Sodium Acetate’s Role in Non‑Toxic Cleaning Solutions
JUN 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Acetate Overview
Sodium acetate, a versatile compound with the chemical formula CH3COONa, plays a significant role in the development of non-toxic cleaning solutions. This salt of acetic acid is formed by the combination of sodium ions and acetate ions, resulting in a white, crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water. Its unique properties make it an attractive ingredient for environmentally friendly cleaning products.
In the context of non-toxic cleaning solutions, sodium acetate serves multiple purposes. Primarily, it acts as a buffering agent, helping to maintain a stable pH level in cleaning formulations. This pH stability is crucial for ensuring consistent cleaning performance and preventing damage to surfaces or materials being cleaned. Additionally, sodium acetate exhibits mild surfactant properties, which contribute to its ability to reduce surface tension and enhance the cleaning power of solutions.
One of the key advantages of sodium acetate in cleaning applications is its biodegradability. As an organic compound derived from natural sources, it readily breaks down in the environment without leaving harmful residues. This characteristic aligns with the growing demand for eco-friendly cleaning products that minimize environmental impact and reduce potential health risks associated with traditional cleaning chemicals.
Sodium acetate also demonstrates excellent water-softening capabilities. In areas with hard water, it can help prevent the formation of mineral deposits and soap scum, enhancing the overall effectiveness of cleaning solutions. This property is particularly valuable in formulations designed for bathroom and kitchen cleaning, where limescale and mineral buildup are common issues.
Furthermore, sodium acetate exhibits mild antimicrobial properties, which can contribute to the hygiene efficacy of cleaning products without relying on harsh chemicals. While not as potent as dedicated antimicrobial agents, this additional benefit supports the development of multi-functional, gentle cleaning solutions suitable for everyday use in households and commercial settings.
In the realm of non-toxic cleaning, sodium acetate is often combined with other natural or biodegradable ingredients to create synergistic formulations. These may include plant-based surfactants, essential oils for fragrance and additional antimicrobial effects, and other eco-friendly compounds that complement its cleaning and buffering properties.
The increasing focus on sustainability and health-conscious consumer preferences has driven research into alternative cleaning agents like sodium acetate. As regulations tighten around the use of potentially harmful chemicals in household and industrial products, the role of sodium acetate in non-toxic cleaning solutions is likely to expand, offering a safe and effective option for manufacturers and consumers alike.
In the context of non-toxic cleaning solutions, sodium acetate serves multiple purposes. Primarily, it acts as a buffering agent, helping to maintain a stable pH level in cleaning formulations. This pH stability is crucial for ensuring consistent cleaning performance and preventing damage to surfaces or materials being cleaned. Additionally, sodium acetate exhibits mild surfactant properties, which contribute to its ability to reduce surface tension and enhance the cleaning power of solutions.
One of the key advantages of sodium acetate in cleaning applications is its biodegradability. As an organic compound derived from natural sources, it readily breaks down in the environment without leaving harmful residues. This characteristic aligns with the growing demand for eco-friendly cleaning products that minimize environmental impact and reduce potential health risks associated with traditional cleaning chemicals.
Sodium acetate also demonstrates excellent water-softening capabilities. In areas with hard water, it can help prevent the formation of mineral deposits and soap scum, enhancing the overall effectiveness of cleaning solutions. This property is particularly valuable in formulations designed for bathroom and kitchen cleaning, where limescale and mineral buildup are common issues.
Furthermore, sodium acetate exhibits mild antimicrobial properties, which can contribute to the hygiene efficacy of cleaning products without relying on harsh chemicals. While not as potent as dedicated antimicrobial agents, this additional benefit supports the development of multi-functional, gentle cleaning solutions suitable for everyday use in households and commercial settings.
In the realm of non-toxic cleaning, sodium acetate is often combined with other natural or biodegradable ingredients to create synergistic formulations. These may include plant-based surfactants, essential oils for fragrance and additional antimicrobial effects, and other eco-friendly compounds that complement its cleaning and buffering properties.
The increasing focus on sustainability and health-conscious consumer preferences has driven research into alternative cleaning agents like sodium acetate. As regulations tighten around the use of potentially harmful chemicals in household and industrial products, the role of sodium acetate in non-toxic cleaning solutions is likely to expand, offering a safe and effective option for manufacturers and consumers alike.
Green Cleaning Market
The green cleaning market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness of environmental issues and health concerns associated with traditional cleaning products. This market segment encompasses a wide range of eco-friendly cleaning solutions, including those utilizing sodium acetate as a key ingredient in non-toxic formulations.
Consumer demand for sustainable and safe cleaning products has been steadily rising, with a notable shift towards natural and biodegradable ingredients. This trend is particularly evident in developed countries, where environmental regulations and consumer preferences are driving the adoption of green cleaning solutions across both residential and commercial sectors.
The market for green cleaning products is characterized by a diverse range of offerings, from all-purpose cleaners and laundry detergents to specialized surface treatments and industrial cleaning solutions. Sodium acetate-based products have gained traction within this market due to their effectiveness, low toxicity, and biodegradability.
Key market drivers include growing environmental consciousness, stringent regulations on chemical usage, and increasing corporate sustainability initiatives. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the demand for safe and effective cleaning solutions, with consumers and businesses alike prioritizing hygiene without compromising on environmental responsibility.
The green cleaning market has also seen a surge in innovation, with companies investing in research and development to create more effective and sustainable formulations. Sodium acetate's role in these innovations has been significant, as it offers a versatile and environmentally friendly alternative to harsher chemicals traditionally used in cleaning products.
Market segmentation reveals strong growth in both consumer and commercial sectors. The residential segment has shown robust expansion, driven by health-conscious consumers seeking safer alternatives for household cleaning. In the commercial sector, industries such as healthcare, hospitality, and food service have been early adopters of green cleaning solutions, including those featuring sodium acetate.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the green cleaning market, with Asia-Pacific showing the fastest growth rate. This regional variation is attributed to differences in environmental regulations, consumer awareness, and economic development. The market is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with sodium acetate-based products playing an increasingly important role in meeting the demand for effective, non-toxic cleaning solutions.
Consumer demand for sustainable and safe cleaning products has been steadily rising, with a notable shift towards natural and biodegradable ingredients. This trend is particularly evident in developed countries, where environmental regulations and consumer preferences are driving the adoption of green cleaning solutions across both residential and commercial sectors.
The market for green cleaning products is characterized by a diverse range of offerings, from all-purpose cleaners and laundry detergents to specialized surface treatments and industrial cleaning solutions. Sodium acetate-based products have gained traction within this market due to their effectiveness, low toxicity, and biodegradability.
Key market drivers include growing environmental consciousness, stringent regulations on chemical usage, and increasing corporate sustainability initiatives. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the demand for safe and effective cleaning solutions, with consumers and businesses alike prioritizing hygiene without compromising on environmental responsibility.
The green cleaning market has also seen a surge in innovation, with companies investing in research and development to create more effective and sustainable formulations. Sodium acetate's role in these innovations has been significant, as it offers a versatile and environmentally friendly alternative to harsher chemicals traditionally used in cleaning products.
Market segmentation reveals strong growth in both consumer and commercial sectors. The residential segment has shown robust expansion, driven by health-conscious consumers seeking safer alternatives for household cleaning. In the commercial sector, industries such as healthcare, hospitality, and food service have been early adopters of green cleaning solutions, including those featuring sodium acetate.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the green cleaning market, with Asia-Pacific showing the fastest growth rate. This regional variation is attributed to differences in environmental regulations, consumer awareness, and economic development. The market is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with sodium acetate-based products playing an increasingly important role in meeting the demand for effective, non-toxic cleaning solutions.
Challenges in Non-Toxic
The development of non-toxic cleaning solutions faces several significant challenges, primarily stemming from the need to balance effectiveness, safety, and environmental impact. One of the key hurdles is finding suitable alternatives to traditional, often toxic, cleaning agents that can match their performance without compromising on safety or eco-friendliness.
Sodium acetate, while promising, presents its own set of challenges in non-toxic cleaning formulations. Its effectiveness as a cleaning agent is limited compared to more aggressive chemicals, necessitating higher concentrations or combination with other ingredients to achieve desired results. This can lead to increased production costs and potential issues with product stability.
Another challenge lies in the pH regulation of cleaning solutions containing sodium acetate. While it can act as a buffer, maintaining the optimal pH range for effective cleaning while ensuring skin and surface safety requires careful formulation. This balancing act becomes even more complex when considering the diverse range of surfaces and contaminants that cleaning products must address.
The solubility of sodium acetate in water is another factor that can pose difficulties. At high concentrations, it may crystallize out of solution, affecting the product's shelf life and performance. This necessitates the use of additional stabilizers or careful control of concentration levels, further complicating the formulation process.
Environmental concerns also present challenges. Although sodium acetate is biodegradable, its production and disposal in large quantities can still have environmental impacts. Ensuring that the entire lifecycle of the cleaning product, from raw material sourcing to disposal, remains environmentally friendly is a complex task that requires ongoing research and development.
Consumer perception and acceptance of non-toxic cleaning solutions pose additional hurdles. Many consumers are accustomed to the strong scents and immediate visual feedback provided by traditional cleaning products. Educating consumers about the benefits of non-toxic alternatives and managing expectations regarding their performance characteristics is crucial for market acceptance.
Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity to the development of non-toxic cleaning solutions. Different regions have varying standards and requirements for what constitutes a "non-toxic" or "green" cleaning product. Navigating these regulatory landscapes while maintaining product efficacy and marketability across different markets can be challenging for manufacturers.
In conclusion, while sodium acetate offers potential as a component in non-toxic cleaning solutions, its integration into effective, safe, and environmentally friendly products faces multiple technical, economic, and regulatory challenges. Overcoming these hurdles requires ongoing research, innovative formulation strategies, and a holistic approach to product development that considers the entire lifecycle and user experience of cleaning solutions.
Sodium acetate, while promising, presents its own set of challenges in non-toxic cleaning formulations. Its effectiveness as a cleaning agent is limited compared to more aggressive chemicals, necessitating higher concentrations or combination with other ingredients to achieve desired results. This can lead to increased production costs and potential issues with product stability.
Another challenge lies in the pH regulation of cleaning solutions containing sodium acetate. While it can act as a buffer, maintaining the optimal pH range for effective cleaning while ensuring skin and surface safety requires careful formulation. This balancing act becomes even more complex when considering the diverse range of surfaces and contaminants that cleaning products must address.
The solubility of sodium acetate in water is another factor that can pose difficulties. At high concentrations, it may crystallize out of solution, affecting the product's shelf life and performance. This necessitates the use of additional stabilizers or careful control of concentration levels, further complicating the formulation process.
Environmental concerns also present challenges. Although sodium acetate is biodegradable, its production and disposal in large quantities can still have environmental impacts. Ensuring that the entire lifecycle of the cleaning product, from raw material sourcing to disposal, remains environmentally friendly is a complex task that requires ongoing research and development.
Consumer perception and acceptance of non-toxic cleaning solutions pose additional hurdles. Many consumers are accustomed to the strong scents and immediate visual feedback provided by traditional cleaning products. Educating consumers about the benefits of non-toxic alternatives and managing expectations regarding their performance characteristics is crucial for market acceptance.
Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity to the development of non-toxic cleaning solutions. Different regions have varying standards and requirements for what constitutes a "non-toxic" or "green" cleaning product. Navigating these regulatory landscapes while maintaining product efficacy and marketability across different markets can be challenging for manufacturers.
In conclusion, while sodium acetate offers potential as a component in non-toxic cleaning solutions, its integration into effective, safe, and environmentally friendly products faces multiple technical, economic, and regulatory challenges. Overcoming these hurdles requires ongoing research, innovative formulation strategies, and a holistic approach to product development that considers the entire lifecycle and user experience of cleaning solutions.
Current Formulations
01 Use of sodium acetate in chemical processes
Sodium acetate is widely used in various chemical processes as a reagent, catalyst, or buffer. It plays a role in reactions such as acetylation, esterification, and pH control. Its applications span across industries including pharmaceuticals, textiles, and food processing.- Use of sodium acetate in heat storage materials: Sodium acetate is utilized in heat storage materials due to its phase change properties. It can absorb and release heat during phase transitions, making it suitable for thermal energy storage applications. These materials can be used in various industries for temperature regulation and energy conservation.
- Sodium acetate in chemical synthesis processes: Sodium acetate serves as a reagent or intermediate in various chemical synthesis processes. It is used in the production of organic compounds, pharmaceuticals, and other industrial chemicals. Its role in these processes can include acting as a buffer, a catalyst, or a source of acetate ions.
- Application of sodium acetate in food preservation: Sodium acetate is employed as a food preservative and flavoring agent. It helps to control acidity and inhibit microbial growth in food products, extending their shelf life. Additionally, it can enhance the taste profile of certain foods and beverages.
- Use of sodium acetate in textile and leather industries: Sodium acetate finds applications in textile and leather processing. It is used in dyeing processes, as a mordant to fix dyes, and in leather tanning operations. Its properties help improve color fastness and overall quality of the treated materials.
- Sodium acetate in environmental and waste treatment: Sodium acetate is utilized in environmental and waste treatment processes. It can be used in wastewater treatment, as a deicer for roads and runways, and in certain bioremediation applications. Its biodegradability and relatively low environmental impact make it suitable for these purposes.
02 Sodium acetate in heat storage and thermal regulation
Sodium acetate trihydrate is utilized in heat packs and thermal energy storage systems due to its phase change properties. It can absorb and release heat at specific temperatures, making it useful for temperature regulation in various applications, including consumer products and industrial processes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Application of sodium acetate in food preservation
Sodium acetate serves as a food preservative and flavoring agent. It helps control acidity, inhibit microbial growth, and enhance taste in various food products. Its use extends to beverages, baked goods, and processed foods to improve shelf life and quality.Expand Specific Solutions04 Sodium acetate in environmental applications
Sodium acetate finds use in environmental remediation and waste treatment processes. It can be employed in the treatment of contaminated soils, wastewater purification, and as a de-icing agent for roads and runways, offering a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional methods.Expand Specific Solutions05 Production methods for sodium acetate
Various methods are employed for the production of sodium acetate, including the reaction of acetic acid with sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate. Advanced techniques focus on improving yield, purity, and energy efficiency in the manufacturing process, often involving specialized equipment and controlled reaction conditions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The market for sodium acetate in non-toxic cleaning solutions is in a growth phase, driven by increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly products. The global green cleaning products market is projected to reach $11.6 billion by 2029, with a CAGR of 6.6%. Technologically, sodium acetate-based solutions are relatively mature, with companies like Henkel, Ecolab, and Unilever leading innovation. These industry giants, along with emerging players like Nanjing Linkage Sustainable Technology and Zhejiang Yishu Environmental Protection Technology, are investing in R&D to enhance product efficacy and sustainability. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established multinational corporations and specialized regional manufacturers, fostering both collaboration and competition in advancing sodium acetate applications in cleaning solutions.
Henkel AG & Co. KGaA
Technical Solution: Henkel has developed a range of non-toxic cleaning solutions incorporating sodium acetate as a key ingredient. Their approach focuses on utilizing sodium acetate's buffering properties to maintain optimal pH levels in cleaning formulations. This allows for effective cleaning while minimizing skin irritation and environmental impact. Henkel's products leverage sodium acetate's ability to neutralize acids and bases, creating stable cleaning solutions that are safe for various surfaces[1]. The company has also explored synergistic effects between sodium acetate and other eco-friendly ingredients to enhance cleaning efficacy without compromising safety[3].
Strengths: Strong R&D capabilities, extensive product range, global market presence. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to traditional cleaning solutions, potential challenges in consumer education about benefits.
Ecolab USA, Inc.
Technical Solution: Ecolab has pioneered the use of sodium acetate in their institutional cleaning solutions, particularly for the hospitality and healthcare sectors. Their technology incorporates sodium acetate as a pH regulator and mild chelating agent, enhancing the removal of mineral deposits and soap scum without harsh chemicals. Ecolab's formulations utilize sodium acetate's ability to form complexes with metal ions, improving the overall cleaning performance in hard water conditions[2]. The company has also developed specialized dispensing systems that optimize the use of sodium acetate-based solutions, ensuring consistent performance and reducing waste[4].
Strengths: Industry-leading expertise in institutional cleaning, advanced dispensing technology. Weaknesses: Higher initial costs for specialized systems, potential limitations in consumer markets.
Sodium Acetate Research
General purpose liquid cleaning composition and method for the preparation thereof
PatentWO2002086041A1
Innovation
- A general-purpose liquid cleaning composition comprising a mixture of caustic soda, oleic acid, dodecyl benzene sulfonic acid, and other additives, which undergoes a neutralization reaction, combined with disinfectants and surfactants like quaternary ammonium base and Sodium Lauryl Ether Sulfate, to create a non-irritating, antibacterial solution suitable for diverse surfaces and materials.
Non-medicated personal care cleansing solution and a method of synthesizing the same
PatentInactiveUS20160010039A1
Innovation
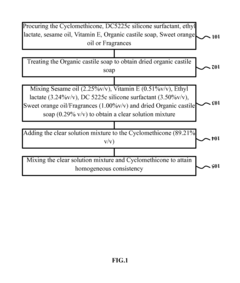
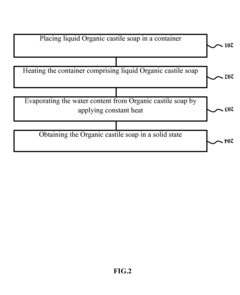
- A water-free non-medicated liquid cleansing solution composition is synthesized using cyclomethicone, DC5225C, ethyl lactate, sesame oil, Vitamin E, organic castile soap, and sweet orange oil or fragrances, which is applied to tissue paper to create a moist wipe for effective cleaning without harsh ingredients.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding sodium acetate's use in non-toxic cleaning solutions is complex and multifaceted, involving various governmental agencies and international bodies. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating cleaning products under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). The EPA maintains a comprehensive inventory of chemical substances and requires manufacturers to submit premanufacture notices for new chemicals or significant new uses of existing chemicals.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also has jurisdiction over certain cleaning products, particularly those used in food processing facilities or medical environments. Sodium acetate, when used in these contexts, must comply with FDA regulations regarding food additives and generally recognized as safe (GRAS) substances.
Internationally, the European Union's Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation governs the use of chemical substances, including those in cleaning products. Manufacturers and importers must register substances with the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and provide safety data for substances produced or imported in quantities over one tonne per year.
The United Nations' Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) provides a standardized approach to hazard communication, which many countries have adopted. This system ensures consistent labeling and safety data sheets for chemical products, including cleaning solutions containing sodium acetate.
In addition to these overarching regulations, many countries have specific laws governing the environmental impact of cleaning products. For instance, the California Air Resources Board (CARB) has stringent regulations on volatile organic compound (VOC) content in consumer products, including cleaning solutions.
Third-party certification programs, such as Green Seal and EcoLogo, have also emerged to provide independent verification of a product's environmental claims. These programs often have their own standards that go beyond regulatory requirements, considering factors like biodegradability, toxicity to aquatic life, and packaging sustainability.
As the demand for non-toxic cleaning solutions grows, regulatory bodies are continually updating their frameworks to address new concerns and scientific findings. This dynamic regulatory landscape requires manufacturers to stay vigilant and adaptable, ensuring their products remain compliant while meeting consumer expectations for safety and efficacy.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also has jurisdiction over certain cleaning products, particularly those used in food processing facilities or medical environments. Sodium acetate, when used in these contexts, must comply with FDA regulations regarding food additives and generally recognized as safe (GRAS) substances.
Internationally, the European Union's Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation governs the use of chemical substances, including those in cleaning products. Manufacturers and importers must register substances with the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and provide safety data for substances produced or imported in quantities over one tonne per year.
The United Nations' Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) provides a standardized approach to hazard communication, which many countries have adopted. This system ensures consistent labeling and safety data sheets for chemical products, including cleaning solutions containing sodium acetate.
In addition to these overarching regulations, many countries have specific laws governing the environmental impact of cleaning products. For instance, the California Air Resources Board (CARB) has stringent regulations on volatile organic compound (VOC) content in consumer products, including cleaning solutions.
Third-party certification programs, such as Green Seal and EcoLogo, have also emerged to provide independent verification of a product's environmental claims. These programs often have their own standards that go beyond regulatory requirements, considering factors like biodegradability, toxicity to aquatic life, and packaging sustainability.
As the demand for non-toxic cleaning solutions grows, regulatory bodies are continually updating their frameworks to address new concerns and scientific findings. This dynamic regulatory landscape requires manufacturers to stay vigilant and adaptable, ensuring their products remain compliant while meeting consumer expectations for safety and efficacy.
Environmental Impact
The use of sodium acetate in non-toxic cleaning solutions has significant environmental implications. As a biodegradable compound, sodium acetate offers a more eco-friendly alternative to traditional cleaning agents. When released into the environment, it breaks down naturally without leaving harmful residues or accumulating in ecosystems. This characteristic reduces the overall environmental footprint of cleaning products and minimizes the risk of water pollution.
Sodium acetate-based cleaning solutions contribute to improved air quality in indoor environments. Unlike many conventional cleaning products that release volatile organic compounds (VOCs), sodium acetate formulations typically have lower VOC emissions. This reduction in harmful airborne chemicals leads to better indoor air quality, benefiting both human health and the environment.
The production process of sodium acetate is relatively environmentally friendly compared to some other cleaning agents. It can be synthesized from renewable resources, such as acetic acid derived from biomass fermentation. This approach aligns with sustainable manufacturing practices and reduces dependence on petrochemical-based ingredients.
In terms of waste management, sodium acetate presents advantages. Its biodegradability means that it can be safely disposed of through conventional wastewater treatment systems without requiring specialized handling or treatment processes. This ease of disposal reduces the burden on waste management infrastructure and lowers the risk of environmental contamination.
The use of sodium acetate in cleaning solutions also supports water conservation efforts. Its effectiveness as a cleaning agent at lower concentrations means that less product is needed to achieve the desired cleaning results. This efficiency translates to reduced water consumption during both the manufacturing process and end-use applications.
From a lifecycle perspective, sodium acetate-based cleaning products generally have a lower environmental impact. The combination of biodegradability, reduced toxicity, and efficient performance contributes to a smaller carbon footprint throughout the product's lifecycle, from production to disposal.
However, it is important to note that while sodium acetate offers significant environmental benefits, its impact is not entirely neutral. The production and transportation of sodium acetate still require energy and resources. Additionally, the environmental impact can vary depending on the specific formulation and other ingredients used in the cleaning solution. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on further optimizing the environmental profile of sodium acetate-based cleaning products.
Sodium acetate-based cleaning solutions contribute to improved air quality in indoor environments. Unlike many conventional cleaning products that release volatile organic compounds (VOCs), sodium acetate formulations typically have lower VOC emissions. This reduction in harmful airborne chemicals leads to better indoor air quality, benefiting both human health and the environment.
The production process of sodium acetate is relatively environmentally friendly compared to some other cleaning agents. It can be synthesized from renewable resources, such as acetic acid derived from biomass fermentation. This approach aligns with sustainable manufacturing practices and reduces dependence on petrochemical-based ingredients.
In terms of waste management, sodium acetate presents advantages. Its biodegradability means that it can be safely disposed of through conventional wastewater treatment systems without requiring specialized handling or treatment processes. This ease of disposal reduces the burden on waste management infrastructure and lowers the risk of environmental contamination.
The use of sodium acetate in cleaning solutions also supports water conservation efforts. Its effectiveness as a cleaning agent at lower concentrations means that less product is needed to achieve the desired cleaning results. This efficiency translates to reduced water consumption during both the manufacturing process and end-use applications.
From a lifecycle perspective, sodium acetate-based cleaning products generally have a lower environmental impact. The combination of biodegradability, reduced toxicity, and efficient performance contributes to a smaller carbon footprint throughout the product's lifecycle, from production to disposal.
However, it is important to note that while sodium acetate offers significant environmental benefits, its impact is not entirely neutral. The production and transportation of sodium acetate still require energy and resources. Additionally, the environmental impact can vary depending on the specific formulation and other ingredients used in the cleaning solution. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on further optimizing the environmental profile of sodium acetate-based cleaning products.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!