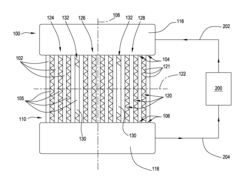
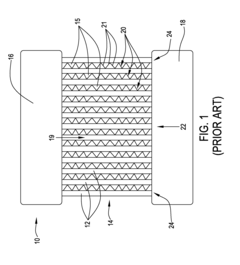
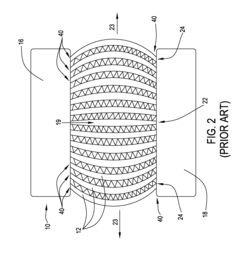
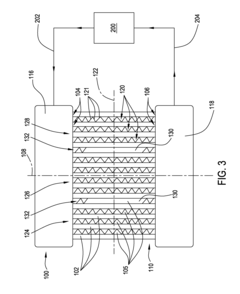
Thermal stress analysis in heat exchanger tubes
OCT 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Heat Exchanger Thermal Stress Background and Objectives
Thermal stress analysis in heat exchangers has evolved significantly over the past decades, driven by increasing demands for efficiency, reliability, and safety in industrial applications. Heat exchangers, as critical components in various industries including power generation, chemical processing, and HVAC systems, are subject to complex thermal gradients that induce mechanical stresses in their tubular components. The historical development of this field traces back to the mid-20th century when rudimentary analytical methods were first applied to understand thermal expansion effects.
The evolution of computational methods, particularly finite element analysis (FEA) in the 1970s and 1980s, revolutionized the approach to thermal stress analysis. This technological progression enabled engineers to model increasingly complex geometries and operating conditions, moving beyond simplified analytical solutions to more realistic representations of heat exchanger behavior under thermal loading.
Current technological trends in this domain include the integration of multi-physics simulation platforms that simultaneously account for fluid dynamics, heat transfer, and structural mechanics. Machine learning algorithms are increasingly being employed to predict failure patterns and optimize design parameters, representing a significant shift toward predictive maintenance strategies and intelligent design methodologies.
The primary objective of thermal stress analysis in heat exchanger tubes is to ensure structural integrity throughout the operational lifecycle while maximizing thermal efficiency. This involves accurately predicting stress distributions under various operating conditions, identifying potential failure modes such as thermal fatigue, creep, and stress corrosion cracking, and developing mitigation strategies to extend service life.
Secondary objectives include optimizing material selection to balance thermal conductivity with mechanical strength, minimizing thermal expansion mismatches between different components, and developing design guidelines that account for transient thermal conditions such as startup, shutdown, and load fluctuations. These objectives are particularly critical in high-temperature applications where material properties exhibit significant temperature dependence.
The technological goals extend to developing more accurate constitutive models that capture the complex behavior of materials under combined thermal and mechanical loading, especially for newer alloys and composite materials being introduced to enhance performance. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on developing real-time monitoring systems that can detect early signs of thermal stress-induced damage before catastrophic failure occurs.
As industrial systems continue to push operational boundaries for greater efficiency and reduced environmental impact, the importance of sophisticated thermal stress analysis techniques becomes increasingly paramount, driving continuous innovation in this specialized field of engineering.
The evolution of computational methods, particularly finite element analysis (FEA) in the 1970s and 1980s, revolutionized the approach to thermal stress analysis. This technological progression enabled engineers to model increasingly complex geometries and operating conditions, moving beyond simplified analytical solutions to more realistic representations of heat exchanger behavior under thermal loading.
Current technological trends in this domain include the integration of multi-physics simulation platforms that simultaneously account for fluid dynamics, heat transfer, and structural mechanics. Machine learning algorithms are increasingly being employed to predict failure patterns and optimize design parameters, representing a significant shift toward predictive maintenance strategies and intelligent design methodologies.
The primary objective of thermal stress analysis in heat exchanger tubes is to ensure structural integrity throughout the operational lifecycle while maximizing thermal efficiency. This involves accurately predicting stress distributions under various operating conditions, identifying potential failure modes such as thermal fatigue, creep, and stress corrosion cracking, and developing mitigation strategies to extend service life.
Secondary objectives include optimizing material selection to balance thermal conductivity with mechanical strength, minimizing thermal expansion mismatches between different components, and developing design guidelines that account for transient thermal conditions such as startup, shutdown, and load fluctuations. These objectives are particularly critical in high-temperature applications where material properties exhibit significant temperature dependence.
The technological goals extend to developing more accurate constitutive models that capture the complex behavior of materials under combined thermal and mechanical loading, especially for newer alloys and composite materials being introduced to enhance performance. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on developing real-time monitoring systems that can detect early signs of thermal stress-induced damage before catastrophic failure occurs.
As industrial systems continue to push operational boundaries for greater efficiency and reduced environmental impact, the importance of sophisticated thermal stress analysis techniques becomes increasingly paramount, driving continuous innovation in this specialized field of engineering.
Market Demand for Advanced Heat Exchanger Solutions
The global market for advanced heat exchanger solutions is experiencing robust growth driven by increasing demands across multiple industrial sectors. Energy efficiency requirements and stringent environmental regulations are compelling industries to adopt more sophisticated heat transfer technologies that can withstand thermal stress while maintaining operational efficiency. The oil and gas sector remains a primary consumer, with refineries and processing plants requiring heat exchangers capable of handling extreme temperature fluctuations and corrosive environments.
Power generation facilities represent another significant market segment, particularly as the transition to renewable energy sources accelerates. These applications demand heat exchangers with enhanced thermal stress management capabilities to accommodate the intermittent nature of renewable energy production. The chemical processing industry similarly requires advanced solutions that can maintain structural integrity under varying thermal loads while handling aggressive chemical compounds.
Market research indicates that the HVAC industry is rapidly adopting next-generation heat exchangers to meet escalating energy efficiency standards in commercial and residential buildings. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions implementing strict building energy codes, creating substantial demand for heat exchangers with superior thermal stress resistance and longer operational lifespans.
The food and beverage sector presents a growing market opportunity, with processing facilities requiring heat exchangers that can withstand frequent thermal cycling during cleaning and sterilization procedures. These applications demand materials and designs specifically engineered to minimize thermal fatigue and stress-induced failures.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing market for advanced heat exchanger technologies, driven by rapid industrialization and infrastructure development in China and India. North America and Europe maintain significant market shares, primarily fueled by replacement demand and regulatory compliance requirements.
End-users across industries are increasingly prioritizing total cost of ownership over initial acquisition costs, creating market demand for heat exchangers with enhanced thermal stress analysis capabilities that can predict and prevent failures. This shift has accelerated interest in smart heat exchangers equipped with monitoring systems that provide real-time thermal stress data and predictive maintenance capabilities.
The market is also witnessing growing demand for customized solutions tailored to specific operational parameters rather than standardized products. This trend reflects the increasing complexity of industrial processes and the recognition that optimized thermal stress management can significantly extend equipment lifespan and reduce maintenance costs.
Power generation facilities represent another significant market segment, particularly as the transition to renewable energy sources accelerates. These applications demand heat exchangers with enhanced thermal stress management capabilities to accommodate the intermittent nature of renewable energy production. The chemical processing industry similarly requires advanced solutions that can maintain structural integrity under varying thermal loads while handling aggressive chemical compounds.
Market research indicates that the HVAC industry is rapidly adopting next-generation heat exchangers to meet escalating energy efficiency standards in commercial and residential buildings. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions implementing strict building energy codes, creating substantial demand for heat exchangers with superior thermal stress resistance and longer operational lifespans.
The food and beverage sector presents a growing market opportunity, with processing facilities requiring heat exchangers that can withstand frequent thermal cycling during cleaning and sterilization procedures. These applications demand materials and designs specifically engineered to minimize thermal fatigue and stress-induced failures.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing market for advanced heat exchanger technologies, driven by rapid industrialization and infrastructure development in China and India. North America and Europe maintain significant market shares, primarily fueled by replacement demand and regulatory compliance requirements.
End-users across industries are increasingly prioritizing total cost of ownership over initial acquisition costs, creating market demand for heat exchangers with enhanced thermal stress analysis capabilities that can predict and prevent failures. This shift has accelerated interest in smart heat exchangers equipped with monitoring systems that provide real-time thermal stress data and predictive maintenance capabilities.
The market is also witnessing growing demand for customized solutions tailored to specific operational parameters rather than standardized products. This trend reflects the increasing complexity of industrial processes and the recognition that optimized thermal stress management can significantly extend equipment lifespan and reduce maintenance costs.
Current Thermal Stress Analysis Techniques and Challenges
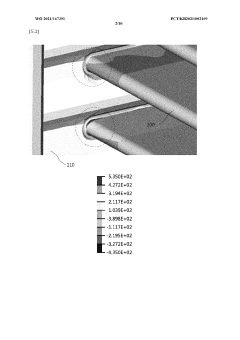
Thermal stress analysis in heat exchanger tubes has evolved significantly over the past decades, employing various methodologies ranging from analytical approaches to advanced computational techniques. Currently, the most widely adopted method is Finite Element Analysis (FEA), which allows engineers to simulate thermal gradients and resulting stresses with high precision. FEA software packages such as ANSYS, ABAQUS, and COMSOL have become industry standards, offering specialized modules for thermal-structural coupling analysis that can account for complex geometries and material behaviors.
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) coupled with heat transfer models represents another powerful technique, particularly valuable for analyzing fluid-structure interactions in heat exchangers. This approach enables simultaneous evaluation of flow patterns, temperature distributions, and resulting thermal stresses, providing comprehensive insights into system behavior under various operating conditions.
Despite these advancements, several significant challenges persist in thermal stress analysis of heat exchanger tubes. Material behavior characterization at elevated temperatures remains problematic, as creep, thermal fatigue, and material property degradation over time introduce considerable complexity. Current models often struggle to accurately represent these time-dependent phenomena, particularly in applications involving extreme temperature cycling.
Multiphysics coupling presents another major challenge, as the interaction between thermal, mechanical, and fluid dynamics requires sophisticated modeling approaches. The computational resources needed for high-fidelity simulations can be prohibitive, especially when analyzing large heat exchanger systems or when performing transient analyses over extended operational periods.
Boundary condition uncertainty significantly impacts analysis accuracy, with practical difficulties in precisely defining thermal loads, contact conditions, and environmental factors. This uncertainty propagates through the analysis chain, potentially leading to substantial deviations between predicted and actual stress distributions.
Non-destructive evaluation techniques for validation purposes have limitations in accessing internal structures of heat exchangers during operation. This creates a gap between theoretical models and practical verification, complicating the validation process for analytical predictions.
Emerging techniques such as reduced-order modeling and machine learning approaches show promise in addressing computational efficiency challenges, but remain in developmental stages for thermal stress applications in heat exchangers. These methods aim to maintain acceptable accuracy while dramatically reducing computational requirements, potentially enabling more comprehensive parametric studies and optimization processes.
Industry standards and codes (ASME, API, etc.) provide guidelines for thermal stress analysis but often lag behind the latest analytical capabilities, creating a disconnect between cutting-edge research and practical implementation in industrial settings.
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) coupled with heat transfer models represents another powerful technique, particularly valuable for analyzing fluid-structure interactions in heat exchangers. This approach enables simultaneous evaluation of flow patterns, temperature distributions, and resulting thermal stresses, providing comprehensive insights into system behavior under various operating conditions.
Despite these advancements, several significant challenges persist in thermal stress analysis of heat exchanger tubes. Material behavior characterization at elevated temperatures remains problematic, as creep, thermal fatigue, and material property degradation over time introduce considerable complexity. Current models often struggle to accurately represent these time-dependent phenomena, particularly in applications involving extreme temperature cycling.
Multiphysics coupling presents another major challenge, as the interaction between thermal, mechanical, and fluid dynamics requires sophisticated modeling approaches. The computational resources needed for high-fidelity simulations can be prohibitive, especially when analyzing large heat exchanger systems or when performing transient analyses over extended operational periods.
Boundary condition uncertainty significantly impacts analysis accuracy, with practical difficulties in precisely defining thermal loads, contact conditions, and environmental factors. This uncertainty propagates through the analysis chain, potentially leading to substantial deviations between predicted and actual stress distributions.
Non-destructive evaluation techniques for validation purposes have limitations in accessing internal structures of heat exchangers during operation. This creates a gap between theoretical models and practical verification, complicating the validation process for analytical predictions.
Emerging techniques such as reduced-order modeling and machine learning approaches show promise in addressing computational efficiency challenges, but remain in developmental stages for thermal stress applications in heat exchangers. These methods aim to maintain acceptable accuracy while dramatically reducing computational requirements, potentially enabling more comprehensive parametric studies and optimization processes.
Industry standards and codes (ASME, API, etc.) provide guidelines for thermal stress analysis but often lag behind the latest analytical capabilities, creating a disconnect between cutting-edge research and practical implementation in industrial settings.
Current Methodologies for Tube Thermal Stress Mitigation
01 Design features to mitigate thermal stress in heat exchanger tubes
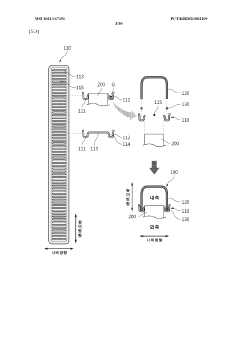
Various design features can be incorporated into heat exchanger tubes to mitigate thermal stress. These include using flexible tube configurations, bellows or expansion joints, and optimized tube geometries that allow for thermal expansion and contraction. Such designs help distribute thermal loads more evenly and prevent localized stress concentrations that could lead to tube failure during temperature fluctuations.- Design features to mitigate thermal stress in heat exchanger tubes: Various design features can be incorporated into heat exchanger tubes to mitigate thermal stress. These include using flexible tube configurations, bellows or expansion joints, and specialized tube geometries that accommodate thermal expansion and contraction. These design elements help distribute stress more evenly throughout the tube structure, preventing localized stress concentrations that could lead to failure during thermal cycling.
- Material selection for thermal stress resistance: The choice of materials plays a crucial role in managing thermal stress in heat exchanger tubes. Materials with favorable thermal expansion coefficients, high thermal conductivity, and good mechanical properties at elevated temperatures are preferred. Specialized alloys, composite materials, and coatings can be used to enhance resistance to thermal fatigue, creep, and corrosion under thermal cycling conditions.
- Thermal stress analysis and monitoring techniques: Advanced analytical methods and monitoring systems are employed to evaluate and track thermal stress in heat exchanger tubes. These include finite element analysis, computational fluid dynamics, thermal imaging, and real-time monitoring systems. These techniques help identify potential stress hotspots, predict failure modes, and optimize operating conditions to extend the service life of heat exchanger components.
- Tube-to-tubesheet connection methods for thermal stress management: The junction between tubes and tubesheets is particularly vulnerable to thermal stress. Various connection methods have been developed to address this issue, including specialized welding techniques, mechanical expansion, hydraulic expansion, and hybrid joining methods. These connections are designed to maintain seal integrity while accommodating differential thermal expansion between tubes and the tubesheet.
- Operational strategies to control thermal stress: Operational approaches can significantly reduce thermal stress in heat exchanger tubes. These include controlled startup and shutdown procedures, temperature ramping protocols, flow distribution optimization, and strategic baffle placement. By managing temperature gradients and flow conditions, these strategies minimize thermal shock and uneven expansion that contribute to stress development in tube materials.
02 Material selection for thermal stress resistance
The choice of materials plays a crucial role in managing thermal stress in heat exchanger tubes. Materials with favorable thermal expansion coefficients, high thermal conductivity, and good mechanical strength at elevated temperatures are preferred. Advanced alloys, composite materials, and ceramics can be used to enhance thermal stress resistance and extend the operational life of heat exchanger tubes under varying temperature conditions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Thermal stress analysis and monitoring systems
Advanced analytical methods and monitoring systems are employed to evaluate and track thermal stress in heat exchanger tubes. These include finite element analysis, computational fluid dynamics, thermal imaging, and real-time monitoring sensors. Such systems help predict potential failure points, optimize operating conditions, and implement preventive maintenance strategies to avoid thermal stress-related failures.Expand Specific Solutions04 Tube connection and support structures
The method of connecting tubes to tube sheets and the design of support structures significantly impact thermal stress distribution. Floating tube sheets, sliding supports, and specialized tube-to-tubesheet joints allow for differential thermal expansion between components. Proper support spacing and configuration help minimize stress concentrations and prevent tube sagging or vibration that could exacerbate thermal stress issues.Expand Specific Solutions05 Operational strategies for thermal stress management
Operational practices can be implemented to manage thermal stress in heat exchanger tubes. These include controlled startup and shutdown procedures, temperature ramping protocols, flow distribution optimization, and fouling prevention measures. Maintaining uniform temperature distributions and avoiding rapid thermal cycling helps extend tube life by minimizing thermal fatigue and associated stress damage.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Heat Exchanger Technology
Thermal stress analysis in heat exchanger tubes is currently in a growth phase, with the global market expected to reach $24.3 billion by 2025, expanding at a CAGR of 6.2%. The competitive landscape features established industrial players like Valeo Thermal Systems, DENSO Corp, and Kelvion Machine Cooling Systems focusing on automotive and industrial applications, while academic institutions such as Xi'an Jiaotong University and Beihang University drive fundamental research. Technology maturity varies across sectors, with automotive applications being most advanced. Companies like Modine Manufacturing and Wieland-Werke lead in material innovation, while Holtec International specializes in nuclear applications. Recent advancements in computational modeling and micro-channel heat exchangers from Hangzhou Sanhua are accelerating industry development.
DENSO Corp.
Technical Solution: DENSO has pioneered an integrated thermal stress analysis platform specifically for automotive heat exchangers that combines experimental validation with numerical modeling. Their approach utilizes a multi-scale modeling technique that bridges micro-scale material behavior with macro-scale component performance. DENSO's system employs infrared thermography coupled with digital image correlation to validate computational models in real-time. Their proprietary algorithms incorporate phase-change phenomena in two-phase heat exchangers and account for material degradation over time. DENSO has implemented machine learning techniques to optimize their simulation parameters based on accumulated test data, enabling more accurate predictions of thermal fatigue failure in complex geometries like microchannel tubes and brazed joints.
Strengths: Exceptional correlation between simulation and real-world performance due to extensive validation protocols. Their approach effectively handles complex geometries and manufacturing variations found in modern compact heat exchangers. Weaknesses: System is primarily optimized for automotive applications and may require significant adaptation for other industrial heat exchanger types.
Behr GmbH & Co. KG
Technical Solution: Behr has developed a comprehensive thermal stress analysis methodology for heat exchanger tubes that integrates material microstructure evolution with mechanical performance. Their approach utilizes crystal plasticity models to predict grain-level deformation and damage accumulation in tube materials under thermal cycling. Behr's technology incorporates residual stress measurements using neutron diffraction techniques to validate their computational models. Their simulation platform accounts for manufacturing process effects, such as tube forming and brazing, which significantly influence thermal stress distribution. Behr has implemented this technology in their design workflow, enabling rapid evaluation of multiple design iterations and material combinations to optimize thermal-mechanical performance.
Strengths: Exceptional ability to predict localized failure mechanisms at critical joints and transitions where thermal stresses concentrate. Their approach effectively accounts for manufacturing process effects on thermal stress distribution. Weaknesses: Requires specialized material characterization data that may not be readily available for all heat exchanger materials and operating conditions.
Critical Patents and Research in Thermal Stress Analysis
Heat exchanger having header structure for dispersing thermal stress
PatentWO2021167391A1
Innovation
- The heat exchanger features a header structure with inclined tube insertion holes and a contact expansion portion to distribute thermal stress, reducing concentration at the tube nose and enhancing the bonding area, thereby reducing damage and breakage.
Thermal Stress Reduction for Heat Exchanger
PatentInactiveUS20140166236A1
Innovation
- Incorporating a design with parallel tubes and expansion gaps between them, along with fin matrices that span the gaps, allowing for thermal expansion and reducing stress by creating separate tube sets with partial fin matrices at the manifolds to limit expansion at stress regions.
Material Science Advancements for Heat Exchanger Applications
Recent advancements in material science have significantly transformed heat exchanger design and performance capabilities. Traditional materials like carbon steel, stainless steel, and copper alloys are increasingly being supplemented or replaced by innovative alternatives that offer superior thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength under extreme temperature conditions.
Composite materials represent a major breakthrough, combining the beneficial properties of multiple materials to create heat exchanger components with enhanced performance characteristics. Polymer matrix composites reinforced with carbon fibers or ceramic particles demonstrate exceptional thermal stability while maintaining structural integrity under cyclic thermal loading conditions.
Nanomaterials and nanocoatings have emerged as revolutionary solutions for heat exchanger applications. The incorporation of carbon nanotubes, graphene, and metal nanoparticles into base materials has shown remarkable improvements in thermal conductivity. Research indicates that nanofluids containing suspended nanoparticles can enhance heat transfer coefficients by 15-40% compared to conventional heat transfer fluids.
High-entropy alloys (HEAs) represent another frontier in material science for heat exchangers. These multi-principal element alloys exhibit outstanding mechanical properties and corrosion resistance at elevated temperatures. Studies have demonstrated that certain HEAs maintain structural stability at temperatures exceeding 1000°C while resisting common forms of corrosion that plague traditional heat exchanger materials.
Surface engineering technologies have evolved to address fouling and scaling issues in heat exchanger tubes. Advanced hydrophobic and oleophobic coatings minimize deposit formation, while antimicrobial surfaces prevent biofouling in water-based systems. These innovations extend maintenance intervals and preserve thermal efficiency over longer operational periods.
Additive manufacturing has revolutionized heat exchanger design possibilities by enabling the production of complex geometries that optimize fluid flow and heat transfer. 3D-printed heat exchangers with intricate internal channels and variable wall thicknesses can be customized to specific thermal requirements while minimizing material usage and weight.
Smart materials with self-healing capabilities represent the cutting edge of heat exchanger material science. These materials can autonomously repair microcracks and damage caused by thermal cycling, significantly extending component lifespan. Preliminary field tests indicate potential service life improvements of 30-50% compared to conventional materials in high-stress thermal environments.
Composite materials represent a major breakthrough, combining the beneficial properties of multiple materials to create heat exchanger components with enhanced performance characteristics. Polymer matrix composites reinforced with carbon fibers or ceramic particles demonstrate exceptional thermal stability while maintaining structural integrity under cyclic thermal loading conditions.
Nanomaterials and nanocoatings have emerged as revolutionary solutions for heat exchanger applications. The incorporation of carbon nanotubes, graphene, and metal nanoparticles into base materials has shown remarkable improvements in thermal conductivity. Research indicates that nanofluids containing suspended nanoparticles can enhance heat transfer coefficients by 15-40% compared to conventional heat transfer fluids.
High-entropy alloys (HEAs) represent another frontier in material science for heat exchangers. These multi-principal element alloys exhibit outstanding mechanical properties and corrosion resistance at elevated temperatures. Studies have demonstrated that certain HEAs maintain structural stability at temperatures exceeding 1000°C while resisting common forms of corrosion that plague traditional heat exchanger materials.
Surface engineering technologies have evolved to address fouling and scaling issues in heat exchanger tubes. Advanced hydrophobic and oleophobic coatings minimize deposit formation, while antimicrobial surfaces prevent biofouling in water-based systems. These innovations extend maintenance intervals and preserve thermal efficiency over longer operational periods.
Additive manufacturing has revolutionized heat exchanger design possibilities by enabling the production of complex geometries that optimize fluid flow and heat transfer. 3D-printed heat exchangers with intricate internal channels and variable wall thicknesses can be customized to specific thermal requirements while minimizing material usage and weight.
Smart materials with self-healing capabilities represent the cutting edge of heat exchanger material science. These materials can autonomously repair microcracks and damage caused by thermal cycling, significantly extending component lifespan. Preliminary field tests indicate potential service life improvements of 30-50% compared to conventional materials in high-stress thermal environments.
Computational Fluid Dynamics Integration in Thermal Analysis
The integration of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) with thermal stress analysis represents a significant advancement in heat exchanger design methodology. CFD simulations provide detailed fluid flow patterns, temperature distributions, and heat transfer coefficients that serve as critical inputs for accurate thermal stress analysis. This integration enables engineers to visualize complex flow phenomena such as turbulence, recirculation zones, and boundary layer development that directly impact thermal gradients within heat exchanger tubes.
Modern CFD software packages now offer seamless coupling with structural analysis tools, creating a multiphysics environment where fluid-structure interactions can be modeled simultaneously. This coupled approach eliminates the traditional sequential process where CFD results would be manually transferred to structural analysis software, reducing both potential data transfer errors and analysis time. The real-time data exchange between fluid and structural domains ensures that thermal stresses are calculated based on the most accurate temperature profiles.
Mesh compatibility between CFD and structural models presents a significant technical challenge in this integration. While CFD typically requires fine meshes near walls to capture boundary layer effects, structural models often utilize coarser meshes to optimize computational efficiency. Advanced mapping algorithms have been developed to transfer data between these disparate mesh structures while preserving solution accuracy and physical consistency.
Parallel computing capabilities have substantially enhanced the practical implementation of integrated CFD-thermal stress analyses. Modern high-performance computing clusters can now handle the intensive computational requirements of coupled simulations, making previously impractical analyses feasible for industrial applications. This computational power enables parametric studies and optimization routines that would be prohibitively time-consuming with traditional methods.
Machine learning techniques are emerging as valuable tools to further enhance CFD-thermal stress integration. Neural networks trained on extensive simulation datasets can predict thermal stress distributions under various operating conditions without running full simulations, dramatically reducing computational costs for routine design iterations. These AI-assisted approaches are particularly valuable during preliminary design phases when numerous configurations must be rapidly evaluated.
The integration of CFD with thermal stress analysis has transformed heat exchanger design from an experience-based practice to a science-driven process. Engineers can now identify potential failure points before physical prototyping, optimize material distribution to minimize thermal stresses, and extend equipment lifespan through more accurate fatigue life predictions based on realistic operating conditions.
Modern CFD software packages now offer seamless coupling with structural analysis tools, creating a multiphysics environment where fluid-structure interactions can be modeled simultaneously. This coupled approach eliminates the traditional sequential process where CFD results would be manually transferred to structural analysis software, reducing both potential data transfer errors and analysis time. The real-time data exchange between fluid and structural domains ensures that thermal stresses are calculated based on the most accurate temperature profiles.
Mesh compatibility between CFD and structural models presents a significant technical challenge in this integration. While CFD typically requires fine meshes near walls to capture boundary layer effects, structural models often utilize coarser meshes to optimize computational efficiency. Advanced mapping algorithms have been developed to transfer data between these disparate mesh structures while preserving solution accuracy and physical consistency.
Parallel computing capabilities have substantially enhanced the practical implementation of integrated CFD-thermal stress analyses. Modern high-performance computing clusters can now handle the intensive computational requirements of coupled simulations, making previously impractical analyses feasible for industrial applications. This computational power enables parametric studies and optimization routines that would be prohibitively time-consuming with traditional methods.
Machine learning techniques are emerging as valuable tools to further enhance CFD-thermal stress integration. Neural networks trained on extensive simulation datasets can predict thermal stress distributions under various operating conditions without running full simulations, dramatically reducing computational costs for routine design iterations. These AI-assisted approaches are particularly valuable during preliminary design phases when numerous configurations must be rapidly evaluated.
The integration of CFD with thermal stress analysis has transformed heat exchanger design from an experience-based practice to a science-driven process. Engineers can now identify potential failure points before physical prototyping, optimize material distribution to minimize thermal stresses, and extend equipment lifespan through more accurate fatigue life predictions based on realistic operating conditions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!