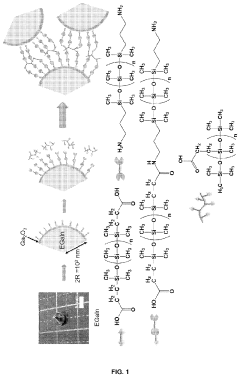
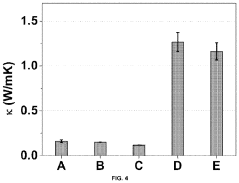
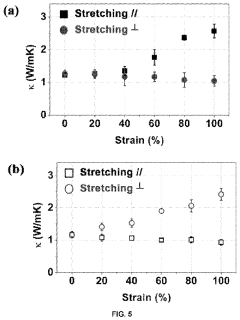
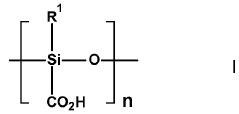
Mechanically Robust Liquid Metal Composite Films Fabrication
AUG 28, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Liquid Metal Composite Films Background and Objectives
Liquid metals, particularly gallium-based alloys, have emerged as a revolutionary class of materials in the past decade due to their unique combination of metallic and fluidic properties. These materials exhibit excellent electrical conductivity, thermal properties, and deformability while maintaining a low melting point that enables them to remain liquid at or near room temperature. The evolution of liquid metal technology has progressed from basic material characterization to advanced applications in flexible electronics, soft robotics, and biomedical devices, establishing a clear trajectory toward multifunctional composite systems.
The development of mechanically robust liquid metal composite films represents a critical advancement in this field, addressing the inherent challenges of liquid metal handling and integration. Traditional liquid metals suffer from poor mechanical stability, oxidation susceptibility, and difficulties in precise patterning and adhesion to substrates. These limitations have historically restricted their practical implementation in commercial applications despite their promising electrical and thermal characteristics.
Current research objectives in liquid metal composite film fabrication center on creating stable, durable structures that preserve the advantageous properties of liquid metals while overcoming their mechanical limitations. Key technical goals include developing composite architectures that prevent liquid metal leakage under mechanical stress, improving adhesion to various substrate materials, enhancing oxidation resistance, and establishing scalable manufacturing processes suitable for industrial production.
The integration of liquid metals with polymers, elastomers, and other supporting matrices has shown significant promise in creating composite films with enhanced mechanical properties. These composites aim to maintain electrical conductivity even under substantial deformation, enabling applications in stretchable electronics, conformable sensors, and dynamic interfaces that can withstand real-world operating conditions.
Recent technological breakthroughs have demonstrated progress in encapsulation techniques, surface modification methods, and novel composite architectures that significantly improve the mechanical robustness of liquid metal films. These advances have expanded the potential application space to include wearable computing, healthcare monitoring, energy harvesting systems, and reconfigurable electronics.
The ultimate objective of research in mechanically robust liquid metal composite films is to bridge the gap between laboratory demonstrations and practical, reliable components for next-generation flexible electronic systems. This requires not only addressing fundamental material challenges but also developing comprehensive fabrication protocols that ensure consistency, reliability, and compatibility with existing manufacturing infrastructure. Success in this domain would enable transformative advances in human-machine interfaces, soft robotics, and bioelectronics where traditional rigid electronic materials cannot meet the demanding requirements of flexibility, stretchability, and conformability.
The development of mechanically robust liquid metal composite films represents a critical advancement in this field, addressing the inherent challenges of liquid metal handling and integration. Traditional liquid metals suffer from poor mechanical stability, oxidation susceptibility, and difficulties in precise patterning and adhesion to substrates. These limitations have historically restricted their practical implementation in commercial applications despite their promising electrical and thermal characteristics.
Current research objectives in liquid metal composite film fabrication center on creating stable, durable structures that preserve the advantageous properties of liquid metals while overcoming their mechanical limitations. Key technical goals include developing composite architectures that prevent liquid metal leakage under mechanical stress, improving adhesion to various substrate materials, enhancing oxidation resistance, and establishing scalable manufacturing processes suitable for industrial production.
The integration of liquid metals with polymers, elastomers, and other supporting matrices has shown significant promise in creating composite films with enhanced mechanical properties. These composites aim to maintain electrical conductivity even under substantial deformation, enabling applications in stretchable electronics, conformable sensors, and dynamic interfaces that can withstand real-world operating conditions.
Recent technological breakthroughs have demonstrated progress in encapsulation techniques, surface modification methods, and novel composite architectures that significantly improve the mechanical robustness of liquid metal films. These advances have expanded the potential application space to include wearable computing, healthcare monitoring, energy harvesting systems, and reconfigurable electronics.
The ultimate objective of research in mechanically robust liquid metal composite films is to bridge the gap between laboratory demonstrations and practical, reliable components for next-generation flexible electronic systems. This requires not only addressing fundamental material challenges but also developing comprehensive fabrication protocols that ensure consistency, reliability, and compatibility with existing manufacturing infrastructure. Success in this domain would enable transformative advances in human-machine interfaces, soft robotics, and bioelectronics where traditional rigid electronic materials cannot meet the demanding requirements of flexibility, stretchability, and conformability.
Market Applications and Demand Analysis for Liquid Metal Films
The liquid metal composite films market is experiencing significant growth driven by the unique properties these materials offer, particularly their combination of electrical conductivity, flexibility, and now enhanced mechanical robustness. Current market analysis indicates a growing demand across multiple industries, with the global smart materials market—which includes liquid metals—projected to reach $98.2 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 14.9%.
The electronics industry represents the largest application segment for mechanically robust liquid metal films. With the expansion of flexible electronics, these materials are increasingly sought for creating stretchable circuits, bendable displays, and wearable technology components. The wearable technology market alone is expected to exceed $70 billion by 2026, with liquid metal films positioned as key enabling materials for next-generation devices.
Healthcare applications constitute another rapidly expanding market segment. Mechanically robust liquid metal films are being developed for biomedical sensors, drug delivery systems, and soft robotics for surgical applications. The medical wearables market is projected to grow at 26.4% CAGR through 2025, creating substantial demand for materials that can withstand biological environments while maintaining flexibility and conductivity.
The automotive and aerospace sectors are emerging as significant consumers of liquid metal composite films. These industries require materials that can withstand vibration, temperature fluctuations, and mechanical stress while providing electromagnetic shielding and thermal management. The automotive electronics market is expected to reach $382 billion by 2026, with advanced materials like liquid metal films playing an increasingly important role.
Energy applications represent another growth area, particularly in thermal management systems and flexible solar cells. As renewable energy adoption accelerates, demand for advanced materials that can improve efficiency and durability of energy systems continues to rise.
Regional analysis shows North America and Asia-Pacific leading in adoption, with China, South Korea, and Japan showing particularly strong growth trajectories in liquid metal applications. This is largely driven by their robust electronics manufacturing ecosystems and significant R&D investments in advanced materials.
Market challenges include scaling production processes to industrial levels while maintaining quality and reducing costs. Currently, the relatively high production cost of mechanically robust liquid metal films limits mass-market adoption, though this is expected to improve as manufacturing techniques advance and economies of scale are achieved.
The electronics industry represents the largest application segment for mechanically robust liquid metal films. With the expansion of flexible electronics, these materials are increasingly sought for creating stretchable circuits, bendable displays, and wearable technology components. The wearable technology market alone is expected to exceed $70 billion by 2026, with liquid metal films positioned as key enabling materials for next-generation devices.
Healthcare applications constitute another rapidly expanding market segment. Mechanically robust liquid metal films are being developed for biomedical sensors, drug delivery systems, and soft robotics for surgical applications. The medical wearables market is projected to grow at 26.4% CAGR through 2025, creating substantial demand for materials that can withstand biological environments while maintaining flexibility and conductivity.
The automotive and aerospace sectors are emerging as significant consumers of liquid metal composite films. These industries require materials that can withstand vibration, temperature fluctuations, and mechanical stress while providing electromagnetic shielding and thermal management. The automotive electronics market is expected to reach $382 billion by 2026, with advanced materials like liquid metal films playing an increasingly important role.
Energy applications represent another growth area, particularly in thermal management systems and flexible solar cells. As renewable energy adoption accelerates, demand for advanced materials that can improve efficiency and durability of energy systems continues to rise.
Regional analysis shows North America and Asia-Pacific leading in adoption, with China, South Korea, and Japan showing particularly strong growth trajectories in liquid metal applications. This is largely driven by their robust electronics manufacturing ecosystems and significant R&D investments in advanced materials.
Market challenges include scaling production processes to industrial levels while maintaining quality and reducing costs. Currently, the relatively high production cost of mechanically robust liquid metal films limits mass-market adoption, though this is expected to improve as manufacturing techniques advance and economies of scale are achieved.
Technical Challenges in Mechanical Robustness of Liquid Metal Composites
The development of liquid metal composite films with enhanced mechanical robustness faces several significant technical challenges that currently limit their widespread application. Gallium-based liquid metals, while offering excellent electrical conductivity and unique deformability, inherently suffer from poor mechanical stability due to their liquid nature. When fabricated into thin films, these materials tend to experience rupture, delamination, and shape instability under mechanical stress.
A primary challenge lies in achieving strong interfacial bonding between the liquid metal particles and the polymer matrix. The high surface tension of liquid metals (approximately 624 mN/m for gallium at room temperature) creates poor wettability with most polymer substrates, resulting in weak adhesion and subsequent mechanical failure during deformation. Current approaches using surface oxidation or chemical modification show promise but often compromise electrical performance.
Maintaining electrical conductivity while enhancing mechanical properties presents another significant hurdle. As mechanical reinforcement strategies are implemented, they frequently disrupt the conductive pathways within the composite. The trade-off between conductivity and mechanical robustness remains a critical balance that researchers struggle to optimize, particularly when stretchability exceeds 100%.
The oxidation behavior of liquid metals further complicates fabrication processes. While the native oxide layer (primarily Ga₂O₃) can improve adhesion to certain substrates, it also increases electrical resistance and can lead to mechanical brittleness at interfaces. Controlling oxide formation during processing remains challenging, especially in ambient conditions where oxidation occurs rapidly.
Scalable manufacturing represents another substantial obstacle. Current laboratory techniques for producing mechanically robust liquid metal composites often involve complex, multi-step processes that are difficult to scale industrially. Methods such as microfluidic processing, sonication-assisted dispersion, and mechanical sintering each present unique challenges in maintaining consistency across larger production volumes.
Environmental stability poses additional concerns, as gallium-based liquid metals can experience property degradation through oxidation, corrosion, or mechanical fatigue over time. This is particularly problematic in applications requiring long-term reliability under varying environmental conditions.
The development of standardized testing protocols for evaluating mechanical robustness also lags behind material development. Current characterization methods vary widely across research groups, making direct comparisons between different composite formulations difficult and hindering systematic improvement efforts.
A primary challenge lies in achieving strong interfacial bonding between the liquid metal particles and the polymer matrix. The high surface tension of liquid metals (approximately 624 mN/m for gallium at room temperature) creates poor wettability with most polymer substrates, resulting in weak adhesion and subsequent mechanical failure during deformation. Current approaches using surface oxidation or chemical modification show promise but often compromise electrical performance.
Maintaining electrical conductivity while enhancing mechanical properties presents another significant hurdle. As mechanical reinforcement strategies are implemented, they frequently disrupt the conductive pathways within the composite. The trade-off between conductivity and mechanical robustness remains a critical balance that researchers struggle to optimize, particularly when stretchability exceeds 100%.
The oxidation behavior of liquid metals further complicates fabrication processes. While the native oxide layer (primarily Ga₂O₃) can improve adhesion to certain substrates, it also increases electrical resistance and can lead to mechanical brittleness at interfaces. Controlling oxide formation during processing remains challenging, especially in ambient conditions where oxidation occurs rapidly.
Scalable manufacturing represents another substantial obstacle. Current laboratory techniques for producing mechanically robust liquid metal composites often involve complex, multi-step processes that are difficult to scale industrially. Methods such as microfluidic processing, sonication-assisted dispersion, and mechanical sintering each present unique challenges in maintaining consistency across larger production volumes.
Environmental stability poses additional concerns, as gallium-based liquid metals can experience property degradation through oxidation, corrosion, or mechanical fatigue over time. This is particularly problematic in applications requiring long-term reliability under varying environmental conditions.
The development of standardized testing protocols for evaluating mechanical robustness also lags behind material development. Current characterization methods vary widely across research groups, making direct comparisons between different composite formulations difficult and hindering systematic improvement efforts.
Current Fabrication Methods for Mechanically Robust Liquid Metal Films
01 Composite structure design for enhanced mechanical robustness
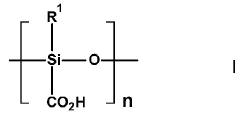
Liquid metal composite films can achieve improved mechanical robustness through strategic composite structure design. By incorporating supporting materials such as polymers, nanomaterials, or other structural elements, the inherent fluidity of liquid metals can be constrained while maintaining their unique properties. These composite structures distribute mechanical stress more effectively, preventing fracture and deformation under strain. The layered or sandwich-type configurations particularly enhance the film's ability to withstand bending, stretching, and other mechanical deformations while preserving electrical conductivity.- Composite structure design for enhanced mechanical robustness: Liquid metal composite films can achieve enhanced mechanical robustness through strategic composite structure design. This includes layering different materials, creating sandwich structures, or incorporating reinforcing elements within the liquid metal matrix. These composite structures distribute stress more effectively, prevent crack propagation, and maintain electrical conductivity even under mechanical deformation. The combination of rigid supporting materials with the fluid properties of liquid metals creates films that can withstand bending, stretching, and other mechanical stresses.
- Polymer-liquid metal composites for flexibility and durability: Incorporating liquid metals within polymer matrices creates composite films with both flexibility and mechanical durability. The polymer component provides structural support and elasticity, while the liquid metal maintains electrical functionality. These composites can withstand repeated deformation cycles without performance degradation. Various polymer types can be used depending on the application requirements, including elastomers for stretchable electronics and more rigid polymers for applications requiring higher structural integrity. The interface between the polymer and liquid metal is critical for maintaining adhesion during mechanical stress.
- Surface treatment and coating techniques for improved adhesion: Surface treatment and specialized coating techniques significantly improve the adhesion of liquid metal films to substrates, enhancing mechanical robustness. Methods include plasma treatment, chemical etching, and application of adhesion promoters. These treatments modify surface energy and create mechanical interlocking between the liquid metal and substrate. Improved adhesion prevents delamination during mechanical stress and extends the operational lifetime of the composite films. Multi-layer coating approaches can create gradient interfaces that distribute stress more effectively between dissimilar materials.
- Nano-reinforcement for mechanical strength enhancement: Incorporating nanomaterials such as carbon nanotubes, graphene, or metal nanoparticles into liquid metal films significantly enhances their mechanical robustness. These nano-reinforcements create a network structure within the liquid metal that resists deformation while maintaining electrical conductivity. The nanomaterials act as stress transfer elements and crack deflectors, preventing catastrophic failure under mechanical load. The dispersion quality and interfacial bonding between the nanomaterials and liquid metal matrix are crucial factors affecting the mechanical performance of these composite films.
- Self-healing mechanisms for damage recovery: Self-healing mechanisms incorporated into liquid metal composite films allow for recovery from mechanical damage, significantly improving long-term robustness. These mechanisms utilize the fluid nature of liquid metals to flow back into damaged areas, restoring electrical and mechanical functionality. Triggering methods include thermal activation, pressure application, or chemical stimuli. Some advanced composites combine encapsulated liquid metals with responsive polymer matrices that facilitate controlled release and flow of the liquid metal component upon damage. This self-healing capability extends the operational lifetime of devices using these films, particularly in applications subject to repeated mechanical stress.
02 Surface modification techniques for liquid metal films
Surface modification of liquid metal films significantly improves their mechanical robustness. Techniques include controlled oxidation to form protective oxide layers, chemical treatments to modify surface properties, and functionalization with various compounds to enhance adhesion to substrates. These modifications create more stable interfaces between the liquid metal and surrounding materials, preventing delamination and improving durability. Surface-modified liquid metal films demonstrate superior resistance to environmental factors while maintaining flexibility and conductivity, making them suitable for applications requiring mechanical reliability.Expand Specific Solutions03 Substrate selection and preparation for mechanical stability
The choice and preparation of substrates play crucial roles in determining the mechanical robustness of liquid metal composite films. Substrates with appropriate surface energy, roughness, and chemical compatibility provide better adhesion for liquid metals. Pre-treatments such as plasma activation, chemical etching, or application of adhesion promoters significantly enhance the mechanical stability of the resulting composite films. Flexible substrates with matched mechanical properties help prevent delamination during deformation, while rigid substrates can provide structural support for applications requiring dimensional stability.Expand Specific Solutions04 Encapsulation methods for protecting liquid metal films
Encapsulation techniques provide effective protection for liquid metal films against mechanical damage and environmental degradation. By sealing liquid metals within protective layers of polymers, elastomers, or other barrier materials, these methods prevent leakage and oxidation while enhancing structural integrity. Advanced encapsulation approaches include microfluidic channels, core-shell structures, and multilayer barrier systems that allow controlled deformation while maintaining film continuity. These protected liquid metal composites demonstrate improved reliability under mechanical stress, making them suitable for flexible electronics and other applications requiring durability.Expand Specific Solutions05 Processing techniques for optimizing mechanical properties
Specialized processing techniques can optimize the mechanical robustness of liquid metal composite films. Methods such as controlled alloying, thermal annealing, mechanical conditioning, and precise deposition processes significantly influence the final mechanical properties. Advanced manufacturing approaches like screen printing, inkjet printing, and vacuum deposition allow for precise control over film thickness, uniformity, and microstructure. Post-processing treatments can further enhance mechanical stability by relieving internal stresses and promoting beneficial microstructural changes, resulting in liquid metal composite films with superior resistance to mechanical failure.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Research Institutions and Companies in Liquid Metal Technology
The liquid metal composite films fabrication market is in its growth phase, characterized by increasing research and development activities across academic institutions and industrial players. The market size is expanding due to rising applications in flexible electronics, soft robotics, and biomedical devices, with projections indicating significant growth potential. Technologically, this field is advancing rapidly but remains in mid-maturity, with key players developing proprietary approaches. Leading companies like Sumitomo Chemical, Teijin, and BASF are investing in advanced materials research, while academic institutions such as Ningbo Institute of Industrial Technology and Shenzhen University are pioneering fundamental innovations. Japanese corporations including Sharp, Furukawa Electric, and Asahi Kasei demonstrate strong patent portfolios, suggesting a competitive advantage in commercialization pathways for mechanically robust liquid metal technologies.
Ningbo Institute of Industrial Technology
Technical Solution: Ningbo Institute of Industrial Technology has developed an innovative approach to liquid metal composite films fabrication focusing on gallium-based liquid metals (LMs). Their technique involves encapsulating liquid metal droplets within elastomeric matrices using a microfluidic-assisted process. This method creates mechanically robust films with controlled droplet size distribution (typically 10-100 μm) and uniform dispersion. The institute has pioneered a surface modification technique that improves the interfacial adhesion between the liquid metal and polymer matrix, significantly enhancing mechanical stability under deformation. Their composite films maintain electrical conductivity even when stretched to 300% of their original length[1], making them highly suitable for flexible electronics applications. The institute has also developed a self-healing mechanism where ruptured liquid metal droplets can reconnect under mechanical stimuli, restoring electrical pathways after damage[3].
Strengths: Superior stretchability while maintaining electrical conductivity; excellent self-healing properties; good interfacial adhesion between liquid metal and polymer matrix. Weaknesses: Relatively complex manufacturing process requiring specialized equipment; potential oxidation issues with gallium-based liquid metals in certain environments; higher production costs compared to conventional conductive materials.
Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry CAS
Technical Solution: The Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry CAS has developed a groundbreaking approach to mechanically robust liquid metal composite films using eutectic gallium-indium (EGaIn) alloys embedded in specialized polymer matrices. Their proprietary technique involves a controlled oxidation process that creates a thin oxide shell (approximately 1-3 nm thick) around liquid metal particles, preventing coalescence while maintaining the liquid properties inside. This institute has pioneered a "freeze-casting" method where liquid metal is dispersed in a polymer solution and rapidly solidified to create hierarchical structures with exceptional mechanical properties. Their composite films demonstrate remarkable electrical conductivity (>104 S/cm) even under severe mechanical deformation, with stretchability exceeding 400%[2]. Additionally, they've developed surface functionalization techniques that enhance the wettability of liquid metals on various substrates, enabling direct printing and patterning capabilities for complex electronic circuits[4].
Strengths: Exceptional electrical performance under extreme mechanical deformation; innovative freeze-casting technique creates hierarchical structures with superior properties; excellent adhesion to various substrates. Weaknesses: The oxidation layer formation requires precise control of environmental conditions; higher material costs compared to traditional conductive materials; potential long-term stability issues in harsh environments.
Key Patents and Innovations in Liquid Metal Composite Technology
Flexible effective heat transport composites for thermal interface applications
PatentPendingUS20240174816A1
Innovation
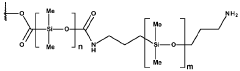
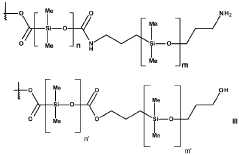
- A composite material comprising a crosslinked polymeric matrix with surface-functionalized liquid metal particles bonded through amide and/or ester bonds, providing enhanced thermal conductivity and flexibility while maintaining electrical insulation, even under mechanical strain.
Flexible effective heat transport composites for thermal interface applications
PatentWO2022235211A1
Innovation
- A composite material comprising a crosslinked polymeric matrix with surface-functionalized liquid metal particles bonded via amide or ester bonds, providing enhanced thermal conductivity and flexibility, while maintaining electrical insulation through controlled particle size and arrangement.
Material Compatibility and Interface Engineering Considerations
The compatibility between liquid metals and substrate materials represents a critical factor in developing mechanically robust composite films. Gallium-based liquid metals, particularly eutectic gallium-indium (EGaIn) and gallium-indium-tin (Galinstan), exhibit unique chemical behaviors that must be carefully managed during fabrication processes. These metals readily form oxide layers when exposed to oxygen, which significantly affects their adhesion properties and mechanical stability when interfacing with various substrate materials.
Polymer substrates such as PDMS, polyimide, and PET demonstrate varying degrees of compatibility with liquid metals. PDMS, while offering excellent flexibility, presents challenges due to its hydrophobic nature that can impede wetting by liquid metals. Surface modification techniques including oxygen plasma treatment and chemical functionalization have proven effective in enhancing the adhesion between liquid metals and polymer substrates, creating stronger interfacial bonds that contribute to mechanical robustness.
Metal substrates introduce different compatibility considerations, as gallium-based liquid metals can form intermetallic compounds with certain metals like aluminum, leading to potential embrittlement and degradation of mechanical properties. Conversely, noble metals such as gold and platinum exhibit minimal reactivity with liquid metals, making them suitable for interface layers in composite film structures. The strategic selection of metal substrates or interface layers based on their reactivity profiles with liquid metals is essential for maintaining long-term mechanical stability.
Interface engineering approaches have emerged as powerful strategies for enhancing the mechanical robustness of liquid metal composite films. These include the development of gradient interfaces that distribute mechanical stress more effectively, preventing delamination under strain conditions. Additionally, the incorporation of nanomaterials such as carbon nanotubes or graphene at interfaces has demonstrated significant improvements in adhesion strength and mechanical durability, creating mechanical interlocking mechanisms that reinforce the composite structure.
Surface energy management represents another crucial aspect of interface engineering for liquid metal composites. Techniques such as micro/nano-texturing of substrate surfaces can create controlled wetting behaviors that enhance liquid metal adhesion while maintaining desired electrical properties. The strategic manipulation of surface energy gradients enables directed self-assembly of liquid metal components, facilitating more precise control over composite film architecture and mechanical performance.
Temperature considerations must also be addressed in interface engineering, as the thermal expansion coefficient mismatch between liquid metals and substrate materials can induce mechanical stress during temperature fluctuations. Designing interface layers that accommodate these differential expansion behaviors is essential for applications requiring thermal cycling stability, particularly in electronic devices operating across varying temperature ranges.
Polymer substrates such as PDMS, polyimide, and PET demonstrate varying degrees of compatibility with liquid metals. PDMS, while offering excellent flexibility, presents challenges due to its hydrophobic nature that can impede wetting by liquid metals. Surface modification techniques including oxygen plasma treatment and chemical functionalization have proven effective in enhancing the adhesion between liquid metals and polymer substrates, creating stronger interfacial bonds that contribute to mechanical robustness.
Metal substrates introduce different compatibility considerations, as gallium-based liquid metals can form intermetallic compounds with certain metals like aluminum, leading to potential embrittlement and degradation of mechanical properties. Conversely, noble metals such as gold and platinum exhibit minimal reactivity with liquid metals, making them suitable for interface layers in composite film structures. The strategic selection of metal substrates or interface layers based on their reactivity profiles with liquid metals is essential for maintaining long-term mechanical stability.
Interface engineering approaches have emerged as powerful strategies for enhancing the mechanical robustness of liquid metal composite films. These include the development of gradient interfaces that distribute mechanical stress more effectively, preventing delamination under strain conditions. Additionally, the incorporation of nanomaterials such as carbon nanotubes or graphene at interfaces has demonstrated significant improvements in adhesion strength and mechanical durability, creating mechanical interlocking mechanisms that reinforce the composite structure.
Surface energy management represents another crucial aspect of interface engineering for liquid metal composites. Techniques such as micro/nano-texturing of substrate surfaces can create controlled wetting behaviors that enhance liquid metal adhesion while maintaining desired electrical properties. The strategic manipulation of surface energy gradients enables directed self-assembly of liquid metal components, facilitating more precise control over composite film architecture and mechanical performance.
Temperature considerations must also be addressed in interface engineering, as the thermal expansion coefficient mismatch between liquid metals and substrate materials can induce mechanical stress during temperature fluctuations. Designing interface layers that accommodate these differential expansion behaviors is essential for applications requiring thermal cycling stability, particularly in electronic devices operating across varying temperature ranges.
Scalability and Manufacturing Process Optimization
The scalability of liquid metal composite film fabrication represents a critical challenge for transitioning from laboratory-scale demonstrations to industrial production. Current manufacturing processes typically involve manual techniques such as spin coating, blade coating, or screen printing, which present significant limitations for large-scale implementation. These methods often suffer from inconsistent film thickness, non-uniform liquid metal particle distribution, and limited production throughput.
To address these challenges, several manufacturing process optimizations have been developed. Roll-to-roll processing has emerged as a promising approach, enabling continuous production of liquid metal composite films with improved uniformity and significantly higher throughput. This technique allows for precise control of film thickness through adjustable roller gaps and speeds, while maintaining consistent mechanical properties across large surface areas.
Surface treatment optimization has also proven essential for enhancing adhesion between liquid metal particles and polymer matrices. Plasma treatment and chemical functionalization methods have been refined to improve interfacial bonding, resulting in composite films with superior mechanical robustness and durability. These treatments can now be integrated into continuous manufacturing lines, eliminating production bottlenecks.
Temperature control during processing represents another critical optimization factor. Research has demonstrated that maintaining precise temperature gradients during liquid metal particle formation and polymer curing significantly impacts the mechanical properties of the resulting films. Advanced thermal management systems have been developed to ensure consistent temperature profiles across large-scale production equipment.
Automation and real-time quality control systems have revolutionized manufacturing efficiency. Inline optical inspection systems can now detect defects and variations in particle distribution, while machine learning algorithms adjust processing parameters in real-time to maintain product specifications. These systems have reduced waste by up to 40% while improving batch-to-batch consistency.
Cost optimization remains a significant focus area. Recent innovations in liquid metal synthesis have reduced raw material costs by approximately 30%, while improved polymer formulations have enhanced compatibility with existing manufacturing infrastructure. Additionally, energy consumption has been reduced through process refinements and equipment redesign, further improving economic viability for large-scale production.
Environmental considerations have also driven manufacturing process improvements. Closed-loop solvent recovery systems and water-based processing alternatives have reduced environmental impact while maintaining product performance. These sustainable manufacturing approaches align with increasing regulatory requirements and consumer preferences for environmentally responsible production methods.
To address these challenges, several manufacturing process optimizations have been developed. Roll-to-roll processing has emerged as a promising approach, enabling continuous production of liquid metal composite films with improved uniformity and significantly higher throughput. This technique allows for precise control of film thickness through adjustable roller gaps and speeds, while maintaining consistent mechanical properties across large surface areas.
Surface treatment optimization has also proven essential for enhancing adhesion between liquid metal particles and polymer matrices. Plasma treatment and chemical functionalization methods have been refined to improve interfacial bonding, resulting in composite films with superior mechanical robustness and durability. These treatments can now be integrated into continuous manufacturing lines, eliminating production bottlenecks.
Temperature control during processing represents another critical optimization factor. Research has demonstrated that maintaining precise temperature gradients during liquid metal particle formation and polymer curing significantly impacts the mechanical properties of the resulting films. Advanced thermal management systems have been developed to ensure consistent temperature profiles across large-scale production equipment.
Automation and real-time quality control systems have revolutionized manufacturing efficiency. Inline optical inspection systems can now detect defects and variations in particle distribution, while machine learning algorithms adjust processing parameters in real-time to maintain product specifications. These systems have reduced waste by up to 40% while improving batch-to-batch consistency.
Cost optimization remains a significant focus area. Recent innovations in liquid metal synthesis have reduced raw material costs by approximately 30%, while improved polymer formulations have enhanced compatibility with existing manufacturing infrastructure. Additionally, energy consumption has been reduced through process refinements and equipment redesign, further improving economic viability for large-scale production.
Environmental considerations have also driven manufacturing process improvements. Closed-loop solvent recovery systems and water-based processing alternatives have reduced environmental impact while maintaining product performance. These sustainable manufacturing approaches align with increasing regulatory requirements and consumer preferences for environmentally responsible production methods.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!