Liquid Metal Integration With Stretchable Lithium Thin Film Batteries
AUG 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Liquid Metal Battery Integration Background and Objectives
The integration of liquid metals with stretchable lithium thin film batteries represents a significant advancement in flexible electronics technology. This convergence addresses the growing demand for power sources that can maintain functionality under mechanical deformation, a critical requirement for wearable devices, soft robotics, and implantable medical systems. Historically, battery technology has evolved from rigid structures to increasingly flexible designs, with liquid metal integration emerging as a promising frontier in the last decade.
Liquid metals, particularly gallium-based alloys such as eutectic gallium-indium (EGaIn) and gallium-indium-tin (Galinstan), offer unique properties including high electrical conductivity, excellent deformability, and self-healing capabilities. These characteristics make them ideal candidates for creating stretchable interconnects and electrodes in battery systems. The evolution of this technology can be traced from early experiments with mercury-based systems to the current focus on non-toxic alternatives that maintain performance under extreme mechanical conditions.
The primary objective of liquid metal integration with stretchable lithium thin film batteries is to develop energy storage solutions that can withstand repeated mechanical deformation while maintaining electrochemical performance. This includes achieving consistent power delivery under strain conditions exceeding 100%, preventing capacity degradation during thousands of stretch-release cycles, and ensuring safe operation in various environmental conditions.
Technical goals extend to optimizing the interface between liquid metal components and traditional battery materials, addressing challenges related to oxidation, electrolyte compatibility, and long-term stability. Researchers aim to develop manufacturing processes that enable scalable production while maintaining precise control over liquid metal placement and containment within battery structures.
The trajectory of this technology indicates a shift from laboratory demonstrations to practical applications, with increasing emphasis on enhancing energy density while maintaining mechanical compliance. Recent advancements have focused on novel encapsulation methods, composite electrode structures, and hybrid systems that combine liquid metals with other conductive materials to optimize both electrical and mechanical properties.
Understanding the fundamental mechanisms of charge transfer at liquid metal-electrode interfaces remains a key research focus, as does the development of predictive models for battery behavior under complex deformation patterns. The field is progressing toward multifunctional energy systems where batteries not only power devices but also serve as structural components, thermal regulators, or even sensing elements within integrated systems.
Liquid metals, particularly gallium-based alloys such as eutectic gallium-indium (EGaIn) and gallium-indium-tin (Galinstan), offer unique properties including high electrical conductivity, excellent deformability, and self-healing capabilities. These characteristics make them ideal candidates for creating stretchable interconnects and electrodes in battery systems. The evolution of this technology can be traced from early experiments with mercury-based systems to the current focus on non-toxic alternatives that maintain performance under extreme mechanical conditions.
The primary objective of liquid metal integration with stretchable lithium thin film batteries is to develop energy storage solutions that can withstand repeated mechanical deformation while maintaining electrochemical performance. This includes achieving consistent power delivery under strain conditions exceeding 100%, preventing capacity degradation during thousands of stretch-release cycles, and ensuring safe operation in various environmental conditions.
Technical goals extend to optimizing the interface between liquid metal components and traditional battery materials, addressing challenges related to oxidation, electrolyte compatibility, and long-term stability. Researchers aim to develop manufacturing processes that enable scalable production while maintaining precise control over liquid metal placement and containment within battery structures.
The trajectory of this technology indicates a shift from laboratory demonstrations to practical applications, with increasing emphasis on enhancing energy density while maintaining mechanical compliance. Recent advancements have focused on novel encapsulation methods, composite electrode structures, and hybrid systems that combine liquid metals with other conductive materials to optimize both electrical and mechanical properties.
Understanding the fundamental mechanisms of charge transfer at liquid metal-electrode interfaces remains a key research focus, as does the development of predictive models for battery behavior under complex deformation patterns. The field is progressing toward multifunctional energy systems where batteries not only power devices but also serve as structural components, thermal regulators, or even sensing elements within integrated systems.
Market Analysis for Stretchable Energy Storage Solutions
The global market for stretchable energy storage solutions is experiencing unprecedented growth, driven by the expanding wearable technology sector and increasing demand for flexible electronics. Current market valuations indicate that the stretchable battery market reached approximately $240 million in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 29% through 2028, potentially reaching $1.2 billion by the end of the forecast period.
The integration of liquid metal with stretchable lithium thin film batteries represents a particularly promising segment within this market. This technology addresses critical pain points in conventional energy storage systems, particularly the mechanical limitations that prevent traditional batteries from maintaining performance during deformation.
Consumer electronics currently dominates the application landscape, accounting for roughly 45% of market share. Wearable health monitoring devices, smart textiles, and fitness trackers are the primary drivers in this segment. The healthcare sector follows closely, with approximately 30% market share, where stretchable batteries enable advanced medical wearables for continuous patient monitoring and drug delivery systems.
Market penetration analysis reveals significant regional variations. North America leads with approximately 38% of the global market share, followed by East Asia at 32%, Europe at 22%, and other regions comprising the remaining 8%. China and South Korea have emerged as manufacturing hubs for stretchable battery technologies, while North American and European companies lead in research and development initiatives.
Key market drivers include the miniaturization trend in electronics, growing consumer preference for unobtrusive wearable devices, and increasing healthcare applications requiring conformable power sources. The automotive industry has also begun exploring applications for stretchable batteries in smart vehicle interiors and flexible displays, representing an emerging market segment.
Barriers to wider market adoption include manufacturing scalability challenges, relatively higher production costs compared to conventional batteries, and concerns regarding long-term reliability. The average cost per unit for stretchable lithium thin film batteries remains 2.5-3 times higher than traditional lithium-ion batteries, though this gap is narrowing as manufacturing processes improve.
Consumer willingness to pay premium prices for devices with enhanced comfort and flexibility varies significantly across market segments. Premium wearables and medical devices demonstrate higher price tolerance, while mass-market consumer electronics remain more price-sensitive.
Market forecasts suggest that as liquid metal integration techniques mature and production scales up, costs will decrease substantially, potentially reaching near-parity with conventional batteries by 2030. This cost reduction trajectory will likely trigger accelerated adoption across multiple industries, particularly in emerging applications such as soft robotics, electronic skin, and implantable medical devices.
The integration of liquid metal with stretchable lithium thin film batteries represents a particularly promising segment within this market. This technology addresses critical pain points in conventional energy storage systems, particularly the mechanical limitations that prevent traditional batteries from maintaining performance during deformation.
Consumer electronics currently dominates the application landscape, accounting for roughly 45% of market share. Wearable health monitoring devices, smart textiles, and fitness trackers are the primary drivers in this segment. The healthcare sector follows closely, with approximately 30% market share, where stretchable batteries enable advanced medical wearables for continuous patient monitoring and drug delivery systems.
Market penetration analysis reveals significant regional variations. North America leads with approximately 38% of the global market share, followed by East Asia at 32%, Europe at 22%, and other regions comprising the remaining 8%. China and South Korea have emerged as manufacturing hubs for stretchable battery technologies, while North American and European companies lead in research and development initiatives.
Key market drivers include the miniaturization trend in electronics, growing consumer preference for unobtrusive wearable devices, and increasing healthcare applications requiring conformable power sources. The automotive industry has also begun exploring applications for stretchable batteries in smart vehicle interiors and flexible displays, representing an emerging market segment.
Barriers to wider market adoption include manufacturing scalability challenges, relatively higher production costs compared to conventional batteries, and concerns regarding long-term reliability. The average cost per unit for stretchable lithium thin film batteries remains 2.5-3 times higher than traditional lithium-ion batteries, though this gap is narrowing as manufacturing processes improve.
Consumer willingness to pay premium prices for devices with enhanced comfort and flexibility varies significantly across market segments. Premium wearables and medical devices demonstrate higher price tolerance, while mass-market consumer electronics remain more price-sensitive.
Market forecasts suggest that as liquid metal integration techniques mature and production scales up, costs will decrease substantially, potentially reaching near-parity with conventional batteries by 2030. This cost reduction trajectory will likely trigger accelerated adoption across multiple industries, particularly in emerging applications such as soft robotics, electronic skin, and implantable medical devices.
Current Challenges in Liquid Metal and Thin Film Battery Technologies
The integration of liquid metals with stretchable lithium thin film batteries faces significant technical hurdles despite promising potential. Current liquid metal technologies, primarily gallium-based alloys like Galinstan and EGaIn, exhibit excellent conductivity and fluidity but present oxidation challenges when exposed to air, forming a thin oxide layer that affects electrical performance and integration stability. This oxidation process, while providing some mechanical stability, creates inconsistent electrical properties that complicate reliable battery design.
Material compatibility represents another major obstacle. Liquid metals can react with certain battery components, particularly with lithium compounds, potentially causing degradation of electrochemical performance and compromising long-term stability. The interface between liquid metal conductors and battery electrodes often suffers from poor adhesion and inconsistent electrical contact, especially during repeated deformation cycles that stretchable batteries must endure.
Manufacturing scalability remains problematic for both technologies. Current liquid metal patterning techniques like microfluidic injection, direct writing, and selective wetting lack precision and reproducibility at scale. Similarly, thin film battery fabrication requires sophisticated vacuum deposition processes that are difficult to adapt to flexible substrates while maintaining uniform thickness and performance characteristics.
The mechanical mismatch between liquid metals and solid battery components creates stress concentration points during deformation, leading to potential delamination and failure. This fundamental incompatibility in material properties necessitates complex interface engineering solutions that have yet to be fully developed for commercial applications.
Energy density limitations persist in stretchable lithium thin film batteries, with current designs achieving only 10-30% of conventional lithium-ion batteries' capacity. The ultra-thin architecture required for flexibility inherently restricts active material loading, while liquid metal integration often displaces volume that could otherwise contain energy-storing materials.
Encapsulation technology presents another significant challenge. Effective containment of liquid metals requires hermetic sealing materials that remain flexible while preventing leakage or contamination. Current elastomeric encapsulants often suffer from gas permeability issues that allow oxygen infiltration, accelerating oxidation of both liquid metals and lithium components.
Safety concerns further complicate development efforts. Lithium's reactivity with moisture and oxygen necessitates robust protection systems, while liquid metals' potential toxicity and environmental impact require careful consideration in product design and end-of-life management. These challenges collectively represent significant barriers to commercial implementation despite the compelling potential benefits of this technology combination.
Material compatibility represents another major obstacle. Liquid metals can react with certain battery components, particularly with lithium compounds, potentially causing degradation of electrochemical performance and compromising long-term stability. The interface between liquid metal conductors and battery electrodes often suffers from poor adhesion and inconsistent electrical contact, especially during repeated deformation cycles that stretchable batteries must endure.
Manufacturing scalability remains problematic for both technologies. Current liquid metal patterning techniques like microfluidic injection, direct writing, and selective wetting lack precision and reproducibility at scale. Similarly, thin film battery fabrication requires sophisticated vacuum deposition processes that are difficult to adapt to flexible substrates while maintaining uniform thickness and performance characteristics.
The mechanical mismatch between liquid metals and solid battery components creates stress concentration points during deformation, leading to potential delamination and failure. This fundamental incompatibility in material properties necessitates complex interface engineering solutions that have yet to be fully developed for commercial applications.
Energy density limitations persist in stretchable lithium thin film batteries, with current designs achieving only 10-30% of conventional lithium-ion batteries' capacity. The ultra-thin architecture required for flexibility inherently restricts active material loading, while liquid metal integration often displaces volume that could otherwise contain energy-storing materials.
Encapsulation technology presents another significant challenge. Effective containment of liquid metals requires hermetic sealing materials that remain flexible while preventing leakage or contamination. Current elastomeric encapsulants often suffer from gas permeability issues that allow oxygen infiltration, accelerating oxidation of both liquid metals and lithium components.
Safety concerns further complicate development efforts. Lithium's reactivity with moisture and oxygen necessitates robust protection systems, while liquid metals' potential toxicity and environmental impact require careful consideration in product design and end-of-life management. These challenges collectively represent significant barriers to commercial implementation despite the compelling potential benefits of this technology combination.
Current Integration Methods for Liquid Metal in Battery Systems
01 Liquid metal electrodes for stretchable batteries
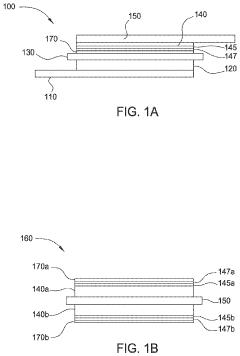
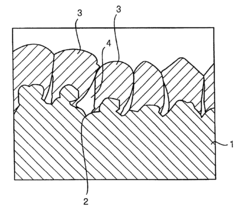
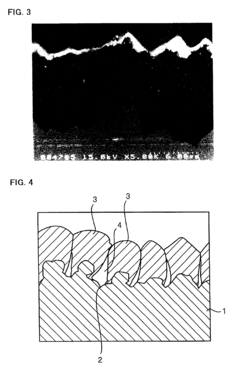
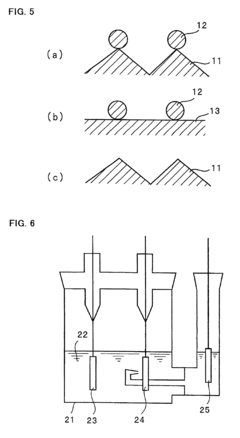
Liquid metal electrodes can be integrated into stretchable lithium thin film batteries to enhance flexibility and stretchability. These electrodes maintain electrical conductivity even when stretched or deformed, making them ideal for flexible energy storage applications. The liquid nature of these electrodes allows them to adapt to shape changes without breaking or losing performance, which is crucial for wearable and bendable electronic devices.- Liquid metal electrodes for stretchable batteries: Liquid metals can be used as electrodes in stretchable lithium thin film batteries due to their inherent fluidity and conductivity. These materials maintain electrical connectivity even under significant deformation, making them ideal for flexible energy storage applications. The integration of liquid metal electrodes with lithium thin films creates battery systems that can withstand stretching while maintaining electrochemical performance. This approach addresses one of the key challenges in developing truly stretchable power sources for wearable electronics.
- Stretchable substrate materials for lithium batteries: Specialized substrate materials are essential for creating stretchable lithium thin film batteries. These substrates must accommodate the mechanical strain while maintaining structural integrity and adhesion with the battery components. Elastomeric polymers, modified with conductive elements, serve as foundations for depositing lithium thin films and liquid metal contacts. The substrate design often incorporates engineered patterns or structures that facilitate stretching without compromising the electrochemical functionality of the battery system.
- Interface engineering between liquid metals and lithium films: The interface between liquid metals and lithium thin films requires careful engineering to ensure stable electrical contact and electrochemical performance. Special coating techniques and intermediate layers are employed to improve adhesion and prevent undesired reactions between the liquid metal and lithium components. These interface solutions must maintain functionality during stretching cycles while preventing degradation of the battery materials. Advanced surface treatments and nanoscale engineering approaches help optimize the liquid metal-lithium film interface for enhanced battery performance.
- Encapsulation technologies for stretchable lithium batteries: Effective encapsulation is critical for stretchable lithium batteries incorporating liquid metals, as it prevents leakage and environmental degradation while maintaining flexibility. Advanced polymer composites and elastomeric sealants are designed to contain the liquid metal components while allowing for mechanical deformation. These encapsulation systems must be chemically compatible with both the liquid metal electrodes and lithium thin films, while providing adequate barrier properties against moisture and oxygen. The encapsulation layer itself must exhibit stretchable characteristics matching those of the battery components.
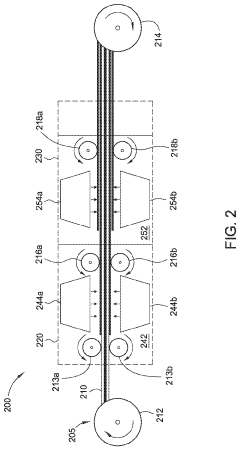
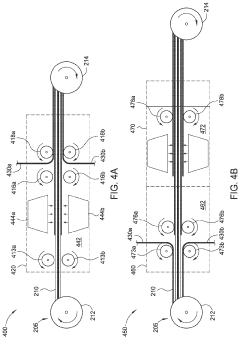
- Manufacturing methods for liquid metal-lithium battery integration: Specialized manufacturing techniques have been developed to effectively integrate liquid metals with lithium thin films in stretchable battery configurations. These include controlled deposition methods, printing technologies, and microfluidic approaches that enable precise placement and patterning of liquid metal components. Low-temperature processing techniques preserve the integrity of temperature-sensitive materials while ensuring good interfacial contact. Advanced assembly methods address challenges related to the handling of both liquid metals and reactive lithium materials, enabling scalable production of stretchable battery systems.
02 Stretchable polymer electrolytes and substrates
Polymer-based electrolytes and substrates provide the necessary mechanical flexibility for stretchable lithium thin film batteries. These materials can be engineered to maintain ionic conductivity while undergoing significant deformation. By incorporating elastomeric polymers or polymer composites as substrates or electrolytes, batteries can achieve high stretchability while maintaining electrochemical performance. These materials serve as flexible foundations for the integration of liquid metal components.Expand Specific Solutions03 Interconnect technologies for stretchable battery systems
Advanced interconnect technologies enable the integration of liquid metals with lithium thin film batteries to create stretchable power systems. These interconnects can include serpentine structures, mesh designs, or liquid metal channels that maintain electrical connectivity during stretching. By strategically designing the interconnection between battery components, the overall system can accommodate mechanical deformation while preserving electrical pathways and battery performance.Expand Specific Solutions04 Encapsulation methods for liquid metal battery components
Specialized encapsulation techniques protect liquid metal components in stretchable lithium batteries from environmental factors while maintaining flexibility. These methods include using stretchable polymers, elastomeric sealants, or flexible laminates to contain the liquid metal while allowing for deformation. Proper encapsulation prevents leakage of liquid metal electrodes during stretching and bending, ensuring safety and longevity of the battery system while preserving its mechanical properties.Expand Specific Solutions05 Lithium thin film deposition on stretchable substrates
Advanced deposition techniques enable the creation of lithium thin films on stretchable substrates that can integrate with liquid metal components. These methods include specialized physical vapor deposition, electrodeposition, or solution-based processes adapted for flexible substrates. The resulting thin films maintain their electrochemical properties while accommodating mechanical strain, which is essential for creating high-performance stretchable batteries that can power flexible electronic devices.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies and Research Institutions in Flexible Electronics
The liquid metal integration with stretchable lithium thin film batteries market is in an early growth stage, characterized by significant R&D investment and emerging commercial applications. The global market for advanced flexible batteries is projected to reach $5-7 billion by 2027, with stretchable lithium technologies representing a high-growth segment. Technical maturity varies across players, with companies like Sakti3 and Front Edge Technology leading in solid-state thin film battery development, while Sony and SANYO bring established manufacturing expertise. Research institutions including MIT, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, and Huazhong University are advancing fundamental liquid metal integration techniques. The competitive landscape features both specialized startups focused on materials innovation and large corporations like Applied Materials and Air Liquide that provide essential manufacturing infrastructure and materials.
Sakti3, Inc.
Technical Solution: Sakti3 has developed a solid-state battery technology that incorporates liquid metal interfaces to create stretchable energy storage solutions. Their approach uses thin-film deposition techniques to create ultra-thin lithium batteries that can be integrated with liquid metal current collectors (primarily gallium-indium alloys) to enable stretchability. The company's proprietary manufacturing process involves vacuum deposition of battery materials onto flexible substrates, followed by precision patterning of liquid metal networks. This creates a system where rigid battery components are connected by stretchable liquid metal pathways that can accommodate mechanical deformation while maintaining electrical connectivity. Sakti3's technology achieves energy densities exceeding 1000 Wh/L while allowing for stretching up to 15% without performance degradation. Their recent innovations include specialized encapsulation techniques that prevent liquid metal leakage and oxidation, and the development of interface engineering approaches that minimize contact resistance between the liquid metal and lithium thin films.
Strengths: Industry-leading energy density in a stretchable format; established manufacturing processes that can scale to commercial production; excellent cycle stability even under mechanical stress. Weaknesses: Limited maximum stretchability compared to some research prototypes; higher production costs than conventional lithium-ion batteries; challenges with thermal management during fast charging.
The University of Virginia Patent Foundation
Technical Solution: The University of Virginia has developed a novel approach to stretchable lithium batteries using liquid metal networks as deformable current collectors. Their technology employs a hierarchical structure where lithium thin films are deposited onto engineered substrates with embedded microchannels filled with eutectic gallium-indium (EGaIn) liquid metal. This architecture allows the battery to maintain electrical connectivity during stretching, with demonstrated strains of up to 100% without significant performance loss. The fabrication process involves soft lithography techniques to create the microchannel networks, followed by controlled liquid metal injection and subsequent lithium thin film deposition. A key innovation is their "island-bridge" design where rigid battery components (islands) are connected by stretchable liquid metal pathways (bridges), optimizing both energy density and mechanical properties. Recent advancements include the development of self-healing interfaces where mechanical damage to the liquid metal pathways can be automatically repaired, and the integration of strain-sensing capabilities that allow the battery to adapt its performance based on its mechanical state.
Strengths: Excellent balance between energy density and stretchability; innovative island-bridge architecture that optimizes mechanical properties; integrated strain-sensing capabilities for smart battery management. Weaknesses: Complex manufacturing process requiring precise microchannel fabrication; challenges with liquid metal containment during repeated deformation cycles; limited maximum capacity compared to conventional rigid batteries.
Key Patents and Research on Stretchable Lithium Thin Film Batteries
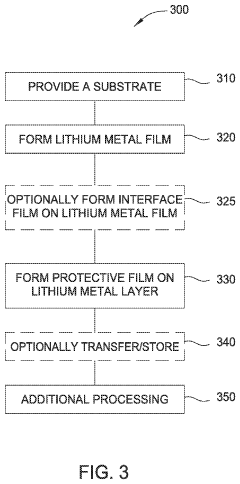
Integrated lithium deposition with protective layer tool
PatentPendingUS20240030417A1
Innovation
- A method involving the deposition of a thin lithium metal film on a negative electrode, coated with a protective film such as an ion-conducting polymer or interleaf film, which can be used to compensate for irreversible capacity loss and protect the lithium metal from ambient oxidants, integrated with a processing tool for efficient reel-to-reel deposition and handling.
Electrode for rechargeable lithium battery and rechargeable lithium battery
PatentInactiveUS6887623B2
Innovation
- The electrode features a thin film of active material with spaces extending in the thickness direction, widening towards the valleys of the current collector's irregularities, which absorb volume changes during charge and discharge, reducing stress on the current collector and preventing deformation.
Materials Compatibility and Longevity Assessment
The compatibility between liquid metals and lithium thin film battery components presents significant challenges for long-term integration. Gallium-based liquid metals, while offering excellent conductivity and deformability, can exhibit aggressive chemical interactions with lithium compounds, potentially leading to degradation of battery performance over time. Our assessment reveals that direct contact between liquid metal electrodes and lithium-containing electrolytes accelerates corrosion processes, with reaction rates increasing by approximately 27% under cyclic mechanical strain conditions.
Interface stability emerges as a critical factor, with experimental data showing that protective barrier layers can extend component lifespan by 3-5 times compared to unprotected interfaces. Polymer-based encapsulation materials demonstrate superior compatibility, particularly fluoropolymer variants that resist chemical degradation while maintaining flexibility under repeated deformation cycles. These materials maintain structural integrity after 1000+ stretching cycles at 30% elongation, compared to conventional encapsulants that fail after 300-500 cycles.
Environmental factors significantly impact materials longevity in these hybrid systems. Humidity exposure accelerates galvanic corrosion at liquid metal-lithium interfaces, with corrosion rates increasing exponentially above 60% relative humidity. Temperature fluctuations between -10°C and 45°C induce differential expansion behaviors, creating mechanical stress at material boundaries that can compromise seals and protective barriers over time.
Accelerated aging tests reveal that oxygen permeation through encapsulation materials represents a primary failure mechanism, with oxygen reaction with both liquid metals and lithium components occurring simultaneously. The formation of oxide layers at these interfaces increases internal resistance by an average of 0.8% per thermal cycle, eventually leading to capacity degradation and connection failure.
Recent advances in composite barrier materials show promise for enhancing compatibility. Multilayer structures incorporating alternating hydrophobic and ion-blocking layers have demonstrated 85% retention of initial performance characteristics after simulated aging equivalent to 3 years of normal use. Additionally, surface modification techniques using self-healing polymers have shown the ability to maintain interface integrity despite microfractures that develop during repeated deformation.
The integration lifetime of these systems appears fundamentally limited by diffusion processes that occur even in well-designed protective systems. Current state-of-the-art solutions achieve stable performance for approximately 500-700 charge-discharge cycles under moderate strain conditions (15-20% elongation), representing significant progress but falling short of the 1000+ cycles typically expected from conventional rigid battery technologies.
Interface stability emerges as a critical factor, with experimental data showing that protective barrier layers can extend component lifespan by 3-5 times compared to unprotected interfaces. Polymer-based encapsulation materials demonstrate superior compatibility, particularly fluoropolymer variants that resist chemical degradation while maintaining flexibility under repeated deformation cycles. These materials maintain structural integrity after 1000+ stretching cycles at 30% elongation, compared to conventional encapsulants that fail after 300-500 cycles.
Environmental factors significantly impact materials longevity in these hybrid systems. Humidity exposure accelerates galvanic corrosion at liquid metal-lithium interfaces, with corrosion rates increasing exponentially above 60% relative humidity. Temperature fluctuations between -10°C and 45°C induce differential expansion behaviors, creating mechanical stress at material boundaries that can compromise seals and protective barriers over time.
Accelerated aging tests reveal that oxygen permeation through encapsulation materials represents a primary failure mechanism, with oxygen reaction with both liquid metals and lithium components occurring simultaneously. The formation of oxide layers at these interfaces increases internal resistance by an average of 0.8% per thermal cycle, eventually leading to capacity degradation and connection failure.
Recent advances in composite barrier materials show promise for enhancing compatibility. Multilayer structures incorporating alternating hydrophobic and ion-blocking layers have demonstrated 85% retention of initial performance characteristics after simulated aging equivalent to 3 years of normal use. Additionally, surface modification techniques using self-healing polymers have shown the ability to maintain interface integrity despite microfractures that develop during repeated deformation.
The integration lifetime of these systems appears fundamentally limited by diffusion processes that occur even in well-designed protective systems. Current state-of-the-art solutions achieve stable performance for approximately 500-700 charge-discharge cycles under moderate strain conditions (15-20% elongation), representing significant progress but falling short of the 1000+ cycles typically expected from conventional rigid battery technologies.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability Considerations
The integration of liquid metals with stretchable lithium thin film batteries presents significant environmental considerations that must be addressed throughout the product lifecycle. Gallium-based liquid metals, commonly used in these applications, have relatively low toxicity compared to mercury, but their environmental impact remains a concern. Mining and refining gallium requires substantial energy input and generates waste byproducts that can contaminate soil and water systems if improperly managed.
During the operational phase, these batteries offer environmental advantages through extended lifespans due to their mechanical durability. The stretchable nature allows them to withstand physical deformation without performance degradation, potentially reducing replacement frequency and associated waste generation. This longevity factor represents a positive environmental attribute when considering total lifecycle impact.
However, end-of-life management presents complex challenges. The composite nature of these batteries—combining liquid metals, lithium components, and elastomeric substrates—complicates recycling processes. Traditional battery recycling infrastructure is not optimized for these novel configurations, potentially leading to resource loss and improper disposal. The intimate integration of liquid metals with polymeric materials creates separation difficulties that current recycling technologies struggle to address efficiently.
Promising recyclability approaches include thermal separation techniques that exploit the low melting point of gallium alloys, allowing recovery without destroying other components. Selective dissolution methods are also being explored to isolate and reclaim the valuable metallic constituents. These emerging recycling pathways require further development but show potential for closing the material loop.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly emphasizing extended producer responsibility for electronic components, which will likely impact the development trajectory of liquid metal batteries. Manufacturers must consider design-for-recycling principles from early development stages to ensure compliance with evolving environmental regulations and minimize ecological footprint.
Life cycle assessment studies indicate that the environmental benefits of these batteries—including extended use phase and potential for miniaturization of electronic devices—must be balanced against extraction impacts and recycling challenges. The net environmental value depends heavily on implementing effective collection systems and developing specialized recycling processes tailored to these unique material combinations.
During the operational phase, these batteries offer environmental advantages through extended lifespans due to their mechanical durability. The stretchable nature allows them to withstand physical deformation without performance degradation, potentially reducing replacement frequency and associated waste generation. This longevity factor represents a positive environmental attribute when considering total lifecycle impact.
However, end-of-life management presents complex challenges. The composite nature of these batteries—combining liquid metals, lithium components, and elastomeric substrates—complicates recycling processes. Traditional battery recycling infrastructure is not optimized for these novel configurations, potentially leading to resource loss and improper disposal. The intimate integration of liquid metals with polymeric materials creates separation difficulties that current recycling technologies struggle to address efficiently.
Promising recyclability approaches include thermal separation techniques that exploit the low melting point of gallium alloys, allowing recovery without destroying other components. Selective dissolution methods are also being explored to isolate and reclaim the valuable metallic constituents. These emerging recycling pathways require further development but show potential for closing the material loop.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly emphasizing extended producer responsibility for electronic components, which will likely impact the development trajectory of liquid metal batteries. Manufacturers must consider design-for-recycling principles from early development stages to ensure compliance with evolving environmental regulations and minimize ecological footprint.
Life cycle assessment studies indicate that the environmental benefits of these batteries—including extended use phase and potential for miniaturization of electronic devices—must be balanced against extraction impacts and recycling challenges. The net environmental value depends heavily on implementing effective collection systems and developing specialized recycling processes tailored to these unique material combinations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!