Quantify Lithium with ICP-MS: Procedure and Challenges
SEP 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
ICP-MS Lithium Quantification Background and Objectives
Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) has emerged as a pivotal analytical technique in the quantification of lithium since its commercial introduction in the 1980s. The evolution of this technology has been marked by significant improvements in sensitivity, precision, and sample throughput capabilities, making it increasingly valuable for lithium analysis across multiple industries. Initially developed for geological applications, ICP-MS has expanded its utility to pharmaceutical, environmental, and energy storage sectors where accurate lithium quantification is critical.
The global transition toward renewable energy and electric mobility has dramatically increased the demand for lithium, driving the need for more sophisticated analytical methods. Between 2015 and 2023, the global lithium market has experienced a compound annual growth rate exceeding 20%, highlighting the strategic importance of precise lithium quantification techniques. This surge underscores the necessity for continued advancement in ICP-MS methodologies specifically optimized for lithium analysis.
Current ICP-MS technology enables detection limits for lithium in the parts-per-trillion range, representing a thousand-fold improvement over earlier analytical methods such as flame photometry or atomic absorption spectroscopy. However, lithium quantification presents unique challenges due to its low atomic mass, potential for memory effects, and susceptibility to various interferences that can compromise measurement accuracy.
The primary objective of lithium quantification via ICP-MS is to establish robust, reproducible protocols that overcome these inherent challenges while maintaining high analytical performance across diverse sample matrices. This includes developing standardized procedures for sample preparation, instrument calibration, and data processing that can be reliably implemented in both research and industrial settings.
Additionally, there is growing interest in adapting ICP-MS techniques for rapid, high-throughput lithium analysis to support quality control in battery manufacturing and recycling processes. The ability to quickly and accurately determine lithium content in various materials has become essential for optimizing production efficiency and ensuring product quality in the expanding lithium-ion battery industry.
Future technological objectives include enhancing the specificity of lithium detection in complex matrices, reducing sample preparation requirements, and developing portable or online ICP-MS systems capable of real-time lithium monitoring. These advancements would significantly benefit mining operations, battery production facilities, and environmental monitoring programs where timely lithium quantification is increasingly valuable.
As regulatory frameworks evolve to address the environmental impacts of lithium extraction and processing, there is also a pressing need for standardized ICP-MS methodologies that can support compliance monitoring and sustainable resource management practices across the lithium value chain.
The global transition toward renewable energy and electric mobility has dramatically increased the demand for lithium, driving the need for more sophisticated analytical methods. Between 2015 and 2023, the global lithium market has experienced a compound annual growth rate exceeding 20%, highlighting the strategic importance of precise lithium quantification techniques. This surge underscores the necessity for continued advancement in ICP-MS methodologies specifically optimized for lithium analysis.
Current ICP-MS technology enables detection limits for lithium in the parts-per-trillion range, representing a thousand-fold improvement over earlier analytical methods such as flame photometry or atomic absorption spectroscopy. However, lithium quantification presents unique challenges due to its low atomic mass, potential for memory effects, and susceptibility to various interferences that can compromise measurement accuracy.
The primary objective of lithium quantification via ICP-MS is to establish robust, reproducible protocols that overcome these inherent challenges while maintaining high analytical performance across diverse sample matrices. This includes developing standardized procedures for sample preparation, instrument calibration, and data processing that can be reliably implemented in both research and industrial settings.
Additionally, there is growing interest in adapting ICP-MS techniques for rapid, high-throughput lithium analysis to support quality control in battery manufacturing and recycling processes. The ability to quickly and accurately determine lithium content in various materials has become essential for optimizing production efficiency and ensuring product quality in the expanding lithium-ion battery industry.
Future technological objectives include enhancing the specificity of lithium detection in complex matrices, reducing sample preparation requirements, and developing portable or online ICP-MS systems capable of real-time lithium monitoring. These advancements would significantly benefit mining operations, battery production facilities, and environmental monitoring programs where timely lithium quantification is increasingly valuable.
As regulatory frameworks evolve to address the environmental impacts of lithium extraction and processing, there is also a pressing need for standardized ICP-MS methodologies that can support compliance monitoring and sustainable resource management practices across the lithium value chain.
Market Demand Analysis for Lithium Quantification Methods
The global market for lithium quantification methods is experiencing unprecedented growth, primarily driven by the expanding electric vehicle (EV) industry and renewable energy storage systems. The lithium-ion battery market, valued at approximately $46.2 billion in 2022, is projected to reach $182.5 billion by 2030, representing a CAGR of 18.7%. This exponential growth directly translates to increased demand for precise lithium quantification technologies, particularly ICP-MS (Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry).
The battery manufacturing sector constitutes the largest market segment for lithium quantification methods, accounting for roughly 65% of the total demand. Quality control requirements in this sector have become increasingly stringent, with manufacturers requiring detection limits in the parts-per-trillion range and accuracy levels exceeding 99.5%. This precision is critical as even minor variations in lithium content can significantly impact battery performance and safety characteristics.
Environmental monitoring represents another rapidly growing application area, expanding at 22.3% annually. Regulatory bodies worldwide have implemented stricter guidelines for lithium monitoring in water systems and soil, particularly in regions with lithium mining operations. The healthcare sector also demonstrates increasing demand for lithium quantification, especially for therapeutic drug monitoring in psychiatric treatments.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the market with a 42% share, led by China, Japan, and South Korea – countries with established battery manufacturing ecosystems. North America follows at 28%, with significant growth observed in research institutions and emerging battery production facilities. Europe accounts for 24% of the market, with particularly strong demand from Germany and Scandinavian countries focusing on renewable energy solutions.
The market landscape is further shaped by technological preferences, with ICP-MS holding approximately 38% market share among lithium quantification methods due to its superior sensitivity and multi-element analysis capabilities. Alternative technologies like atomic absorption spectroscopy (22%) and ion chromatography (17%) maintain significant market presence in specific application niches.
Industry surveys indicate that end-users prioritize three key factors when selecting lithium quantification methods: analytical precision (cited by 87% of respondents), sample throughput capacity (76%), and total cost of ownership (71%). These market drivers are pushing technology providers to develop more automated, high-throughput ICP-MS solutions with enhanced matrix tolerance for complex lithium-containing samples.
The battery manufacturing sector constitutes the largest market segment for lithium quantification methods, accounting for roughly 65% of the total demand. Quality control requirements in this sector have become increasingly stringent, with manufacturers requiring detection limits in the parts-per-trillion range and accuracy levels exceeding 99.5%. This precision is critical as even minor variations in lithium content can significantly impact battery performance and safety characteristics.
Environmental monitoring represents another rapidly growing application area, expanding at 22.3% annually. Regulatory bodies worldwide have implemented stricter guidelines for lithium monitoring in water systems and soil, particularly in regions with lithium mining operations. The healthcare sector also demonstrates increasing demand for lithium quantification, especially for therapeutic drug monitoring in psychiatric treatments.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the market with a 42% share, led by China, Japan, and South Korea – countries with established battery manufacturing ecosystems. North America follows at 28%, with significant growth observed in research institutions and emerging battery production facilities. Europe accounts for 24% of the market, with particularly strong demand from Germany and Scandinavian countries focusing on renewable energy solutions.
The market landscape is further shaped by technological preferences, with ICP-MS holding approximately 38% market share among lithium quantification methods due to its superior sensitivity and multi-element analysis capabilities. Alternative technologies like atomic absorption spectroscopy (22%) and ion chromatography (17%) maintain significant market presence in specific application niches.
Industry surveys indicate that end-users prioritize three key factors when selecting lithium quantification methods: analytical precision (cited by 87% of respondents), sample throughput capacity (76%), and total cost of ownership (71%). These market drivers are pushing technology providers to develop more automated, high-throughput ICP-MS solutions with enhanced matrix tolerance for complex lithium-containing samples.
Current State and Technical Challenges in ICP-MS Lithium Analysis
Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) has emerged as a powerful analytical technique for quantifying lithium, offering exceptional sensitivity and multi-element detection capabilities. Currently, ICP-MS represents the gold standard for lithium analysis in various matrices including geological samples, biological specimens, and industrial materials. The technique achieves detection limits in the parts-per-trillion (ppt) range, significantly outperforming alternative methods such as atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) and inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES).
Despite its advantages, ICP-MS lithium quantification faces several technical challenges. The low atomic mass of lithium (6.94 amu) positions it at the extreme low end of the mass range, where most ICP-MS instruments struggle with sensitivity and stability. This creates fundamental detection challenges that require specialized optimization. Additionally, lithium's first ionization energy (5.39 eV) is relatively high compared to many other elements, resulting in lower ionization efficiency in the plasma and consequently reduced sensitivity.
Matrix effects represent another significant challenge in ICP-MS lithium analysis. High concentrations of sodium, potassium, and other alkali metals commonly present in samples can cause significant signal suppression for lithium. This necessitates careful matrix matching between calibration standards and samples or the implementation of advanced correction techniques such as isotope dilution or standard addition methods.
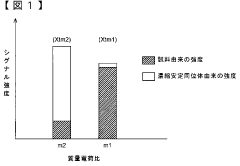
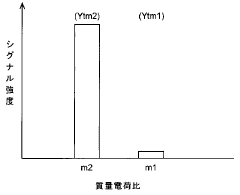
Spectral interferences further complicate lithium quantification. While lithium has two naturally occurring isotopes (⁶Li at 7.59% and ⁷Li at 92.41%), both can suffer from polyatomic interferences. For instance, ⁶Li experiences interference from ¹²C²⁺, while ⁷Li can be affected by ¹⁴N²⁺ and ⁶LiH⁺. These interferences necessitate the use of collision/reaction cell technology or high-resolution mass spectrometers to achieve accurate measurements.
Globally, the technical landscape for ICP-MS lithium analysis varies significantly. North American and European laboratories typically employ advanced triple-quadrupole ICP-MS systems with collision/reaction cell technology to overcome spectral interferences. In contrast, many Asian laboratories have pioneered high-throughput methods optimized for battery material analysis, reflecting regional industrial priorities. Japanese manufacturers have made significant advancements in low-mass sensitivity enhancements for ICP-MS instrumentation.
Sample preparation remains a critical bottleneck in the analytical workflow. Lithium's high mobility and potential for contamination during digestion procedures necessitate clean laboratory conditions. The diverse matrices in which lithium analysis is required—from hard rock minerals to biological fluids—demand matrix-specific sample preparation protocols, adding complexity to standardization efforts across different application domains.
Despite its advantages, ICP-MS lithium quantification faces several technical challenges. The low atomic mass of lithium (6.94 amu) positions it at the extreme low end of the mass range, where most ICP-MS instruments struggle with sensitivity and stability. This creates fundamental detection challenges that require specialized optimization. Additionally, lithium's first ionization energy (5.39 eV) is relatively high compared to many other elements, resulting in lower ionization efficiency in the plasma and consequently reduced sensitivity.
Matrix effects represent another significant challenge in ICP-MS lithium analysis. High concentrations of sodium, potassium, and other alkali metals commonly present in samples can cause significant signal suppression for lithium. This necessitates careful matrix matching between calibration standards and samples or the implementation of advanced correction techniques such as isotope dilution or standard addition methods.
Spectral interferences further complicate lithium quantification. While lithium has two naturally occurring isotopes (⁶Li at 7.59% and ⁷Li at 92.41%), both can suffer from polyatomic interferences. For instance, ⁶Li experiences interference from ¹²C²⁺, while ⁷Li can be affected by ¹⁴N²⁺ and ⁶LiH⁺. These interferences necessitate the use of collision/reaction cell technology or high-resolution mass spectrometers to achieve accurate measurements.
Globally, the technical landscape for ICP-MS lithium analysis varies significantly. North American and European laboratories typically employ advanced triple-quadrupole ICP-MS systems with collision/reaction cell technology to overcome spectral interferences. In contrast, many Asian laboratories have pioneered high-throughput methods optimized for battery material analysis, reflecting regional industrial priorities. Japanese manufacturers have made significant advancements in low-mass sensitivity enhancements for ICP-MS instrumentation.
Sample preparation remains a critical bottleneck in the analytical workflow. Lithium's high mobility and potential for contamination during digestion procedures necessitate clean laboratory conditions. The diverse matrices in which lithium analysis is required—from hard rock minerals to biological fluids—demand matrix-specific sample preparation protocols, adding complexity to standardization efforts across different application domains.
Current Methodologies for Lithium Quantification via ICP-MS
01 Calibration methods for improving ICP-MS quantification accuracy
Various calibration techniques are employed to enhance the accuracy of ICP-MS quantification. These include internal standardization, isotope dilution, standard addition methods, and matrix-matched calibration. These approaches compensate for matrix effects, instrument drift, and signal suppression or enhancement, leading to more reliable quantitative results. Proper calibration is essential for achieving high accuracy in trace element analysis across different sample types.- Calibration methods for improving ICP-MS quantification accuracy: Various calibration techniques are employed to enhance the accuracy of ICP-MS quantification. These include internal standardization, isotope dilution, standard addition methods, and matrix-matched calibration. These approaches compensate for matrix effects, instrument drift, and signal suppression or enhancement, leading to more reliable and accurate quantitative results in complex sample analyses.
- Sample preparation techniques for enhanced quantification accuracy: Proper sample preparation is crucial for accurate ICP-MS quantification. Techniques such as acid digestion, microwave-assisted extraction, dilution protocols, and matrix removal procedures help eliminate interferences and ensure complete analyte recovery. Optimized sample preparation methods reduce matrix effects and contamination risks, thereby improving the overall accuracy of elemental analysis.
- Interference reduction strategies in ICP-MS quantification: Various strategies are employed to reduce interferences in ICP-MS analysis, including collision/reaction cell technology, high-resolution mass spectrometry, and mathematical correction models. These approaches effectively minimize polyatomic, isobaric, and matrix-based interferences that can compromise quantification accuracy, particularly for complex samples containing multiple elements or challenging matrices.
- Instrumental optimization for improved quantification precision: Optimizing instrumental parameters significantly enhances ICP-MS quantification accuracy. This includes fine-tuning plasma conditions, ion optics, detector settings, and integration times. Advanced hardware configurations such as triple quadrupole systems and time-of-flight analyzers provide improved sensitivity and selectivity, contributing to more accurate quantitative measurements across a wide dynamic range.
- Quality control and validation procedures for ICP-MS analysis: Comprehensive quality control and validation procedures are essential for ensuring accurate ICP-MS quantification. These include the use of certified reference materials, method validation protocols, uncertainty estimation, and regular performance verification. Statistical approaches for data evaluation, outlier detection, and trend analysis help maintain analytical quality and provide confidence in the accuracy of quantitative results.
02 Sample preparation techniques for enhanced quantification accuracy
Effective sample preparation is crucial for accurate ICP-MS quantification. This includes digestion methods (acid digestion, microwave-assisted digestion), dilution strategies, and separation techniques to minimize matrix interferences. Proper sample preparation reduces contamination risks, ensures complete analyte extraction, and minimizes spectral and non-spectral interferences that can compromise measurement accuracy. Standardized preparation protocols are essential for reproducible and accurate results.Expand Specific Solutions03 Interference reduction and correction strategies
Various approaches are employed to address interferences in ICP-MS analysis, including collision/reaction cell technology, mathematical correction models, and high-resolution mass spectrometry. These methods effectively reduce or eliminate polyatomic, isobaric, and matrix-based interferences that can compromise quantification accuracy. By minimizing these interferences, more accurate determination of trace elements can be achieved, particularly in complex sample matrices.Expand Specific Solutions04 Instrument optimization and quality control procedures
Optimizing ICP-MS instrument parameters and implementing rigorous quality control procedures significantly improve quantification accuracy. This includes tuning for sensitivity and stability, optimizing plasma conditions, and regular performance verification. Quality control measures such as analyzing certified reference materials, conducting recovery tests, and monitoring instrument drift are essential for maintaining high accuracy. Automated optimization systems can help achieve consistent analytical performance.Expand Specific Solutions05 Advanced ICP-MS technologies for improved quantification
Recent advancements in ICP-MS technology have led to improved quantification accuracy. These include triple quadrupole systems, high-resolution sector field instruments, and time-of-flight mass analyzers. These technologies offer enhanced sensitivity, selectivity, and resolution, allowing for more accurate quantification of trace elements. Integration with automated sample introduction systems and specialized software for data processing further improves analytical performance and reliability.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in ICP-MS Instrumentation and Applications
The ICP-MS lithium quantification market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for lithium in batteries and pharmaceuticals. The global analytical instruments market for lithium analysis is expanding rapidly, with projections exceeding $1.5 billion by 2025. Technologically, ICP-MS for lithium quantification has reached maturity with ongoing refinements. Industry leaders Agilent Technologies, Thermo Fisher Scientific, and Shimadzu dominate with comprehensive solutions, while PerkinElmer (Revvity) and DuPont offer specialized applications. Research institutions like Xiamen University and CEA are advancing methodologies to overcome challenges in lithium isotope analysis. Emerging players like EnergySource Minerals and Jiangsu Leuven Instrument are developing niche solutions for specific industry applications, particularly in battery materials and semiconductor manufacturing.
Agilent Technologies, Inc.
Technical Solution: Agilent Technologies has developed advanced ICP-MS systems specifically optimized for lithium quantification, featuring their patented High Matrix Introduction (HMI) technology that effectively manages high dissolved solid samples common in lithium analysis. Their 7900 ICP-MS system incorporates collision/reaction cell technology with helium mode to minimize polyatomic interferences that typically affect low-mass elements like lithium. Agilent's ICP-MS MassHunter software includes dedicated workflows for battery materials analysis with pre-configured methods for lithium quantification across various matrices. The company has also developed specialized sample introduction systems including the Ultra High Matrix Introduction (UHMI) capability that allows direct measurement of samples with up to 25% total dissolved solids, significantly simplifying sample preparation for lithium-rich materials. Their instruments feature improved sensitivity for lithium detection with limits of detection in the sub-ppb range and enhanced calibration stability through their integrated internal standardization system.
Strengths: Industry-leading sensitivity for lithium detection with sub-ppb detection limits; robust performance with high-matrix samples through HMI technology; comprehensive software solutions specifically designed for battery materials analysis. Weaknesses: Higher initial investment cost compared to some competitors; requires specialized training for optimal operation; consumable costs can be significant for high-throughput laboratories.
Revvity Health Sciences, Inc.
Technical Solution: Revvity Health Sciences (formerly PerkinElmer) has developed the NexION ICP-MS platform with specialized capabilities for lithium quantification in complex matrices. Their system features the patented Universal Cell Technology (UCT) that operates in three modes (Standard, Collision, and Reaction) to effectively eliminate interferences affecting lithium measurements. Revvity's approach includes their All Matrix Solution (AMS) system that enables direct analysis of samples with high dissolved solids content (up to 35%) without requiring extensive dilution, particularly valuable for lithium-rich brines and digested battery materials. The company has engineered specialized sample introduction components including their LumiCoil RF coil technology that provides enhanced plasma stability for challenging lithium matrices. Their Syngistix software platform includes dedicated workflows for battery material analysis with automated QC protocols and specialized calibration approaches. Revvity has also developed the hyphenated LC-ICP-MS methodology for lithium speciation analysis, enabling differentiation between various lithium compounds in complex environmental and biological samples, providing insights beyond total lithium concentration.
Strengths: Superior interference removal capabilities through triple-mode cell technology; excellent tolerance for high-matrix samples; advanced speciation capabilities when coupled with chromatography. Weaknesses: More complex operation requiring specialized training; higher argon consumption compared to some competitors; challenges with ultra-trace lithium analysis in certain biological matrices.
Critical Technical Innovations in Low Mass Element Detection
Method for simultaneous analysis of multiple elements of hair sample by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry(ICP-ms)
PatentInactiveKR100372526B1
Innovation
- A method involving washing hair samples with surfactants and acetone, preparing a sample solution with dilute nitric acid and microwaves, diluting the solution by element-specific factors, and optimizing ICP-MS conditions to minimize interference, using internal standards and correction equations for accurate qualitative and quantitative analysis.
Determination Method of Trace Impurity Elements Using Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometer
PatentInactiveJP4512605B2
Innovation
- A method involving stable isotope dilution mass spectrometry is developed, utilizing a general-purpose quadrupole ICP-MS to quantify trace elements by adding enriched stable isotopes, establishing isotope equilibrium, and correcting for recovery rates and contamination through a series of signal intensity measurements and calibration curves, without the need for precise isotope ratio measurements.
Sample Preparation Optimization for Lithium Analysis
Sample preparation represents a critical phase in the accurate quantification of lithium using ICP-MS (Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry). The optimization of sample preparation protocols directly impacts measurement precision, detection limits, and overall analytical reliability. Current methodologies for lithium sample preparation vary significantly across different matrices, including geological samples, biological specimens, and industrial materials.
For geological samples, conventional acid digestion techniques utilizing hydrofluoric acid (HF) in combination with nitric acid (HNO₃) have demonstrated superior lithium recovery rates compared to single-acid approaches. However, the volatility of lithium compounds during high-temperature digestion presents a significant challenge, often resulting in systematic underestimation of lithium concentrations. Recent advancements have introduced low-temperature, pressure-assisted digestion systems that maintain sample integrity while achieving complete dissolution.
Biological matrices require specialized preparation protocols due to their complex organic composition and typically low lithium concentrations. Microwave-assisted digestion with nitric acid and hydrogen peroxide has emerged as the preferred method, offering reduced contamination risk and enhanced sample throughput. The addition of internal standards, particularly ⁶Li or ⁷Li isotopes not naturally abundant in the sample, significantly improves quantification accuracy by compensating for matrix effects and instrument drift.
Memory effects represent a persistent challenge in lithium analysis, as lithium ions can adhere to sample introduction components, causing cross-contamination between successive measurements. Implementation of extended washout procedures using dilute acids (typically 1-2% HNO₃) supplemented with complexing agents has proven effective in minimizing these carryover effects. Additionally, the incorporation of flow injection analysis systems can substantially reduce sample consumption while maintaining analytical performance.
Standardization of dilution protocols is essential for accurate lithium quantification. Research indicates that matrix-matched calibration standards prepared in the same acid mixture as the digested samples yield superior results compared to simple aqueous standards. For ultra-trace analysis, the clean laboratory environment becomes paramount, with HEPA-filtered workstations and ultra-pure reagents necessary to minimize background contamination.
Recent innovations in sample preparation include automated microextraction techniques and specialized chelating resins that selectively concentrate lithium from complex matrices. These approaches have demonstrated particular utility in environmental monitoring applications where sample volumes may be limited and matrix interferences significant. The development of these specialized preparation methodologies continues to expand the applicability of ICP-MS for lithium quantification across diverse scientific and industrial domains.
For geological samples, conventional acid digestion techniques utilizing hydrofluoric acid (HF) in combination with nitric acid (HNO₃) have demonstrated superior lithium recovery rates compared to single-acid approaches. However, the volatility of lithium compounds during high-temperature digestion presents a significant challenge, often resulting in systematic underestimation of lithium concentrations. Recent advancements have introduced low-temperature, pressure-assisted digestion systems that maintain sample integrity while achieving complete dissolution.
Biological matrices require specialized preparation protocols due to their complex organic composition and typically low lithium concentrations. Microwave-assisted digestion with nitric acid and hydrogen peroxide has emerged as the preferred method, offering reduced contamination risk and enhanced sample throughput. The addition of internal standards, particularly ⁶Li or ⁷Li isotopes not naturally abundant in the sample, significantly improves quantification accuracy by compensating for matrix effects and instrument drift.
Memory effects represent a persistent challenge in lithium analysis, as lithium ions can adhere to sample introduction components, causing cross-contamination between successive measurements. Implementation of extended washout procedures using dilute acids (typically 1-2% HNO₃) supplemented with complexing agents has proven effective in minimizing these carryover effects. Additionally, the incorporation of flow injection analysis systems can substantially reduce sample consumption while maintaining analytical performance.
Standardization of dilution protocols is essential for accurate lithium quantification. Research indicates that matrix-matched calibration standards prepared in the same acid mixture as the digested samples yield superior results compared to simple aqueous standards. For ultra-trace analysis, the clean laboratory environment becomes paramount, with HEPA-filtered workstations and ultra-pure reagents necessary to minimize background contamination.
Recent innovations in sample preparation include automated microextraction techniques and specialized chelating resins that selectively concentrate lithium from complex matrices. These approaches have demonstrated particular utility in environmental monitoring applications where sample volumes may be limited and matrix interferences significant. The development of these specialized preparation methodologies continues to expand the applicability of ICP-MS for lithium quantification across diverse scientific and industrial domains.
Interference Management Strategies in Low Mass Element Detection
Managing interference is a critical challenge in ICP-MS analysis of lithium, particularly due to its low atomic mass. The primary interferences affecting lithium detection include isobaric overlaps, polyatomic species, and background noise that can significantly impact measurement accuracy. Traditional approaches to interference management include mathematical correction algorithms that compensate for known interferences by measuring alternative isotopes and applying correction factors.
Collision/reaction cell technology represents a significant advancement in interference management for lithium quantification. These cells, positioned between the ion optics and mass analyzer, utilize collision gases (such as helium) or reaction gases (such as hydrogen or ammonia) to selectively remove or transform interfering species. For lithium analysis, hydrogen gas is particularly effective as it can react with many polyatomic interferences while leaving lithium ions relatively unaffected.
Cool plasma techniques offer another valuable approach for low mass element detection. By operating the ICP at reduced power (600-800W versus the typical 1200-1500W), certain plasma-based interferences are minimized. This technique is especially beneficial for lithium analysis as it reduces argon-based polyatomic species that can interfere with 7Li measurements. However, this approach requires careful optimization as it may reduce overall sensitivity.
High-resolution mass spectrometry provides an alternative strategy by physically separating ions with similar mass-to-charge ratios. Modern high-resolution ICP-MS instruments can achieve resolution exceeding 10,000, allowing differentiation between lithium isotopes and potential interferences. While effective, this approach typically comes with higher instrument costs and potentially reduced sensitivity compared to standard quadrupole systems.
Matrix separation techniques, including chromatographic methods and chemical extraction, can be implemented prior to ICP-MS analysis to isolate lithium from potential interfering elements. Ion chromatography coupled with ICP-MS has proven particularly effective for lithium analysis in complex matrices such as biological samples and brines, where high concentrations of sodium and other alkali metals may cause spectral and non-spectral interferences.
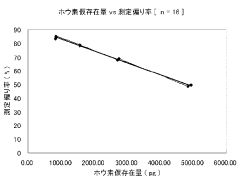
Isotope dilution methods represent one of the most accurate approaches for managing interferences in lithium quantification. By adding isotopically enriched lithium standards to samples, analysts can compensate for matrix effects and signal drift. This technique is particularly valuable for high-precision applications in geochemistry and materials science, though it requires access to enriched isotope standards and careful method development.
Collision/reaction cell technology represents a significant advancement in interference management for lithium quantification. These cells, positioned between the ion optics and mass analyzer, utilize collision gases (such as helium) or reaction gases (such as hydrogen or ammonia) to selectively remove or transform interfering species. For lithium analysis, hydrogen gas is particularly effective as it can react with many polyatomic interferences while leaving lithium ions relatively unaffected.
Cool plasma techniques offer another valuable approach for low mass element detection. By operating the ICP at reduced power (600-800W versus the typical 1200-1500W), certain plasma-based interferences are minimized. This technique is especially beneficial for lithium analysis as it reduces argon-based polyatomic species that can interfere with 7Li measurements. However, this approach requires careful optimization as it may reduce overall sensitivity.
High-resolution mass spectrometry provides an alternative strategy by physically separating ions with similar mass-to-charge ratios. Modern high-resolution ICP-MS instruments can achieve resolution exceeding 10,000, allowing differentiation between lithium isotopes and potential interferences. While effective, this approach typically comes with higher instrument costs and potentially reduced sensitivity compared to standard quadrupole systems.
Matrix separation techniques, including chromatographic methods and chemical extraction, can be implemented prior to ICP-MS analysis to isolate lithium from potential interfering elements. Ion chromatography coupled with ICP-MS has proven particularly effective for lithium analysis in complex matrices such as biological samples and brines, where high concentrations of sodium and other alkali metals may cause spectral and non-spectral interferences.
Isotope dilution methods represent one of the most accurate approaches for managing interferences in lithium quantification. By adding isotopically enriched lithium standards to samples, analysts can compensate for matrix effects and signal drift. This technique is particularly valuable for high-precision applications in geochemistry and materials science, though it requires access to enriched isotope standards and careful method development.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!