hybrid welding systems that combine elements of both technologies to potentially offer optimized cost-performance ratios for specific applications. These hybrid approaches represent a significant trend in welding technology development and may indicate future directions for the industry.
Finally, this research aims to forecast technological developments in both welding methods over the next five to ten years, with particular attention to advancements that might significantly alter the cost-effectiveness equation. This forward-looking component will help organizations develop strategic technology roadmaps that account for both current economic realities and future technological possibilities.
The global welding market has experienced steady growth, reaching approximately $20 billion in 2022, with automotive, aerospace, and electronics manufacturing driving significant demand. Within this landscape, resistance welding has traditionally dominated industrial applications due to its established infrastructure and relatively lower initial investment costs. However, laser welding has gained substantial market share over the past two decades, particularly in high-precision industries.
Recent technological advancements have dramatically improved the efficiency and capabilities of both welding methods. Resistance welding has seen innovations in control systems and electrode materials, while laser welding has benefited from fiber laser technology, which offers higher energy efficiency and beam quality. These developments have blurred the once-clear cost distinctions between these technologies, necessitating a comprehensive reassessment of their economic viability across different applications.
The primary objective of this technical research is to conduct a detailed cost-effectiveness analysis comparing laser welding and resistance welding across various industrial applications. This analysis aims to establish quantifiable metrics for evaluating total ownership costs, including initial investment, operational expenses, maintenance requirements, and production outcomes such as quality, speed, and material versatility.
Additionally, this research seeks to identify specific application thresholds where each technology demonstrates superior economic performance. By establishing these thresholds, manufacturers can make more informed decisions about welding technology investments based on their specific production requirements, volume expectations, and quality standards.
The analysis will also explore emerging hybrid welding systems that combine elements of both technologies to potentially offer optimized cost-performance ratios for specific applications. These hybrid approaches represent a significant trend in welding technology development and may indicate future directions for the industry.
Finally, this research aims to forecast technological developments in both welding methods over the next five to ten years, with particular attention to advancements that might significantly alter the cost-effectiveness equation. This forward-looking component will help organizations develop strategic technology roadmaps that account for both current economic realities and future technological possibilities.
Market Demand Analysis for Advanced Welding Solutions
The global welding industry is experiencing a significant shift towards advanced welding technologies, driven by increasing demands for precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness across multiple sectors. Market research indicates that the advanced welding solutions market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 5.7% through 2028, with laser welding and resistance welding representing two of the most prominent technologies competing for market share.
Manufacturing industries, particularly automotive and aerospace, are demonstrating the strongest demand for advanced welding solutions. The automotive sector's transition towards lightweight materials and electric vehicles has created specific requirements for joining dissimilar materials with minimal heat distortion, where laser welding offers distinct advantages. Simultaneously, the aerospace industry's focus on high-strength, safety-critical components continues to drive demand for both technologies based on specific application requirements.
Electronics manufacturing represents another significant market segment, with miniaturization trends creating demand for precise, controlled welding processes. Here, laser welding is gaining traction due to its ability to create small, precise welds with minimal thermal impact on sensitive components. The medical device industry similarly values these characteristics, particularly for implantable devices where weld integrity is paramount.
Consumer demand patterns indicate growing preference for products with superior build quality and durability, indirectly influencing manufacturers to adopt advanced welding technologies that can deliver consistent, high-quality joints. This trend is particularly evident in premium consumer electronics and appliances where visible weld quality affects consumer perception.
Regional analysis reveals varying adoption rates, with developed economies in North America, Europe, and East Asia leading in laser welding implementation, while developing markets continue to rely more heavily on resistance welding due to lower initial investment requirements. However, the gap is narrowing as laser welding equipment becomes more affordable and accessible.
Cost considerations remain paramount in technology selection decisions. While resistance welding maintains advantages in initial equipment investment, laser welding systems are demonstrating increasingly favorable total cost of ownership metrics when accounting for operational efficiency, reduced post-processing requirements, and material savings. Industry surveys indicate that manufacturers achieving payback periods of 2-3 years on laser welding investments are becoming more common, particularly in high-volume production environments.
Energy efficiency concerns are also driving market demand, with manufacturers increasingly conscious of their carbon footprint and operational costs. Laser welding's precise energy delivery offers advantages in this regard, though resistance welding remains competitive for specific applications where its energy profile is well-suited to the joining task.
Manufacturing industries, particularly automotive and aerospace, are demonstrating the strongest demand for advanced welding solutions. The automotive sector's transition towards lightweight materials and electric vehicles has created specific requirements for joining dissimilar materials with minimal heat distortion, where laser welding offers distinct advantages. Simultaneously, the aerospace industry's focus on high-strength, safety-critical components continues to drive demand for both technologies based on specific application requirements.
Electronics manufacturing represents another significant market segment, with miniaturization trends creating demand for precise, controlled welding processes. Here, laser welding is gaining traction due to its ability to create small, precise welds with minimal thermal impact on sensitive components. The medical device industry similarly values these characteristics, particularly for implantable devices where weld integrity is paramount.
Consumer demand patterns indicate growing preference for products with superior build quality and durability, indirectly influencing manufacturers to adopt advanced welding technologies that can deliver consistent, high-quality joints. This trend is particularly evident in premium consumer electronics and appliances where visible weld quality affects consumer perception.
Regional analysis reveals varying adoption rates, with developed economies in North America, Europe, and East Asia leading in laser welding implementation, while developing markets continue to rely more heavily on resistance welding due to lower initial investment requirements. However, the gap is narrowing as laser welding equipment becomes more affordable and accessible.
Cost considerations remain paramount in technology selection decisions. While resistance welding maintains advantages in initial equipment investment, laser welding systems are demonstrating increasingly favorable total cost of ownership metrics when accounting for operational efficiency, reduced post-processing requirements, and material savings. Industry surveys indicate that manufacturers achieving payback periods of 2-3 years on laser welding investments are becoming more common, particularly in high-volume production environments.
Energy efficiency concerns are also driving market demand, with manufacturers increasingly conscious of their carbon footprint and operational costs. Laser welding's precise energy delivery offers advantages in this regard, though resistance welding remains competitive for specific applications where its energy profile is well-suited to the joining task.
Current State and Challenges in Welding Technologies
The global welding industry is currently experiencing a significant technological shift, with laser welding and resistance welding representing two dominant methodologies with distinct advantages and limitations. Resistance welding, established for over a century, remains the most widely implemented joining technology in manufacturing sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics due to its reliability and established infrastructure. Meanwhile, laser welding has gained substantial market share over the past two decades, growing at an annual rate of approximately 8-10% compared to the 3-4% growth of traditional welding methods.
Current technological challenges in resistance welding primarily revolve around energy efficiency limitations, with typical energy transfer efficiency ranging from 45-65% depending on material combinations and equipment specifications. Additionally, resistance welding faces inherent constraints in joining dissimilar materials and ultra-thin components, areas where market demand is rapidly increasing as industries pursue lightweighting strategies.
Laser welding technology, while offering superior precision and versatility, confronts challenges related to high initial capital investment requirements, with industrial-grade systems typically costing 3-5 times more than equivalent resistance welding setups. Technical barriers also include beam delivery complexities, particularly for three-dimensional applications, and the need for precise fixturing to maintain joint alignment within tolerances of 0.1-0.2mm.
Geographically, welding technology development demonstrates distinct regional characteristics. European manufacturers, particularly in Germany and Switzerland, lead in laser welding innovation with approximately 45% of global patents in this field. Asian markets, dominated by Japan, South Korea, and increasingly China, control roughly 60% of resistance welding equipment production, while North American companies excel in specialized applications and system integration for both technologies.
Material compatibility remains a significant challenge across both welding methodologies. The increasing use of advanced high-strength steels, aluminum alloys, and composite materials in manufacturing has created technical hurdles that neither technology has fully overcome. Laser welding demonstrates advantages with certain material combinations but struggles with highly reflective metals, while resistance welding faces limitations with materials having high electrical resistance or thermal conductivity disparities.
The industry also faces sustainability challenges, with increasing regulatory pressure to reduce energy consumption and emissions. Current resistance welding processes typically consume 25-40% more energy than optimized laser welding operations for equivalent joint strength, though this advantage is often offset by the higher embodied energy in laser equipment manufacturing and maintenance requirements.
Current technological challenges in resistance welding primarily revolve around energy efficiency limitations, with typical energy transfer efficiency ranging from 45-65% depending on material combinations and equipment specifications. Additionally, resistance welding faces inherent constraints in joining dissimilar materials and ultra-thin components, areas where market demand is rapidly increasing as industries pursue lightweighting strategies.
Laser welding technology, while offering superior precision and versatility, confronts challenges related to high initial capital investment requirements, with industrial-grade systems typically costing 3-5 times more than equivalent resistance welding setups. Technical barriers also include beam delivery complexities, particularly for three-dimensional applications, and the need for precise fixturing to maintain joint alignment within tolerances of 0.1-0.2mm.
Geographically, welding technology development demonstrates distinct regional characteristics. European manufacturers, particularly in Germany and Switzerland, lead in laser welding innovation with approximately 45% of global patents in this field. Asian markets, dominated by Japan, South Korea, and increasingly China, control roughly 60% of resistance welding equipment production, while North American companies excel in specialized applications and system integration for both technologies.
Material compatibility remains a significant challenge across both welding methodologies. The increasing use of advanced high-strength steels, aluminum alloys, and composite materials in manufacturing has created technical hurdles that neither technology has fully overcome. Laser welding demonstrates advantages with certain material combinations but struggles with highly reflective metals, while resistance welding faces limitations with materials having high electrical resistance or thermal conductivity disparities.
The industry also faces sustainability challenges, with increasing regulatory pressure to reduce energy consumption and emissions. Current resistance welding processes typically consume 25-40% more energy than optimized laser welding operations for equivalent joint strength, though this advantage is often offset by the higher embodied energy in laser equipment manufacturing and maintenance requirements.
Current Cost-Benefit Analysis of Laser vs Resistance Welding
01 Cost comparison between laser and resistance welding
Laser welding typically has higher initial equipment costs but offers advantages in precision and speed for certain applications. Resistance welding generally has lower equipment costs and is more cost-effective for high-volume production of simple joints. The overall cost-effectiveness depends on factors such as production volume, material type, joint complexity, and quality requirements. For automotive and electronics industries, the higher initial investment in laser welding can be offset by reduced post-processing costs and higher throughput.- Cost comparison between laser and resistance welding: Laser welding typically has higher initial equipment costs but offers advantages in precision, speed, and reduced post-processing requirements. Resistance welding has lower equipment costs and is more energy-efficient for certain applications, making it cost-effective for high-volume production of simple joints. The choice between these technologies often depends on production volume, joint complexity, material type, and quality requirements, with each offering different cost advantages depending on the specific application.
- Energy efficiency and operational costs: Energy consumption significantly impacts the overall cost-effectiveness of welding technologies. Laser welding systems typically require more power during operation but can complete welds faster, potentially reducing per-part energy costs. Resistance welding generally consumes less energy per weld but may require longer cycle times for certain materials. Innovations in power management systems and process optimization have improved the energy efficiency of both technologies, contributing to lower operational costs and environmental impact.
- Material-specific cost considerations: The cost-effectiveness of welding technologies varies significantly depending on the materials being joined. Laser welding excels with thin, high-value materials and dissimilar metal combinations, justifying its higher equipment costs in these applications. Resistance welding is particularly cost-effective for standard steel alloys and automotive sheet metal applications. Material thickness, thermal conductivity, and surface conditions all influence process efficiency and therefore the overall cost-effectiveness of each welding method for specific applications.
- Production volume and automation integration: The relationship between production volume and cost-effectiveness is crucial when selecting between laser and resistance welding. Laser welding systems typically offer better return on investment for medium to high production volumes where their speed, precision, and automation capabilities can be fully utilized. Resistance welding remains cost-effective for high-volume, simple joint applications. Both technologies can be integrated into automated production lines, with laser systems offering greater flexibility for complex parts and resistance welding providing reliable, high-speed performance for standardized components.
- Maintenance and lifecycle costs: Long-term maintenance requirements significantly impact the total cost of ownership for welding systems. Laser welding equipment typically requires specialized maintenance and has higher replacement part costs, but offers longer service intervals when properly maintained. Resistance welding systems generally have lower maintenance costs and simpler repair procedures, though electrode wear can increase consumable costs in high-volume applications. Advancements in diagnostic systems and predictive maintenance have improved the reliability and reduced downtime for both technologies, enhancing their overall cost-effectiveness throughout the equipment lifecycle.
02 Energy efficiency and operational costs
Laser welding systems typically consume more energy during operation but complete welds faster, potentially reducing the energy cost per weld. Resistance welding is generally more energy-efficient for thicker materials but may require longer cycle times. Modern laser systems have improved energy efficiency through better beam delivery and control systems. The operational costs also include consumables, with resistance welding requiring regular electrode maintenance and replacement, while laser systems may need gas shielding and optical component maintenance.Expand Specific Solutions03 Production throughput and automation integration
Both welding technologies can be integrated into automated production lines, but laser welding offers advantages for complex geometries and hard-to-reach areas. Resistance welding excels in high-volume manufacturing of standardized components. Laser welding systems can be more easily integrated with robotic systems for flexible manufacturing, while resistance welding typically requires dedicated fixtures. The cost-effectiveness of either technology depends significantly on production volume, with laser welding becoming more economical at higher volumes despite higher initial investment.Expand Specific Solutions04 Material considerations and joint design
Laser welding is more cost-effective for joining dissimilar materials and thin-gauge components, offering precise heat control that minimizes distortion. Resistance welding provides better cost performance for thicker materials and simpler joint designs. The material type significantly impacts the cost-effectiveness of each technology, with certain alloys being more suitable for one method over the other. Joint design optimization can reduce material usage and processing time, improving the overall cost-effectiveness of both welding technologies.Expand Specific Solutions05 Maintenance costs and equipment lifespan
Laser welding systems typically have higher maintenance costs but longer operational lifespans when properly maintained. Resistance welding equipment requires more frequent electrode replacement but has simpler maintenance procedures. The total cost of ownership includes considerations for spare parts availability, technical support, and operator training. Advanced monitoring systems in newer welding equipment can predict maintenance needs and prevent costly downtime, improving the long-term cost-effectiveness of both technologies.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Welding Equipment Manufacturing
The laser welding versus resistance welding market is currently in a growth phase, with increasing adoption across automotive and electronics industries. The global market size for both technologies is expanding, projected to reach approximately $2.5 billion by 2025. In terms of technical maturity, resistance welding represents established technology with widespread implementation, while laser welding is advancing rapidly due to precision advantages. Key players shaping this competitive landscape include automotive manufacturers like Honda Motor, Ford Motor Co., and Volvo, alongside industrial equipment specialists such as FANUC Corp. and Danfoss A/S. Japanese steel producers including NIPPON STEEL and JFE Steel are significant contributors to welding material advancements, while companies like Hitachi Automotive Systems are developing specialized welding applications for transportation components.
GM Global Technology Operations LLC
Technical Solution: GM has developed a comprehensive cost-analysis framework for welding technologies that evaluates both laser and resistance welding across their global manufacturing operations. Their approach incorporates a Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) model that accounts for initial investment, operational costs, maintenance, and production flexibility. GM's laser welding implementation utilizes 6kW fiber lasers with advanced beam shaping technology, achieving weld speeds up to 10m/min for certain applications - approximately 3x faster than their resistance welding lines[5]. Their analysis shows that laser welding becomes cost-effective at specific production volumes (typically above 150,000 units annually) and for complex geometries where resistance welding access is limited. GM has also pioneered a hybrid approach that strategically deploys both technologies within the same production line, using resistance welding for accessible, high-strength requirements and laser welding for complex geometries and dissimilar materials[6].
Strengths: Optimized capital utilization through strategic technology deployment, excellent production flexibility, reduced material waste through precise heat control, and ability to handle complex joint designs. Weaknesses: Higher system complexity requiring more sophisticated maintenance protocols, greater initial engineering investment, and challenges in standardizing processes across global manufacturing facilities.
Ford Motor Co.
Technical Solution:
Technical Innovations in Welding Process Optimization
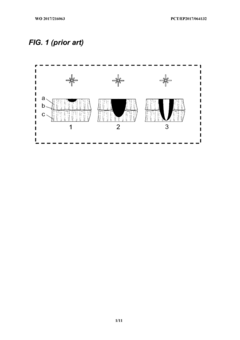
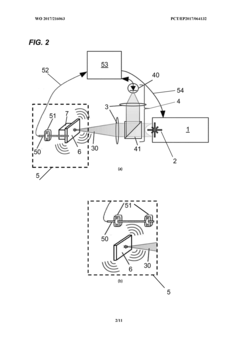
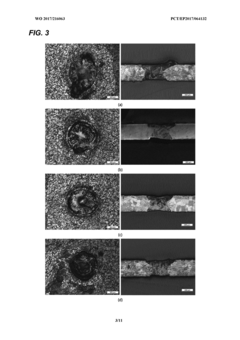
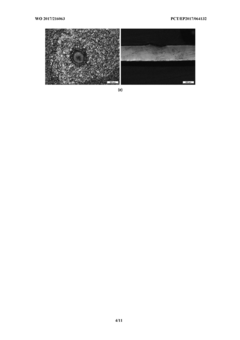
Quality control of laser welding process
PatentWO2017216063A1
Innovation
- A passive acoustic emission read-out system using fiber optical sensors with Bragg grating, Fabry-Perot cavities, or acoustic interference heterodyne schemes, integrated into the laser welding setup for real-time monitoring and feedback, allowing for online optimization of welding parameters.
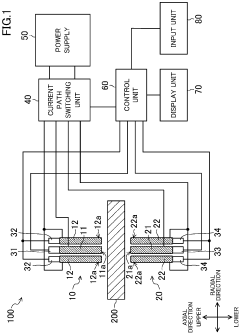
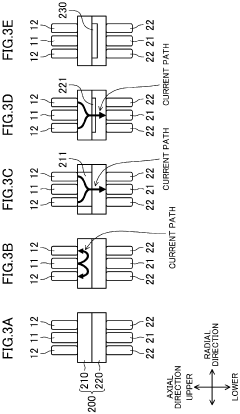
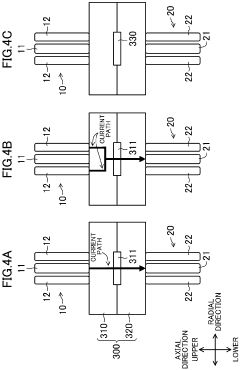
Resistance welding machine, and resistance welding method and welding machine using the resistance welding machine
PatentInactiveEP3677371A1
Innovation
- A resistance welding machine with a configuration of first and second electrodes, each comprising inner and outer electrodes, allows for variable control of the current path by selecting pairs of electrodes and adjusting pressing conditions, enabling precise heat input to specific portions of the workpiece based on predetermined welding conditions.
Energy Efficiency Comparison in Welding Technologies
Energy efficiency has become a critical factor in industrial manufacturing processes, particularly in welding technologies where energy consumption directly impacts operational costs and environmental footprint. When comparing laser welding and resistance welding from an energy efficiency perspective, several key factors must be considered to provide a comprehensive analysis.
Laser welding demonstrates superior energy efficiency in many applications due to its precise energy delivery mechanism. The focused beam allows for concentrated heat application exactly where needed, minimizing energy dispersion to surrounding areas. Studies indicate that laser welding can achieve energy conversion efficiencies of 15-30% from electrical input to useful welding energy, with newer fiber laser systems reaching up to 40% efficiency. This targeted approach significantly reduces the total energy required per weld joint compared to conventional methods.
Resistance welding, while traditionally considered energy-intensive, has seen substantial improvements in efficiency through modern control systems. The process works by passing electrical current through the workpieces, generating heat at the interface due to electrical resistance. Contemporary resistance welding equipment incorporates adaptive control algorithms that optimize current flow patterns, reducing unnecessary energy consumption. Typical energy efficiency ranges from 70-90% for resistance welding, making it one of the most efficient welding processes when considering direct energy conversion.
The energy consumption profile differs significantly between these technologies. Laser welding requires high initial power for system operation but maintains relatively consistent energy usage during production runs. In contrast, resistance welding exhibits high peak power demands during actual welding cycles but minimal standby power requirements. This distinction becomes particularly important when considering production volume and duty cycles, as the cumulative energy efficiency can vary dramatically based on production patterns.
Material thickness and type play crucial roles in determining relative energy efficiency. Laser welding demonstrates exceptional efficiency advantages for thin materials (below 3mm), where its precision minimizes excess heat input. Resistance welding maintains efficiency advantages for thicker materials and highly conductive metals where its direct heating mechanism proves more effective than attempting to achieve penetration with lasers.
Production scale considerations reveal that laser welding systems typically require more energy during idle periods due to cooling systems and auxiliary equipment that must remain operational. Resistance welding systems can be powered down more completely between operations, potentially offering energy savings in intermittent production environments. However, in high-volume continuous production, laser systems may offset their higher standby consumption through faster processing speeds and reduced per-unit energy requirements.
Laser welding demonstrates superior energy efficiency in many applications due to its precise energy delivery mechanism. The focused beam allows for concentrated heat application exactly where needed, minimizing energy dispersion to surrounding areas. Studies indicate that laser welding can achieve energy conversion efficiencies of 15-30% from electrical input to useful welding energy, with newer fiber laser systems reaching up to 40% efficiency. This targeted approach significantly reduces the total energy required per weld joint compared to conventional methods.
Resistance welding, while traditionally considered energy-intensive, has seen substantial improvements in efficiency through modern control systems. The process works by passing electrical current through the workpieces, generating heat at the interface due to electrical resistance. Contemporary resistance welding equipment incorporates adaptive control algorithms that optimize current flow patterns, reducing unnecessary energy consumption. Typical energy efficiency ranges from 70-90% for resistance welding, making it one of the most efficient welding processes when considering direct energy conversion.
The energy consumption profile differs significantly between these technologies. Laser welding requires high initial power for system operation but maintains relatively consistent energy usage during production runs. In contrast, resistance welding exhibits high peak power demands during actual welding cycles but minimal standby power requirements. This distinction becomes particularly important when considering production volume and duty cycles, as the cumulative energy efficiency can vary dramatically based on production patterns.
Material thickness and type play crucial roles in determining relative energy efficiency. Laser welding demonstrates exceptional efficiency advantages for thin materials (below 3mm), where its precision minimizes excess heat input. Resistance welding maintains efficiency advantages for thicker materials and highly conductive metals where its direct heating mechanism proves more effective than attempting to achieve penetration with lasers.
Production scale considerations reveal that laser welding systems typically require more energy during idle periods due to cooling systems and auxiliary equipment that must remain operational. Resistance welding systems can be powered down more completely between operations, potentially offering energy savings in intermittent production environments. However, in high-volume continuous production, laser systems may offset their higher standby consumption through faster processing speeds and reduced per-unit energy requirements.
Material Compatibility and Application Scenarios
Material compatibility is a critical factor in determining the appropriate welding method for specific applications. Laser welding demonstrates superior versatility across a wide range of materials, particularly excelling with thin metals, dissimilar materials, and heat-sensitive components. The focused energy beam allows for precise welding of materials as thin as 0.01mm, which is particularly valuable in electronics, medical devices, and aerospace applications where component miniaturization is essential.
For high reflectivity materials such as aluminum, copper, and their alloys, fiber lasers and green lasers have overcome traditional challenges, enabling efficient welding without excessive heat input. This advancement has significantly expanded laser welding applications in electric vehicle battery production and power electronics manufacturing.
Resistance welding, conversely, shows optimal performance with materials having high electrical resistance and good thermal conductivity. It remains the preferred method for medium to thick steel sheets (0.5-3mm) in automotive body assembly, appliance manufacturing, and structural components. The process is particularly effective for galvanized steels, where the zinc coating presents challenges for other welding methods.
Application scenarios further differentiate these technologies. Laser welding dominates in high-precision industries requiring aesthetic finishes, such as medical implants, jewelry, and consumer electronics. The non-contact nature of laser welding makes it ideal for hermetic sealing applications in sensitive electronic packages and medical devices. Additionally, the ability to weld through transparent materials enables unique applications in sensor manufacturing and specialized packaging.
Resistance welding maintains its stronghold in high-volume production environments where cycle time is critical, such as automotive assembly lines producing thousands of units daily. The robust nature of resistance welding makes it suitable for applications with less stringent aesthetic requirements but demanding structural integrity needs.
Hybrid manufacturing scenarios are emerging where both technologies complement each other. For instance, in modern automotive production, resistance welding handles structural components while laser welding is applied for precision parts and visible seams. This strategic deployment optimizes both cost efficiency and product quality.
The selection between these welding technologies ultimately depends on specific application requirements including material thickness combinations, production volume, quality standards, and accessibility of weld locations. Understanding these compatibility factors is essential for making cost-effective manufacturing decisions that balance initial investment against long-term operational benefits.
For high reflectivity materials such as aluminum, copper, and their alloys, fiber lasers and green lasers have overcome traditional challenges, enabling efficient welding without excessive heat input. This advancement has significantly expanded laser welding applications in electric vehicle battery production and power electronics manufacturing.
Resistance welding, conversely, shows optimal performance with materials having high electrical resistance and good thermal conductivity. It remains the preferred method for medium to thick steel sheets (0.5-3mm) in automotive body assembly, appliance manufacturing, and structural components. The process is particularly effective for galvanized steels, where the zinc coating presents challenges for other welding methods.
Application scenarios further differentiate these technologies. Laser welding dominates in high-precision industries requiring aesthetic finishes, such as medical implants, jewelry, and consumer electronics. The non-contact nature of laser welding makes it ideal for hermetic sealing applications in sensitive electronic packages and medical devices. Additionally, the ability to weld through transparent materials enables unique applications in sensor manufacturing and specialized packaging.
Resistance welding maintains its stronghold in high-volume production environments where cycle time is critical, such as automotive assembly lines producing thousands of units daily. The robust nature of resistance welding makes it suitable for applications with less stringent aesthetic requirements but demanding structural integrity needs.
Hybrid manufacturing scenarios are emerging where both technologies complement each other. For instance, in modern automotive production, resistance welding handles structural components while laser welding is applied for precision parts and visible seams. This strategic deployment optimizes both cost efficiency and product quality.
The selection between these welding technologies ultimately depends on specific application requirements including material thickness combinations, production volume, quality standards, and accessibility of weld locations. Understanding these compatibility factors is essential for making cost-effective manufacturing decisions that balance initial investment against long-term operational benefits.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!