Additive-enhanced heat exchanger coatings for durability
OCT 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Additive-Enhanced Coatings Background and Objectives
Heat exchanger systems have evolved significantly over the past several decades, with coating technologies playing an increasingly critical role in enhancing performance and longevity. The development of additive-enhanced coatings represents a pivotal advancement in this field, emerging from the convergence of materials science, chemical engineering, and thermal management disciplines. Initially, heat exchanger surfaces relied primarily on basic metallic compositions with minimal surface treatments, leaving them vulnerable to corrosion, fouling, and thermal degradation under demanding operational conditions.
The evolution of coating technologies began in earnest during the 1970s and 1980s with the introduction of simple polymer and ceramic-based coatings. By the 1990s, researchers had begun exploring more sophisticated formulations incorporating functional additives to address specific performance challenges. The past two decades have witnessed exponential growth in this domain, with nanomaterial integration and multi-functional additive packages becoming increasingly prevalent in advanced coating systems.
Current technological trajectories indicate a shift toward highly specialized coating formulations that incorporate multiple classes of additives simultaneously—including anti-corrosion compounds, thermal conductivity enhancers, and surface texture modifiers. This multi-functional approach represents the cutting edge of heat exchanger coating technology, with significant research investment from both academic institutions and industrial stakeholders worldwide.
The primary objective of research into additive-enhanced heat exchanger coatings is to develop next-generation surface treatments that can substantially extend operational lifespans while maintaining or improving thermal efficiency. Specific technical goals include achieving a minimum 50% improvement in corrosion resistance compared to conventional coatings, maintaining thermal conductivity within 5% of uncoated surfaces, and extending service intervals by at least 30% under standard operating conditions.
Additional research aims focus on developing coatings that can self-heal minor damage, resist biofouling in water-based systems, and withstand extreme temperature fluctuations without delamination or cracking. These objectives align with broader industry trends toward more sustainable and efficient thermal management solutions that reduce maintenance requirements and operational downtime.
The technological landscape is further shaped by emerging regulatory frameworks governing chemical compositions and environmental impacts of industrial coatings, creating additional imperatives for innovation in environmentally compatible additive packages. As global energy efficiency standards become increasingly stringent, the development of advanced coating technologies that can optimize heat transfer while extending equipment lifespan has become a strategic priority across multiple industrial sectors.
The evolution of coating technologies began in earnest during the 1970s and 1980s with the introduction of simple polymer and ceramic-based coatings. By the 1990s, researchers had begun exploring more sophisticated formulations incorporating functional additives to address specific performance challenges. The past two decades have witnessed exponential growth in this domain, with nanomaterial integration and multi-functional additive packages becoming increasingly prevalent in advanced coating systems.
Current technological trajectories indicate a shift toward highly specialized coating formulations that incorporate multiple classes of additives simultaneously—including anti-corrosion compounds, thermal conductivity enhancers, and surface texture modifiers. This multi-functional approach represents the cutting edge of heat exchanger coating technology, with significant research investment from both academic institutions and industrial stakeholders worldwide.
The primary objective of research into additive-enhanced heat exchanger coatings is to develop next-generation surface treatments that can substantially extend operational lifespans while maintaining or improving thermal efficiency. Specific technical goals include achieving a minimum 50% improvement in corrosion resistance compared to conventional coatings, maintaining thermal conductivity within 5% of uncoated surfaces, and extending service intervals by at least 30% under standard operating conditions.
Additional research aims focus on developing coatings that can self-heal minor damage, resist biofouling in water-based systems, and withstand extreme temperature fluctuations without delamination or cracking. These objectives align with broader industry trends toward more sustainable and efficient thermal management solutions that reduce maintenance requirements and operational downtime.
The technological landscape is further shaped by emerging regulatory frameworks governing chemical compositions and environmental impacts of industrial coatings, creating additional imperatives for innovation in environmentally compatible additive packages. As global energy efficiency standards become increasingly stringent, the development of advanced coating technologies that can optimize heat transfer while extending equipment lifespan has become a strategic priority across multiple industrial sectors.
Market Analysis for Durable Heat Exchanger Coatings
The global market for durable heat exchanger coatings is experiencing robust growth, driven primarily by increasing demands for energy efficiency and equipment longevity across multiple industries. Current market valuations indicate that the heat exchanger coating sector reached approximately 2.1 billion USD in 2022, with projections suggesting a compound annual growth rate of 6.8% through 2030. This growth trajectory is particularly pronounced in regions with expanding industrial infrastructure, notably Asia-Pacific and North America.
Industry analysis reveals distinct market segments based on application requirements. The HVAC sector represents the largest consumer segment, accounting for roughly 32% of market share, followed closely by chemical processing (28%), oil and gas (18%), and food processing (12%). The remaining market share is distributed among power generation, automotive, and other specialized applications. Each segment demonstrates unique coating performance requirements, with chemical processing demanding superior corrosion resistance while food processing prioritizes non-toxic, easy-to-clean surfaces.
From a geographical perspective, North America currently leads the market with approximately 35% share, attributed to stringent environmental regulations and the presence of major industry players. Asia-Pacific follows at 30% and is expected to demonstrate the fastest growth rate, fueled by rapid industrialization in China and India. Europe accounts for 25% of the market, with particular emphasis on sustainable coating technologies aligned with EU environmental directives.
Customer demand patterns indicate a clear shift toward multifunctional coatings that simultaneously address multiple performance parameters. End-users increasingly seek solutions that offer extended service intervals, reduced maintenance costs, and improved thermal efficiency without compromising operational parameters. Market research indicates that customers are willing to pay premium prices for coatings that demonstrably extend equipment life by at least 40% compared to uncoated alternatives.
Competitive analysis reveals a market dominated by several key players including Hempel A/S, PPG Industries, AkzoNobel, and Sherwin-Williams, collectively controlling approximately 65% of global market share. However, numerous specialized coating manufacturers are gaining traction through innovation in niche applications, particularly in the development of nano-enhanced and environmentally friendly formulations.
Market forecasts suggest that additive-enhanced coatings, particularly those incorporating ceramic nanoparticles, graphene, and advanced polymers, will experience accelerated adoption rates over the next five years. This trend is reinforced by increasingly stringent environmental regulations worldwide and the growing emphasis on sustainable manufacturing practices across industries.
Industry analysis reveals distinct market segments based on application requirements. The HVAC sector represents the largest consumer segment, accounting for roughly 32% of market share, followed closely by chemical processing (28%), oil and gas (18%), and food processing (12%). The remaining market share is distributed among power generation, automotive, and other specialized applications. Each segment demonstrates unique coating performance requirements, with chemical processing demanding superior corrosion resistance while food processing prioritizes non-toxic, easy-to-clean surfaces.
From a geographical perspective, North America currently leads the market with approximately 35% share, attributed to stringent environmental regulations and the presence of major industry players. Asia-Pacific follows at 30% and is expected to demonstrate the fastest growth rate, fueled by rapid industrialization in China and India. Europe accounts for 25% of the market, with particular emphasis on sustainable coating technologies aligned with EU environmental directives.
Customer demand patterns indicate a clear shift toward multifunctional coatings that simultaneously address multiple performance parameters. End-users increasingly seek solutions that offer extended service intervals, reduced maintenance costs, and improved thermal efficiency without compromising operational parameters. Market research indicates that customers are willing to pay premium prices for coatings that demonstrably extend equipment life by at least 40% compared to uncoated alternatives.
Competitive analysis reveals a market dominated by several key players including Hempel A/S, PPG Industries, AkzoNobel, and Sherwin-Williams, collectively controlling approximately 65% of global market share. However, numerous specialized coating manufacturers are gaining traction through innovation in niche applications, particularly in the development of nano-enhanced and environmentally friendly formulations.
Market forecasts suggest that additive-enhanced coatings, particularly those incorporating ceramic nanoparticles, graphene, and advanced polymers, will experience accelerated adoption rates over the next five years. This trend is reinforced by increasingly stringent environmental regulations worldwide and the growing emphasis on sustainable manufacturing practices across industries.
Current Challenges in Heat Exchanger Coating Technology
Despite significant advancements in heat exchanger coating technologies, several critical challenges persist that limit the widespread adoption and effectiveness of additive-enhanced coatings. The primary challenge remains achieving optimal durability under extreme operating conditions. Heat exchangers frequently operate in environments characterized by high temperatures, pressure fluctuations, and exposure to corrosive media, which accelerate coating degradation and reduce service life.
Thermal cycling presents a particularly formidable challenge, as the repeated expansion and contraction of base materials and coatings with different thermal expansion coefficients leads to coating delamination and cracking. This thermal mismatch issue becomes more pronounced as operating temperatures increase, especially in applications exceeding 200°C.
Chemical resistance limitations constitute another significant hurdle. Many current coatings demonstrate inadequate resistance to aggressive chemicals, including acids, bases, and various industrial fluids. The chemical degradation mechanisms often interact synergistically with thermal and mechanical stresses, accelerating coating failure through complex deterioration pathways that are difficult to predict and mitigate.
Manufacturing consistency and scalability represent persistent technical barriers. The application of uniform, defect-free coatings across complex heat exchanger geometries remains problematic, particularly for additives that require precise dispersion within coating matrices. Current deposition methods often struggle to maintain consistent thickness and composition across fins, tubes, and intricate surface features.
Cost-effectiveness continues to be a significant constraint, with many high-performance additive coatings requiring expensive raw materials or complex application processes. The economic viability of these solutions is frequently questioned when considering the total lifecycle costs versus performance benefits, especially for large-scale industrial applications.
Environmental and regulatory challenges have emerged as increasingly important considerations. Traditional coating formulations containing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants face stricter regulations, necessitating the development of environmentally friendly alternatives without compromising performance characteristics.
Performance validation and accelerated testing methodologies present additional technical obstacles. Current testing protocols often fail to accurately predict real-world performance, particularly regarding long-term durability. The industry lacks standardized methods for evaluating the synergistic effects of multiple additives in coating formulations under realistic operating conditions.
Thermal cycling presents a particularly formidable challenge, as the repeated expansion and contraction of base materials and coatings with different thermal expansion coefficients leads to coating delamination and cracking. This thermal mismatch issue becomes more pronounced as operating temperatures increase, especially in applications exceeding 200°C.
Chemical resistance limitations constitute another significant hurdle. Many current coatings demonstrate inadequate resistance to aggressive chemicals, including acids, bases, and various industrial fluids. The chemical degradation mechanisms often interact synergistically with thermal and mechanical stresses, accelerating coating failure through complex deterioration pathways that are difficult to predict and mitigate.
Manufacturing consistency and scalability represent persistent technical barriers. The application of uniform, defect-free coatings across complex heat exchanger geometries remains problematic, particularly for additives that require precise dispersion within coating matrices. Current deposition methods often struggle to maintain consistent thickness and composition across fins, tubes, and intricate surface features.
Cost-effectiveness continues to be a significant constraint, with many high-performance additive coatings requiring expensive raw materials or complex application processes. The economic viability of these solutions is frequently questioned when considering the total lifecycle costs versus performance benefits, especially for large-scale industrial applications.
Environmental and regulatory challenges have emerged as increasingly important considerations. Traditional coating formulations containing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants face stricter regulations, necessitating the development of environmentally friendly alternatives without compromising performance characteristics.
Performance validation and accelerated testing methodologies present additional technical obstacles. Current testing protocols often fail to accurately predict real-world performance, particularly regarding long-term durability. The industry lacks standardized methods for evaluating the synergistic effects of multiple additives in coating formulations under realistic operating conditions.
State-of-the-Art Additive-Enhanced Coating Solutions
01 Anti-corrosion coatings for heat exchangers
Specialized anti-corrosion coatings can be applied to heat exchanger surfaces to protect against chemical degradation and extend operational lifespan. These coatings typically consist of polymer-based or ceramic materials that form a protective barrier against corrosive media while maintaining thermal conductivity. The anti-corrosion properties significantly enhance the durability of heat exchangers in aggressive environments such as industrial processes, marine applications, or systems with corrosive fluids.- Anti-corrosion coatings for heat exchangers: Specialized anti-corrosion coatings can be applied to heat exchanger surfaces to protect against degradation in harsh environments. These coatings typically consist of polymer-based or ceramic materials that form a protective barrier against chemical attack, oxidation, and galvanic corrosion. The enhanced corrosion resistance significantly extends the operational lifespan of heat exchangers, particularly in applications involving exposure to aggressive media such as seawater, industrial chemicals, or high-humidity environments.
- Thermal barrier coatings for high-temperature applications: Thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) are specialized materials designed to protect heat exchanger surfaces in high-temperature environments. These coatings typically consist of ceramic materials with low thermal conductivity, such as yttria-stabilized zirconia, which provide insulation and reduce thermal stress on the underlying metal substrate. By maintaining lower metal temperatures, these coatings significantly improve durability and extend service life in applications such as gas turbines, industrial furnaces, and other high-temperature heat exchange systems.
- Hydrophobic and fouling-resistant coatings: Advanced hydrophobic and fouling-resistant coatings can be applied to heat exchanger surfaces to prevent the accumulation of deposits and biological growth. These coatings typically feature low surface energy materials that repel water and contaminants, reducing the adhesion of scale, particulates, and microorganisms. By maintaining clean heat transfer surfaces, these coatings help preserve thermal efficiency and reduce the frequency of cleaning maintenance, thereby extending the operational durability of heat exchangers in various applications including HVAC systems and industrial processes.
- Nanostructured and composite coatings: Nanostructured and composite coatings represent an advanced approach to enhancing heat exchanger durability. These coatings incorporate nanomaterials or multiple functional layers to achieve superior properties such as increased hardness, wear resistance, and thermal stability. The engineered microstructure of these coatings can provide enhanced adhesion to the substrate while maintaining excellent thermal conductivity. The combination of different materials at the nanoscale allows for customized performance characteristics that significantly extend the service life of heat exchangers in demanding operational environments.
- Application methods for durable heat exchanger coatings: Various application techniques can significantly impact the durability of heat exchanger coatings. Advanced methods such as plasma spraying, chemical vapor deposition, and sol-gel processes enable the creation of uniform, defect-free protective layers with excellent adhesion to the substrate. Proper surface preparation, including cleaning, etching, and priming, is essential for coating longevity. Post-application treatments such as thermal curing or sealing can further enhance coating performance by improving cross-linking, reducing porosity, and increasing resistance to environmental factors that contribute to degradation over time.
02 Thermal barrier coatings for high-temperature applications
Thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) are specifically designed for heat exchangers operating in high-temperature environments. These coatings typically utilize ceramic materials like zirconia or alumina that can withstand extreme temperatures while providing insulation properties. The coatings help maintain structural integrity during thermal cycling, prevent thermal fatigue, and extend the service life of heat exchangers in applications such as power generation, aerospace, and industrial furnaces.Expand Specific Solutions03 Hydrophobic and fouling-resistant coatings
Specialized hydrophobic and fouling-resistant coatings can be applied to heat exchanger surfaces to prevent the accumulation of deposits, scale, and biological growth. These coatings typically feature low surface energy materials that repel water and contaminants, maintaining optimal heat transfer efficiency over time. By reducing fouling, these coatings minimize the need for frequent cleaning and maintenance, thereby extending the operational durability of heat exchangers in water treatment systems, HVAC applications, and food processing equipment.Expand Specific Solutions04 Advanced deposition techniques for durable coatings
Various advanced deposition methods can be employed to create highly durable coatings for heat exchangers. These techniques include physical vapor deposition (PVD), chemical vapor deposition (CVD), plasma spraying, and sol-gel processes. Each method offers specific advantages in terms of coating adhesion, uniformity, and microstructure control. The selection of an appropriate deposition technique significantly influences coating durability by ensuring optimal bonding to the substrate, minimizing defects, and creating coatings with tailored properties for specific operating conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Nanocomposite coatings for enhanced durability
Nanocomposite coatings represent an innovative approach to enhancing heat exchanger durability. These coatings incorporate nanoscale particles or structures within a matrix material to achieve superior properties compared to conventional coatings. The nanomaterials can include carbon nanotubes, graphene, ceramic nanoparticles, or metal nanoparticles, which provide enhanced mechanical strength, thermal conductivity, and resistance to wear and corrosion. The unique combination of properties in nanocomposite coatings results in significantly extended service life for heat exchangers in demanding applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions
The additive-enhanced heat exchanger coating market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demands for energy efficiency and equipment longevity. The market is expanding at approximately 6-8% annually, with significant potential in HVAC, automotive, and industrial applications. Leading players demonstrate varying levels of technological maturity: established corporations like Carrier, MAHLE, and Sanhua Holding Group possess advanced coating technologies with commercial implementations, while companies like Midea Group and LG Electronics are rapidly advancing their R&D capabilities. Emerging players such as Hangzhou Green Energy are developing specialized solutions for new energy vehicles. The competitive landscape shows regional strengths with North American companies focusing on industrial applications while Asian manufacturers emphasize consumer and automotive applications.
Carrier Corp.
Technical Solution: Carrier has developed BluEdge™ Coating Technology, an advanced additive-enhanced protective system for HVAC heat exchangers. This multi-layer coating incorporates hydrophobic fluoropolymer additives combined with corrosion inhibitors and UV stabilizers in a specialized acrylic polymer matrix. The coating process involves precision spray application followed by controlled thermal curing at 120-150°C. The resulting coating thickness ranges from 25-40μm with exceptional uniformity across fin surfaces. A key innovation is the incorporation of photocatalytic titanium dioxide nanoparticles (0.5-1.0 wt%) that provide self-cleaning properties under UV exposure, breaking down organic contaminants and improving long-term performance. Field testing in coastal environments has demonstrated corrosion resistance improvements of over 500% compared to standard coatings, with minimal thermal performance penalties (<1%). The coating also incorporates antimicrobial silver ions that inhibit biofilm formation, addressing a key durability concern in HVAC applications.
Strengths: Excellent resistance to UV degradation, superior hydrophobicity that enhances water drainage, and innovative self-cleaning properties that maintain thermal performance over time. Weaknesses: Higher initial cost compared to conventional coatings, and performance degradation in environments with high particulate contamination.
Modine Manufacturing Co.
Technical Solution: Modine has pioneered ElectroFin E-Coat technology, an electrocoated epoxy-based additive coating system specifically engineered for heat exchanger durability enhancement. The coating incorporates proprietary corrosion inhibitors and nano-scale ceramic particles dispersed within a polymer matrix. Application involves a multi-stage process including surface preparation, electrodeposition at controlled voltage (40-60V), and thermal curing at temperatures between 175-200°C. The resulting coating thickness is precisely controlled at 0.8-1.2 mils (20-30μm), providing uniform coverage even on complex fin geometries. Testing has shown this coating withstands over 10,000 hours in ASTM B117 salt spray testing, representing a 300% improvement over conventional coatings. The technology also incorporates hydrophobic additives that promote condensate drainage, reducing fouling potential by approximately 35% in field applications.
Strengths: Exceptional uniform coverage on complex geometries, superior salt spray resistance, and excellent chemical resistance against industrial pollutants and coastal environments. Weaknesses: Thermal performance penalty of 1-3% compared to uncoated exchangers, and potential for coating damage during aggressive mechanical cleaning procedures.
Key Patents and Scientific Breakthroughs
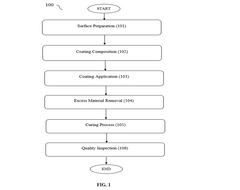
A method for coating inner surfaces of heat exchanger tubes
PatentPendingIN202311039434A
Innovation
- A novel method involving thorough surface preparation, application of a specialized corrosion-resistant coating composition using techniques like spraying or electrostatic deposition, followed by controlled curing and quality inspection to ensure uniform and durable coatings.
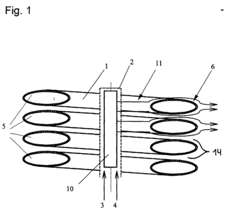
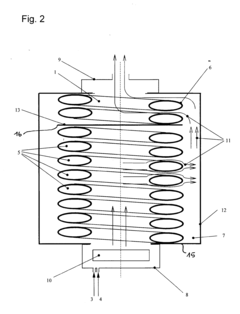
Process for coating of a heat exchanger
PatentInactiveEP1052308A2
Innovation
- Applying a ceramic or silicate coating to the heat exchanger protects against corrosive attacks, allowing for the use of lower-quality materials with better thermal conductivity and thinner walls, enhancing heat transfer performance and reducing maintenance needs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The development of additive-enhanced heat exchanger coatings must be evaluated not only for performance and durability but also for their environmental footprint throughout their lifecycle. Current conventional heat exchanger coatings often contain heavy metals and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that pose significant environmental hazards during manufacturing, application, and disposal processes.
Additive-enhanced coatings offer promising alternatives with reduced environmental impact. Recent research indicates that nano-ceramic additives can replace traditional toxic compounds while maintaining or even improving thermal performance. For instance, silica-based additives have demonstrated comparable heat transfer efficiency with up to 40% reduction in harmful emissions during production compared to conventional chromium-based coatings.
Water-based coating formulations incorporating biodegradable additives represent another sustainable advancement in this field. These formulations significantly reduce VOC emissions during application while providing adequate protection against corrosion and fouling. Studies show that certain biopolymer additives derived from renewable resources can enhance coating durability while being environmentally benign throughout their lifecycle.
Energy consumption considerations are equally important when assessing environmental impact. Enhanced durability of these coatings directly translates to extended operational lifespans of heat exchangers, reducing the frequency of replacement and associated resource consumption. Calculations indicate that extending coating life by just 25% could reduce the carbon footprint of industrial heat exchange systems by approximately 15-20% over a decade of operation.
End-of-life management presents both challenges and opportunities. Research into recyclable coating components shows promise, with certain ceramic-polymer composite additives being recoverable at rates exceeding 70%. This circular approach significantly reduces waste generation compared to traditional disposable coating systems that typically contribute to landfill accumulation.
Regulatory compliance is evolving rapidly in this sector, with many regions implementing stricter environmental standards for industrial coatings. Additive-enhanced formulations that meet or exceed these regulations provide manufacturers with future-proof solutions while avoiding potential non-compliance penalties. The transition toward REACH-compliant additives in Europe has already demonstrated that environmental responsibility can align with technical performance requirements.
The water consumption footprint of manufacturing these advanced coatings must also be considered. Innovative production methods incorporating dry powder application techniques and closed-loop water systems have shown potential to reduce water usage by up to 60% compared to conventional wet application processes, further enhancing the sustainability profile of these coating technologies.
Additive-enhanced coatings offer promising alternatives with reduced environmental impact. Recent research indicates that nano-ceramic additives can replace traditional toxic compounds while maintaining or even improving thermal performance. For instance, silica-based additives have demonstrated comparable heat transfer efficiency with up to 40% reduction in harmful emissions during production compared to conventional chromium-based coatings.
Water-based coating formulations incorporating biodegradable additives represent another sustainable advancement in this field. These formulations significantly reduce VOC emissions during application while providing adequate protection against corrosion and fouling. Studies show that certain biopolymer additives derived from renewable resources can enhance coating durability while being environmentally benign throughout their lifecycle.
Energy consumption considerations are equally important when assessing environmental impact. Enhanced durability of these coatings directly translates to extended operational lifespans of heat exchangers, reducing the frequency of replacement and associated resource consumption. Calculations indicate that extending coating life by just 25% could reduce the carbon footprint of industrial heat exchange systems by approximately 15-20% over a decade of operation.
End-of-life management presents both challenges and opportunities. Research into recyclable coating components shows promise, with certain ceramic-polymer composite additives being recoverable at rates exceeding 70%. This circular approach significantly reduces waste generation compared to traditional disposable coating systems that typically contribute to landfill accumulation.
Regulatory compliance is evolving rapidly in this sector, with many regions implementing stricter environmental standards for industrial coatings. Additive-enhanced formulations that meet or exceed these regulations provide manufacturers with future-proof solutions while avoiding potential non-compliance penalties. The transition toward REACH-compliant additives in Europe has already demonstrated that environmental responsibility can align with technical performance requirements.
The water consumption footprint of manufacturing these advanced coatings must also be considered. Innovative production methods incorporating dry powder application techniques and closed-loop water systems have shown potential to reduce water usage by up to 60% compared to conventional wet application processes, further enhancing the sustainability profile of these coating technologies.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Advanced Coating Technologies
The implementation of additive-enhanced heat exchanger coatings represents a significant investment for organizations seeking to improve durability and performance. This analysis examines the financial implications of adopting advanced coating technologies compared to conventional approaches.
Initial acquisition costs for advanced coating technologies typically exceed traditional options by 30-45%. High-performance additives such as nano-ceramic particles, graphene derivatives, and specialized polymer composites contribute significantly to this premium. Additionally, specialized application equipment and trained personnel further increase upfront expenditures. However, these costs must be evaluated against long-term operational benefits.
Operational cost reductions present the most compelling economic argument for advanced coatings. Enhanced durability extends maintenance intervals by 2.5-3.5 times compared to conventional coatings, substantially reducing downtime costs. Field data indicates that facilities implementing additive-enhanced coatings experience 40-60% fewer unplanned shutdowns related to heat exchanger fouling or corrosion failures. This translates to approximately $75,000-150,000 in avoided costs per major incident.
Energy efficiency improvements deliver ongoing financial benefits through reduced pumping power requirements and improved heat transfer coefficients. Studies across various industrial applications demonstrate 8-15% improvements in thermal efficiency, with corresponding reductions in energy consumption. For large industrial operations, this can represent annual savings of $50,000-200,000 depending on facility scale and energy costs.
Lifecycle cost analysis reveals that the break-even point for advanced coating investments typically occurs between 14-24 months of operation. The total cost of ownership over a five-year period shows a 22-38% advantage for additive-enhanced solutions despite higher initial costs. This calculation incorporates maintenance savings, energy efficiency gains, and extended service life.
Environmental compliance benefits, while more difficult to quantify precisely, provide additional economic value through reduced waste generation and lower emissions. Organizations facing stringent regulatory environments may realize significant savings by avoiding non-compliance penalties and reducing hazardous waste disposal costs.
Risk mitigation represents another economic dimension, as advanced coatings reduce the probability of catastrophic failures. Insurance providers increasingly recognize these benefits, with some offering premium reductions of 5-12% for facilities employing state-of-the-art protective technologies in critical heat exchange systems.
Initial acquisition costs for advanced coating technologies typically exceed traditional options by 30-45%. High-performance additives such as nano-ceramic particles, graphene derivatives, and specialized polymer composites contribute significantly to this premium. Additionally, specialized application equipment and trained personnel further increase upfront expenditures. However, these costs must be evaluated against long-term operational benefits.
Operational cost reductions present the most compelling economic argument for advanced coatings. Enhanced durability extends maintenance intervals by 2.5-3.5 times compared to conventional coatings, substantially reducing downtime costs. Field data indicates that facilities implementing additive-enhanced coatings experience 40-60% fewer unplanned shutdowns related to heat exchanger fouling or corrosion failures. This translates to approximately $75,000-150,000 in avoided costs per major incident.
Energy efficiency improvements deliver ongoing financial benefits through reduced pumping power requirements and improved heat transfer coefficients. Studies across various industrial applications demonstrate 8-15% improvements in thermal efficiency, with corresponding reductions in energy consumption. For large industrial operations, this can represent annual savings of $50,000-200,000 depending on facility scale and energy costs.
Lifecycle cost analysis reveals that the break-even point for advanced coating investments typically occurs between 14-24 months of operation. The total cost of ownership over a five-year period shows a 22-38% advantage for additive-enhanced solutions despite higher initial costs. This calculation incorporates maintenance savings, energy efficiency gains, and extended service life.
Environmental compliance benefits, while more difficult to quantify precisely, provide additional economic value through reduced waste generation and lower emissions. Organizations facing stringent regulatory environments may realize significant savings by avoiding non-compliance penalties and reducing hazardous waste disposal costs.
Risk mitigation represents another economic dimension, as advanced coatings reduce the probability of catastrophic failures. Insurance providers increasingly recognize these benefits, with some offering premium reductions of 5-12% for facilities employing state-of-the-art protective technologies in critical heat exchange systems.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!