Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is a widely used thermoplastic derived from ethylene polymerization under high-pressure free-radical conditions. Known for its flexibility, chemical resistance, and lightweight form, LDPE has become an essential material across industries such as packaging, healthcare, and construction. As global sustainability goals accelerate, LDPE emerges as a recyclable and adaptable solution to reduce plastic waste, enhance processing efficiency, and support circularity.
This article explores LDPE’s composition, key material properties, application domains, comparative performance, and research frontiers—leveraging insights from PatSnap Eureka AI Agent.
Material Composition & Key Properties
- LDPE is produced from ethylene monomers via high-pressure radical polymerization, resulting in a branched polymer structure.
- This structure imparts excellent flexibility and transparency, though at the expense of tensile strength compared to HDPE.
- Key properties include:
- High ductility and toughness
- Excellent moisture and chemical resistance
- Low density and melt viscosity
- Ease of extrusion and molding into films, containers, and sheets
- Recyclability (Resin ID Code #4) with improved reprocessing technologies

Application Domains
1. Sustainable Packaging & Circular Economy
Modern packaging systems face urgent needs for lower environmental impact, thinner materials, and increased recyclability. LDPE enables lightweight, flexible films with strong sealability and process efficiency. It also supports circular economy strategies through film reprocessing, additive-enhanced recycling, and biodegradable LDPE blends.
Research Frontlines:
Emerging solutions include nanocomposite barrier films, bio-based LDPE production, and closed-loop recycling integration.
Related Reports:
- LDPE and Circular Economy: Achieving Sustainability Goals
- Innovations in LDPE Film Manufacturing Processes
- Reducing Waste with LDPE Recycling Techniques
- Enhancing LDPE Recyclability: Techniques and Methods
- Exploring Biodegradable Alternatives to LDPE
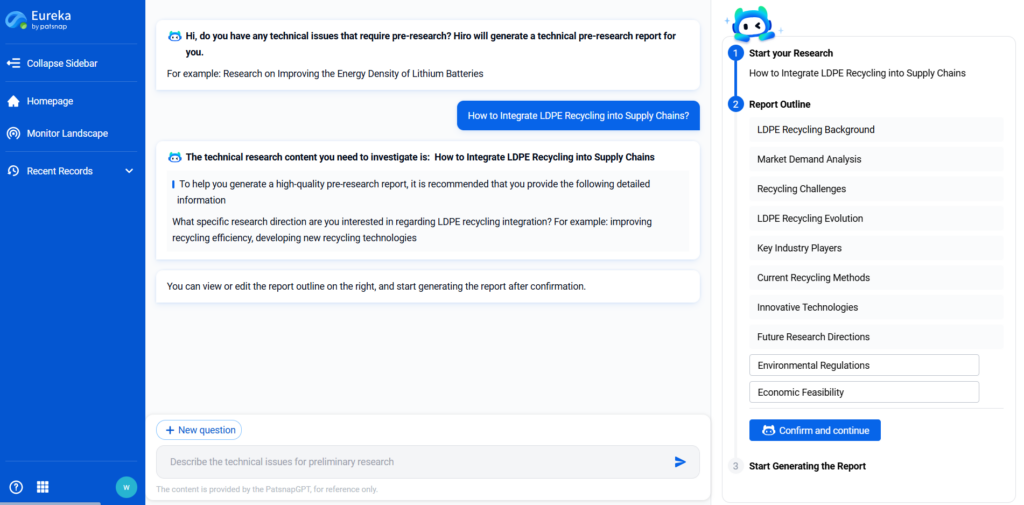
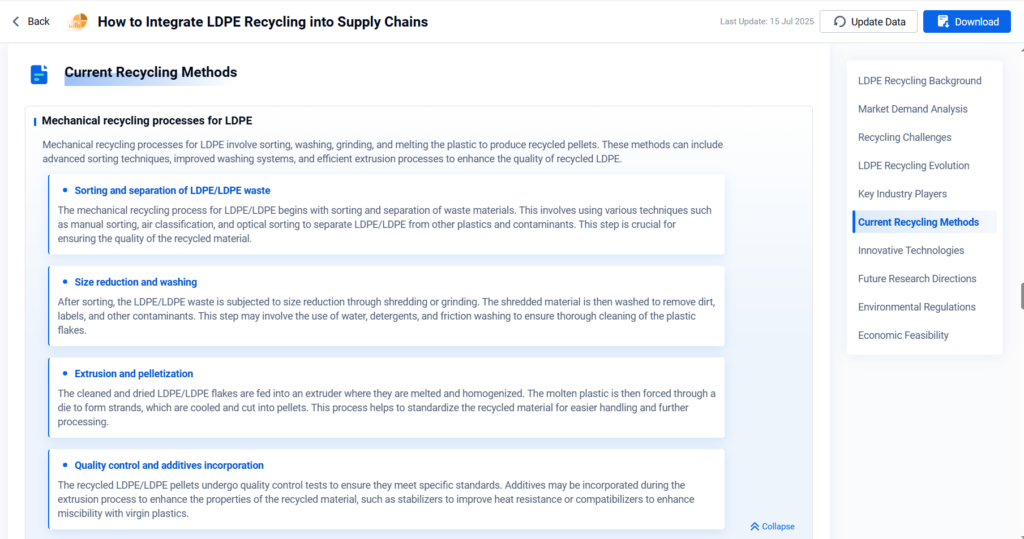
- How to Integrate LDPE Recycling into Supply Chains?
- Future of LDPE in Automotive Applications
2. Biomedical & Healthcare Applications
Medical-grade packaging and devices demand flexible, sterile, and non-toxic materials. LDPE meets these needs with its chemical inertness, sealability, and ease of molding. It is widely used in IV bags, tubing, and pharmaceutical packaging, often replacing PVC due to lower toxicity concerns.
Research Frontlines:
R&D focuses on antimicrobial LDPE films, multilayer medical packaging, and compliance with regulatory frameworks.
Related Reports:
- LDPE in Healthcare: Safe and Flexible Solutions
- LDPE in Medical Devices: Flexible and Sterile Solutions
- LDPE and Food Safety: Ensuring Compliance and Quality
- Understanding LDPE Environmental Impact and Solutions
- Enhancing LDPE Transparency for Improved Aesthetics
- LDPE’s Role in Reducing Plastic Waste Globally
- How to Implement LDPE Recycling Programs in Industry?
3. Construction & Infrastructure
In building applications, LDPE provides moisture barriers, vapor retarders, and protective sheeting. Its durability, flexibility, and weather resistance make it ideal for foundations, piping insulation, and concrete protection.
Research Frontlines:
Innovations involve reinforced LDPE membranes, improved bonding with concrete, and compatibility with green building codes.
Related Reports:
- LDPE in Construction: Durable and Cost-Effective Solutions
- How to Improve LDPE Thermal Stability in Applications?
- How to Enhance LDPE Impact Resistance for Durability?
- How to Improve LDPE Film Surface Properties?
- How to Address Challenges in LDPE Disposal?
- LDPE and Food Safety: Ensuring Compliance and Quality
- LDPE Market Growth: Trends and Predictions
4. Electronics & Industrial Insulation
LDPE’s excellent dielectric properties and flexibility support applications in wire insulation, flexible electronic components, and protective films. It replaces traditional rigid plastics in dynamic assemblies requiring formability and abrasion resistance.
Research Frontlines:
Ongoing work explores flame-retardant LDPE blends, high-frequency insulation, and UV-stabilized electronics-grade films.
Related Reports:
- LDPE in Electronics: Insulation and Protection Benefits
- How to Enhance LDPE Products with Nanotechnology?
- How to Improve Heat Seal Strength in LDPE Packaging?
- How to Boost LDPE’s Mechanical Properties?
- Exploring LDPE’s Role in Sustainable Design
- How to Optimize LDPE for Cold Storage Applications?
- Innovations in LDPE Barrier Film Technologies
5. Agricultural Films & Environmental Protection
In agriculture, LDPE films are used for mulching, greenhouse covers, and irrigation linings. Their UV resistance, durability, and transparency help control temperature and moisture while reducing chemical usage.
Research Frontlines:
Studies aim to improve biodegradability, enhance UV shielding, and integrate LDPE in precision agriculture systems.
Related Reports:
- LDPE in Agriculture: Solutions for Crop Protection
- How to Create Biodegradable LDPE Composites?
- Exploring Renewable Feedstocks for LDPE Production
- How to Advance LDPE Extrusion Techniques?
- Progress in LDPE Degradation Techniques
- How to Develop Bio-Based Alternatives to LDPE?
- Advancing LDPE’s Role in Resource-Efficient Packaging
Comparative Advantages & Limitations
Advantages:
- Lightweight and easy to process
- High flexibility and impact resistance
- Cost-effective for high-volume packaging
- Chemical inertness and moisture barrier properties
- Increasing recyclability with modern technologies
Limitations:
- Lower tensile strength and heat resistance compared to HDPE
- Limited biodegradability unless modified
- Vulnerable to UV degradation without stabilizers
- Downcycling common in recycling streams
Compared to PET, LDPE offers superior flexibility but lower gas barrier performance. Versus HDPE, it is softer and more ductile, but less mechanically robust.
Future Outlook & Research Frontiers
In the next decade, LDPE innovation will target:
- Bio-based and biodegradable LDPE alternatives
- Smart packaging films with anti-microbial/anti-fog properties
- Nano-enhanced blends for strength and barrier improvement
- Closed-loop supply chain integration
- Digitally traceable LDPE products for circular tracking
Keywords: Circular packaging, Biodegradable polymers, LDPE nanocomposites, Green building films, Advanced recyclability
Conclusion & Strategic Takeaways
LDPE remains a foundational polymer in global packaging and industrial systems. Its adaptability, processability, and evolving recyclability make it a strategic material for achieving sustainability goals across sectors. With R&D driving bio-based innovations and circular solutions, LDPE’s relevance will persist in shaping the future of materials engineering.
Accelerate Innovation with PatSnap Eureka AI Agent
LDPE innovation spans packaging science, polymer chemistry, and sustainability engineering. PatSnap Eureka AI Agent enables users to:
- Analyze global IP trends and competitor strategies in LDPE
- Visualize keyword clusters and innovation trajectories
- Uncover white space opportunities in bio-LDPE and recycling tech
👉 Tap into the power of PatSnap Eureka AI Agentand turn LDPE data into actionable innovation