Heat exchanger surface coating for fouling prevention
OCT 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Heat Exchanger Fouling Background and Objectives
Heat exchanger fouling is a persistent challenge that has plagued industrial operations since the inception of heat transfer equipment. This phenomenon occurs when unwanted materials accumulate on heat transfer surfaces, forming insulating layers that impede thermal efficiency. Historical data indicates that fouling-related issues account for approximately 2.5-5% of global industrial energy consumption, translating to billions of dollars in annual economic losses across sectors including petrochemical, food processing, power generation, and HVAC systems.
The evolution of heat exchanger technology has been significantly influenced by efforts to mitigate fouling. Early approaches in the mid-20th century focused primarily on mechanical cleaning and operational adjustments. The 1970s energy crisis catalyzed research into more sophisticated anti-fouling strategies, with surface engineering emerging as a promising direction by the 1990s. Recent decades have witnessed accelerated development in advanced coating technologies, driven by environmental regulations and energy efficiency mandates.
Fouling mechanisms vary considerably across applications, encompassing crystallization, particulate deposition, chemical reactions, biological growth, and corrosion products. Each mechanism demands specific preventive strategies, with surface coatings increasingly recognized as a versatile solution capable of addressing multiple fouling types simultaneously.
The technical objectives for heat exchanger surface coatings focus on several critical parameters. Primary goals include reducing surface energy to minimize adhesion of foulants, creating smooth surfaces with low roughness to inhibit initial deposition, and incorporating antimicrobial properties to prevent biofouling. Additional objectives encompass thermal conductivity preservation, mechanical durability under operational conditions, and chemical stability in aggressive environments.
Current research trajectories aim to develop multifunctional coatings that combine hydrophobicity, oleophobicity, and antimicrobial properties while maintaining excellent heat transfer characteristics. Emerging approaches include stimuli-responsive surfaces that can adapt to changing operational conditions and self-healing coatings capable of maintaining integrity over extended service periods.
The anticipated technological evolution suggests a shift toward biomimetic designs inspired by natural anti-fouling surfaces such as lotus leaves and shark skin. Concurrently, integration with digital technologies for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance represents an emerging frontier that could revolutionize fouling management strategies in heat exchange systems.
The evolution of heat exchanger technology has been significantly influenced by efforts to mitigate fouling. Early approaches in the mid-20th century focused primarily on mechanical cleaning and operational adjustments. The 1970s energy crisis catalyzed research into more sophisticated anti-fouling strategies, with surface engineering emerging as a promising direction by the 1990s. Recent decades have witnessed accelerated development in advanced coating technologies, driven by environmental regulations and energy efficiency mandates.
Fouling mechanisms vary considerably across applications, encompassing crystallization, particulate deposition, chemical reactions, biological growth, and corrosion products. Each mechanism demands specific preventive strategies, with surface coatings increasingly recognized as a versatile solution capable of addressing multiple fouling types simultaneously.
The technical objectives for heat exchanger surface coatings focus on several critical parameters. Primary goals include reducing surface energy to minimize adhesion of foulants, creating smooth surfaces with low roughness to inhibit initial deposition, and incorporating antimicrobial properties to prevent biofouling. Additional objectives encompass thermal conductivity preservation, mechanical durability under operational conditions, and chemical stability in aggressive environments.
Current research trajectories aim to develop multifunctional coatings that combine hydrophobicity, oleophobicity, and antimicrobial properties while maintaining excellent heat transfer characteristics. Emerging approaches include stimuli-responsive surfaces that can adapt to changing operational conditions and self-healing coatings capable of maintaining integrity over extended service periods.
The anticipated technological evolution suggests a shift toward biomimetic designs inspired by natural anti-fouling surfaces such as lotus leaves and shark skin. Concurrently, integration with digital technologies for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance represents an emerging frontier that could revolutionize fouling management strategies in heat exchange systems.
Market Analysis for Anti-Fouling Coating Solutions
The global market for anti-fouling coating solutions in heat exchangers is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing industrial demand for energy efficiency and operational cost reduction. Current market valuations indicate that the anti-fouling coatings sector for industrial applications reached approximately 3.2 billion USD in 2022, with heat exchanger applications constituting about 18% of this market. Industry analysts project a compound annual growth rate of 5.7% through 2028, outpacing many other industrial coating segments.
The oil and gas industry remains the largest consumer of anti-fouling coatings for heat exchangers, accounting for nearly 32% of market demand. This is followed closely by power generation (24%), chemical processing (19%), food and beverage (12%), and marine applications (8%). The remaining 5% is distributed across various industries including pharmaceuticals and HVAC systems. Regional analysis shows North America and Europe as mature markets with stable growth rates of 4-5%, while Asia-Pacific demonstrates accelerated adoption with growth rates exceeding 7% annually.
Customer demand is increasingly focused on environmentally sustainable solutions, particularly as regulatory frameworks worldwide tighten restrictions on traditional biocide-containing coatings. The European Union's Biocidal Products Regulation and similar legislation in North America have created significant market shifts toward non-toxic alternatives. This regulatory landscape has accelerated innovation in bio-inspired and non-leaching coating technologies, which now represent the fastest-growing segment with 12% year-over-year expansion.
Cost-benefit analyses reveal compelling economic incentives for anti-fouling coating adoption. Industrial facilities implementing advanced anti-fouling coatings report average energy savings of 15-20% in heat exchange operations, with payback periods typically ranging from 8 to 14 months depending on application severity and operational parameters. Maintenance cost reductions average 30% due to extended cleaning intervals and reduced mechanical cleaning requirements.
Market segmentation by coating type shows polymer-based coatings leading with 41% market share, followed by ceramic and glass coatings (27%), hydrophobic and superhydrophobic solutions (18%), and emerging graphene and carbon nanotube-enhanced coatings (9%). The remaining 5% comprises specialized niche solutions including biomimetic technologies. Premium pricing tiers are emerging for coatings offering extended performance guarantees, with some manufacturers now offering 5-7 year performance warranties compared to the industry standard of 2-3 years.
Customer purchasing decisions increasingly prioritize total cost of ownership over initial application costs, creating opportunities for premium solutions that demonstrate superior longevity and performance metrics. This shift has intensified competition among coating manufacturers to provide comprehensive performance data and lifecycle cost analyses as standard components of their value propositions.
The oil and gas industry remains the largest consumer of anti-fouling coatings for heat exchangers, accounting for nearly 32% of market demand. This is followed closely by power generation (24%), chemical processing (19%), food and beverage (12%), and marine applications (8%). The remaining 5% is distributed across various industries including pharmaceuticals and HVAC systems. Regional analysis shows North America and Europe as mature markets with stable growth rates of 4-5%, while Asia-Pacific demonstrates accelerated adoption with growth rates exceeding 7% annually.
Customer demand is increasingly focused on environmentally sustainable solutions, particularly as regulatory frameworks worldwide tighten restrictions on traditional biocide-containing coatings. The European Union's Biocidal Products Regulation and similar legislation in North America have created significant market shifts toward non-toxic alternatives. This regulatory landscape has accelerated innovation in bio-inspired and non-leaching coating technologies, which now represent the fastest-growing segment with 12% year-over-year expansion.
Cost-benefit analyses reveal compelling economic incentives for anti-fouling coating adoption. Industrial facilities implementing advanced anti-fouling coatings report average energy savings of 15-20% in heat exchange operations, with payback periods typically ranging from 8 to 14 months depending on application severity and operational parameters. Maintenance cost reductions average 30% due to extended cleaning intervals and reduced mechanical cleaning requirements.
Market segmentation by coating type shows polymer-based coatings leading with 41% market share, followed by ceramic and glass coatings (27%), hydrophobic and superhydrophobic solutions (18%), and emerging graphene and carbon nanotube-enhanced coatings (9%). The remaining 5% comprises specialized niche solutions including biomimetic technologies. Premium pricing tiers are emerging for coatings offering extended performance guarantees, with some manufacturers now offering 5-7 year performance warranties compared to the industry standard of 2-3 years.
Customer purchasing decisions increasingly prioritize total cost of ownership over initial application costs, creating opportunities for premium solutions that demonstrate superior longevity and performance metrics. This shift has intensified competition among coating manufacturers to provide comprehensive performance data and lifecycle cost analyses as standard components of their value propositions.
Current Anti-Fouling Technologies and Barriers
The heat exchanger fouling prevention industry currently employs several key anti-fouling technologies, each with specific advantages and limitations. Physical surface modifications represent one major approach, including super-hydrophobic coatings that create water-repellent surfaces with contact angles exceeding 150°. These coatings significantly reduce the adhesion of fouling particles but often suffer from mechanical durability issues when exposed to high-velocity fluid flows or abrasive particles.
Antimicrobial coatings incorporating silver, copper, or zinc nanoparticles effectively combat biofouling by releasing ions that disrupt microbial cell membranes. However, these coatings face challenges related to ion depletion over time, resulting in diminished effectiveness and potential environmental concerns regarding metal ion discharge into process streams.
Self-polishing coatings represent another innovative solution, designed to gradually erode in controlled patterns, continuously exposing fresh anti-fouling surfaces. While effective for marine applications, their application in industrial heat exchangers remains limited due to concerns about coating debris contaminating process fluids and unpredictable erosion rates under varying flow conditions.
Slippery liquid-infused porous surfaces (SLIPS) technology has emerged as a promising approach, utilizing a stable liquid layer trapped within a micro-textured substrate to prevent fouling adhesion. Despite showing excellent anti-fouling properties in laboratory settings, SLIPS faces significant barriers regarding liquid retention under high shear forces and temperature fluctuations typical in industrial heat exchangers.
Photocatalytic coatings, primarily based on titanium dioxide (TiO₂), decompose organic foulants through light-activated oxidation reactions. Their effectiveness is limited by light penetration constraints in enclosed heat exchanger systems and reduced activity in high-temperature environments, restricting their practical application to specific scenarios.
Several critical barriers impede widespread adoption of advanced anti-fouling coatings. Cost considerations remain paramount, with specialized coatings often increasing equipment expenses by 15-30%, creating adoption hesitancy despite potential long-term operational savings. Durability concerns persist across all coating technologies, with most solutions demonstrating performance degradation under industrial conditions within 6-18 months, falling short of the 3-5 year service intervals preferred by industry.
Application challenges further complicate implementation, as many coating technologies require specialized application procedures incompatible with existing manufacturing processes or field retrofitting. Regulatory compliance presents additional hurdles, particularly for coatings containing biocides or nanomaterials, which face increasing scrutiny regarding environmental impact and safety profiles across different jurisdictions.
Antimicrobial coatings incorporating silver, copper, or zinc nanoparticles effectively combat biofouling by releasing ions that disrupt microbial cell membranes. However, these coatings face challenges related to ion depletion over time, resulting in diminished effectiveness and potential environmental concerns regarding metal ion discharge into process streams.
Self-polishing coatings represent another innovative solution, designed to gradually erode in controlled patterns, continuously exposing fresh anti-fouling surfaces. While effective for marine applications, their application in industrial heat exchangers remains limited due to concerns about coating debris contaminating process fluids and unpredictable erosion rates under varying flow conditions.
Slippery liquid-infused porous surfaces (SLIPS) technology has emerged as a promising approach, utilizing a stable liquid layer trapped within a micro-textured substrate to prevent fouling adhesion. Despite showing excellent anti-fouling properties in laboratory settings, SLIPS faces significant barriers regarding liquid retention under high shear forces and temperature fluctuations typical in industrial heat exchangers.
Photocatalytic coatings, primarily based on titanium dioxide (TiO₂), decompose organic foulants through light-activated oxidation reactions. Their effectiveness is limited by light penetration constraints in enclosed heat exchanger systems and reduced activity in high-temperature environments, restricting their practical application to specific scenarios.
Several critical barriers impede widespread adoption of advanced anti-fouling coatings. Cost considerations remain paramount, with specialized coatings often increasing equipment expenses by 15-30%, creating adoption hesitancy despite potential long-term operational savings. Durability concerns persist across all coating technologies, with most solutions demonstrating performance degradation under industrial conditions within 6-18 months, falling short of the 3-5 year service intervals preferred by industry.
Application challenges further complicate implementation, as many coating technologies require specialized application procedures incompatible with existing manufacturing processes or field retrofitting. Regulatory compliance presents additional hurdles, particularly for coatings containing biocides or nanomaterials, which face increasing scrutiny regarding environmental impact and safety profiles across different jurisdictions.
Existing Anti-Fouling Coating Solutions
01 Anti-fouling coatings for heat exchanger surfaces
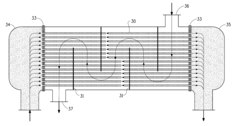
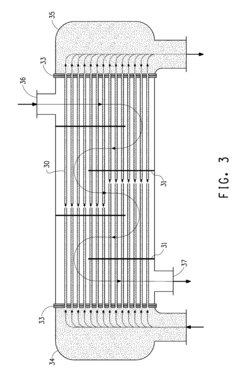
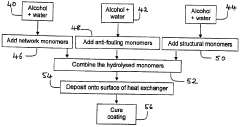
Various specialized coatings can be applied to heat exchanger surfaces to prevent fouling. These coatings create a barrier that inhibits the adhesion of deposits, scale, and biological growth. The coatings typically have low surface energy properties that make it difficult for contaminants to adhere to the heat exchanger surfaces. Some coatings also incorporate antimicrobial properties to prevent biofilm formation, which is a common cause of fouling in heat exchangers.- Anti-fouling coatings for heat exchanger surfaces: Various anti-fouling coatings can be applied to heat exchanger surfaces to prevent the accumulation of deposits. These coatings create a barrier that inhibits the adhesion of fouling materials such as scale, biological growth, and particulate matter. The coatings may include hydrophobic materials, polymer-based solutions, or specialized compounds that reduce surface energy and make it difficult for contaminants to adhere to the heat exchanger surfaces.
- Self-cleaning surface treatments: Self-cleaning surface treatments for heat exchangers incorporate materials that actively repel or break down fouling substances. These treatments may include photocatalytic materials that decompose organic deposits when exposed to light, or surfaces with micro/nano-texturing that creates a lotus effect, causing liquids and associated contaminants to bead up and roll off rather than adhere to the surface. These self-cleaning mechanisms significantly extend the operational periods between manual cleaning interventions.
- Metal-based protective coatings: Metal-based protective coatings provide both corrosion resistance and fouling prevention for heat exchanger surfaces. These coatings may include copper, zinc, nickel, or alloy compositions that offer antimicrobial properties to prevent biological fouling while also protecting against chemical attack. The metal coatings can be applied through various methods including electroplating, thermal spraying, or vapor deposition to create durable surfaces that maintain heat transfer efficiency while resisting fouling.
- Nanoparticle-enhanced surface modifications: Nanoparticle-enhanced surface modifications incorporate nanoscale materials into coatings to improve fouling resistance in heat exchangers. These nanoparticles can include silver, titanium dioxide, or carbon-based materials that provide antimicrobial properties, enhanced surface smoothness, or catalytic effects that prevent deposit formation. The nanoscale nature of these additives allows for thin coatings that don't significantly impede heat transfer while providing superior fouling resistance compared to conventional coatings.
- Chemical treatment systems for continuous fouling prevention: Chemical treatment systems provide continuous protection against fouling in heat exchangers by introducing anti-scaling, dispersing, or biocidal agents into the fluid stream. These systems may include controlled-release mechanisms that maintain optimal chemical concentrations, pH adjustment systems to prevent precipitation of scale-forming minerals, or oxidizing agents that prevent biological growth. The chemical treatments can be tailored to specific fouling challenges based on the operating conditions and fluid characteristics of the heat exchanger system.
02 Hydrophobic and oleophobic surface treatments
Hydrophobic and oleophobic surface treatments can be applied to heat exchanger surfaces to repel both water and oil-based contaminants. These treatments modify the surface properties to reduce the wettability of the heat exchanger surfaces, making it difficult for fouling materials to adhere. The hydrophobic and oleophobic properties help maintain clean surfaces and efficient heat transfer by preventing the accumulation of deposits. These treatments can be applied through various methods including chemical vapor deposition, sol-gel processes, or direct application of fluoropolymer-based compounds.Expand Specific Solutions03 Nanostructured and self-cleaning coatings
Nanostructured coatings provide enhanced anti-fouling properties through their unique surface morphology. These coatings often incorporate nanoparticles or create nanoscale patterns on the heat exchanger surface that reduce contact area for potential foulants. Some nanostructured coatings also exhibit self-cleaning properties, where contaminants are easily removed by fluid flow or minimal cleaning efforts. The nanoscale features can create superhydrophobic surfaces that significantly reduce fouling adhesion and improve the overall efficiency and maintenance requirements of heat exchangers.Expand Specific Solutions04 Metal-based and catalytic anti-fouling systems
Metal-based coatings, particularly those incorporating copper, silver, or zinc, can provide effective anti-fouling properties for heat exchangers. These metals have inherent antimicrobial properties that prevent biological fouling. Additionally, catalytic coatings can be applied that actively break down organic foulants through catalytic reactions. These systems not only prevent the initial adhesion of fouling materials but can also help degrade existing deposits, extending the operational time between cleaning cycles and maintaining optimal heat transfer efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions05 Polymer and composite protective layers
Polymer-based and composite coatings can be applied to heat exchanger surfaces to provide protection against fouling. These coatings typically consist of thermally conductive polymers or polymer-matrix composites that maintain heat transfer efficiency while providing anti-fouling properties. The polymers can be modified with additives to enhance specific properties such as chemical resistance, thermal stability, or surface smoothness. Some composite coatings incorporate particles or fibers that improve mechanical durability while maintaining anti-fouling characteristics, making them suitable for harsh operating environments.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies in Heat Exchanger Coating Industry
The heat exchanger surface coating market for fouling prevention is currently in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by energy efficiency requirements and operational cost reduction needs across industries. The global market size is estimated to be expanding at a CAGR of 5-7%, reaching approximately $1.2-1.5 billion by 2025. Major players include established petrochemical companies (ExxonMobil, BASF, China National Petroleum, Sinopec) alongside specialized coating technology providers (SilcoTek, SiOx ApS). The technology landscape shows varying maturity levels, with companies like Alfa Laval and Sanhua leading in commercial applications, while academic institutions (South China University of Technology, Tianjin University) focus on next-generation solutions. Emerging players like HurRain NanoTech are introducing innovative nanomaterial-based coatings, indicating a dynamic competitive environment with significant R&D investment.
ExxonMobil Technology & Engineering Co.
Technical Solution: ExxonMobil has developed proprietary FIBER FILM® technology for heat exchanger surface coating that creates a thin, hydrophobic barrier on metal surfaces. This technology utilizes fluoropolymer-based coatings that significantly reduce fouling by preventing the adhesion of deposits on heat transfer surfaces. The coating creates a low surface energy interface that inhibits the attachment of particulates, scale, and biological matter. ExxonMobil's approach combines surface chemistry modifications with engineered surface textures to optimize both the chemical and physical aspects of fouling prevention. Their research has demonstrated fouling reduction rates of up to 90% in certain applications, particularly in crude oil processing units where asphaltene and wax deposition are common fouling mechanisms. The company has implemented this technology across multiple refineries globally, with documented energy savings of 15-30% and extended run times between cleaning cycles.
Strengths: Superior hydrophobicity leading to excellent anti-fouling properties; proven track record in harsh petrochemical environments; significant energy savings and maintenance cost reduction. Weaknesses: Higher initial implementation costs; potential durability concerns in extremely high-temperature applications; may require specialized application techniques.
Alfa Laval Corporate AB
Technical Solution: Alfa Laval has pioneered several advanced surface coating technologies for heat exchangers, with their flagship StayClean™ solution being particularly notable. This technology employs a modified titanium oxide coating with photocatalytic properties that actively breaks down organic foulants when exposed to light. For industrial applications without light exposure, they've developed a complementary technology using nano-structured surface modifications that create an ultra-smooth surface with minimal nucleation sites. Their coatings are applied through a proprietary vapor deposition process that ensures uniform coverage even on complex plate geometries. Independent testing has shown these coatings can reduce cleaning frequency by up to 70% in dairy processing applications and extend operational time between cleanings by 3-5 times in various industrial settings. Alfa Laval's coatings are particularly effective against crystallization fouling and biological fouling, making them ideal for food, beverage, and pharmaceutical applications.
Strengths: Exceptional performance in food and pharmaceutical applications; non-toxic and environmentally friendly formulations; compatible with CIP (Clean-in-Place) systems; proven longevity. Weaknesses: Less effective in extremely high-temperature applications; higher initial cost compared to uncoated exchangers; some limitations in highly acidic environments.
Key Patents and Innovations in Surface Modification
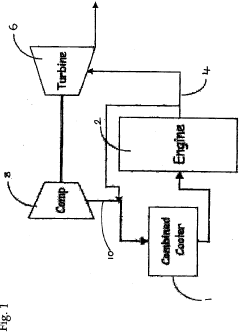
Process for Treating Water in Heavy Oil Production Using Coated Heat Exchange Units
PatentActiveUS20110139451A1
Innovation
- Applying a multi-layer coating comprising a melt flowable copolymer of tetrafluoroethylene to the interior or exterior surfaces of heat exchange unit tubes, which provides an anti-stick surface, reducing deposition of foulants and maintaining thermal conductivity across a wide temperature range.
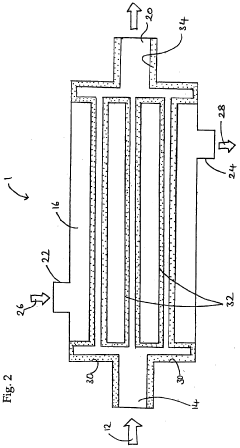
Anti-fouling coating
PatentInactiveGB2428604A
Innovation
- A siloxane-based coating with silicon, oxygen, and fluorinated alkyl groups forms a continuous, inert, and self-regenerating layer on heat exchanger surfaces, reducing fouling through low surface energy and even fluorination distribution, allowing chemical bonding without mechanical substrate preparation, and maintaining anti-fouling properties even when worn.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The environmental impact of heat exchanger fouling extends far beyond operational inefficiencies. Fouling necessitates frequent cleaning cycles that typically involve harsh chemical cleaners containing acids, alkalis, and solvents. These chemicals, when discharged, contribute significantly to water pollution and can disrupt aquatic ecosystems. Additionally, the energy penalties associated with fouled heat exchangers translate directly to increased carbon emissions—estimates suggest fouling is responsible for approximately 2.5% of global CO2 emissions from industrial operations.
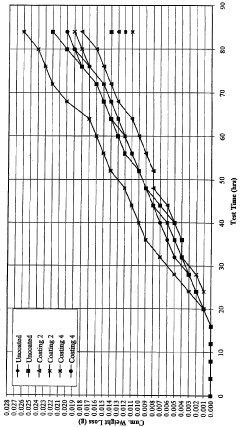
Surface coatings designed for fouling prevention offer substantial environmental benefits. Advanced hydrophobic coatings can reduce cleaning frequency by up to 70%, dramatically decreasing chemical cleaner usage and associated wastewater treatment requirements. Furthermore, by maintaining optimal heat transfer efficiency, these coatings can reduce energy consumption by 15-30% compared to untreated surfaces, with corresponding reductions in greenhouse gas emissions.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies of various coating technologies reveal important sustainability considerations. While fluoropolymer coatings demonstrate excellent fouling resistance, their production involves perfluorinated compounds with high global warming potential. In contrast, sol-gel silica-based coatings and biomimetic surfaces inspired by natural anti-fouling mechanisms (such as lotus leaf structures) typically have lower environmental footprints during manufacturing.
The durability of anti-fouling coatings represents another critical sustainability factor. First-generation coatings often required replacement within 6-12 months, creating waste and resource consumption cycles. Modern ceramic-polymer hybrid coatings can maintain effectiveness for 3-5 years, significantly improving the sustainability profile of these solutions. Some manufacturers have implemented coating recovery and recycling programs, further reducing environmental impact.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly influence coating technology development. The EU's REACH regulations and similar initiatives worldwide have restricted certain biocidal compounds previously used in anti-fouling formulations, driving innovation toward environmentally benign alternatives. This regulatory landscape has accelerated research into nature-inspired solutions and "green chemistry" approaches that minimize hazardous substances while maintaining performance.
The economic case for environmentally sustainable coatings continues to strengthen as carbon pricing mechanisms expand globally. Organizations implementing advanced anti-fouling coatings can potentially qualify for carbon credits or environmental certifications, creating additional value beyond operational savings. This alignment of environmental and economic incentives suggests sustainable coating technologies will likely dominate future market development.
Surface coatings designed for fouling prevention offer substantial environmental benefits. Advanced hydrophobic coatings can reduce cleaning frequency by up to 70%, dramatically decreasing chemical cleaner usage and associated wastewater treatment requirements. Furthermore, by maintaining optimal heat transfer efficiency, these coatings can reduce energy consumption by 15-30% compared to untreated surfaces, with corresponding reductions in greenhouse gas emissions.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies of various coating technologies reveal important sustainability considerations. While fluoropolymer coatings demonstrate excellent fouling resistance, their production involves perfluorinated compounds with high global warming potential. In contrast, sol-gel silica-based coatings and biomimetic surfaces inspired by natural anti-fouling mechanisms (such as lotus leaf structures) typically have lower environmental footprints during manufacturing.
The durability of anti-fouling coatings represents another critical sustainability factor. First-generation coatings often required replacement within 6-12 months, creating waste and resource consumption cycles. Modern ceramic-polymer hybrid coatings can maintain effectiveness for 3-5 years, significantly improving the sustainability profile of these solutions. Some manufacturers have implemented coating recovery and recycling programs, further reducing environmental impact.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly influence coating technology development. The EU's REACH regulations and similar initiatives worldwide have restricted certain biocidal compounds previously used in anti-fouling formulations, driving innovation toward environmentally benign alternatives. This regulatory landscape has accelerated research into nature-inspired solutions and "green chemistry" approaches that minimize hazardous substances while maintaining performance.
The economic case for environmentally sustainable coatings continues to strengthen as carbon pricing mechanisms expand globally. Organizations implementing advanced anti-fouling coatings can potentially qualify for carbon credits or environmental certifications, creating additional value beyond operational savings. This alignment of environmental and economic incentives suggests sustainable coating technologies will likely dominate future market development.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Anti-Fouling Technologies
The implementation of anti-fouling technologies for heat exchanger surfaces requires careful economic evaluation to justify investment decisions. When analyzing the cost-benefit ratio of these technologies, initial capital expenditure must be weighed against long-term operational savings. Typical installation costs for advanced anti-fouling coatings range from $150-300 per square meter of heat transfer surface, with specialized nano-coatings commanding premium prices up to $500 per square meter. These figures vary significantly based on coating type, application method, and exchanger geometry complexity.
Operational cost reductions represent the primary benefit stream, with energy efficiency improvements typically ranging from 15-30% depending on the process fluid and operating conditions. In high-fouling environments such as oil refineries or food processing plants, maintenance interval extensions from quarterly to annual cleaning cycles can reduce downtime costs by 60-75%. Labor savings for cleaning operations average $5,000-15,000 per maintenance event for medium-sized industrial exchangers.
Extended equipment lifespan provides additional economic value, with properly coated exchangers demonstrating 3-7 years of additional service life before major refurbishment or replacement. This translates to deferred capital expenditure of $50,000-250,000 depending on exchanger size and application.
Return on investment calculations indicate payback periods ranging from 8-24 months for most industrial applications. Chemical processing and petroleum refining industries typically experience the shortest payback periods (8-12 months) due to severe fouling conditions, while HVAC and food processing applications may require 18-24 months to reach break-even.
Environmental compliance benefits, though harder to quantify directly, include reduced chemical cleaning agent usage (30-50% reduction) and associated waste disposal costs. Carbon footprint reductions from improved energy efficiency contribute to corporate sustainability goals and may qualify for carbon credit programs in certain jurisdictions.
Sensitivity analysis reveals that anti-fouling technology economics are most influenced by process fluid fouling propensity, operating temperature, and flow velocity. Technologies demonstrating the highest ROI are typically hydrophobic polymer coatings for low-temperature applications and ceramic-metallic composites for high-temperature environments, with lifetime cost savings ratios of 1:4 and 1:6 respectively when compared to uncoated surfaces over a ten-year operational period.
Operational cost reductions represent the primary benefit stream, with energy efficiency improvements typically ranging from 15-30% depending on the process fluid and operating conditions. In high-fouling environments such as oil refineries or food processing plants, maintenance interval extensions from quarterly to annual cleaning cycles can reduce downtime costs by 60-75%. Labor savings for cleaning operations average $5,000-15,000 per maintenance event for medium-sized industrial exchangers.
Extended equipment lifespan provides additional economic value, with properly coated exchangers demonstrating 3-7 years of additional service life before major refurbishment or replacement. This translates to deferred capital expenditure of $50,000-250,000 depending on exchanger size and application.
Return on investment calculations indicate payback periods ranging from 8-24 months for most industrial applications. Chemical processing and petroleum refining industries typically experience the shortest payback periods (8-12 months) due to severe fouling conditions, while HVAC and food processing applications may require 18-24 months to reach break-even.
Environmental compliance benefits, though harder to quantify directly, include reduced chemical cleaning agent usage (30-50% reduction) and associated waste disposal costs. Carbon footprint reductions from improved energy efficiency contribute to corporate sustainability goals and may qualify for carbon credit programs in certain jurisdictions.
Sensitivity analysis reveals that anti-fouling technology economics are most influenced by process fluid fouling propensity, operating temperature, and flow velocity. Technologies demonstrating the highest ROI are typically hydrophobic polymer coatings for low-temperature applications and ceramic-metallic composites for high-temperature environments, with lifetime cost savings ratios of 1:4 and 1:6 respectively when compared to uncoated surfaces over a ten-year operational period.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!