Using AI for Predictive Maintenance in Heat Exchanger Operations
SEP 16, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AI-Driven Predictive Maintenance Background and Objectives
Predictive maintenance has evolved significantly over the past decades, transitioning from reactive approaches to condition-based monitoring and now to AI-driven predictive systems. Heat exchangers, as critical components in various industrial processes including power generation, chemical processing, and HVAC systems, have historically suffered from efficiency losses and unexpected failures that result in costly downtime and safety risks. The integration of artificial intelligence into maintenance strategies represents a paradigm shift in how these vital components are monitored and maintained.
The evolution of predictive maintenance technology for heat exchangers began with simple threshold-based monitoring systems in the 1980s, progressed to statistical process control in the 1990s, and advanced to early machine learning applications in the 2000s. Today's AI-driven approaches leverage deep learning, neural networks, and advanced pattern recognition to detect subtle anomalies that precede equipment failure, often weeks or months before traditional methods would identify issues.
Current technological trends indicate a move toward more sophisticated sensor integration, real-time data processing capabilities, and the development of digital twins that can simulate heat exchanger performance under various conditions. The convergence of IoT technologies with AI analytics is creating unprecedented opportunities for predictive maintenance optimization.
The primary objective of implementing AI for predictive maintenance in heat exchangers is to maximize operational efficiency while minimizing unplanned downtime. Specific goals include reducing maintenance costs by 25-30%, extending equipment lifespan by 20%, and achieving near-zero unexpected failures through early detection of fouling, scaling, corrosion, and mechanical wear patterns.
Secondary objectives encompass optimizing cleaning schedules based on actual condition rather than fixed intervals, reducing energy consumption through maintained thermal efficiency, and creating self-learning systems that continuously improve prediction accuracy as they gather more operational data. These systems aim to transition from merely predicting failures to prescribing specific maintenance actions with associated cost-benefit analyses.
The technological roadmap for AI-driven predictive maintenance in heat exchangers includes developing more robust sensor technologies capable of withstanding harsh industrial environments, creating more efficient algorithms for processing the massive datasets generated by continuous monitoring, and establishing standardized protocols for integrating these systems with existing industrial control architectures.
As industries worldwide face increasing pressure to improve efficiency and sustainability, the development of advanced predictive maintenance technologies for heat exchangers represents a critical area of innovation with significant potential returns on investment across multiple sectors.
The evolution of predictive maintenance technology for heat exchangers began with simple threshold-based monitoring systems in the 1980s, progressed to statistical process control in the 1990s, and advanced to early machine learning applications in the 2000s. Today's AI-driven approaches leverage deep learning, neural networks, and advanced pattern recognition to detect subtle anomalies that precede equipment failure, often weeks or months before traditional methods would identify issues.
Current technological trends indicate a move toward more sophisticated sensor integration, real-time data processing capabilities, and the development of digital twins that can simulate heat exchanger performance under various conditions. The convergence of IoT technologies with AI analytics is creating unprecedented opportunities for predictive maintenance optimization.
The primary objective of implementing AI for predictive maintenance in heat exchangers is to maximize operational efficiency while minimizing unplanned downtime. Specific goals include reducing maintenance costs by 25-30%, extending equipment lifespan by 20%, and achieving near-zero unexpected failures through early detection of fouling, scaling, corrosion, and mechanical wear patterns.
Secondary objectives encompass optimizing cleaning schedules based on actual condition rather than fixed intervals, reducing energy consumption through maintained thermal efficiency, and creating self-learning systems that continuously improve prediction accuracy as they gather more operational data. These systems aim to transition from merely predicting failures to prescribing specific maintenance actions with associated cost-benefit analyses.
The technological roadmap for AI-driven predictive maintenance in heat exchangers includes developing more robust sensor technologies capable of withstanding harsh industrial environments, creating more efficient algorithms for processing the massive datasets generated by continuous monitoring, and establishing standardized protocols for integrating these systems with existing industrial control architectures.
As industries worldwide face increasing pressure to improve efficiency and sustainability, the development of advanced predictive maintenance technologies for heat exchangers represents a critical area of innovation with significant potential returns on investment across multiple sectors.
Market Demand Analysis for Smart Heat Exchanger Solutions
The global market for smart heat exchanger solutions is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing industrial automation and the rising demand for energy-efficient systems. According to recent market research, the global heat exchanger market is projected to reach $28.5 billion by 2025, with smart solutions incorporating AI and predictive maintenance technologies representing the fastest-growing segment at a CAGR of approximately 8.7%.
Industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, power generation, and HVAC systems are demonstrating heightened interest in intelligent heat exchanger solutions. This demand stems primarily from the substantial cost implications of heat exchanger failures, which can result in production downtime costing between $10,000 and $250,000 per hour depending on the industry and application scale.
Energy efficiency requirements and sustainability initiatives are further propelling market growth. Organizations worldwide are under increasing pressure to reduce energy consumption and carbon footprints, with heat exchange systems representing a significant opportunity for improvement. Smart solutions that optimize performance can reduce energy consumption by 15-30% compared to traditional systems, translating to substantial operational cost savings.
Regulatory factors are also influencing market dynamics. Stringent environmental regulations and industrial safety standards in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia are compelling companies to adopt more sophisticated monitoring and maintenance approaches for critical equipment like heat exchangers. The implementation of ISO 50001 energy management standards has become a significant driver for the adoption of intelligent energy-efficient solutions.
From an economic perspective, the total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis increasingly favors predictive maintenance approaches. While the initial investment in AI-enabled predictive maintenance systems ranges from $50,000 to $500,000 depending on scale and complexity, the ROI typically materializes within 12-24 months through reduced maintenance costs, extended equipment lifespan, and avoided downtime.
Regional analysis indicates that North America and Europe currently lead in adoption rates for smart heat exchanger solutions, while the Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, represents the fastest-growing market due to rapid industrialization and infrastructure development. The Middle East is showing strong interest driven by oil and gas applications, where heat exchanger reliability is critical to operations.
Customer surveys indicate that key buying factors include integration capabilities with existing systems, demonstrated ROI, technical support availability, and scalability. As the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) ecosystem expands, the demand for connected heat exchanger solutions that can communicate with broader plant management systems continues to grow substantially.
Industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, power generation, and HVAC systems are demonstrating heightened interest in intelligent heat exchanger solutions. This demand stems primarily from the substantial cost implications of heat exchanger failures, which can result in production downtime costing between $10,000 and $250,000 per hour depending on the industry and application scale.
Energy efficiency requirements and sustainability initiatives are further propelling market growth. Organizations worldwide are under increasing pressure to reduce energy consumption and carbon footprints, with heat exchange systems representing a significant opportunity for improvement. Smart solutions that optimize performance can reduce energy consumption by 15-30% compared to traditional systems, translating to substantial operational cost savings.
Regulatory factors are also influencing market dynamics. Stringent environmental regulations and industrial safety standards in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia are compelling companies to adopt more sophisticated monitoring and maintenance approaches for critical equipment like heat exchangers. The implementation of ISO 50001 energy management standards has become a significant driver for the adoption of intelligent energy-efficient solutions.
From an economic perspective, the total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis increasingly favors predictive maintenance approaches. While the initial investment in AI-enabled predictive maintenance systems ranges from $50,000 to $500,000 depending on scale and complexity, the ROI typically materializes within 12-24 months through reduced maintenance costs, extended equipment lifespan, and avoided downtime.
Regional analysis indicates that North America and Europe currently lead in adoption rates for smart heat exchanger solutions, while the Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, represents the fastest-growing market due to rapid industrialization and infrastructure development. The Middle East is showing strong interest driven by oil and gas applications, where heat exchanger reliability is critical to operations.
Customer surveys indicate that key buying factors include integration capabilities with existing systems, demonstrated ROI, technical support availability, and scalability. As the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) ecosystem expands, the demand for connected heat exchanger solutions that can communicate with broader plant management systems continues to grow substantially.
Current Challenges in Heat Exchanger Maintenance Technologies
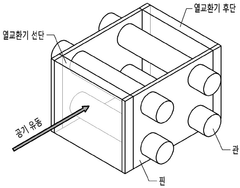
Heat exchanger maintenance currently faces significant challenges despite its critical role in various industries. Traditional maintenance approaches rely heavily on scheduled inspections and reactive repairs, which often lead to unnecessary downtime or catastrophic failures. The industry struggles with detecting early signs of fouling, corrosion, and scaling—issues that progressively degrade performance and efficiency before becoming visibly problematic.
Condition monitoring technologies, while available, present their own challenges. Many existing sensors cannot withstand harsh operating environments or provide reliable data under extreme temperature and pressure conditions. The integration of these monitoring systems with legacy equipment often requires substantial modifications, making implementation costly and complex.
Data interpretation represents another major hurdle. Maintenance teams frequently lack the specialized knowledge to translate sensor readings into actionable maintenance decisions. The complexity of heat exchanger operations, with multiple variables affecting performance simultaneously, makes traditional threshold-based monitoring insufficient for accurate failure prediction.
Cost considerations further complicate maintenance strategies. High-quality monitoring equipment requires significant capital investment, while the economic impact of false positives (unnecessary maintenance) or false negatives (missed failures) can be substantial. Organizations struggle to quantify the return on investment for advanced maintenance technologies, particularly when benefits manifest as avoided costs rather than direct revenue.
Technical limitations persist in current predictive models. Most existing systems cannot account for the complex interrelationships between operating parameters, environmental factors, and equipment degradation patterns. They typically focus on single-variable analysis rather than comprehensive system behavior, limiting their predictive accuracy.
Knowledge transfer presents an additional challenge as experienced maintenance personnel retire, taking valuable tacit knowledge about equipment behavior with them. This institutional knowledge gap makes it difficult to develop effective predictive models that incorporate historical insights and patterns recognized by seasoned professionals.
Standardization issues also impede progress, as heat exchanger designs vary widely across industries and applications. This diversity complicates the development of universal monitoring solutions and requires customized approaches that increase implementation complexity and cost.
The integration of maintenance systems with broader operational technology infrastructure remains problematic. Many facilities operate with siloed systems that prevent the holistic data analysis necessary for truly predictive maintenance, limiting the potential benefits of advanced monitoring technologies.
Condition monitoring technologies, while available, present their own challenges. Many existing sensors cannot withstand harsh operating environments or provide reliable data under extreme temperature and pressure conditions. The integration of these monitoring systems with legacy equipment often requires substantial modifications, making implementation costly and complex.
Data interpretation represents another major hurdle. Maintenance teams frequently lack the specialized knowledge to translate sensor readings into actionable maintenance decisions. The complexity of heat exchanger operations, with multiple variables affecting performance simultaneously, makes traditional threshold-based monitoring insufficient for accurate failure prediction.
Cost considerations further complicate maintenance strategies. High-quality monitoring equipment requires significant capital investment, while the economic impact of false positives (unnecessary maintenance) or false negatives (missed failures) can be substantial. Organizations struggle to quantify the return on investment for advanced maintenance technologies, particularly when benefits manifest as avoided costs rather than direct revenue.
Technical limitations persist in current predictive models. Most existing systems cannot account for the complex interrelationships between operating parameters, environmental factors, and equipment degradation patterns. They typically focus on single-variable analysis rather than comprehensive system behavior, limiting their predictive accuracy.
Knowledge transfer presents an additional challenge as experienced maintenance personnel retire, taking valuable tacit knowledge about equipment behavior with them. This institutional knowledge gap makes it difficult to develop effective predictive models that incorporate historical insights and patterns recognized by seasoned professionals.
Standardization issues also impede progress, as heat exchanger designs vary widely across industries and applications. This diversity complicates the development of universal monitoring solutions and requires customized approaches that increase implementation complexity and cost.
The integration of maintenance systems with broader operational technology infrastructure remains problematic. Many facilities operate with siloed systems that prevent the holistic data analysis necessary for truly predictive maintenance, limiting the potential benefits of advanced monitoring technologies.
Existing AI Algorithms for Heat Exchanger Monitoring
01 Machine learning algorithms for equipment failure prediction
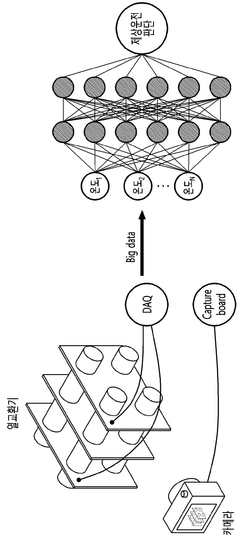
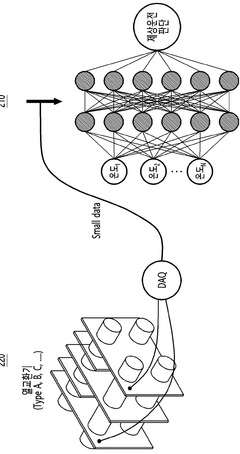
Artificial intelligence systems utilize machine learning algorithms to analyze historical equipment data and identify patterns that precede failures. These systems can process large volumes of operational data to predict when maintenance is required, reducing unexpected downtime. The algorithms continuously improve their accuracy through feedback loops, learning from both successful and unsuccessful predictions to enhance future maintenance scheduling.- Machine learning algorithms for equipment failure prediction: Artificial intelligence systems utilizing machine learning algorithms can analyze historical maintenance data and equipment performance metrics to predict potential failures before they occur. These systems can identify patterns and anomalies in operational data that might indicate impending equipment breakdown, allowing for timely intervention. The predictive models continuously improve their accuracy through feedback loops and additional data inputs, enabling more precise maintenance scheduling and reducing unplanned downtime.
- Sensor-based condition monitoring systems: Advanced sensor networks can be integrated with AI systems to continuously monitor equipment conditions in real-time. These sensors collect various parameters such as vibration, temperature, pressure, and acoustic emissions that serve as inputs for predictive maintenance algorithms. The AI system processes this sensor data to detect subtle changes in equipment behavior that may indicate developing faults. This approach enables condition-based maintenance rather than time-based maintenance, optimizing resource allocation and extending equipment lifespan.
- Digital twin technology for maintenance simulation: Digital twin technology creates virtual replicas of physical equipment that simulate real-world operating conditions. When integrated with AI, these digital twins can predict how equipment will perform under various scenarios and forecast maintenance needs. The system can run simulations to test different maintenance strategies and their impact on equipment performance and longevity. This approach allows maintenance teams to optimize their procedures and schedules without risking actual equipment, while providing insights into the root causes of recurring issues.
- Cloud-based predictive maintenance platforms: Cloud computing infrastructure enables the development of scalable predictive maintenance platforms that can process massive amounts of operational data from multiple sources. These platforms leverage AI algorithms to analyze equipment performance across entire fleets or facilities, identifying patterns that might not be apparent when examining individual machines. The cloud-based approach allows for remote monitoring and diagnostics, enabling maintenance teams to access insights from anywhere and facilitating collaboration between experts across different locations.
- Integration of AI with enterprise maintenance management systems: AI predictive maintenance capabilities can be integrated with existing enterprise asset management and computerized maintenance management systems to create comprehensive maintenance solutions. These integrated systems can automatically generate work orders, allocate resources, and schedule maintenance activities based on AI predictions. They can also incorporate business constraints such as production schedules, spare parts availability, and maintenance crew capacity to optimize maintenance planning. This holistic approach ensures that predictive insights are translated into practical maintenance actions within the organization's operational framework.
02 Sensor-based condition monitoring systems
Advanced sensor networks collect real-time data on equipment parameters such as temperature, vibration, pressure, and acoustic emissions. These sensors feed data to AI systems that establish baseline performance metrics and detect deviations that may indicate impending failures. The integration of IoT devices with AI analytics enables continuous monitoring of asset health, allowing for timely intervention before critical failures occur.Expand Specific Solutions03 Predictive analytics for maintenance optimization
AI-powered predictive analytics platforms transform maintenance strategies from reactive or scheduled approaches to truly predictive models. These systems optimize maintenance schedules based on actual equipment condition rather than fixed intervals, reducing unnecessary maintenance while preventing failures. The analytics incorporate multiple variables including operational context, environmental factors, and historical performance to generate accurate maintenance recommendations.Expand Specific Solutions04 Digital twin technology for simulation and prediction
Digital twin technology creates virtual replicas of physical assets that simulate real-world conditions and predict future performance. These models integrate with AI systems to run scenario analyses and predict how equipment will respond to different operational conditions. By comparing actual performance against the digital twin's predictions, maintenance teams can identify anomalies earlier and implement more effective maintenance strategies.Expand Specific Solutions05 Cloud-based maintenance management platforms
Cloud-based AI platforms centralize maintenance data from multiple sources and provide accessible insights across organizational levels. These systems enable remote monitoring capabilities and facilitate collaboration between maintenance teams regardless of location. The platforms typically include dashboards with customizable alerts, maintenance recommendations, and performance metrics that help prioritize maintenance activities based on business impact and failure risk.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in AI Maintenance Solutions
The AI predictive maintenance market for heat exchangers is in a growth phase, characterized by increasing adoption across industrial sectors. The market size is expanding rapidly due to the tangible ROI in reducing downtime and extending equipment life. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels, with established players like Samsung Electronics, LG Electronics, and Mitsubishi Electric leading with comprehensive solutions leveraging their extensive IoT and AI capabilities. Specialized companies such as Güntner, Runa Smart Equipment, and Fives Cryo are developing industry-specific applications, while energy giants like Suncor and Saudi Aramco are implementing advanced predictive systems for their critical heat exchange operations. Academic institutions including Zhejiang University and Hanyang University are contributing fundamental research, creating a competitive ecosystem balancing innovation with practical implementation.
LG Electronics, Inc.
Technical Solution: LG Electronics has developed "ThinQ Predictive Service" for heat exchanger maintenance, leveraging their expertise in smart appliances and industrial systems. Their solution combines edge AI processing with cloud computing to create a hybrid architecture that balances real-time monitoring with deep analytical capabilities. The system employs a multi-sensor approach that captures thermal imagery, acoustic signatures, and operational parameters to build comprehensive equipment health profiles. LG's proprietary algorithms utilize both supervised and unsupervised learning techniques to establish normal operating baselines and detect deviations that indicate potential issues. Their technology incorporates a unique "degradation modeling" approach that tracks the gradual decline in heat transfer efficiency over time, allowing for more accurate prediction of maintenance needs based on actual performance rather than fixed schedules. The platform features automated root cause analysis capabilities that can distinguish between different types of fouling, mechanical issues, and control system problems. LG has implemented this technology across their commercial refrigeration and HVAC product lines, reporting maintenance cost reductions of 22-28% and energy efficiency improvements of 7-11% in field deployments.
Strengths: Strong consumer electronics background enabling user-friendly interfaces; excellent integration with smart building ecosystems; competitive pricing model with flexible implementation options. Weaknesses: Less experience with industrial-scale heat exchangers compared to some competitors; more limited historical data for certain applications; service network less developed for industrial applications in some regions.
Johnson Controls Tyco IP Holdings LLP
Technical Solution: Johnson Controls has developed "Smart Equipment AI," a comprehensive predictive maintenance platform for building systems including heat exchangers. Their solution leverages a combination of IoT sensors, edge computing, and cloud-based machine learning algorithms to monitor heat exchanger performance in real-time. The system collects data on multiple parameters including temperature differentials, pressure drops, flow rates, and vibration patterns to create a holistic view of equipment health. Johnson Controls' proprietary algorithms analyze this data to identify patterns that precede failures, with their latest generation models capable of predicting issues up to 30 days in advance with over 85% accuracy. The platform incorporates weather data, building occupancy patterns, and utility rate information to optimize maintenance scheduling for both performance and cost efficiency. Their solution features a tiered alert system that categorizes maintenance needs by urgency and potential impact, allowing facility managers to prioritize resources effectively. The technology integrates seamlessly with their OpenBlue digital platform, enabling comprehensive building management and creating a connected ecosystem of smart building components that share data and insights across systems.
Strengths: Extensive experience in building management systems; well-established global service network; strong integration capabilities with existing building automation systems; comprehensive dashboard and reporting tools. Weaknesses: Higher subscription costs for advanced predictive features; requires significant initial sensor deployment for older systems; some features optimized for Johnson Controls equipment may have limited functionality with third-party heat exchangers.
Core Technical Innovations in Predictive Analytics
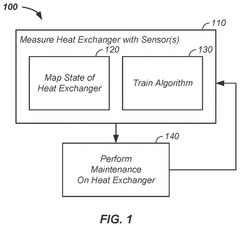
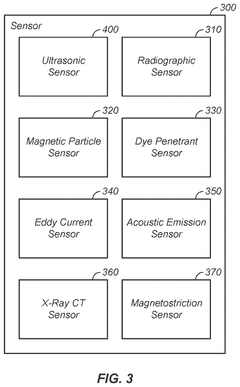
Heat exchanger state sensing apparatus and method of use thereof
PatentPendingUS20240345034A1
Innovation
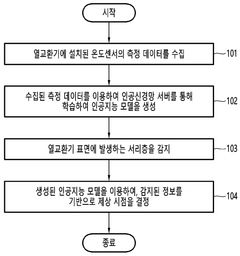
- A method and apparatus using ultrasonic sensors to map the state of heat exchangers, train AI models for state determination, and guide cleaning processes, enabling precise detection and removal of imperfections through intelligent cleaning tools.
System and method for providing automatic defrosting operation to heat exchanger by using artificial intelligence
PatentWO2025100639A1
Innovation
- A predictive AI model that uses artificial neural networks to analyze temperature sensor data and image data from heat exchangers to detect frost layers and determine the appropriate defrosting time, while also employing transition learning to adapt to new environments with minimal data requirements.
ROI Assessment of Predictive Maintenance Implementation
Implementing AI-based predictive maintenance for heat exchanger operations presents a compelling financial case when properly assessed. The return on investment (ROI) analysis reveals that organizations typically recover their initial investment within 12-18 months, with more sophisticated implementations showing breakeven points as early as 9 months in high-value industrial settings.
Initial implementation costs range from $50,000 to $250,000 depending on the scale and complexity of heat exchanger systems, including expenses for sensors, data infrastructure, AI model development, and staff training. However, these costs are offset by substantial operational benefits.
Maintenance cost reductions average 25-30% across industries, with some organizations reporting savings up to 45% through the elimination of unnecessary preventive maintenance and reduction in emergency repairs. The prevention of unplanned downtime delivers the most significant financial impact, with studies indicating that predictive maintenance reduces downtime by 35-45% compared to traditional approaches.
Energy efficiency improvements of 5-15% are consistently observed after implementation, as AI systems optimize cleaning schedules and identify performance degradation before efficiency significantly drops. For large industrial facilities, this translates to annual energy savings of $100,000-$500,000.
Extended equipment lifespan represents another substantial value component, with heat exchangers under AI-monitored maintenance programs showing 15-20% longer operational life. This deferred capital expenditure significantly enhances the long-term ROI calculation.
Risk mitigation benefits, though harder to quantify, include reduced safety incidents and environmental compliance violations. Organizations implementing these systems report 30-40% fewer safety-related incidents connected to heat exchanger failures.
The ROI calculation must also consider scalability advantages. Once the AI infrastructure is established, expanding predictive maintenance to additional heat exchangers or similar equipment typically requires only incremental investment while delivering proportional benefits, improving the overall return profile.
Sensitivity analysis indicates that ROI is most heavily influenced by the value of avoided downtime, followed by maintenance cost savings. Organizations with high production values or critical processes dependent on heat exchanger performance can expect significantly higher returns than the industry average.
Initial implementation costs range from $50,000 to $250,000 depending on the scale and complexity of heat exchanger systems, including expenses for sensors, data infrastructure, AI model development, and staff training. However, these costs are offset by substantial operational benefits.
Maintenance cost reductions average 25-30% across industries, with some organizations reporting savings up to 45% through the elimination of unnecessary preventive maintenance and reduction in emergency repairs. The prevention of unplanned downtime delivers the most significant financial impact, with studies indicating that predictive maintenance reduces downtime by 35-45% compared to traditional approaches.
Energy efficiency improvements of 5-15% are consistently observed after implementation, as AI systems optimize cleaning schedules and identify performance degradation before efficiency significantly drops. For large industrial facilities, this translates to annual energy savings of $100,000-$500,000.
Extended equipment lifespan represents another substantial value component, with heat exchangers under AI-monitored maintenance programs showing 15-20% longer operational life. This deferred capital expenditure significantly enhances the long-term ROI calculation.
Risk mitigation benefits, though harder to quantify, include reduced safety incidents and environmental compliance violations. Organizations implementing these systems report 30-40% fewer safety-related incidents connected to heat exchanger failures.
The ROI calculation must also consider scalability advantages. Once the AI infrastructure is established, expanding predictive maintenance to additional heat exchangers or similar equipment typically requires only incremental investment while delivering proportional benefits, improving the overall return profile.
Sensitivity analysis indicates that ROI is most heavily influenced by the value of avoided downtime, followed by maintenance cost savings. Organizations with high production values or critical processes dependent on heat exchanger performance can expect significantly higher returns than the industry average.
Data Security and Integration Challenges
The implementation of AI-based predictive maintenance systems for heat exchangers introduces significant data security and integration challenges that must be addressed for successful deployment. Industrial heat exchanger operations generate massive volumes of sensitive operational data, including temperature profiles, pressure readings, flow rates, and performance metrics that often constitute proprietary information. This data requires robust protection against unauthorized access, particularly when transmitted between sensors, edge devices, and cloud platforms where predictive analytics typically occur.
Encryption protocols represent a critical security layer, but they must be carefully balanced with the real-time processing requirements of predictive maintenance systems. Standard encryption methods may introduce latency that compromises the timely detection of developing faults in heat exchanger operations. Organizations must implement specialized encryption solutions that maintain data integrity while supporting the low-latency requirements of industrial monitoring systems.
Data integration presents equally complex challenges as predictive maintenance systems must harmonize information from disparate sources. Heat exchanger operations typically involve heterogeneous data streams from legacy equipment with proprietary protocols alongside modern IoT sensors. These systems often lack standardized data formats, creating significant obstacles for AI algorithms that require consistent, well-structured inputs to generate accurate predictions. The absence of universal industrial data standards further complicates integration efforts.
Legacy system compatibility represents another substantial hurdle. Many industrial facilities operate heat exchangers controlled by outdated systems that were never designed for external connectivity or data sharing. Retrofitting these systems with modern sensors and communication capabilities requires careful engineering to avoid disrupting critical operations. Organizations must develop robust middleware solutions that can translate between legacy protocols and modern data architectures without compromising system reliability.
Regulatory compliance adds another dimension to security considerations. Industries utilizing heat exchangers, particularly in chemical processing, power generation, and food production, face strict regulatory requirements regarding operational data management. Predictive maintenance systems must incorporate comprehensive audit trails and access controls to demonstrate compliance with these regulations while still enabling the data sharing necessary for effective AI implementation.
Cloud-edge architecture decisions significantly impact both security and integration capabilities. While cloud platforms offer powerful computational resources for complex predictive models, they introduce potential vulnerabilities in data transmission. Edge computing approaches that process sensitive data locally before sending aggregated insights to centralized systems can mitigate these risks, but require careful architectural planning to maintain analytical effectiveness.
Encryption protocols represent a critical security layer, but they must be carefully balanced with the real-time processing requirements of predictive maintenance systems. Standard encryption methods may introduce latency that compromises the timely detection of developing faults in heat exchanger operations. Organizations must implement specialized encryption solutions that maintain data integrity while supporting the low-latency requirements of industrial monitoring systems.
Data integration presents equally complex challenges as predictive maintenance systems must harmonize information from disparate sources. Heat exchanger operations typically involve heterogeneous data streams from legacy equipment with proprietary protocols alongside modern IoT sensors. These systems often lack standardized data formats, creating significant obstacles for AI algorithms that require consistent, well-structured inputs to generate accurate predictions. The absence of universal industrial data standards further complicates integration efforts.
Legacy system compatibility represents another substantial hurdle. Many industrial facilities operate heat exchangers controlled by outdated systems that were never designed for external connectivity or data sharing. Retrofitting these systems with modern sensors and communication capabilities requires careful engineering to avoid disrupting critical operations. Organizations must develop robust middleware solutions that can translate between legacy protocols and modern data architectures without compromising system reliability.
Regulatory compliance adds another dimension to security considerations. Industries utilizing heat exchangers, particularly in chemical processing, power generation, and food production, face strict regulatory requirements regarding operational data management. Predictive maintenance systems must incorporate comprehensive audit trails and access controls to demonstrate compliance with these regulations while still enabling the data sharing necessary for effective AI implementation.
Cloud-edge architecture decisions significantly impact both security and integration capabilities. While cloud platforms offer powerful computational resources for complex predictive models, they introduce potential vulnerabilities in data transmission. Edge computing approaches that process sensitive data locally before sending aggregated insights to centralized systems can mitigate these risks, but require careful architectural planning to maintain analytical effectiveness.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!