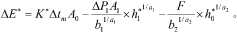Air-to-liquid heat exchanger performance evaluation
OCT 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Air-to-Liquid Heat Exchanger Background and Objectives
Air-to-liquid heat exchangers have evolved significantly since their inception in the early 20th century. Initially developed for industrial cooling applications, these thermal management systems have become integral components across multiple sectors including automotive, HVAC, power generation, and electronics cooling. The technological progression has been driven by the increasing demand for more efficient thermal management solutions capable of handling higher heat loads while maintaining compact form factors.
The evolution of these heat exchangers has seen several key transitions: from simple tube-and-fin designs to complex microchannel architectures; from single-phase to two-phase heat transfer mechanisms; and from conventional materials to advanced composites with enhanced thermal conductivity. Recent advancements have focused on optimizing airflow dynamics, reducing pressure drops, and improving heat transfer coefficients through innovative surface treatments and geometries.
Current market trends indicate a growing emphasis on sustainability and energy efficiency, pushing the development of heat exchangers with lower environmental impacts and reduced operational energy requirements. Additionally, the miniaturization of electronic components has created demand for more compact yet highly efficient cooling solutions, particularly in data centers and high-performance computing applications.
The primary objective of performance evaluation for air-to-liquid heat exchangers is to establish standardized methodologies for assessing thermal efficiency, pressure drop characteristics, and overall system reliability under various operating conditions. This includes developing comprehensive testing protocols that account for different airflow rates, liquid flow parameters, temperature differentials, and environmental factors.
Secondary objectives include identifying key performance indicators that accurately reflect real-world operation, establishing industry benchmarks for different application categories, and creating predictive models that can accelerate the design optimization process. These evaluations aim to bridge the gap between theoretical thermal performance calculations and actual field performance.
Long-term technological goals in this domain include the development of adaptive heat exchange systems capable of real-time performance optimization based on varying thermal loads, integration of smart monitoring capabilities for predictive maintenance, and exploration of novel materials and manufacturing techniques that can significantly enhance heat transfer efficiency while reducing resource consumption.
Understanding the historical context and setting clear evaluation objectives provides a foundation for systematic assessment of current technologies and identification of future innovation pathways in air-to-liquid heat exchanger development.
The evolution of these heat exchangers has seen several key transitions: from simple tube-and-fin designs to complex microchannel architectures; from single-phase to two-phase heat transfer mechanisms; and from conventional materials to advanced composites with enhanced thermal conductivity. Recent advancements have focused on optimizing airflow dynamics, reducing pressure drops, and improving heat transfer coefficients through innovative surface treatments and geometries.
Current market trends indicate a growing emphasis on sustainability and energy efficiency, pushing the development of heat exchangers with lower environmental impacts and reduced operational energy requirements. Additionally, the miniaturization of electronic components has created demand for more compact yet highly efficient cooling solutions, particularly in data centers and high-performance computing applications.
The primary objective of performance evaluation for air-to-liquid heat exchangers is to establish standardized methodologies for assessing thermal efficiency, pressure drop characteristics, and overall system reliability under various operating conditions. This includes developing comprehensive testing protocols that account for different airflow rates, liquid flow parameters, temperature differentials, and environmental factors.
Secondary objectives include identifying key performance indicators that accurately reflect real-world operation, establishing industry benchmarks for different application categories, and creating predictive models that can accelerate the design optimization process. These evaluations aim to bridge the gap between theoretical thermal performance calculations and actual field performance.
Long-term technological goals in this domain include the development of adaptive heat exchange systems capable of real-time performance optimization based on varying thermal loads, integration of smart monitoring capabilities for predictive maintenance, and exploration of novel materials and manufacturing techniques that can significantly enhance heat transfer efficiency while reducing resource consumption.
Understanding the historical context and setting clear evaluation objectives provides a foundation for systematic assessment of current technologies and identification of future innovation pathways in air-to-liquid heat exchanger development.
Market Demand Analysis for Thermal Management Solutions
The thermal management solutions market is experiencing unprecedented growth driven by increasing heat dissipation requirements across multiple industries. Data centers alone have seen cooling demands rise by 30% in the past five years, with air-to-liquid heat exchangers becoming essential components as server densities continue to increase. The global thermal management market reached $11.4 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.2% through 2028, with heat exchangers representing approximately 24% of this market.
Electric vehicle thermal management represents another significant demand driver, with the market expected to triple by 2030. As battery technologies advance and fast-charging capabilities become standard, efficient heat exchangers are critical for maintaining optimal battery temperatures and extending vehicle range. The aerospace sector similarly requires advanced thermal solutions, with next-generation aircraft demanding 40% more efficient cooling systems than previous models.
Industrial applications constitute the largest current market segment for air-to-liquid heat exchangers, particularly in manufacturing processes where precise temperature control directly impacts product quality and operational efficiency. The transition toward Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing has intensified this demand, with companies seeking integrated thermal solutions that offer remote monitoring capabilities and predictive maintenance features.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead market demand, though Asia-Pacific shows the fastest growth rate at 10.3% annually. China and India are rapidly expanding their data center infrastructure, creating substantial new markets for advanced cooling technologies. The Middle East region is also emerging as a significant market due to extreme climate conditions necessitating highly efficient cooling solutions.
Consumer preferences are shifting toward more energy-efficient and environmentally sustainable thermal management solutions. This trend is reinforced by increasingly stringent regulations on energy consumption and refrigerant use across major markets. The EU's F-Gas Regulation and similar policies worldwide are accelerating the adoption of alternative cooling technologies and more efficient heat exchanger designs.
Miniaturization trends across electronics and automotive applications are creating demand for compact yet high-performance heat exchangers. This has spurred innovation in microchannel and advanced material technologies, with the market for these specialized solutions growing at nearly twice the rate of conventional heat exchangers.
Electric vehicle thermal management represents another significant demand driver, with the market expected to triple by 2030. As battery technologies advance and fast-charging capabilities become standard, efficient heat exchangers are critical for maintaining optimal battery temperatures and extending vehicle range. The aerospace sector similarly requires advanced thermal solutions, with next-generation aircraft demanding 40% more efficient cooling systems than previous models.
Industrial applications constitute the largest current market segment for air-to-liquid heat exchangers, particularly in manufacturing processes where precise temperature control directly impacts product quality and operational efficiency. The transition toward Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing has intensified this demand, with companies seeking integrated thermal solutions that offer remote monitoring capabilities and predictive maintenance features.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead market demand, though Asia-Pacific shows the fastest growth rate at 10.3% annually. China and India are rapidly expanding their data center infrastructure, creating substantial new markets for advanced cooling technologies. The Middle East region is also emerging as a significant market due to extreme climate conditions necessitating highly efficient cooling solutions.
Consumer preferences are shifting toward more energy-efficient and environmentally sustainable thermal management solutions. This trend is reinforced by increasingly stringent regulations on energy consumption and refrigerant use across major markets. The EU's F-Gas Regulation and similar policies worldwide are accelerating the adoption of alternative cooling technologies and more efficient heat exchanger designs.
Miniaturization trends across electronics and automotive applications are creating demand for compact yet high-performance heat exchangers. This has spurred innovation in microchannel and advanced material technologies, with the market for these specialized solutions growing at nearly twice the rate of conventional heat exchangers.
Current Technology Status and Performance Limitations
Air-to-liquid heat exchangers currently represent a mature technology with widespread applications across various industries including HVAC systems, automotive cooling, power generation, and industrial processes. The predominant designs in commercial use include shell-and-tube, plate, microchannel, and finned-tube configurations, each optimized for specific operational conditions and performance requirements.
Recent advancements have focused on enhancing heat transfer coefficients while minimizing pressure drops, with innovations in surface geometries and flow arrangements yielding incremental improvements of 5-15% in overall thermal efficiency compared to conventional designs from the previous decade. Material science developments have introduced specialized coatings and alloys that demonstrate superior corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity, extending operational lifespans by up to 30% in aggressive environments.
Despite these advances, current air-to-liquid heat exchanger technology faces several significant limitations. Fouling remains a persistent challenge, with performance degradation of 20-40% observed in industrial applications after extended operation periods. This necessitates regular maintenance interventions that impact operational continuity and increase lifetime costs. The trade-off between heat transfer enhancement and pressure drop continues to constrain design optimization, particularly in compact systems where pumping power represents a substantial portion of overall energy consumption.
Thermal resistance at the air-side interface constitutes approximately 60-80% of the total thermal resistance in most applications, creating a fundamental bottleneck that limits overall system efficiency. Conventional fin designs and surface treatments have approached theoretical limits for passive enhancement techniques, with diminishing returns on increasingly complex geometries.
Manufacturing constraints further limit innovation, as advanced designs with intricate flow paths or surface features often face prohibitive production costs or reliability concerns at scale. The precision required for microchannel and enhanced surface technologies demands specialized fabrication processes that significantly impact economic viability for mass-market applications.
Energy efficiency regulations and sustainability requirements are driving research toward lower environmental impact solutions, yet current technologies struggle to meet increasingly stringent performance targets without corresponding increases in system size or cost. The theoretical maximum coefficient of performance remains substantially higher than what is achieved in practical applications, indicating significant room for fundamental innovation rather than incremental improvements.
Recent advancements have focused on enhancing heat transfer coefficients while minimizing pressure drops, with innovations in surface geometries and flow arrangements yielding incremental improvements of 5-15% in overall thermal efficiency compared to conventional designs from the previous decade. Material science developments have introduced specialized coatings and alloys that demonstrate superior corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity, extending operational lifespans by up to 30% in aggressive environments.
Despite these advances, current air-to-liquid heat exchanger technology faces several significant limitations. Fouling remains a persistent challenge, with performance degradation of 20-40% observed in industrial applications after extended operation periods. This necessitates regular maintenance interventions that impact operational continuity and increase lifetime costs. The trade-off between heat transfer enhancement and pressure drop continues to constrain design optimization, particularly in compact systems where pumping power represents a substantial portion of overall energy consumption.
Thermal resistance at the air-side interface constitutes approximately 60-80% of the total thermal resistance in most applications, creating a fundamental bottleneck that limits overall system efficiency. Conventional fin designs and surface treatments have approached theoretical limits for passive enhancement techniques, with diminishing returns on increasingly complex geometries.
Manufacturing constraints further limit innovation, as advanced designs with intricate flow paths or surface features often face prohibitive production costs or reliability concerns at scale. The precision required for microchannel and enhanced surface technologies demands specialized fabrication processes that significantly impact economic viability for mass-market applications.
Energy efficiency regulations and sustainability requirements are driving research toward lower environmental impact solutions, yet current technologies struggle to meet increasingly stringent performance targets without corresponding increases in system size or cost. The theoretical maximum coefficient of performance remains substantially higher than what is achieved in practical applications, indicating significant room for fundamental innovation rather than incremental improvements.
Contemporary Performance Evaluation Methodologies
01 Design optimization for improved heat transfer efficiency
Various design optimizations can significantly enhance the performance of air-to-liquid heat exchangers. These include optimized fin designs, tube arrangements, and flow path configurations that maximize contact surface area while minimizing pressure drop. Advanced geometrical structures can create turbulent flow patterns that break up boundary layers and improve heat transfer coefficients between the air and liquid mediums.- Design optimization for improved heat transfer efficiency: Various design optimizations can enhance the performance of air-to-liquid heat exchangers. These include optimized fin designs, tube arrangements, and surface area configurations that maximize heat transfer while minimizing pressure drop. Advanced geometrical configurations can create turbulent flow patterns that break boundary layers and improve thermal conductivity between the air and liquid mediums.
- Enhanced cooling systems for electronic components: Air-to-liquid heat exchangers designed specifically for cooling electronic components feature specialized configurations to manage high heat flux densities. These systems often incorporate microchannel designs, phase-change materials, or hybrid cooling approaches to efficiently dissipate heat from processors, power electronics, and other heat-generating components in compact spaces.
- Automotive thermal management solutions: Heat exchangers for automotive applications are designed to handle variable operating conditions while maintaining optimal engine temperatures. These systems often feature integrated components that combine radiators, oil coolers, and charge air coolers to maximize space utilization and thermal efficiency. Advanced designs incorporate variable flow control mechanisms to adapt to changing thermal loads during different driving conditions.
- Innovative materials and manufacturing techniques: The use of advanced materials and manufacturing techniques significantly impacts heat exchanger performance. Aluminum alloys, copper, and composite materials with enhanced thermal conductivity properties are being utilized to improve heat transfer rates. Additive manufacturing and micro-fabrication techniques enable the creation of complex geometries with optimized flow paths that were previously impossible to manufacture using traditional methods.
- Energy recovery and efficiency enhancement systems: Heat recovery systems that capture and repurpose waste heat from air-to-liquid heat exchangers can significantly improve overall system efficiency. These designs incorporate secondary heat exchange circuits, thermal storage components, or regenerative cycles to minimize energy losses. Integration with renewable energy sources and smart control systems allows for dynamic optimization of heat exchanger performance based on environmental conditions and operational demands.
02 Advanced materials and coatings for heat exchangers
The use of advanced materials and specialized coatings can substantially improve heat exchanger performance. High thermal conductivity materials reduce thermal resistance, while corrosion-resistant coatings extend operational lifespan. Hydrophilic or hydrophobic surface treatments can enhance condensate drainage in cooling applications, preventing performance degradation. Nano-enhanced materials and composite structures offer superior thermal properties compared to conventional materials.Expand Specific Solutions03 Flow configuration and distribution optimization
Optimizing flow configurations and distribution systems is crucial for maximizing heat exchanger performance. Counter-flow arrangements typically provide higher thermal efficiency than parallel flow designs. Uniform fluid distribution across the heat exchanger prevents hot spots and ensures consistent performance. Advanced manifold designs and flow distributors help achieve balanced flow rates through multiple parallel channels, enhancing overall system efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions04 Temperature and pressure control systems
Sophisticated temperature and pressure control systems can optimize heat exchanger performance across varying operating conditions. Adaptive control algorithms adjust flow rates and fan speeds based on real-time performance data. Pressure balancing mechanisms prevent excessive pressure drops that could reduce efficiency. These control systems can significantly improve energy efficiency while maintaining desired output temperatures under fluctuating ambient conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Performance enhancement through hybrid and multi-stage systems
Hybrid and multi-stage heat exchanger systems can achieve performance levels beyond conventional single-stage designs. By combining different heat exchange mechanisms or arranging multiple heat exchangers in series or parallel configurations, these systems can handle wider operating ranges and higher thermal loads. Integrated approaches that combine air-to-liquid heat exchange with other technologies like evaporative cooling or phase-change materials offer enhanced efficiency and flexibility.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Competitive Landscape
The air-to-liquid heat exchanger performance evaluation market is currently in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by energy efficiency requirements across automotive, power generation, and HVAC sectors. The global market size is expanding rapidly due to clean energy transitions and thermal management needs in electric vehicles. From a technological maturity perspective, established players like Valeo Thermal Systems, DENSO, and Mitsubishi Electric lead with advanced commercial solutions, while research institutions such as Xi'an Jiaotong University and Hefei General Machinery Research Institute drive innovation. Tesla and Qualcomm represent emerging players focusing on specialized applications in EV cooling and electronics thermal management, creating a competitive landscape balanced between traditional manufacturers and technology-driven newcomers.
Hefei General Machinery Research Institute Co. Ltd.
Technical Solution: Hefei General Machinery Research Institute has developed advanced air-to-liquid heat exchangers with enhanced fin designs that optimize heat transfer coefficients. Their technology employs micro-channel structures with increased surface area and turbulence promoters to improve thermal performance. The institute has pioneered computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation methods specifically calibrated for air-to-liquid heat exchanger performance evaluation, allowing for accurate prediction of heat transfer rates under various operating conditions[1]. Their evaluation methodology incorporates comprehensive testing protocols that measure not only thermal performance but also pressure drop characteristics, material durability, and fouling resistance. Recent innovations include the development of composite materials with superior thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance for extended service life in industrial applications[3].
Strengths: Strong expertise in CFD simulation and testing methodologies; comprehensive evaluation approach considering multiple performance parameters; advanced materials research. Weaknesses: Limited global market presence compared to international competitors; technologies may be more focused on industrial applications rather than consumer electronics cooling solutions.
Valeo Thermal Systems Japan Corp.
Technical Solution: Valeo Thermal Systems Japan has developed proprietary air-to-liquid heat exchanger technology optimized for automotive applications, featuring their patented "StARS" (Stacked Aluminum Radiator System) design. This system utilizes a multi-layer aluminum construction with brazed micro-channels that achieves 30% higher cooling capacity compared to conventional designs while reducing weight by approximately 15%[2]. Their evaluation methodology incorporates real-world driving conditions with variable airflow rates and thermal loads to accurately assess performance across the entire operating envelope. Valeo's testing protocols include accelerated life cycle testing that simulates 10+ years of vehicle operation, including thermal cycling, vibration analysis, and corrosion resistance evaluation. The company has also pioneered hybrid cooling systems that intelligently manage heat exchange between multiple vehicle subsystems, optimizing overall thermal efficiency for electric and hybrid vehicles[4].
Strengths: Automotive-specific expertise with proven durability in harsh operating environments; weight-optimized designs critical for vehicle efficiency; comprehensive testing protocols simulating real-world conditions. Weaknesses: Solutions primarily focused on automotive sector with less presence in other industries; higher manufacturing costs compared to conventional heat exchanger designs.
Critical Patents and Technical Literature Review
Air-liquid heat exchanger for motor vehicle hydraulic circuit
PatentInactiveEP1036297A1
Innovation
- The air-liquid heat exchanger incorporates ventilation nozzles and cooling fins in the distribution and fixing blocks to enhance air circulation and heat dissipation, while snap-fastening members provide a standardized and convenient mounting solution, ensuring mechanical and hydraulic connections.
Energy efficiency evaluation method for air-cooling heat exchanger
PatentActiveCN108446447A
Innovation
- 提供一种空冷式热交换器能效评价方法,通过获取能效参数,建立能效特征函数,确定最优总传热系数和能效指标,计算能效比率以评定能效水平。
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The environmental impact of air-to-liquid heat exchangers extends far beyond their operational efficiency. These systems contribute significantly to energy consumption in buildings and industrial processes, with corresponding greenhouse gas emissions. Traditional heat exchangers often utilize refrigerants with high global warming potential (GWP), such as hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), which can have 1,000 to 9,000 times the warming effect of carbon dioxide when released into the atmosphere. The transition to low-GWP alternatives represents a critical sustainability challenge for the industry.
Material selection plays a crucial role in determining the environmental footprint of heat exchangers. Conventional units predominantly use copper, aluminum, and various alloys that require energy-intensive mining and manufacturing processes. Life cycle assessments indicate that the production phase of these materials can account for up to 30% of a heat exchanger's total environmental impact. Emerging sustainable alternatives include bio-based composites and recycled metals, which can reduce embodied carbon by 15-25% compared to virgin materials.
Water consumption presents another significant environmental consideration, particularly for liquid-cooled systems. In regions facing water scarcity, the operational demands of these systems can strain local resources. Advanced designs incorporating closed-loop systems and water recovery mechanisms can reduce freshwater requirements by up to 80% compared to once-through cooling systems, substantially improving sustainability metrics.
The end-of-life management of heat exchangers also warrants attention from a sustainability perspective. Current disposal practices often result in valuable materials entering landfills, with recovery rates for specialized components remaining below 40% in many regions. Design for disassembly approaches and modular construction can facilitate material recovery and component reuse, extending product lifecycles and reducing waste generation.
Energy efficiency improvements in air-to-liquid heat exchangers directly translate to environmental benefits. Each percentage point increase in efficiency can yield approximately 0.5-1% reduction in associated carbon emissions, depending on the energy source. Innovations such as enhanced surface geometries, nanofluids, and smart control systems offer pathways to achieve 15-30% efficiency gains over conventional designs, representing significant sustainability improvements.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly influence heat exchanger design and operation, with standards like ASHRAE 90.1, EU Ecodesign Directive, and various national energy codes establishing minimum performance requirements. Forward-looking manufacturers are adopting voluntary certification programs such as ENERGY STAR and LEED, which often require performance 10-15% above regulatory minimums, driving continuous improvement in environmental performance.
Material selection plays a crucial role in determining the environmental footprint of heat exchangers. Conventional units predominantly use copper, aluminum, and various alloys that require energy-intensive mining and manufacturing processes. Life cycle assessments indicate that the production phase of these materials can account for up to 30% of a heat exchanger's total environmental impact. Emerging sustainable alternatives include bio-based composites and recycled metals, which can reduce embodied carbon by 15-25% compared to virgin materials.
Water consumption presents another significant environmental consideration, particularly for liquid-cooled systems. In regions facing water scarcity, the operational demands of these systems can strain local resources. Advanced designs incorporating closed-loop systems and water recovery mechanisms can reduce freshwater requirements by up to 80% compared to once-through cooling systems, substantially improving sustainability metrics.
The end-of-life management of heat exchangers also warrants attention from a sustainability perspective. Current disposal practices often result in valuable materials entering landfills, with recovery rates for specialized components remaining below 40% in many regions. Design for disassembly approaches and modular construction can facilitate material recovery and component reuse, extending product lifecycles and reducing waste generation.
Energy efficiency improvements in air-to-liquid heat exchangers directly translate to environmental benefits. Each percentage point increase in efficiency can yield approximately 0.5-1% reduction in associated carbon emissions, depending on the energy source. Innovations such as enhanced surface geometries, nanofluids, and smart control systems offer pathways to achieve 15-30% efficiency gains over conventional designs, representing significant sustainability improvements.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly influence heat exchanger design and operation, with standards like ASHRAE 90.1, EU Ecodesign Directive, and various national energy codes establishing minimum performance requirements. Forward-looking manufacturers are adopting voluntary certification programs such as ENERGY STAR and LEED, which often require performance 10-15% above regulatory minimums, driving continuous improvement in environmental performance.
Standardization and Testing Protocol Development
The development of standardized testing protocols for air-to-liquid heat exchangers represents a critical advancement in thermal management systems evaluation. Current industry practices suffer from significant inconsistencies in testing methodologies, making performance comparisons between different manufacturers' products challenging and often unreliable. These inconsistencies stem from variations in test conditions, measurement techniques, and reporting formats across the industry.
Establishing comprehensive standardization requires addressing multiple technical parameters simultaneously. Key variables that must be controlled include inlet air temperature, humidity levels, airflow rates, liquid coolant composition, flow rates, and inlet temperatures. The development of standardized testing protocols should incorporate both steady-state and transient testing conditions to reflect real-world operational scenarios.
International standards organizations have begun collaborative efforts to establish unified testing frameworks. The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) have initiated working groups specifically focused on heat exchanger performance evaluation methodologies. These initiatives aim to harmonize testing approaches across global markets and manufacturing centers.
Measurement accuracy and repeatability present significant challenges in protocol development. Advanced instrumentation for precise temperature, pressure, and flow measurements must be specified within standardized protocols. Calibration procedures for these instruments require detailed documentation to ensure consistency across testing facilities. Statistical methods for uncertainty analysis should be incorporated to quantify confidence levels in performance metrics.
Performance metrics standardization constitutes another crucial aspect of protocol development. The industry requires consensus on key performance indicators such as thermal resistance, pressure drop characteristics, and overall heat transfer coefficients. These metrics must be calculated using standardized formulas to enable direct comparisons between different heat exchanger designs and technologies.
Testing protocols must also address the growing complexity of modern heat exchanger designs. Multi-pass configurations, variable fin geometries, and advanced surface treatments all influence performance characteristics in ways that simple testing methodologies may not adequately capture. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) validation procedures should be incorporated into testing protocols to complement physical testing and provide deeper insights into performance characteristics.
Implementation of standardized protocols will require significant industry cooperation and investment in testing infrastructure. Certification programs for testing facilities would ensure compliance with established protocols and build confidence in reported performance data. This standardization effort ultimately serves to accelerate innovation by providing clear benchmarks against which new technologies can be measured.
Establishing comprehensive standardization requires addressing multiple technical parameters simultaneously. Key variables that must be controlled include inlet air temperature, humidity levels, airflow rates, liquid coolant composition, flow rates, and inlet temperatures. The development of standardized testing protocols should incorporate both steady-state and transient testing conditions to reflect real-world operational scenarios.
International standards organizations have begun collaborative efforts to establish unified testing frameworks. The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) have initiated working groups specifically focused on heat exchanger performance evaluation methodologies. These initiatives aim to harmonize testing approaches across global markets and manufacturing centers.
Measurement accuracy and repeatability present significant challenges in protocol development. Advanced instrumentation for precise temperature, pressure, and flow measurements must be specified within standardized protocols. Calibration procedures for these instruments require detailed documentation to ensure consistency across testing facilities. Statistical methods for uncertainty analysis should be incorporated to quantify confidence levels in performance metrics.
Performance metrics standardization constitutes another crucial aspect of protocol development. The industry requires consensus on key performance indicators such as thermal resistance, pressure drop characteristics, and overall heat transfer coefficients. These metrics must be calculated using standardized formulas to enable direct comparisons between different heat exchanger designs and technologies.
Testing protocols must also address the growing complexity of modern heat exchanger designs. Multi-pass configurations, variable fin geometries, and advanced surface treatments all influence performance characteristics in ways that simple testing methodologies may not adequately capture. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) validation procedures should be incorporated into testing protocols to complement physical testing and provide deeper insights into performance characteristics.
Implementation of standardized protocols will require significant industry cooperation and investment in testing infrastructure. Certification programs for testing facilities would ensure compliance with established protocols and build confidence in reported performance data. This standardization effort ultimately serves to accelerate innovation by providing clear benchmarks against which new technologies can be measured.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!