Lithium Chloride vs Lithium Carbonate: Chemical Stability
AUG 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Compounds Evolution and Research Objectives
Lithium compounds have undergone significant evolution since their discovery in the early 19th century. Initially identified in mineral form, lithium's journey from obscurity to industrial prominence reflects the broader narrative of chemical innovation. The first major milestone occurred in 1817 when Johan August Arfwedson discovered lithium in petalite ore, though it wasn't isolated as a pure metal until 1821 by William Thomas Brande. Early applications were primarily medicinal, with lithium salts used to treat gout and mental disorders.
The mid-20th century marked a pivotal shift as lithium compounds transitioned from pharmaceutical curiosities to industrial staples. Lithium carbonate (Li₂CO₃) emerged as the predominant commercial form due to its relative stability and versatility in applications ranging from ceramics to aluminum production. Concurrently, lithium chloride (LiCl) found specialized applications in air conditioning systems and as a precursor in lithium metal production.
The energy crisis of the 1970s catalyzed renewed interest in lithium chemistry, particularly for energy storage applications. This period saw intensive research into the electrochemical properties of various lithium compounds, establishing the foundation for modern lithium-ion battery technology. The chemical stability differences between lithium chloride and lithium carbonate became increasingly relevant during this era, as researchers sought optimal compounds for specific applications.
Recent decades have witnessed exponential growth in lithium compound research, driven primarily by the electric vehicle revolution and renewable energy storage demands. The global lithium market has expanded from approximately $1 billion in 2000 to over $30 billion by 2020, reflecting the strategic importance of these compounds in modern technology ecosystems.
Our research objectives focus on comprehensively comparing the chemical stability profiles of lithium chloride and lithium carbonate across diverse environmental conditions and application scenarios. Specifically, we aim to: (1) quantify stability differences under varying temperature, humidity, and pressure conditions; (2) evaluate reactivity patterns with common industrial materials and contaminants; (3) assess long-term degradation mechanisms and their impact on performance in energy storage applications; and (4) identify potential stabilization strategies for enhancing the performance envelope of both compounds.
This investigation addresses a critical knowledge gap in the industrial application of lithium compounds, particularly as demand intensifies for more robust and reliable lithium-based technologies. By establishing definitive stability parameters, this research will inform material selection decisions across multiple industries, potentially unlocking new application domains where the specific stability characteristics of either compound provide competitive advantages.
The mid-20th century marked a pivotal shift as lithium compounds transitioned from pharmaceutical curiosities to industrial staples. Lithium carbonate (Li₂CO₃) emerged as the predominant commercial form due to its relative stability and versatility in applications ranging from ceramics to aluminum production. Concurrently, lithium chloride (LiCl) found specialized applications in air conditioning systems and as a precursor in lithium metal production.
The energy crisis of the 1970s catalyzed renewed interest in lithium chemistry, particularly for energy storage applications. This period saw intensive research into the electrochemical properties of various lithium compounds, establishing the foundation for modern lithium-ion battery technology. The chemical stability differences between lithium chloride and lithium carbonate became increasingly relevant during this era, as researchers sought optimal compounds for specific applications.
Recent decades have witnessed exponential growth in lithium compound research, driven primarily by the electric vehicle revolution and renewable energy storage demands. The global lithium market has expanded from approximately $1 billion in 2000 to over $30 billion by 2020, reflecting the strategic importance of these compounds in modern technology ecosystems.
Our research objectives focus on comprehensively comparing the chemical stability profiles of lithium chloride and lithium carbonate across diverse environmental conditions and application scenarios. Specifically, we aim to: (1) quantify stability differences under varying temperature, humidity, and pressure conditions; (2) evaluate reactivity patterns with common industrial materials and contaminants; (3) assess long-term degradation mechanisms and their impact on performance in energy storage applications; and (4) identify potential stabilization strategies for enhancing the performance envelope of both compounds.
This investigation addresses a critical knowledge gap in the industrial application of lithium compounds, particularly as demand intensifies for more robust and reliable lithium-based technologies. By establishing definitive stability parameters, this research will inform material selection decisions across multiple industries, potentially unlocking new application domains where the specific stability characteristics of either compound provide competitive advantages.
Market Applications and Demand Analysis for Lithium Salts
The global lithium market has experienced significant growth in recent years, primarily driven by the expanding electric vehicle (EV) industry and renewable energy storage systems. Lithium salts, particularly lithium carbonate and lithium chloride, serve as critical components in various industrial applications, with distinct market demands based on their chemical stability characteristics.
Lithium carbonate dominates the market with approximately 65% share of global lithium compound consumption. Its primary application remains in lithium-ion battery production, where its relative stability at higher temperatures and lower reactivity with moisture make it preferable for large-scale manufacturing processes. The EV sector alone accounts for over 40% of lithium carbonate demand, with annual growth rates exceeding 20% in major markets including China, Europe, and North America.
Lithium chloride, while representing a smaller market segment, has shown accelerated growth in specialized applications where its higher solubility and reactivity provide advantages. The compound has gained traction in air conditioning systems, industrial dehumidification processes, and certain pharmaceutical applications. The technical glass and ceramics industry has also increased consumption of lithium chloride by 15% annually over the past three years due to its superior fluxing properties.
The chemical stability differences between these compounds have created distinct market segments. Lithium carbonate's lower hygroscopicity and greater thermal stability have positioned it as the preferred choice for battery manufacturing, ceramics, and aluminum production. Meanwhile, lithium chloride's higher reactivity and excellent moisture absorption capabilities have created growing demand in humidity control systems, particularly in regions with extreme climate conditions.
Geographically, the demand distribution shows interesting patterns related to stability requirements. Asian markets, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, consume over 70% of global lithium carbonate production, aligned with their dominant position in battery manufacturing. European markets show increasing demand for both compounds, with lithium chloride gaining market share in pharmaceutical and specialty chemical applications where its specific reactivity profile offers advantages.
Price sensitivity analysis reveals that lithium carbonate commands a premium in applications requiring long-term stability, while lithium chloride's market value is more closely tied to its performance in reactive applications. This pricing dynamic has influenced supply chain strategies, with manufacturers increasingly developing specialized formulations optimized for specific stability requirements.
Future market projections indicate continued growth for both compounds, with lithium carbonate maintaining dominance in energy storage applications. However, lithium chloride is expected to see accelerated adoption in emerging technologies including next-generation batteries, pharmaceutical synthesis, and advanced materials processing where its unique chemical properties offer competitive advantages.
Lithium carbonate dominates the market with approximately 65% share of global lithium compound consumption. Its primary application remains in lithium-ion battery production, where its relative stability at higher temperatures and lower reactivity with moisture make it preferable for large-scale manufacturing processes. The EV sector alone accounts for over 40% of lithium carbonate demand, with annual growth rates exceeding 20% in major markets including China, Europe, and North America.
Lithium chloride, while representing a smaller market segment, has shown accelerated growth in specialized applications where its higher solubility and reactivity provide advantages. The compound has gained traction in air conditioning systems, industrial dehumidification processes, and certain pharmaceutical applications. The technical glass and ceramics industry has also increased consumption of lithium chloride by 15% annually over the past three years due to its superior fluxing properties.
The chemical stability differences between these compounds have created distinct market segments. Lithium carbonate's lower hygroscopicity and greater thermal stability have positioned it as the preferred choice for battery manufacturing, ceramics, and aluminum production. Meanwhile, lithium chloride's higher reactivity and excellent moisture absorption capabilities have created growing demand in humidity control systems, particularly in regions with extreme climate conditions.
Geographically, the demand distribution shows interesting patterns related to stability requirements. Asian markets, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, consume over 70% of global lithium carbonate production, aligned with their dominant position in battery manufacturing. European markets show increasing demand for both compounds, with lithium chloride gaining market share in pharmaceutical and specialty chemical applications where its specific reactivity profile offers advantages.
Price sensitivity analysis reveals that lithium carbonate commands a premium in applications requiring long-term stability, while lithium chloride's market value is more closely tied to its performance in reactive applications. This pricing dynamic has influenced supply chain strategies, with manufacturers increasingly developing specialized formulations optimized for specific stability requirements.
Future market projections indicate continued growth for both compounds, with lithium carbonate maintaining dominance in energy storage applications. However, lithium chloride is expected to see accelerated adoption in emerging technologies including next-generation batteries, pharmaceutical synthesis, and advanced materials processing where its unique chemical properties offer competitive advantages.
Current Stability Challenges in Lithium Compounds
Lithium compounds, particularly lithium chloride (LiCl) and lithium carbonate (Li2CO3), face significant stability challenges that impact their performance in various applications. The hygroscopic nature of lithium chloride presents a major obstacle, as it readily absorbs moisture from the atmosphere, leading to deliquescence and formation of hydrates. This moisture sensitivity compromises the compound's stability during storage and handling, necessitating stringent environmental controls to maintain product integrity.
In contrast, lithium carbonate exhibits greater stability under ambient conditions but demonstrates vulnerability to thermal decomposition at elevated temperatures. When heated above 1200°C, lithium carbonate decomposes to form lithium oxide and carbon dioxide, limiting its utility in high-temperature applications. This thermal instability requires careful process control in manufacturing settings where temperature management is critical.
Both compounds face challenges related to reactivity with atmospheric carbon dioxide and oxygen. Lithium chloride, when exposed to air over extended periods, can undergo partial conversion to lithium carbonate and lithium hydroxide. Lithium carbonate, while more stable against atmospheric moisture, may still undergo surface reactions that affect purity and performance characteristics in sensitive applications such as battery production.
pH stability represents another significant challenge. Lithium chloride maintains stability across a broader pH range compared to lithium carbonate, which exhibits decreased solubility and potential precipitation in alkaline environments. This pH-dependent behavior necessitates careful consideration in formulation development and application design, particularly in pharmaceutical and electrochemical contexts.
Long-term storage stability differs markedly between these compounds. Lithium chloride requires hermetically sealed containers with desiccants to prevent moisture absorption and subsequent degradation. Lithium carbonate, while more forgiving, still requires protection from extreme environmental conditions to prevent particle agglomeration and surface reactivity changes that can impact performance in precision applications.
Manufacturing consistency presents additional challenges, as both compounds can exhibit batch-to-batch variability in particle size distribution, crystal morphology, and trace impurity profiles. These variations, though subtle, can significantly impact performance in applications requiring high purity and consistent physical properties, such as lithium-ion battery production and pharmaceutical formulations.
The stability challenges extend to solution behavior, where lithium chloride demonstrates excellent solubility but potential for complex formation with other solution components. Lithium carbonate, with its lower solubility, presents challenges in achieving consistent concentration in aqueous systems, particularly at scale.
In contrast, lithium carbonate exhibits greater stability under ambient conditions but demonstrates vulnerability to thermal decomposition at elevated temperatures. When heated above 1200°C, lithium carbonate decomposes to form lithium oxide and carbon dioxide, limiting its utility in high-temperature applications. This thermal instability requires careful process control in manufacturing settings where temperature management is critical.
Both compounds face challenges related to reactivity with atmospheric carbon dioxide and oxygen. Lithium chloride, when exposed to air over extended periods, can undergo partial conversion to lithium carbonate and lithium hydroxide. Lithium carbonate, while more stable against atmospheric moisture, may still undergo surface reactions that affect purity and performance characteristics in sensitive applications such as battery production.
pH stability represents another significant challenge. Lithium chloride maintains stability across a broader pH range compared to lithium carbonate, which exhibits decreased solubility and potential precipitation in alkaline environments. This pH-dependent behavior necessitates careful consideration in formulation development and application design, particularly in pharmaceutical and electrochemical contexts.
Long-term storage stability differs markedly between these compounds. Lithium chloride requires hermetically sealed containers with desiccants to prevent moisture absorption and subsequent degradation. Lithium carbonate, while more forgiving, still requires protection from extreme environmental conditions to prevent particle agglomeration and surface reactivity changes that can impact performance in precision applications.
Manufacturing consistency presents additional challenges, as both compounds can exhibit batch-to-batch variability in particle size distribution, crystal morphology, and trace impurity profiles. These variations, though subtle, can significantly impact performance in applications requiring high purity and consistent physical properties, such as lithium-ion battery production and pharmaceutical formulations.
The stability challenges extend to solution behavior, where lithium chloride demonstrates excellent solubility but potential for complex formation with other solution components. Lithium carbonate, with its lower solubility, presents challenges in achieving consistent concentration in aqueous systems, particularly at scale.
Comparative Analysis of LiCl and Li2CO3 Stability Properties
01 Stability factors of lithium compounds in storage and processing
The chemical stability of lithium chloride and lithium carbonate is influenced by various factors during storage and processing. These compounds can be sensitive to environmental conditions such as humidity, temperature, and exposure to air. Proper storage conditions and handling procedures are essential to maintain their chemical integrity. Stabilizing agents and specific packaging methods can be employed to enhance the long-term stability of these lithium compounds.- Stability factors of lithium compounds in storage and processing: The chemical stability of lithium chloride and lithium carbonate is influenced by various factors during storage and processing. These compounds can be affected by temperature, humidity, and exposure to air. Proper storage conditions, such as keeping them in sealed containers away from moisture, can help maintain their stability. Additionally, the particle size and crystalline structure of these compounds can impact their stability during processing and subsequent applications.
- Stabilization methods for lithium compounds in solution: Various methods can be employed to enhance the stability of lithium chloride and lithium carbonate in solution. These include pH adjustment, addition of stabilizing agents, and control of solution concentration. Maintaining specific temperature ranges during solution preparation and storage can also prevent degradation. Some processes involve the use of protective coatings or encapsulation techniques to shield the lithium compounds from reactive environments, thereby improving their long-term stability in liquid formulations.
- Comparative stability of lithium chloride versus lithium carbonate: Lithium chloride and lithium carbonate exhibit different stability profiles under various conditions. Lithium chloride tends to be more hygroscopic and may absorb moisture from the atmosphere more readily than lithium carbonate. However, lithium carbonate can decompose under acidic conditions, releasing carbon dioxide. The relative stability of these compounds is important when selecting the appropriate lithium source for specific applications, particularly in environments with varying humidity, temperature, or pH levels.
- Stability improvements through compound modifications: The chemical stability of lithium chloride and lithium carbonate can be enhanced through various modifications to their structure or composition. These modifications may include doping with other elements, creating composite materials, or altering the crystalline structure. Such modifications can reduce reactivity with environmental factors, improve thermal stability, and extend shelf life. Advanced processing techniques can also be employed to create more stable forms of these compounds for specialized applications.
- Stability considerations in industrial applications: In industrial applications, the stability of lithium chloride and lithium carbonate is critical for process efficiency and product quality. These compounds must maintain their chemical integrity during extraction, purification, and conversion processes. Factors such as reaction kinetics, presence of impurities, and process conditions can affect stability. Industrial processes often incorporate specific stabilization steps, monitoring protocols, and quality control measures to ensure the consistent performance of these lithium compounds in applications ranging from battery production to pharmaceutical manufacturing.
02 Stability in lithium extraction and processing methods
Various extraction and processing methods affect the chemical stability of lithium chloride and lithium carbonate. These methods include direct lithium extraction from brines, conversion processes between different lithium compounds, and purification techniques. The stability of these compounds during processing is critical for maintaining product quality and process efficiency. Factors such as pH control, temperature management, and reaction time optimization can significantly impact the stability of lithium compounds during extraction and processing.Expand Specific Solutions03 Impurity effects on lithium compound stability
Impurities can significantly affect the chemical stability of lithium chloride and lithium carbonate. Common impurities include sodium, calcium, magnesium, and various metal ions that may be present in raw materials or introduced during processing. These impurities can catalyze degradation reactions, form unwanted complexes, or alter the physical properties of the lithium compounds. Purification techniques and quality control measures are essential to minimize impurity-related stability issues.Expand Specific Solutions04 Thermal and hydrolytic stability considerations
Lithium chloride and lithium carbonate exhibit different thermal and hydrolytic stability profiles. Lithium chloride is highly hygroscopic and can absorb moisture from the air, potentially leading to solution formation and chemical changes. Lithium carbonate has limited solubility in water but can undergo decomposition at elevated temperatures. Understanding these stability characteristics is crucial for applications in battery production, pharmaceuticals, and industrial processes where these compounds are exposed to varying temperature and moisture conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Stabilization techniques for lithium compounds
Various stabilization techniques can be employed to enhance the chemical stability of lithium chloride and lithium carbonate. These include coating technologies, encapsulation methods, addition of stabilizing agents, and controlled atmosphere processing. Advanced formulation approaches can protect these compounds from moisture, oxidation, and other degradation pathways. Innovative packaging solutions and storage protocols also play a significant role in maintaining the long-term stability of lithium compounds for various applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Lithium Compound Manufacturing
The lithium compound market is in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by the expanding electric vehicle and energy storage sectors. The market size for lithium compounds is projected to grow significantly, with lithium chloride gaining attention for its superior chemical stability compared to lithium carbonate in certain applications. Major players like Ganfeng Lithium, CATL, and LG Chem are investing heavily in lithium chloride technology, while automotive companies such as Toyota, Hyundai, and Renault are exploring its use in next-generation batteries. Research institutions including Cornell University and Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft are advancing the fundamental understanding of lithium chloride's stability advantages, particularly for high-temperature applications and extended cycle life requirements.
Rockwood Lithium
Technical Solution: Rockwood Lithium (now part of Albemarle Corporation) has developed proprietary processes for manufacturing high-purity lithium chloride with enhanced chemical stability. Their approach involves controlled precipitation techniques that minimize impurities and reduce moisture sensitivity. The company has pioneered a multi-stage purification system that achieves 99.9% purity lithium chloride with significantly improved shelf life compared to conventional products. Their research demonstrates that properly stabilized lithium chloride can maintain consistent performance in battery applications despite its hygroscopic nature. Rockwood has also developed specialized packaging and handling protocols to preserve the chemical integrity of lithium chloride during transportation and storage, addressing one of the key challenges in its industrial application.
Strengths: Superior purification technology resulting in higher stability lithium chloride; established supply chain and production capacity; extensive experience in lithium chemistry. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to lithium carbonate; requires more complex handling procedures; still faces inherent hygroscopic challenges of lithium chloride.
Ganfeng Lithium Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Ganfeng Lithium has developed an integrated approach to lithium compound stability, focusing on both lithium chloride and lithium carbonate production. Their proprietary technology includes a direct lithium extraction process that produces lithium chloride as an intermediate, which can either be converted to carbonate or stabilized for direct use. Their research has demonstrated that controlled crystallization conditions can significantly improve lithium chloride stability by reducing surface area and incorporating specific stabilizing agents. For lithium carbonate, they've developed a microencapsulation technique that protects particles from atmospheric carbon dioxide and moisture, extending shelf life and maintaining consistent electrochemical performance. Ganfeng has also pioneered comparative stability testing protocols that quantify degradation rates under various environmental conditions.
Strengths: Vertically integrated production capabilities; advanced stabilization technologies for both compounds; large-scale production experience. Weaknesses: Higher production costs for stabilized lithium chloride; technology still being optimized for extreme environmental conditions; requires specialized handling equipment.
Critical Patents and Research on Lithium Salt Stability
Lithium oxyhalide cell with improved safety and voltage delay characteristics
PatentInactiveUS6780542B2
Innovation
- Exposing lithium anodes to gaseous carbon dioxide prior to cell assembly forms a lithium carbonate passivation layer, improving safety and voltage delay characteristics by reducing internal resistance and preventing short circuits.
Production of lithium compounds directly from lithium containing brines
PatentInactiveUS20090214414A1
Innovation
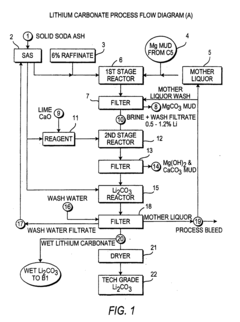
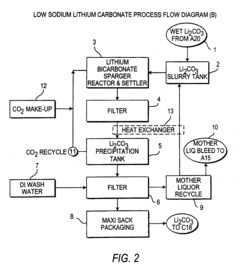
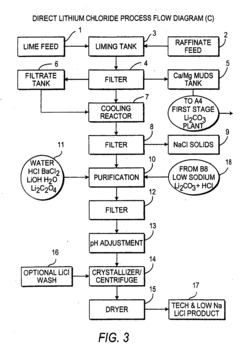
- A novel process that reduces the number of processing steps by directly producing high purity lithium carbonate and lithium chloride from natural brines using a carbon dioxide/bicarbonate cycle and hydrochloric acid reaction, eliminating the need for lithium hydroxide monohydrate recrystallization and incorporating a continuous purification system with ion exchange columns to achieve low sodium content.
Environmental Impact of Lithium Compound Processing
The environmental impact of lithium compound processing varies significantly between lithium chloride and lithium carbonate production methods. Lithium chloride processing typically involves direct extraction from brines or hard rock through hydrometallurgical processes, which generally requires less energy but potentially consumes more water resources. The brine extraction method, predominantly used in salt flats of South America, creates large evaporation ponds that alter local ecosystems and can lead to groundwater depletion, affecting surrounding communities and wildlife habitats.
In contrast, lithium carbonate processing from hard rock sources (spodumene) involves energy-intensive mining operations, crushing, and thermal treatments at temperatures exceeding 1000°C, resulting in higher carbon emissions. The subsequent acid leaching processes generate acidic waste streams requiring neutralization and proper disposal to prevent soil and water contamination.
Chemical stability differences between these compounds further influence their environmental footprints. Lithium chloride's hygroscopic nature necessitates more stringent handling protocols and specialized containment systems to prevent environmental release. Its higher water solubility increases the risk of waterway contamination in case of accidental spills, potentially affecting aquatic ecosystems more severely than lithium carbonate.
Waste management presents another significant environmental consideration. Lithium chloride production generates chloride-rich waste streams that can increase salinity in receiving water bodies, while lithium carbonate processing produces alkaline residues. Both require different remediation approaches and tailored waste treatment facilities to minimize ecological damage.
Water consumption metrics reveal that producing one ton of lithium compounds can require between 500-2000 cubic meters of water, with lithium chloride processes generally falling on the higher end of this spectrum due to evaporative techniques. This intensive water usage becomes particularly problematic in arid regions where lithium extraction competes with agricultural and drinking water needs.
Recent technological innovations aim to reduce these environmental impacts through closed-loop processing systems, direct lithium extraction technologies, and water recycling initiatives. Several companies have developed membrane-based separation techniques that can reduce water consumption by up to 70% compared to traditional evaporation methods, while simultaneously decreasing processing time from months to days.
Regulatory frameworks governing lithium compound processing vary globally, with stricter environmental standards emerging in response to increased awareness of lithium extraction's ecological footprint. The industry is gradually moving toward more sustainable practices, including the development of lithium recycling from spent batteries, which could significantly reduce the need for primary extraction and its associated environmental impacts.
In contrast, lithium carbonate processing from hard rock sources (spodumene) involves energy-intensive mining operations, crushing, and thermal treatments at temperatures exceeding 1000°C, resulting in higher carbon emissions. The subsequent acid leaching processes generate acidic waste streams requiring neutralization and proper disposal to prevent soil and water contamination.
Chemical stability differences between these compounds further influence their environmental footprints. Lithium chloride's hygroscopic nature necessitates more stringent handling protocols and specialized containment systems to prevent environmental release. Its higher water solubility increases the risk of waterway contamination in case of accidental spills, potentially affecting aquatic ecosystems more severely than lithium carbonate.
Waste management presents another significant environmental consideration. Lithium chloride production generates chloride-rich waste streams that can increase salinity in receiving water bodies, while lithium carbonate processing produces alkaline residues. Both require different remediation approaches and tailored waste treatment facilities to minimize ecological damage.
Water consumption metrics reveal that producing one ton of lithium compounds can require between 500-2000 cubic meters of water, with lithium chloride processes generally falling on the higher end of this spectrum due to evaporative techniques. This intensive water usage becomes particularly problematic in arid regions where lithium extraction competes with agricultural and drinking water needs.
Recent technological innovations aim to reduce these environmental impacts through closed-loop processing systems, direct lithium extraction technologies, and water recycling initiatives. Several companies have developed membrane-based separation techniques that can reduce water consumption by up to 70% compared to traditional evaporation methods, while simultaneously decreasing processing time from months to days.
Regulatory frameworks governing lithium compound processing vary globally, with stricter environmental standards emerging in response to increased awareness of lithium extraction's ecological footprint. The industry is gradually moving toward more sustainable practices, including the development of lithium recycling from spent batteries, which could significantly reduce the need for primary extraction and its associated environmental impacts.
Safety Protocols for Lithium Salt Handling and Storage
The handling and storage of lithium salts, particularly lithium chloride and lithium carbonate, require stringent safety protocols due to their reactive nature and potential health hazards. These compounds demand specific handling procedures that address their unique chemical properties and stability characteristics.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is mandatory when handling lithium salts. This includes chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, lab coats, and in some cases, respiratory protection. Lithium chloride, being more hygroscopic than lithium carbonate, requires additional precautions to prevent moisture absorption which can lead to degradation and potential reactivity issues.
Storage conditions significantly impact the stability of these compounds. Lithium chloride should be stored in tightly sealed containers in dry environments, preferably with desiccants, to prevent deliquescence. Lithium carbonate, while more stable in ambient conditions, should still be protected from excessive humidity and temperature fluctuations that could compromise its integrity.
Segregation protocols must be implemented to prevent cross-contamination and dangerous chemical reactions. Both lithium salts should be stored away from incompatible materials, particularly strong acids which can cause violent reactions. Lithium chloride requires additional separation from oxidizing agents and metals due to its greater reactivity profile compared to lithium carbonate.
Emergency response procedures should be clearly documented and accessible. This includes spill management protocols tailored to each compound's properties. For lithium chloride spills, avoiding water contact is crucial as it can generate heat and potentially hazardous hydrogen chloride gas. Lithium carbonate spills, while less reactive, should still be contained promptly to prevent environmental contamination.
Regular staff training on the specific hazards of lithium compounds is essential. This should cover recognition of stability issues, such as color changes or clumping that may indicate degradation or contamination. Training should emphasize the different stability profiles of lithium chloride versus lithium carbonate, with the former requiring more stringent monitoring due to its hygroscopic nature.
Inventory management systems should track storage conditions, shelf life, and potential degradation indicators. Lithium chloride typically requires more frequent inspection due to its greater susceptibility to environmental factors. Documentation should include stability testing results and any observed changes in physical properties that might indicate compromised chemical integrity.
Waste disposal procedures must comply with local regulations while addressing the specific chemical properties of each compound. Lithium chloride waste requires particular attention due to its water solubility and potential environmental impact, whereas lithium carbonate disposal may focus more on preventing particulate dispersion.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is mandatory when handling lithium salts. This includes chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, lab coats, and in some cases, respiratory protection. Lithium chloride, being more hygroscopic than lithium carbonate, requires additional precautions to prevent moisture absorption which can lead to degradation and potential reactivity issues.
Storage conditions significantly impact the stability of these compounds. Lithium chloride should be stored in tightly sealed containers in dry environments, preferably with desiccants, to prevent deliquescence. Lithium carbonate, while more stable in ambient conditions, should still be protected from excessive humidity and temperature fluctuations that could compromise its integrity.
Segregation protocols must be implemented to prevent cross-contamination and dangerous chemical reactions. Both lithium salts should be stored away from incompatible materials, particularly strong acids which can cause violent reactions. Lithium chloride requires additional separation from oxidizing agents and metals due to its greater reactivity profile compared to lithium carbonate.
Emergency response procedures should be clearly documented and accessible. This includes spill management protocols tailored to each compound's properties. For lithium chloride spills, avoiding water contact is crucial as it can generate heat and potentially hazardous hydrogen chloride gas. Lithium carbonate spills, while less reactive, should still be contained promptly to prevent environmental contamination.
Regular staff training on the specific hazards of lithium compounds is essential. This should cover recognition of stability issues, such as color changes or clumping that may indicate degradation or contamination. Training should emphasize the different stability profiles of lithium chloride versus lithium carbonate, with the former requiring more stringent monitoring due to its hygroscopic nature.
Inventory management systems should track storage conditions, shelf life, and potential degradation indicators. Lithium chloride typically requires more frequent inspection due to its greater susceptibility to environmental factors. Documentation should include stability testing results and any observed changes in physical properties that might indicate compromised chemical integrity.
Waste disposal procedures must comply with local regulations while addressing the specific chemical properties of each compound. Lithium chloride waste requires particular attention due to its water solubility and potential environmental impact, whereas lithium carbonate disposal may focus more on preventing particulate dispersion.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!