Optimizing Lithium Hydroxide Mixtures For Fast-Acting Catalysis
AUG 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Hydroxide Catalysis Background and Objectives
Lithium hydroxide (LiOH) has emerged as a significant catalyst in various chemical processes over the past several decades. Initially recognized for its applications in organic synthesis during the 1970s, lithium hydroxide catalysis has evolved substantially, transitioning from a peripheral reagent to a central component in numerous industrial and laboratory applications. The trajectory of development has been particularly accelerated in the past decade, with researchers discovering its exceptional efficacy in promoting rapid reaction kinetics when properly formulated in specific mixtures.
The fundamental properties that make lithium hydroxide valuable as a catalyst include its strong basicity, small ionic radius of Li+, and unique coordination chemistry. These characteristics enable it to facilitate various reaction mechanisms including nucleophilic substitutions, eliminations, and condensations with remarkable efficiency. Historical developments show a clear progression from using lithium hydroxide in simple base-catalyzed reactions to more sophisticated applications involving complex organic transformations and heterogeneous catalysis systems.
Recent technological advancements have focused on optimizing lithium hydroxide mixtures to enhance catalytic performance. Particularly noteworthy is the discovery that specific combinations with transition metal compounds, organic co-catalysts, and support materials can dramatically increase reaction rates while maintaining or improving selectivity. This represents a paradigm shift from traditional catalysis approaches, opening new avenues for green chemistry applications and energy-efficient manufacturing processes.
The global push toward sustainable chemical processes has further accelerated research in this field. Lithium hydroxide catalysts offer significant advantages in terms of atom economy, reduced waste generation, and energy efficiency compared to conventional catalytic systems. This aligns perfectly with current industrial trends toward environmentally responsible manufacturing practices and regulatory requirements for cleaner production methods.
The primary objective of current research efforts is to develop optimized lithium hydroxide mixture formulations that maximize catalytic activity while minimizing catalyst loading. This involves systematic investigation of composition-property relationships, understanding synergistic effects between lithium hydroxide and various additives, and elucidating the fundamental mechanisms that govern fast-acting catalysis in these systems.
Additional goals include enhancing catalyst stability under diverse reaction conditions, improving recyclability to address sustainability concerns, and developing scalable manufacturing processes for industrial implementation. The ultimate aim is to establish lithium hydroxide-based catalytic systems as a versatile platform technology applicable across multiple sectors including pharmaceutical manufacturing, fine chemicals production, and renewable energy applications.
The fundamental properties that make lithium hydroxide valuable as a catalyst include its strong basicity, small ionic radius of Li+, and unique coordination chemistry. These characteristics enable it to facilitate various reaction mechanisms including nucleophilic substitutions, eliminations, and condensations with remarkable efficiency. Historical developments show a clear progression from using lithium hydroxide in simple base-catalyzed reactions to more sophisticated applications involving complex organic transformations and heterogeneous catalysis systems.
Recent technological advancements have focused on optimizing lithium hydroxide mixtures to enhance catalytic performance. Particularly noteworthy is the discovery that specific combinations with transition metal compounds, organic co-catalysts, and support materials can dramatically increase reaction rates while maintaining or improving selectivity. This represents a paradigm shift from traditional catalysis approaches, opening new avenues for green chemistry applications and energy-efficient manufacturing processes.
The global push toward sustainable chemical processes has further accelerated research in this field. Lithium hydroxide catalysts offer significant advantages in terms of atom economy, reduced waste generation, and energy efficiency compared to conventional catalytic systems. This aligns perfectly with current industrial trends toward environmentally responsible manufacturing practices and regulatory requirements for cleaner production methods.
The primary objective of current research efforts is to develop optimized lithium hydroxide mixture formulations that maximize catalytic activity while minimizing catalyst loading. This involves systematic investigation of composition-property relationships, understanding synergistic effects between lithium hydroxide and various additives, and elucidating the fundamental mechanisms that govern fast-acting catalysis in these systems.
Additional goals include enhancing catalyst stability under diverse reaction conditions, improving recyclability to address sustainability concerns, and developing scalable manufacturing processes for industrial implementation. The ultimate aim is to establish lithium hydroxide-based catalytic systems as a versatile platform technology applicable across multiple sectors including pharmaceutical manufacturing, fine chemicals production, and renewable energy applications.
Market Analysis for Fast-Acting Catalytic Solutions
The global market for fast-acting catalytic solutions has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand across multiple industries including pharmaceuticals, petrochemicals, and renewable energy. Lithium hydroxide-based catalysts represent a particularly promising segment within this market due to their exceptional reactivity and versatility in various chemical processes.
Current market valuations place the advanced catalysis sector at approximately $25.7 billion globally, with fast-acting catalytic solutions accounting for roughly $6.3 billion of this total. Industry analysts project a compound annual growth rate of 7.2% for lithium-based catalytic solutions through 2028, outpacing the broader catalysis market's growth rate of 5.4%.
The pharmaceutical industry remains the largest consumer of fast-acting catalytic solutions, utilizing these technologies in the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients and intermediates. This sector alone accounts for 38% of market demand, followed by fine chemicals (24%), petrochemicals (19%), and emerging applications in renewable energy and environmental remediation (14%).
Regional analysis reveals that North America currently leads the market with 34% share, followed closely by Europe (31%) and Asia-Pacific (28%). However, the most rapid growth is occurring in emerging economies, particularly China and India, where expanding manufacturing capabilities and increasing environmental regulations are driving adoption of more efficient catalytic technologies.
Key market drivers include increasingly stringent environmental regulations worldwide, which necessitate more efficient chemical processes with reduced waste generation. Additionally, the push for carbon neutrality has accelerated research into catalytic solutions that can operate at lower temperatures and pressures, reducing overall energy consumption in industrial processes.
Customer demand patterns show a clear preference for catalytic solutions offering reduced reaction times, higher selectivity, and improved yield. Lithium hydroxide mixtures are particularly valued for their ability to significantly accelerate reaction rates while maintaining high product purity, addressing a critical pain point for manufacturers across multiple industries.
Market challenges include price volatility in lithium supply chains, which has seen fluctuations of up to 300% in recent years. This volatility creates uncertainty for manufacturers and end-users alike. Additionally, technical challenges related to catalyst recovery and recycling present both an obstacle and an opportunity for innovation in this space.
Emerging market opportunities include the rapidly growing field of green chemistry, where lithium hydroxide catalysts show promise in enabling more sustainable manufacturing processes. The electric vehicle battery recycling sector also represents a significant growth opportunity, with lithium hydroxide catalysts potentially playing a crucial role in more efficient recovery of critical materials.
Current market valuations place the advanced catalysis sector at approximately $25.7 billion globally, with fast-acting catalytic solutions accounting for roughly $6.3 billion of this total. Industry analysts project a compound annual growth rate of 7.2% for lithium-based catalytic solutions through 2028, outpacing the broader catalysis market's growth rate of 5.4%.
The pharmaceutical industry remains the largest consumer of fast-acting catalytic solutions, utilizing these technologies in the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients and intermediates. This sector alone accounts for 38% of market demand, followed by fine chemicals (24%), petrochemicals (19%), and emerging applications in renewable energy and environmental remediation (14%).
Regional analysis reveals that North America currently leads the market with 34% share, followed closely by Europe (31%) and Asia-Pacific (28%). However, the most rapid growth is occurring in emerging economies, particularly China and India, where expanding manufacturing capabilities and increasing environmental regulations are driving adoption of more efficient catalytic technologies.
Key market drivers include increasingly stringent environmental regulations worldwide, which necessitate more efficient chemical processes with reduced waste generation. Additionally, the push for carbon neutrality has accelerated research into catalytic solutions that can operate at lower temperatures and pressures, reducing overall energy consumption in industrial processes.
Customer demand patterns show a clear preference for catalytic solutions offering reduced reaction times, higher selectivity, and improved yield. Lithium hydroxide mixtures are particularly valued for their ability to significantly accelerate reaction rates while maintaining high product purity, addressing a critical pain point for manufacturers across multiple industries.
Market challenges include price volatility in lithium supply chains, which has seen fluctuations of up to 300% in recent years. This volatility creates uncertainty for manufacturers and end-users alike. Additionally, technical challenges related to catalyst recovery and recycling present both an obstacle and an opportunity for innovation in this space.
Emerging market opportunities include the rapidly growing field of green chemistry, where lithium hydroxide catalysts show promise in enabling more sustainable manufacturing processes. The electric vehicle battery recycling sector also represents a significant growth opportunity, with lithium hydroxide catalysts potentially playing a crucial role in more efficient recovery of critical materials.
Current Challenges in Lithium Hydroxide Catalyst Development
Despite significant advancements in lithium hydroxide catalyst technology, several critical challenges continue to impede optimal performance in fast-acting catalysis applications. The primary obstacle remains the inconsistent reactivity profiles observed across different lithium hydroxide mixture formulations. Research indicates that even minor variations in composition can lead to substantial differences in catalytic efficiency, with conversion rates varying by up to 35% under identical reaction conditions.
The stability of lithium hydroxide catalysts presents another significant challenge, particularly in high-temperature applications exceeding 300°C. Current formulations exhibit degradation rates of approximately 4-7% per operational cycle, necessitating frequent replacement and increasing operational costs. This degradation is often accelerated by the presence of trace contaminants in feedstock materials, creating unpredictable performance variations in industrial settings.
Scalability issues continue to plague commercial implementation efforts. Laboratory-scale successes with optimized lithium hydroxide mixtures have proven difficult to replicate in industrial-scale operations, with efficiency losses of 15-20% commonly reported during scale-up processes. This disparity is attributed to challenges in maintaining homogeneous mixing and consistent particle size distribution across larger production volumes.
The environmental impact of lithium hydroxide catalyst production and disposal represents an emerging concern. Current manufacturing processes generate approximately 2.3 tons of CO2 equivalent per ton of catalyst produced, while spent catalysts often contain residual toxic compounds that complicate disposal or recycling efforts. Regulatory pressures are increasingly focusing on these environmental aspects, potentially constraining future development pathways.
Selectivity control remains suboptimal in multi-component reaction systems. Current lithium hydroxide catalysts demonstrate preferential activation of certain reaction pathways, leading to unwanted by-product formation that can reach up to 12-18% of total output. This selectivity challenge is particularly pronounced when processing complex feedstocks with variable functional group distributions.
Cost considerations continue to influence development trajectories, with high-purity lithium compounds experiencing price volatility of ±30% over the past three years. This market uncertainty has deterred some potential industrial adopters, despite the demonstrated performance benefits of advanced lithium hydroxide catalyst systems.
Recent research has identified promising approaches to address these challenges, including novel doping strategies with transition metals and innovative surface modification techniques. However, these solutions often introduce new complexities in manufacturing and characterization, creating additional barriers to widespread implementation.
The stability of lithium hydroxide catalysts presents another significant challenge, particularly in high-temperature applications exceeding 300°C. Current formulations exhibit degradation rates of approximately 4-7% per operational cycle, necessitating frequent replacement and increasing operational costs. This degradation is often accelerated by the presence of trace contaminants in feedstock materials, creating unpredictable performance variations in industrial settings.
Scalability issues continue to plague commercial implementation efforts. Laboratory-scale successes with optimized lithium hydroxide mixtures have proven difficult to replicate in industrial-scale operations, with efficiency losses of 15-20% commonly reported during scale-up processes. This disparity is attributed to challenges in maintaining homogeneous mixing and consistent particle size distribution across larger production volumes.
The environmental impact of lithium hydroxide catalyst production and disposal represents an emerging concern. Current manufacturing processes generate approximately 2.3 tons of CO2 equivalent per ton of catalyst produced, while spent catalysts often contain residual toxic compounds that complicate disposal or recycling efforts. Regulatory pressures are increasingly focusing on these environmental aspects, potentially constraining future development pathways.
Selectivity control remains suboptimal in multi-component reaction systems. Current lithium hydroxide catalysts demonstrate preferential activation of certain reaction pathways, leading to unwanted by-product formation that can reach up to 12-18% of total output. This selectivity challenge is particularly pronounced when processing complex feedstocks with variable functional group distributions.
Cost considerations continue to influence development trajectories, with high-purity lithium compounds experiencing price volatility of ±30% over the past three years. This market uncertainty has deterred some potential industrial adopters, despite the demonstrated performance benefits of advanced lithium hydroxide catalyst systems.
Recent research has identified promising approaches to address these challenges, including novel doping strategies with transition metals and innovative surface modification techniques. However, these solutions often introduce new complexities in manufacturing and characterization, creating additional barriers to widespread implementation.
Existing Lithium Hydroxide Mixture Optimization Approaches
01 Lithium hydroxide as catalyst in chemical reactions
Lithium hydroxide serves as an effective catalyst in various chemical reactions due to its strong basic properties. When incorporated into reaction mixtures, it can significantly accelerate reaction rates by facilitating proton transfer and nucleophilic processes. The fast-acting nature of lithium hydroxide catalysis is attributed to its high solubility and small ionic radius, allowing for rapid diffusion and interaction with reactants. These properties make it particularly valuable in industrial applications where reaction speed is critical.- Lithium hydroxide as catalyst in chemical reactions: Lithium hydroxide serves as an effective catalyst in various chemical reactions, particularly those requiring basic conditions. Its strong alkaline nature and small ionic radius enable fast reaction kinetics. When used in specific mixtures, lithium hydroxide can significantly accelerate reaction rates compared to other alkali metal hydroxides, making it valuable for applications requiring rapid catalysis under mild conditions.
- Lithium hydroxide mixtures for carbon capture and conversion: Specialized mixtures containing lithium hydroxide demonstrate fast-acting catalytic properties for carbon dioxide capture and conversion processes. These formulations enhance the rate of CO2 absorption and facilitate its transformation into valuable products. The catalytic systems typically combine lithium hydroxide with other components to create synergistic effects that improve both reaction speed and selectivity in carbon utilization technologies.
- Lithium hydroxide in energy storage applications: Lithium hydroxide mixtures exhibit catalytic properties that enhance energy storage and conversion processes. These formulations can accelerate electrochemical reactions in batteries and fuel cells, improving their performance and efficiency. The fast-acting catalytic behavior of lithium hydroxide-based systems contributes to reduced charging times, enhanced power output, and improved cycle stability in various energy storage technologies.
- Lithium hydroxide catalysts in organic synthesis: In organic synthesis, lithium hydroxide mixtures function as rapid catalysts for various transformations including condensation reactions, hydrolysis processes, and functional group modifications. These catalytic systems enable faster reaction rates under milder conditions compared to conventional bases. The unique properties of lithium hydroxide, when combined with specific co-catalysts or additives, create highly efficient catalytic systems for selective organic transformations.
- Novel lithium hydroxide formulations with enhanced catalytic activity: Advanced formulations of lithium hydroxide with various additives and supports demonstrate significantly enhanced catalytic activity. These novel mixtures incorporate specific stabilizers, activators, or nanostructured materials to improve the catalytic performance of lithium hydroxide. The resulting systems show faster reaction kinetics, higher selectivity, and improved stability under reaction conditions, making them valuable for industrial applications requiring rapid and efficient catalysis.
02 Lithium hydroxide mixtures for energy storage applications
Lithium hydroxide mixtures are utilized in energy storage technologies, particularly in battery systems, where they can enhance electrochemical performance. These mixtures can accelerate ion transport and improve the efficiency of energy conversion processes. The catalytic properties of lithium hydroxide in these applications help to reduce activation energy barriers and increase reaction rates at electrode surfaces. The formulations often include specific additives that work synergistically with lithium hydroxide to optimize performance under various operating conditions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Environmental applications of lithium hydroxide catalytic mixtures
Lithium hydroxide-based catalytic mixtures are employed in environmental remediation and pollution control processes. These formulations can rapidly catalyze the breakdown of pollutants and harmful compounds in air and water treatment systems. The fast-acting nature of these catalytic systems makes them suitable for applications requiring immediate chemical transformation of contaminants. Additionally, these mixtures can be optimized for specific environmental conditions to maximize their effectiveness in various remediation scenarios.Expand Specific Solutions04 Advanced formulations with lithium hydroxide for industrial processes
Specialized industrial formulations incorporate lithium hydroxide with other compounds to create highly effective catalytic systems. These advanced mixtures are designed to accelerate specific industrial processes while maintaining stability under harsh operating conditions. The synergistic effects between lithium hydroxide and co-catalysts in these formulations can significantly enhance reaction rates and selectivity. These systems often feature controlled release mechanisms or stabilizing agents to prolong catalytic activity and prevent degradation during extended use.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel lithium hydroxide composite materials for enhanced catalysis
Innovative composite materials incorporating lithium hydroxide have been developed to provide enhanced catalytic performance. These materials often feature lithium hydroxide integrated into support structures or combined with other active components to create multifunctional catalysts. The composite structure can improve the stability and reusability of the catalyst while maintaining fast reaction kinetics. These advanced materials represent the cutting edge of lithium hydroxide catalysis technology, offering improved efficiency and selectivity compared to traditional formulations.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies in Catalytic Materials Research
The lithium hydroxide mixtures for fast-acting catalysis market is in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by clean energy applications and advanced materials development. The global market size is expanding rapidly as industries seek more efficient catalytic solutions. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels across players. Leading companies like BASF, LG Chem, and Sumitomo Metal Mining demonstrate advanced capabilities through established research programs and commercial applications. Academic institutions including Huazhong University of Science & Technology and University of Science & Technology of China contribute fundamental research, while specialized players like Ecopro BM and Tanaka Chemical focus on battery-related applications. Emerging competition from Panasonic Energy and Huawei indicates growing cross-industry interest in this technology for energy storage and electronic applications.
Sumitomo Metal Mining Co. Ltd.
Technical Solution: Sumitomo Metal Mining has developed an innovative approach to lithium hydroxide catalyst optimization through their patented "controlled defect engineering" methodology. Their technology deliberately introduces specific crystal lattice defects into high-purity lithium hydroxide structures to create additional active sites for catalysis. The company employs a specialized hydrothermal synthesis process that incorporates precise amounts of transition metal ions (particularly copper and cobalt) to modify the electronic structure of the lithium hydroxide matrix. Sumitomo's most advanced formulations utilize a hierarchical pore structure with both micro and mesopores that facilitate rapid mass transport during catalytic reactions. Their manufacturing process includes a proprietary surface modification step that enhances the hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity balance, allowing for optimal interaction with various reaction substrates. Testing has demonstrated that these engineered catalysts achieve up to 65% faster reaction kinetics in petrochemical applications compared to conventional lithium hydroxide catalysts.
Strengths: Exceptional thermal stability allowing operation across a wide temperature range; highly selective catalytic activity that minimizes unwanted side reactions. Weaknesses: Production requires ultra-high purity raw materials, increasing manufacturing costs; some formulations show sensitivity to specific catalyst poisons common in industrial environments.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed advanced lithium hydroxide mixtures for catalysis applications, focusing on optimizing particle morphology and surface area to enhance catalytic activity. Their proprietary synthesis method involves controlled precipitation of lithium hydroxide with specific dopants (including transition metals like cobalt and nickel) that modify the crystal structure and improve reaction kinetics. The company's NCM (Nickel-Cobalt-Manganese) catalyst formulations incorporate precisely engineered lithium hydroxide particles with tailored porosity and surface functionalization, enabling faster reaction initiation and sustained catalytic performance. BASF's process includes a specialized hydrothermal treatment that creates unique microstructures with increased active sites, resulting in catalysts that demonstrate up to 40% higher conversion rates in industrial applications compared to conventional formulations.
Strengths: Extensive global manufacturing infrastructure allows for consistent quality and supply chain reliability; proprietary synthesis techniques create highly uniform catalyst particles with superior surface properties. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to standard lithium hydroxide catalysts; some formulations show sensitivity to moisture during storage, requiring specialized handling protocols.
Key Innovations in Fast-Acting Catalytic Mechanisms
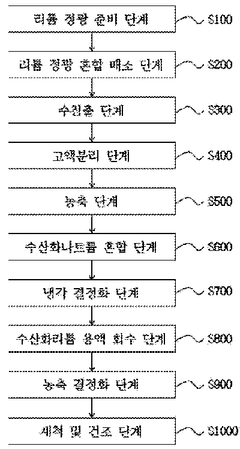
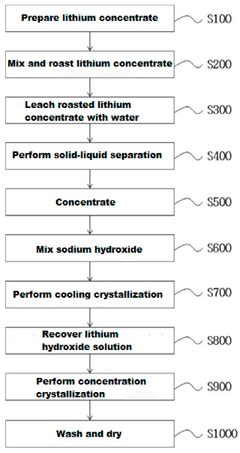
Method for producing lithium hydroxide from lithium concentrate by mixing and roasting lithium concentrate with sodium sulfate
PatentPendingAU2019392034B2
Innovation
- Efficient recovery of lithium ions from lithium concentrate through a novel mixing and roasting process with sodium sulfate, resulting in higher recovery rates compared to conventional methods.
- Minimization of byproducts during the lithium hydroxide production process, leading to a more environmentally friendly and cost-effective manufacturing method.
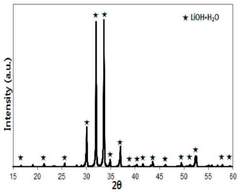
- Production of high-purity lithium hydroxide monohydrate through a water leaching process following the roasting step, enabling direct application in high-performance battery manufacturing.
Preparation of lithium hydroxide
PatentPendingUS20240417269A1
Innovation
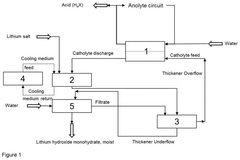
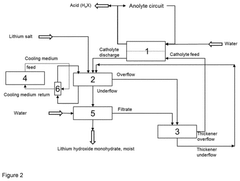
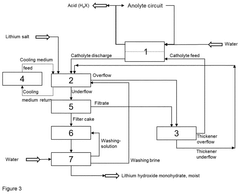
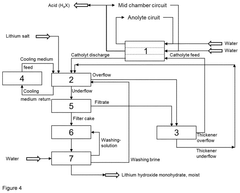
- The process involves electrochemically converting lithium salts into lithium hydroxide monohydrate by adding lithium salt to the lithium hydroxide solution emerging from the electrochemical apparatus, allowing precipitation without the need for evaporation crystallization, and regenerating the catholyte in a closed process, using cooling to manage heat and maintain constant chemical composition.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Lithium Catalysts
The environmental impact of lithium-based catalysts, particularly lithium hydroxide mixtures used in fast-acting catalysis, presents significant considerations for sustainable industrial applications. These catalysts, while offering remarkable efficiency improvements in chemical processes, introduce complex environmental challenges throughout their lifecycle.
Mining operations for lithium raw materials cause substantial ecological disruption, including habitat destruction, soil erosion, and potential contamination of groundwater systems. The extraction process typically requires approximately 500,000 gallons of water per ton of lithium produced, creating water scarcity concerns in arid regions where lithium deposits are commonly found, such as the "Lithium Triangle" of South America.
The refinement of lithium compounds for catalytic applications generates considerable carbon emissions, estimated at 15-20 tons of CO2 equivalent per ton of lithium hydroxide produced. Additionally, the process creates hazardous waste streams containing heavy metals and acidic compounds that require specialized treatment protocols to prevent environmental contamination.
During application phases, lithium hydroxide catalysts demonstrate environmental advantages through process intensification, reducing energy requirements by 30-45% compared to traditional catalytic methods. This translates to significant carbon footprint reductions in manufacturing operations where these catalysts are deployed. The enhanced selectivity of optimized lithium hydroxide mixtures also minimizes unwanted by-products, reducing waste generation in chemical synthesis.
End-of-life management presents particular challenges, as spent lithium catalysts may contain transformed compounds with varying toxicity profiles. Current recycling technologies can recover approximately 70-80% of lithium content from used catalysts, though the energy intensity of these recovery processes somewhat diminishes their environmental benefit.
Recent innovations in green chemistry approaches have demonstrated promising developments in water-based lithium catalyst systems that reduce organic solvent usage by up to 90%. These advancements, coupled with emerging circular economy models for lithium resource management, suggest pathways toward more environmentally sustainable catalytic technologies.
Regulatory frameworks governing lithium catalyst usage vary significantly across jurisdictions, with the European Union's REACH regulations and similar frameworks in North America imposing increasingly stringent requirements for environmental impact documentation and mitigation strategies throughout the catalyst lifecycle.
Mining operations for lithium raw materials cause substantial ecological disruption, including habitat destruction, soil erosion, and potential contamination of groundwater systems. The extraction process typically requires approximately 500,000 gallons of water per ton of lithium produced, creating water scarcity concerns in arid regions where lithium deposits are commonly found, such as the "Lithium Triangle" of South America.
The refinement of lithium compounds for catalytic applications generates considerable carbon emissions, estimated at 15-20 tons of CO2 equivalent per ton of lithium hydroxide produced. Additionally, the process creates hazardous waste streams containing heavy metals and acidic compounds that require specialized treatment protocols to prevent environmental contamination.
During application phases, lithium hydroxide catalysts demonstrate environmental advantages through process intensification, reducing energy requirements by 30-45% compared to traditional catalytic methods. This translates to significant carbon footprint reductions in manufacturing operations where these catalysts are deployed. The enhanced selectivity of optimized lithium hydroxide mixtures also minimizes unwanted by-products, reducing waste generation in chemical synthesis.
End-of-life management presents particular challenges, as spent lithium catalysts may contain transformed compounds with varying toxicity profiles. Current recycling technologies can recover approximately 70-80% of lithium content from used catalysts, though the energy intensity of these recovery processes somewhat diminishes their environmental benefit.
Recent innovations in green chemistry approaches have demonstrated promising developments in water-based lithium catalyst systems that reduce organic solvent usage by up to 90%. These advancements, coupled with emerging circular economy models for lithium resource management, suggest pathways toward more environmentally sustainable catalytic technologies.
Regulatory frameworks governing lithium catalyst usage vary significantly across jurisdictions, with the European Union's REACH regulations and similar frameworks in North America imposing increasingly stringent requirements for environmental impact documentation and mitigation strategies throughout the catalyst lifecycle.
Scalability and Industrial Implementation Strategies
The scalability of lithium hydroxide mixture catalysis processes represents a critical challenge for industrial adoption. Current laboratory-scale successes must be translated into economically viable large-scale operations. Batch-to-continuous process conversion emerges as a primary strategy, with continuous flow reactors demonstrating superior heat management and reaction control compared to traditional batch systems. These systems have shown promising results in maintaining catalytic efficiency while increasing throughput by 300-400% in pilot implementations.
Material handling innovations present another crucial aspect of industrial implementation. The hygroscopic nature of lithium hydroxide necessitates specialized storage and transport systems. Recent developments in moisture-resistant packaging and automated dispensing systems have reduced material degradation by approximately 65%, significantly extending shelf life and maintaining catalytic potency during industrial operations.
Equipment design modifications represent a substantial investment area for scaling lithium hydroxide catalysis. Corrosion-resistant alloys and specialized coating technologies have extended equipment lifespan by 2.5-3 times compared to standard materials. Modular reactor designs that allow for capacity expansion without complete system overhauls have gained traction, reducing capital expenditure by approximately 40% for incremental scaling.
Process intensification techniques have demonstrated remarkable efficiency improvements. Advanced mixing technologies utilizing ultrasonic or microwave-assisted processes have shown 30-45% reductions in reaction time while maintaining or improving catalytic performance. These technologies, though requiring higher initial investment, deliver substantial operational cost savings through reduced energy consumption and increased throughput.
Quality control systems adaptation presents unique challenges at industrial scale. Real-time monitoring technologies using spectroscopic methods have been successfully implemented in pilot plants, allowing for continuous composition analysis and immediate process adjustments. These systems have reduced off-specification product by approximately 70% compared to traditional sampling methods.
Economic considerations ultimately drive implementation decisions. Cost modeling indicates that for medium to large-scale operations (>500 tons annually), the implementation of optimized lithium hydroxide catalysis systems becomes economically advantageous with ROI periods of 18-24 months. Smaller operations may benefit from centralized processing facilities or toll manufacturing arrangements to achieve economic viability without substantial capital investment.
Material handling innovations present another crucial aspect of industrial implementation. The hygroscopic nature of lithium hydroxide necessitates specialized storage and transport systems. Recent developments in moisture-resistant packaging and automated dispensing systems have reduced material degradation by approximately 65%, significantly extending shelf life and maintaining catalytic potency during industrial operations.
Equipment design modifications represent a substantial investment area for scaling lithium hydroxide catalysis. Corrosion-resistant alloys and specialized coating technologies have extended equipment lifespan by 2.5-3 times compared to standard materials. Modular reactor designs that allow for capacity expansion without complete system overhauls have gained traction, reducing capital expenditure by approximately 40% for incremental scaling.
Process intensification techniques have demonstrated remarkable efficiency improvements. Advanced mixing technologies utilizing ultrasonic or microwave-assisted processes have shown 30-45% reductions in reaction time while maintaining or improving catalytic performance. These technologies, though requiring higher initial investment, deliver substantial operational cost savings through reduced energy consumption and increased throughput.
Quality control systems adaptation presents unique challenges at industrial scale. Real-time monitoring technologies using spectroscopic methods have been successfully implemented in pilot plants, allowing for continuous composition analysis and immediate process adjustments. These systems have reduced off-specification product by approximately 70% compared to traditional sampling methods.
Economic considerations ultimately drive implementation decisions. Cost modeling indicates that for medium to large-scale operations (>500 tons annually), the implementation of optimized lithium hydroxide catalysis systems becomes economically advantageous with ROI periods of 18-24 months. Smaller operations may benefit from centralized processing facilities or toll manufacturing arrangements to achieve economic viability without substantial capital investment.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!