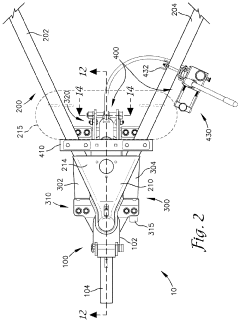
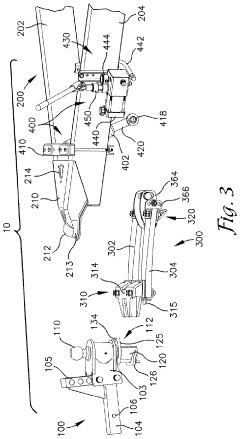
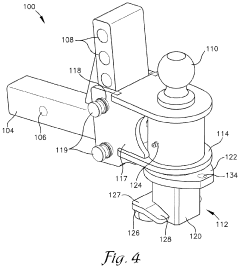
Pintle Hitch Influence on Trailer Weight Distribution Metrics
AUG 12, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Pintle Hitch Evolution
The pintle hitch has undergone significant evolution since its inception, adapting to changing vehicle designs and towing requirements. Initially developed for military applications in the early 20th century, the pintle hitch was designed to provide a robust and flexible coupling system for heavy-duty towing in challenging terrains.
In the 1940s and 1950s, the pintle hitch gained popularity in commercial and agricultural sectors due to its durability and ability to handle heavy loads. The basic design consisted of a hook-like protrusion (the pintle) on the towing vehicle, which would engage with a ring or eye on the trailer. This simple yet effective mechanism allowed for greater articulation and movement between the towing vehicle and trailer, making it ideal for off-road and uneven terrain applications.
As vehicle technology advanced in the 1960s and 1970s, pintle hitches began to incorporate safety features such as locking mechanisms and secondary attachment points. These improvements addressed concerns about accidental uncoupling and enhanced overall towing safety. During this period, manufacturers also started experimenting with different materials, moving from cast iron to high-strength steel alloys to reduce weight while maintaining structural integrity.
The 1980s and 1990s saw a shift towards more specialized pintle hitch designs. Adjustable-height pintles were introduced, allowing for better compatibility with various trailer heights and improving weight distribution. Additionally, combination pintle hitches that incorporated a ball mount alongside the traditional pintle hook began to emerge, offering greater versatility for different types of trailers.
In the early 2000s, the focus shifted towards improving the weight distribution capabilities of pintle hitches. Engineers began to explore how the pintle hitch design could be optimized to better manage trailer weight and reduce stress on the towing vehicle. This led to the development of integrated weight distribution systems within pintle hitches, utilizing spring bars or other mechanisms to distribute the trailer's tongue weight more evenly across the towing vehicle's axles.
Recent advancements in the 2010s and beyond have seen the integration of electronic systems into pintle hitch designs. These include sensors for monitoring hitch load, trailer sway detection, and even automated coupling systems. Such innovations aim to enhance safety, ease of use, and overall towing performance.
The ongoing evolution of pintle hitches continues to focus on improving weight distribution metrics, as evidenced by recent patents and research papers. Engineers are exploring novel designs that incorporate dynamic load sensing and active weight redistribution mechanisms, aiming to optimize trailer stability and handling across various driving conditions.
In the 1940s and 1950s, the pintle hitch gained popularity in commercial and agricultural sectors due to its durability and ability to handle heavy loads. The basic design consisted of a hook-like protrusion (the pintle) on the towing vehicle, which would engage with a ring or eye on the trailer. This simple yet effective mechanism allowed for greater articulation and movement between the towing vehicle and trailer, making it ideal for off-road and uneven terrain applications.
As vehicle technology advanced in the 1960s and 1970s, pintle hitches began to incorporate safety features such as locking mechanisms and secondary attachment points. These improvements addressed concerns about accidental uncoupling and enhanced overall towing safety. During this period, manufacturers also started experimenting with different materials, moving from cast iron to high-strength steel alloys to reduce weight while maintaining structural integrity.
The 1980s and 1990s saw a shift towards more specialized pintle hitch designs. Adjustable-height pintles were introduced, allowing for better compatibility with various trailer heights and improving weight distribution. Additionally, combination pintle hitches that incorporated a ball mount alongside the traditional pintle hook began to emerge, offering greater versatility for different types of trailers.
In the early 2000s, the focus shifted towards improving the weight distribution capabilities of pintle hitches. Engineers began to explore how the pintle hitch design could be optimized to better manage trailer weight and reduce stress on the towing vehicle. This led to the development of integrated weight distribution systems within pintle hitches, utilizing spring bars or other mechanisms to distribute the trailer's tongue weight more evenly across the towing vehicle's axles.
Recent advancements in the 2010s and beyond have seen the integration of electronic systems into pintle hitch designs. These include sensors for monitoring hitch load, trailer sway detection, and even automated coupling systems. Such innovations aim to enhance safety, ease of use, and overall towing performance.
The ongoing evolution of pintle hitches continues to focus on improving weight distribution metrics, as evidenced by recent patents and research papers. Engineers are exploring novel designs that incorporate dynamic load sensing and active weight redistribution mechanisms, aiming to optimize trailer stability and handling across various driving conditions.
Trailer Weight Market
The trailer weight market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand for recreational vehicles, cargo transportation, and construction equipment. This market segment encompasses a wide range of trailer types, including travel trailers, utility trailers, flatbed trailers, and specialized trailers for specific industries. The global trailer market size was valued at approximately $25 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $35 billion by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 6.5%.
The North American market, particularly the United States, dominates the global trailer weight market, accounting for nearly 40% of the total market share. This dominance is attributed to the popularity of recreational vehicles and the robust logistics industry in the region. Europe follows closely, with countries like Germany, France, and the United Kingdom contributing significantly to market growth. The Asia-Pacific region, led by China and India, is expected to witness the fastest growth rate in the coming years due to rapid industrialization and infrastructure development.
In terms of trailer weight categories, light-duty trailers (under 3,500 lbs) constitute the largest segment, representing approximately 60% of the market. These trailers are widely used for personal and small business applications. Medium-duty trailers (3,500-26,000 lbs) account for about 30% of the market, primarily serving commercial and industrial needs. Heavy-duty trailers (over 26,000 lbs) make up the remaining 10%, catering to specialized transportation requirements in industries such as construction and mining.
The trailer weight market is influenced by several factors, including economic conditions, fuel prices, and regulatory policies. The COVID-19 pandemic initially caused a temporary slowdown in market growth due to supply chain disruptions and reduced consumer spending. However, the market has shown resilience, with a surge in demand for recreational vehicles and home delivery services contributing to a quick recovery.
Technological advancements are playing a crucial role in shaping the trailer weight market. Innovations in materials science, such as the use of lightweight composites and high-strength steel, are enabling manufacturers to produce trailers with improved weight-to-payload ratios. Additionally, the integration of smart technologies, including telematics and advanced braking systems, is enhancing trailer safety and efficiency, further driving market growth.
The competitive landscape of the trailer weight market is characterized by a mix of established players and emerging companies. Key market players include Wabash National Corporation, Great Dane LLC, Utility Trailer Manufacturing Company, and Schmitz Cargobull AG. These companies are focusing on product innovation, strategic partnerships, and geographical expansion to maintain their market positions and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
The North American market, particularly the United States, dominates the global trailer weight market, accounting for nearly 40% of the total market share. This dominance is attributed to the popularity of recreational vehicles and the robust logistics industry in the region. Europe follows closely, with countries like Germany, France, and the United Kingdom contributing significantly to market growth. The Asia-Pacific region, led by China and India, is expected to witness the fastest growth rate in the coming years due to rapid industrialization and infrastructure development.
In terms of trailer weight categories, light-duty trailers (under 3,500 lbs) constitute the largest segment, representing approximately 60% of the market. These trailers are widely used for personal and small business applications. Medium-duty trailers (3,500-26,000 lbs) account for about 30% of the market, primarily serving commercial and industrial needs. Heavy-duty trailers (over 26,000 lbs) make up the remaining 10%, catering to specialized transportation requirements in industries such as construction and mining.
The trailer weight market is influenced by several factors, including economic conditions, fuel prices, and regulatory policies. The COVID-19 pandemic initially caused a temporary slowdown in market growth due to supply chain disruptions and reduced consumer spending. However, the market has shown resilience, with a surge in demand for recreational vehicles and home delivery services contributing to a quick recovery.
Technological advancements are playing a crucial role in shaping the trailer weight market. Innovations in materials science, such as the use of lightweight composites and high-strength steel, are enabling manufacturers to produce trailers with improved weight-to-payload ratios. Additionally, the integration of smart technologies, including telematics and advanced braking systems, is enhancing trailer safety and efficiency, further driving market growth.
The competitive landscape of the trailer weight market is characterized by a mix of established players and emerging companies. Key market players include Wabash National Corporation, Great Dane LLC, Utility Trailer Manufacturing Company, and Schmitz Cargobull AG. These companies are focusing on product innovation, strategic partnerships, and geographical expansion to maintain their market positions and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Hitch Tech Challenges
The development of pintle hitch technology for trailer weight distribution faces several significant challenges. One of the primary issues is achieving optimal weight distribution across the towing vehicle and trailer. The pintle hitch's design, while robust and suitable for heavy-duty applications, can sometimes lead to uneven weight distribution, potentially affecting vehicle stability and handling.
Another challenge lies in the integration of advanced sensing and control systems with traditional pintle hitch designs. As the automotive industry moves towards more intelligent and connected vehicles, there is a growing need to incorporate smart technologies into hitching systems. This includes real-time monitoring of weight distribution, automated adjustment mechanisms, and integration with vehicle stability control systems.
The durability and wear resistance of pintle hitch components under varying load conditions present ongoing challenges. The constant stress and movement experienced by these components, especially in off-road or harsh environments, require continuous innovation in materials science and engineering to enhance longevity and reliability.
Noise reduction is another area of concern in pintle hitch technology. The characteristic play in the pintle-lunette connection, while allowing for greater articulation, can result in increased noise levels during operation. Developing solutions that maintain the hitch's flexibility while minimizing noise pollution is a key focus for engineers.
Compatibility across different vehicle and trailer types poses a significant challenge. As the range of towing vehicles and trailers expands, ensuring that pintle hitch systems can adapt to various configurations without compromising safety or performance becomes increasingly complex. This includes addressing issues related to different heights, weights, and coupling mechanisms.
The impact of pintle hitches on fuel efficiency is an emerging concern, particularly as environmental regulations become more stringent. The additional weight and potential aerodynamic drag introduced by these systems can affect overall vehicle efficiency. Developing lighter, more aerodynamic designs without sacrificing strength and safety is a critical challenge.
Lastly, the integration of pintle hitch systems with emerging autonomous vehicle technologies presents new and complex challenges. As self-driving capabilities advance, hitching systems must evolve to interface seamlessly with these technologies, ensuring safe and efficient operation in both manned and unmanned towing scenarios.
Another challenge lies in the integration of advanced sensing and control systems with traditional pintle hitch designs. As the automotive industry moves towards more intelligent and connected vehicles, there is a growing need to incorporate smart technologies into hitching systems. This includes real-time monitoring of weight distribution, automated adjustment mechanisms, and integration with vehicle stability control systems.
The durability and wear resistance of pintle hitch components under varying load conditions present ongoing challenges. The constant stress and movement experienced by these components, especially in off-road or harsh environments, require continuous innovation in materials science and engineering to enhance longevity and reliability.
Noise reduction is another area of concern in pintle hitch technology. The characteristic play in the pintle-lunette connection, while allowing for greater articulation, can result in increased noise levels during operation. Developing solutions that maintain the hitch's flexibility while minimizing noise pollution is a key focus for engineers.
Compatibility across different vehicle and trailer types poses a significant challenge. As the range of towing vehicles and trailers expands, ensuring that pintle hitch systems can adapt to various configurations without compromising safety or performance becomes increasingly complex. This includes addressing issues related to different heights, weights, and coupling mechanisms.
The impact of pintle hitches on fuel efficiency is an emerging concern, particularly as environmental regulations become more stringent. The additional weight and potential aerodynamic drag introduced by these systems can affect overall vehicle efficiency. Developing lighter, more aerodynamic designs without sacrificing strength and safety is a critical challenge.
Lastly, the integration of pintle hitch systems with emerging autonomous vehicle technologies presents new and complex challenges. As self-driving capabilities advance, hitching systems must evolve to interface seamlessly with these technologies, ensuring safe and efficient operation in both manned and unmanned towing scenarios.
Weight Distribution Tech
01 Weight distribution systems for pintle hitches
Weight distribution systems are designed for pintle hitches to improve towing stability and safety. These systems help distribute the tongue weight of the trailer more evenly across the towing vehicle's axles, reducing sway and improving handling. They typically involve spring bars or other mechanisms that transfer weight from the rear of the towing vehicle to its front axle and the trailer's axles.- Weight distribution systems for pintle hitches: Weight distribution systems are designed for pintle hitches to improve towing stability and safety. These systems typically include spring bars or other mechanisms that help distribute the tongue weight of the trailer more evenly across the towing vehicle's axles. This distribution reduces sway, improves steering control, and enhances overall towing performance.
- Adjustable pintle hitch assemblies: Adjustable pintle hitch assemblies allow for customization of the hitch position and angle. These designs often feature multiple mounting holes or adjustable components that enable users to optimize the hitch setup for different trailers or towing conditions. The ability to adjust the hitch can help achieve better weight distribution and improve overall towing stability.
- Integration of sway control with weight distribution: Some pintle hitch designs incorporate sway control features alongside weight distribution mechanisms. These integrated systems work together to minimize trailer sway while ensuring proper weight distribution. The combination of these features enhances towing stability, particularly in challenging conditions such as high winds or during emergency maneuvers.
- Electronic weight distribution and monitoring systems: Advanced pintle hitch designs may include electronic sensors and control systems to actively monitor and adjust weight distribution. These systems can provide real-time feedback on tongue weight, axle loads, and overall weight distribution. Some may even automatically adjust the hitch or suspension components to maintain optimal weight distribution during towing.
- Multi-functional pintle hitch designs: Some pintle hitch designs incorporate multiple functions beyond basic weight distribution. These may include integrated brake controllers, articulation joints for off-road use, or quick-disconnect mechanisms for easy trailer attachment and detachment. These multi-functional designs aim to improve overall towing versatility while maintaining proper weight distribution.
02 Adjustable pintle hitch assemblies
Adjustable pintle hitch assemblies allow for customization of the hitch position and angle to accommodate different trailer heights and weights. These systems often include multiple adjustment points or sliding mechanisms that enable users to optimize the towing setup for various trailer configurations, enhancing weight distribution and towing performance.Expand Specific Solutions03 Integration of sway control with weight distribution
Advanced pintle hitch systems incorporate sway control features alongside weight distribution mechanisms. These integrated systems work together to minimize trailer sway caused by crosswinds, passing vehicles, or sudden maneuvers, while simultaneously ensuring proper weight distribution. This combination enhances overall towing stability and safety.Expand Specific Solutions04 Electronic weight distribution and monitoring
Electronic systems for weight distribution in pintle hitches utilize sensors and control units to actively monitor and adjust weight distribution during towing. These systems can provide real-time feedback to the driver about tongue weight, axle loads, and overall weight distribution, allowing for dynamic adjustments to maintain optimal towing conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Multi-functional pintle hitch designs
Multi-functional pintle hitch designs incorporate weight distribution features along with other capabilities such as height adjustment, quick-release mechanisms, or compatibility with multiple trailer coupling types. These versatile designs aim to provide a single solution for various towing needs while ensuring proper weight distribution across different trailer configurations.Expand Specific Solutions
Towing Industry Players
The competitive landscape for "Pintle Hitch Influence on Trailer Weight Distribution Metrics" is in a growth phase, with increasing market size due to rising demand for towing solutions. The technology is moderately mature, with established players like Weigh Safe LLC and Horizon Global Americas leading innovation. Companies such as B&W Trailer Hitches and Curt Manufacturing are also contributing to advancements. The market is seeing new entrants like Hall Labs LLC, indicating potential for further technological developments. Major automotive companies like Ford and Polaris are also involved, suggesting broader industry interest in this technology.
Weigh Safe LLC
Technical Solution: Weigh Safe LLC has developed an innovative pintle hitch system that incorporates built-in weight distribution and sway control features. Their technology utilizes a patented design that combines a pintle hook with an integrated scale and adjustable spring bars. This system allows for real-time monitoring of tongue weight and provides dynamic weight distribution capabilities[1]. The pintle hitch design enables a wider range of articulation compared to traditional ball hitches, making it suitable for various trailer types and off-road conditions. Weigh Safe's system also includes a sway control mechanism that helps stabilize the trailer during travel, reducing the risk of trailer sway and improving overall safety[2].
Strengths: Real-time tongue weight monitoring, integrated weight distribution, and sway control in a single system. Suitable for a wide range of trailer types and conditions. Weaknesses: May be more complex and expensive than traditional pintle hitches. Requires user familiarity with the system for optimal performance.
Horizon Global Americas, Inc.
Technical Solution: Horizon Global Americas, Inc. has developed a sophisticated pintle hitch system that focuses on optimizing trailer weight distribution through advanced engineering and materials. Their technology incorporates a high-strength steel construction with a unique geometry that enhances load distribution across the towing vehicle's axles. The company's pintle hitch design features an adjustable height mechanism that allows for precise alignment with various trailer configurations[3]. Additionally, Horizon Global has implemented a proprietary friction-based sway control system that works in conjunction with the pintle hitch to minimize trailer movement. This integrated approach helps maintain proper weight distribution even under challenging road conditions or during sudden maneuvers[4].
Strengths: High-strength construction, adjustable height for versatility, integrated sway control system. Suitable for heavy-duty applications. Weaknesses: May be overengineered for lighter trailer applications. Potentially higher cost due to advanced features.
Pintle Hitch Innovations
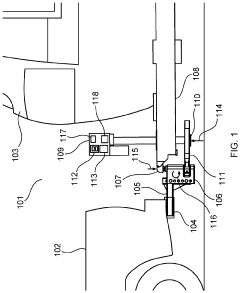
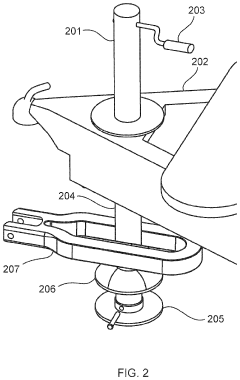
Weight distribution hitch
PatentActiveUS11331970B2
Innovation
- A weight distribution hitch system with a single moment bar and a jack mechanism that provides an upward force, allowing for easier setup and adjustment without disconnecting brackets, and includes a bearing surface for secure attachment and load measurement, enabling balanced weight distribution and sway control.
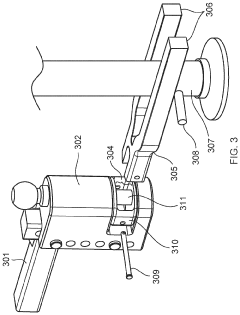
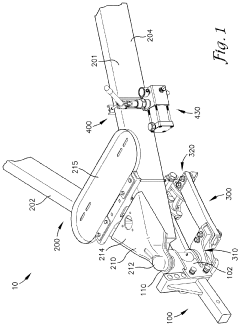
Weight distributing hitch system
PatentPendingUS20240010035A1
Innovation
- A weight distributing hitch system incorporating a spring arm assembly with a linear actuator assembly, allowing for remote adjustment of spring arm tension using a hydraulic actuator, which can be easily installed and operated to distribute load evenly across the towing vehicle's axles.
Safety Regulations
Safety regulations play a crucial role in governing the use of pintle hitches and their influence on trailer weight distribution metrics. These regulations are designed to ensure the safe operation of vehicles towing trailers, minimizing the risk of accidents and enhancing overall road safety.
In the United States, the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) sets forth guidelines for commercial motor vehicles, including those using pintle hitches. These regulations specify requirements for proper weight distribution, hitch strength, and safety chain usage. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) also provides standards for light-duty vehicles towing trailers, which include specifications for pintle hitch installations and weight distribution systems.
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) has developed standards specifically addressing pintle hitches, such as SAE J847 and SAE J849. These standards outline the design, testing, and performance requirements for pintle hitches, ensuring they can safely handle the loads and stresses associated with towing operations.
European regulations, such as those set by the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE), provide similar guidelines for pintle hitches and trailer weight distribution. Regulation No. 55 of UNECE addresses mechanical coupling components between vehicles and trailers, including pintle hitches, and specifies requirements for their design and testing.
Many countries have adopted or adapted these international standards into their national regulations. For instance, Australia's Vehicle Standards Bulletin (VSB) 1 includes requirements for pintle hitches and trailer couplings, while Canada's Motor Vehicle Safety Regulations incorporate similar safety standards for towing equipment.
Safety regulations typically mandate that pintle hitches must be properly rated for the gross trailer weight (GTW) and tongue weight of the trailer being towed. They also specify requirements for the vertical load capacity and the D-value, which represents the theoretical horizontal reference force between the towing vehicle and the trailer.
Furthermore, regulations often require the use of safety chains or cables as a secondary coupling system in case of hitch failure. These safety devices must be properly sized and attached to prevent the trailer from completely separating from the towing vehicle in the event of a hitch malfunction.
Weight distribution requirements are also addressed in safety regulations, with guidelines for proper load distribution between the trailer axles and the tow vehicle. This includes specifications for tongue weight percentages and the use of weight distribution systems when necessary to maintain safe handling characteristics.
As technology advances, safety regulations continue to evolve to address new challenges and incorporate improved safety features. This includes the integration of electronic stability control systems and trailer sway control technologies, which can significantly enhance the safety of vehicles using pintle hitches for towing operations.
In the United States, the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) sets forth guidelines for commercial motor vehicles, including those using pintle hitches. These regulations specify requirements for proper weight distribution, hitch strength, and safety chain usage. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) also provides standards for light-duty vehicles towing trailers, which include specifications for pintle hitch installations and weight distribution systems.
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) has developed standards specifically addressing pintle hitches, such as SAE J847 and SAE J849. These standards outline the design, testing, and performance requirements for pintle hitches, ensuring they can safely handle the loads and stresses associated with towing operations.
European regulations, such as those set by the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE), provide similar guidelines for pintle hitches and trailer weight distribution. Regulation No. 55 of UNECE addresses mechanical coupling components between vehicles and trailers, including pintle hitches, and specifies requirements for their design and testing.
Many countries have adopted or adapted these international standards into their national regulations. For instance, Australia's Vehicle Standards Bulletin (VSB) 1 includes requirements for pintle hitches and trailer couplings, while Canada's Motor Vehicle Safety Regulations incorporate similar safety standards for towing equipment.
Safety regulations typically mandate that pintle hitches must be properly rated for the gross trailer weight (GTW) and tongue weight of the trailer being towed. They also specify requirements for the vertical load capacity and the D-value, which represents the theoretical horizontal reference force between the towing vehicle and the trailer.
Furthermore, regulations often require the use of safety chains or cables as a secondary coupling system in case of hitch failure. These safety devices must be properly sized and attached to prevent the trailer from completely separating from the towing vehicle in the event of a hitch malfunction.
Weight distribution requirements are also addressed in safety regulations, with guidelines for proper load distribution between the trailer axles and the tow vehicle. This includes specifications for tongue weight percentages and the use of weight distribution systems when necessary to maintain safe handling characteristics.
As technology advances, safety regulations continue to evolve to address new challenges and incorporate improved safety features. This includes the integration of electronic stability control systems and trailer sway control technologies, which can significantly enhance the safety of vehicles using pintle hitches for towing operations.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of pintle hitch systems and their influence on trailer weight distribution metrics is a crucial consideration in the transportation industry. These systems play a significant role in determining the overall ecological footprint of towing operations, affecting fuel consumption, emissions, and road wear.
One of the primary environmental concerns related to pintle hitch systems is their effect on fuel efficiency. The weight distribution facilitated by these hitches can significantly impact the towing vehicle's fuel consumption. Improper weight distribution may lead to increased drag and resistance, resulting in higher fuel consumption and, consequently, increased carbon emissions. Conversely, optimized weight distribution can improve fuel efficiency, reducing the environmental impact of towing operations.
The durability and longevity of pintle hitch systems also contribute to their environmental impact. High-quality, well-designed hitches that effectively distribute trailer weight can reduce wear and tear on both the towing vehicle and the trailer. This increased durability translates to less frequent replacements and repairs, ultimately reducing the demand for raw materials and energy required for manufacturing new components.
Road wear is another critical environmental factor influenced by pintle hitch systems and trailer weight distribution. Proper weight distribution helps minimize the stress placed on road surfaces, potentially reducing the frequency and extent of road maintenance and repairs. This, in turn, leads to decreased consumption of materials and energy associated with road construction and maintenance activities.
The materials used in pintle hitch manufacturing also play a role in their environmental impact. The production of these components often involves metals and other materials that require energy-intensive extraction and processing. However, advancements in materials science and manufacturing techniques have led to the development of lighter, yet equally strong, materials for pintle hitches. These innovations can contribute to overall weight reduction and improved fuel efficiency.
Noise pollution is another environmental concern associated with pintle hitch systems. The interaction between the hitch and trailer can generate noise, particularly when weight distribution is suboptimal. Improved designs that enhance weight distribution and reduce vibration can help mitigate this form of pollution, contributing to a quieter and more environmentally friendly transportation ecosystem.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of pintle hitch systems and their influence on trailer weight distribution metrics is multifaceted. By optimizing these systems for improved weight distribution, manufacturers and users can contribute to reduced fuel consumption, lower emissions, decreased road wear, and minimized noise pollution. As environmental concerns continue to shape industry practices, the development of more eco-friendly pintle hitch systems will likely remain a focus of innovation in the transportation sector.
One of the primary environmental concerns related to pintle hitch systems is their effect on fuel efficiency. The weight distribution facilitated by these hitches can significantly impact the towing vehicle's fuel consumption. Improper weight distribution may lead to increased drag and resistance, resulting in higher fuel consumption and, consequently, increased carbon emissions. Conversely, optimized weight distribution can improve fuel efficiency, reducing the environmental impact of towing operations.
The durability and longevity of pintle hitch systems also contribute to their environmental impact. High-quality, well-designed hitches that effectively distribute trailer weight can reduce wear and tear on both the towing vehicle and the trailer. This increased durability translates to less frequent replacements and repairs, ultimately reducing the demand for raw materials and energy required for manufacturing new components.
Road wear is another critical environmental factor influenced by pintle hitch systems and trailer weight distribution. Proper weight distribution helps minimize the stress placed on road surfaces, potentially reducing the frequency and extent of road maintenance and repairs. This, in turn, leads to decreased consumption of materials and energy associated with road construction and maintenance activities.
The materials used in pintle hitch manufacturing also play a role in their environmental impact. The production of these components often involves metals and other materials that require energy-intensive extraction and processing. However, advancements in materials science and manufacturing techniques have led to the development of lighter, yet equally strong, materials for pintle hitches. These innovations can contribute to overall weight reduction and improved fuel efficiency.
Noise pollution is another environmental concern associated with pintle hitch systems. The interaction between the hitch and trailer can generate noise, particularly when weight distribution is suboptimal. Improved designs that enhance weight distribution and reduce vibration can help mitigate this form of pollution, contributing to a quieter and more environmentally friendly transportation ecosystem.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of pintle hitch systems and their influence on trailer weight distribution metrics is multifaceted. By optimizing these systems for improved weight distribution, manufacturers and users can contribute to reduced fuel consumption, lower emissions, decreased road wear, and minimized noise pollution. As environmental concerns continue to shape industry practices, the development of more eco-friendly pintle hitch systems will likely remain a focus of innovation in the transportation sector.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!