Compact heat exchanger design for energy efficiency
OCT 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Compact Heat Exchanger Technology Evolution and Objectives
Compact heat exchangers have evolved significantly over the past century, transforming from simple shell-and-tube designs to sophisticated multi-channel microstructures. The evolution began in the early 20th century with basic plate heat exchangers, which offered improved heat transfer efficiency compared to traditional designs. By the 1940s, the introduction of finned-tube heat exchangers marked a significant advancement, enabling higher heat transfer rates in smaller volumes.
The 1960s witnessed the development of plate-fin heat exchangers, which incorporated extended surfaces to enhance heat transfer area without substantially increasing the overall volume. This period established the fundamental principles of compact heat exchanger design that continue to influence modern approaches. The 1970s energy crisis accelerated research into more efficient heat transfer technologies, leading to the emergence of printed circuit heat exchangers in the 1980s.
The 1990s saw the introduction of microchannel heat exchangers, leveraging advances in manufacturing technologies to create extremely compact designs with channel diameters below 1mm. This miniaturization trend continued into the 2000s with the development of polymer-based compact heat exchangers, offering corrosion resistance and cost advantages for specific applications.
Recent technological advancements have focused on additive manufacturing techniques, enabling the creation of complex geometries previously impossible with traditional manufacturing methods. These innovations have allowed for optimized flow paths, enhanced mixing, and reduced pressure drops, significantly improving overall energy efficiency.
The primary objective of compact heat exchanger technology development is to maximize heat transfer rates while minimizing volume, weight, and material usage. This goal addresses the growing demand for energy-efficient systems across various industries, including HVAC, automotive, aerospace, and electronics cooling. Secondary objectives include reducing manufacturing costs, improving durability, and enhancing operational flexibility under varying conditions.
Current research aims to overcome persistent challenges such as fouling resistance, thermal stress management, and manufacturing complexity. The integration of advanced materials, including metal foams, nanofluids, and phase-change materials, represents a promising direction for achieving breakthrough performance improvements. Additionally, the incorporation of smart features for real-time monitoring and adaptive control is emerging as a key objective for next-generation compact heat exchangers.
The technology trajectory indicates a continued push toward multi-functional heat exchangers that can simultaneously address heat transfer, fluid distribution, and structural requirements within increasingly constrained spaces. This evolution aligns with broader sustainability goals, as more efficient heat exchange systems directly contribute to reduced energy consumption and lower carbon emissions across numerous applications.
The 1960s witnessed the development of plate-fin heat exchangers, which incorporated extended surfaces to enhance heat transfer area without substantially increasing the overall volume. This period established the fundamental principles of compact heat exchanger design that continue to influence modern approaches. The 1970s energy crisis accelerated research into more efficient heat transfer technologies, leading to the emergence of printed circuit heat exchangers in the 1980s.
The 1990s saw the introduction of microchannel heat exchangers, leveraging advances in manufacturing technologies to create extremely compact designs with channel diameters below 1mm. This miniaturization trend continued into the 2000s with the development of polymer-based compact heat exchangers, offering corrosion resistance and cost advantages for specific applications.
Recent technological advancements have focused on additive manufacturing techniques, enabling the creation of complex geometries previously impossible with traditional manufacturing methods. These innovations have allowed for optimized flow paths, enhanced mixing, and reduced pressure drops, significantly improving overall energy efficiency.
The primary objective of compact heat exchanger technology development is to maximize heat transfer rates while minimizing volume, weight, and material usage. This goal addresses the growing demand for energy-efficient systems across various industries, including HVAC, automotive, aerospace, and electronics cooling. Secondary objectives include reducing manufacturing costs, improving durability, and enhancing operational flexibility under varying conditions.
Current research aims to overcome persistent challenges such as fouling resistance, thermal stress management, and manufacturing complexity. The integration of advanced materials, including metal foams, nanofluids, and phase-change materials, represents a promising direction for achieving breakthrough performance improvements. Additionally, the incorporation of smart features for real-time monitoring and adaptive control is emerging as a key objective for next-generation compact heat exchangers.
The technology trajectory indicates a continued push toward multi-functional heat exchangers that can simultaneously address heat transfer, fluid distribution, and structural requirements within increasingly constrained spaces. This evolution aligns with broader sustainability goals, as more efficient heat exchange systems directly contribute to reduced energy consumption and lower carbon emissions across numerous applications.
Market Analysis for Energy-Efficient Heat Exchange Solutions
The global market for energy-efficient heat exchange solutions is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing energy costs, stringent environmental regulations, and growing awareness of sustainability issues across industries. The compact heat exchanger segment specifically has emerged as a critical component in this market, with an estimated market value of $9.3 billion in 2022 and projected to reach $13.7 billion by 2027, representing a compound annual growth rate of 8.1%.
Industrial sectors including oil and gas, chemical processing, HVAC, and power generation constitute the primary demand drivers for compact heat exchangers. These industries are increasingly prioritizing energy efficiency to reduce operational costs and meet carbon emission targets. The HVAC sector in particular has shown remarkable adoption rates, with compact heat exchangers becoming standard components in modern building designs that emphasize energy conservation.
Regional analysis reveals that Asia-Pacific currently leads the market, accounting for approximately 35% of global demand, followed by North America (28%) and Europe (25%). China and India represent the fastest-growing markets due to rapid industrialization and infrastructure development. European markets are primarily driven by stringent energy efficiency regulations and sustainability goals set by the European Union.
Consumer behavior trends indicate a growing preference for heat exchange solutions that offer not only energy efficiency but also space optimization and reduced maintenance requirements. This has accelerated innovation in plate heat exchangers and printed circuit heat exchangers, which offer superior thermal performance in compact designs.
Market research indicates that end-users are willing to pay a premium of 15-20% for heat exchange solutions that demonstrate verifiable energy savings of 25% or more compared to conventional systems. This price elasticity varies significantly by industry, with pharmaceutical and food processing sectors showing higher willingness to invest in premium solutions.
Competitive analysis reveals a market dominated by established players like Alfa Laval, Danfoss, and Kelvion, who collectively hold approximately 45% market share. However, emerging companies specializing in advanced materials and manufacturing techniques are gaining traction, particularly in niche applications requiring extreme performance parameters.
Future market projections suggest that microchannel heat exchangers and additive manufacturing-enabled designs will experience the highest growth rates within the compact heat exchanger segment. Additionally, integration with IoT and smart control systems is expected to create a new premium segment focused on predictive maintenance and real-time efficiency optimization.
Industrial sectors including oil and gas, chemical processing, HVAC, and power generation constitute the primary demand drivers for compact heat exchangers. These industries are increasingly prioritizing energy efficiency to reduce operational costs and meet carbon emission targets. The HVAC sector in particular has shown remarkable adoption rates, with compact heat exchangers becoming standard components in modern building designs that emphasize energy conservation.
Regional analysis reveals that Asia-Pacific currently leads the market, accounting for approximately 35% of global demand, followed by North America (28%) and Europe (25%). China and India represent the fastest-growing markets due to rapid industrialization and infrastructure development. European markets are primarily driven by stringent energy efficiency regulations and sustainability goals set by the European Union.
Consumer behavior trends indicate a growing preference for heat exchange solutions that offer not only energy efficiency but also space optimization and reduced maintenance requirements. This has accelerated innovation in plate heat exchangers and printed circuit heat exchangers, which offer superior thermal performance in compact designs.
Market research indicates that end-users are willing to pay a premium of 15-20% for heat exchange solutions that demonstrate verifiable energy savings of 25% or more compared to conventional systems. This price elasticity varies significantly by industry, with pharmaceutical and food processing sectors showing higher willingness to invest in premium solutions.
Competitive analysis reveals a market dominated by established players like Alfa Laval, Danfoss, and Kelvion, who collectively hold approximately 45% market share. However, emerging companies specializing in advanced materials and manufacturing techniques are gaining traction, particularly in niche applications requiring extreme performance parameters.
Future market projections suggest that microchannel heat exchangers and additive manufacturing-enabled designs will experience the highest growth rates within the compact heat exchanger segment. Additionally, integration with IoT and smart control systems is expected to create a new premium segment focused on predictive maintenance and real-time efficiency optimization.
Current Limitations and Technical Barriers in Compact Heat Exchangers
Despite significant advancements in compact heat exchanger technology, several critical limitations continue to impede optimal energy efficiency. The primary challenge remains the inherent trade-off between heat transfer efficiency and pressure drop. As designers pursue more compact configurations with enhanced surface area density, the resulting flow paths become increasingly tortuous, leading to higher pressure drops that require additional pumping power and ultimately reduce overall system efficiency.
Material constraints represent another significant barrier. While high thermal conductivity materials like copper and aluminum are preferred for efficient heat transfer, they often face limitations in high-temperature or corrosive environments. Advanced materials such as specialized alloys or ceramics that could withstand extreme conditions typically come with prohibitive costs or manufacturing challenges, restricting their widespread implementation.
Manufacturing precision presents a persistent obstacle, particularly for micro-channel and printed circuit heat exchangers where channel dimensions may be in the sub-millimeter range. Current manufacturing technologies struggle to consistently produce these fine features with the required tolerances, resulting in performance variations and reliability issues. The complexity of fabricating three-dimensional enhanced surfaces further compounds these manufacturing difficulties.
Fouling and clogging remain especially problematic for compact designs with small flow passages. The reduced hydraulic diameter makes these exchangers particularly vulnerable to performance degradation over time as deposits accumulate on heat transfer surfaces. Current anti-fouling technologies and self-cleaning mechanisms have proven insufficient for maintaining long-term performance in many industrial applications.
Thermal expansion management presents another technical barrier, as the compact nature of these exchangers often results in significant thermal stresses during operation. The differential expansion between materials and components can lead to mechanical failures, particularly at joints and interfaces, limiting operational flexibility and durability.
Flow distribution issues persist in compact designs, where ensuring uniform fluid distribution across multiple parallel channels remains challenging. Non-uniform flow leads to localized hot spots, reduced effective heat transfer area, and overall performance deterioration. Current header designs and flow distribution systems have not fully resolved these issues, especially for two-phase flows.
Finally, accurate modeling and simulation tools for compact heat exchangers still lack the necessary fidelity to predict performance across all operating conditions. The complex geometries and flow patterns in these devices often require computational resources beyond what is practically available for routine design work, forcing engineers to rely on empirical correlations with limited applicability ranges.
Material constraints represent another significant barrier. While high thermal conductivity materials like copper and aluminum are preferred for efficient heat transfer, they often face limitations in high-temperature or corrosive environments. Advanced materials such as specialized alloys or ceramics that could withstand extreme conditions typically come with prohibitive costs or manufacturing challenges, restricting their widespread implementation.
Manufacturing precision presents a persistent obstacle, particularly for micro-channel and printed circuit heat exchangers where channel dimensions may be in the sub-millimeter range. Current manufacturing technologies struggle to consistently produce these fine features with the required tolerances, resulting in performance variations and reliability issues. The complexity of fabricating three-dimensional enhanced surfaces further compounds these manufacturing difficulties.
Fouling and clogging remain especially problematic for compact designs with small flow passages. The reduced hydraulic diameter makes these exchangers particularly vulnerable to performance degradation over time as deposits accumulate on heat transfer surfaces. Current anti-fouling technologies and self-cleaning mechanisms have proven insufficient for maintaining long-term performance in many industrial applications.
Thermal expansion management presents another technical barrier, as the compact nature of these exchangers often results in significant thermal stresses during operation. The differential expansion between materials and components can lead to mechanical failures, particularly at joints and interfaces, limiting operational flexibility and durability.
Flow distribution issues persist in compact designs, where ensuring uniform fluid distribution across multiple parallel channels remains challenging. Non-uniform flow leads to localized hot spots, reduced effective heat transfer area, and overall performance deterioration. Current header designs and flow distribution systems have not fully resolved these issues, especially for two-phase flows.
Finally, accurate modeling and simulation tools for compact heat exchangers still lack the necessary fidelity to predict performance across all operating conditions. The complex geometries and flow patterns in these devices often require computational resources beyond what is practically available for routine design work, forcing engineers to rely on empirical correlations with limited applicability ranges.
State-of-the-Art Compact Heat Exchanger Design Approaches
01 Heat exchanger design optimization
Optimizing the design of heat exchangers can significantly improve energy efficiency. This includes modifications to the structure, geometry, and materials used in heat exchangers to enhance heat transfer rates while minimizing energy consumption. Design innovations such as improved flow patterns, optimized tube arrangements, and enhanced surface areas contribute to better thermal performance and reduced energy requirements.- Heat exchanger design optimization: Optimizing the design of heat exchangers can significantly improve energy efficiency. This includes modifications to the structure, shape, and arrangement of heat transfer surfaces to maximize heat transfer while minimizing pressure drop. Design innovations such as improved fin configurations, tube arrangements, and flow path optimization can enhance thermal performance and reduce energy consumption in various applications.
- Enhanced heat transfer surfaces: Specialized surface treatments and geometries can improve heat transfer efficiency. These include micro-channel designs, enhanced fin structures, and surface modifications that promote turbulence or increase contact area. By improving the heat transfer coefficient at the surface level, these technologies enable more efficient energy exchange with reduced power requirements for pumping or fan operation.
- Waste heat recovery systems: Systems designed to capture and utilize waste heat from industrial processes or equipment operation can significantly improve overall energy efficiency. These systems incorporate heat exchangers to transfer thermal energy that would otherwise be lost to the environment into useful applications such as preheating, power generation, or space heating, thereby reducing primary energy consumption.
- Smart control and monitoring systems: Integration of advanced control systems, sensors, and monitoring technologies enables dynamic optimization of heat exchanger operation. These systems can adjust flow rates, temperatures, and other parameters in real-time based on changing conditions and demand, ensuring that heat exchangers operate at peak efficiency under varying loads and environmental conditions.
- Novel materials and manufacturing techniques: Advanced materials with superior thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, or reduced fouling tendency can enhance heat exchanger performance. Additionally, innovative manufacturing techniques such as 3D printing, diffusion bonding, or advanced welding methods enable the creation of complex geometries and integrated designs that were previously impossible to manufacture, leading to more efficient heat transfer solutions.
02 Enhanced heat transfer surfaces
Specialized surface treatments and configurations can improve heat transfer efficiency in exchangers. These include micro-channel designs, finned surfaces, and textured surfaces that increase the contact area between the heat exchanger and the fluid. By enhancing the heat transfer coefficient, these surface modifications allow for more efficient energy use and can reduce the overall size and material requirements of heat exchange systems.Expand Specific Solutions03 Advanced flow management techniques
Innovative flow management approaches can optimize energy efficiency in heat exchangers. These techniques include turbulence generators, flow distributors, and strategic baffle placement to ensure uniform fluid distribution and minimize pressure drops. By managing the flow dynamics within heat exchangers, these innovations reduce energy losses while maximizing heat transfer rates, resulting in improved overall system efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions04 Waste heat recovery systems
Systems designed to capture and utilize waste heat from industrial processes or equipment can significantly improve overall energy efficiency. These heat recovery systems incorporate specialized heat exchangers that transfer thermal energy from exhaust gases or waste streams to other process fluids or systems. By reclaiming energy that would otherwise be lost, these systems reduce primary energy consumption and operating costs while decreasing environmental impact.Expand Specific Solutions05 Smart control and monitoring systems
Integration of intelligent control systems and monitoring technologies can optimize heat exchanger performance under varying operating conditions. These systems use sensors, algorithms, and automated controls to adjust flow rates, temperatures, and other parameters in real-time. By continuously optimizing operation based on actual conditions and demand, smart control systems can significantly reduce energy consumption while maintaining or improving heat transfer efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions in Heat Exchange Industry
The compact heat exchanger market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing energy efficiency demands across industries. The market size is expanding significantly due to applications in automotive, HVAC, and industrial sectors. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels with established players like Mitsubishi Electric, Danfoss, and MAHLE leading innovation alongside academic institutions such as Xi'an Jiaotong University and Beihang University. Companies like Daikin, Valeo, and Bosch are advancing miniaturization and performance optimization, while specialized manufacturers including Wieland-Werke and Zhejiang Yinlun focus on material innovations. This competitive landscape combines traditional thermal management expertise with emerging technologies for enhanced heat transfer efficiency.
Danfoss A/S
Technical Solution: Danfoss has pioneered micro-plate heat exchanger technology that utilizes innovative herringbone patterns to create controlled turbulence in fluid channels. Their design features asymmetric plate patterns that optimize flow distribution while minimizing dead zones and pressure drop. Danfoss's proprietary "Micro Plate" technology creates dimple patterns precisely engineered to induce secondary flows that disrupt thermal boundary layers without excessive pressure penalties. Their manufacturing process employs advanced copper brazing techniques that ensure uniform material joints with minimal thermal resistance. Danfoss has also developed specialized distribution systems that ensure uniform refrigerant flow across the entire heat transfer surface, addressing a critical limitation in traditional plate heat exchangers. Their latest generation incorporates variable plate geometries within a single unit, optimizing performance for different sections of the heat transfer process.
Strengths: Superior heat transfer efficiency with up to 10% higher COP in refrigeration systems; excellent turndown ratio maintaining performance across wide capacity ranges; and compact form factor reducing material usage by up to 30%. Weaknesses: Higher manufacturing precision requirements increasing production costs; more complex validation requirements; and potential for increased fouling sensitivity in certain applications.
Hanon Systems
Technical Solution: Hanon Systems has developed an innovative compact heat exchanger technology based on their patented "Wave Flow" design. This approach utilizes specially formed wave-like patterns in the flow channels that create controlled vortices and secondary flows, enhancing heat transfer while maintaining manageable pressure drops. Their design incorporates variable amplitude wave patterns that are optimized for different flow regimes and heat transfer requirements across the exchanger. Hanon's manufacturing process employs advanced brazing techniques that ensure uniform material joints with minimal thermal resistance. Their latest generation features integrated phase separation zones for two-phase applications, addressing distribution challenges common in compact evaporators and condensers. Hanon has also developed specialized surface treatments that enhance wettability for condensation applications, significantly improving heat transfer coefficients in these challenging conditions.
Strengths: Excellent thermal-hydraulic performance with up to 25% improvement in heat transfer coefficient per unit pressure drop; superior refrigerant distribution in two-phase applications; and robust resistance to fouling. Weaknesses: More complex manufacturing process requiring specialized tooling; higher material costs due to specialized surface treatments; and challenges in scaling to very small applications.
Key Patents and Innovations in Energy-Efficient Heat Transfer
Heat exchanger and heater with a heat exchanger
PatentInactiveEP2189744A2
Innovation
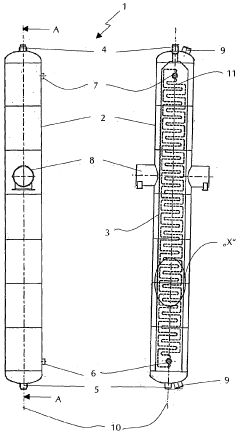
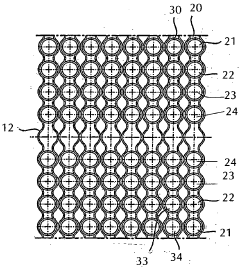
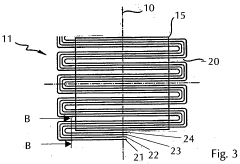
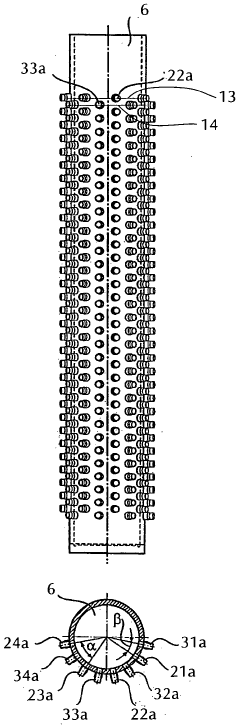
- A compact heat exchanger design featuring a stack of circular plates with eccentric inner and outer channels, allowing for easy assembly and cleaning, and the use of different materials to manage thermal stresses, enabling efficient heat transfer between fluids without the need for complex tooling changes.
Heat exchanger for generating steam for solar power plants
PatentWO2011060870A1
Innovation
- A compact heat exchanger design incorporating a meandering tube bundle within an outer shell, functioning as both a preheater, evaporator, and superheater, where water is preheated, evaporated, and superheated in a single pass, eliminating the need for separate modules and external components, enhancing heat transfer efficiency and reducing material and operational costs.
Materials Science Advancements for Compact Heat Exchangers
Recent advancements in materials science have revolutionized the design and performance of compact heat exchangers, enabling significant improvements in energy efficiency. Traditional materials like copper, aluminum, and stainless steel are being supplemented or replaced by novel materials with superior thermal properties and reduced environmental impact.
Nanomaterials represent one of the most promising developments, with carbon nanotubes and graphene demonstrating thermal conductivity up to 3000 W/m·K, far exceeding conventional metals. These materials allow for exceptionally thin heat transfer surfaces while maintaining structural integrity, dramatically increasing the surface area-to-volume ratio critical for compact designs.
Metal matrix composites (MMCs) combining aluminum with silicon carbide or graphite particles have emerged as practical solutions, offering 20-40% higher thermal conductivity than pure aluminum while maintaining comparable weight. These materials provide excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical strength at elevated temperatures, extending operational lifespans in demanding environments.
Advanced polymer composites with thermally conductive fillers present weight reduction opportunities of up to 60% compared to metal alternatives. These materials offer design flexibility through injection molding and 3D printing processes, enabling complex geometries previously unachievable with traditional manufacturing methods.
High-entropy alloys (HEAs) represent a breakthrough material class, combining five or more principal elements in near-equiatomic proportions. These alloys demonstrate exceptional thermal stability, mechanical properties, and corrosion resistance across wide temperature ranges, making them ideal for extreme operating conditions in compact heat exchangers.
Surface modification technologies have also advanced significantly, with hydrophobic and hydrophilic coatings enhancing heat transfer coefficients by 15-30%. These treatments minimize fouling and scaling, maintaining performance over extended operational periods and reducing maintenance requirements.
Additive manufacturing has transformed material application in heat exchanger design, enabling lattice structures and topologically optimized geometries that maximize heat transfer while minimizing material usage. These manufacturing techniques allow for integrated multi-material solutions that strategically place high-performance materials only where needed, optimizing cost-effectiveness.
Phase change materials (PCMs) incorporated into heat exchanger designs provide thermal energy storage capabilities, smoothing load fluctuations and improving overall system efficiency. Recent developments in microencapsulation techniques have addressed previous limitations regarding containment and cycling stability.
These material advancements collectively enable compact heat exchangers with 30-50% higher energy efficiency than conventional designs while reducing material consumption, manufacturing costs, and environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle.
Nanomaterials represent one of the most promising developments, with carbon nanotubes and graphene demonstrating thermal conductivity up to 3000 W/m·K, far exceeding conventional metals. These materials allow for exceptionally thin heat transfer surfaces while maintaining structural integrity, dramatically increasing the surface area-to-volume ratio critical for compact designs.
Metal matrix composites (MMCs) combining aluminum with silicon carbide or graphite particles have emerged as practical solutions, offering 20-40% higher thermal conductivity than pure aluminum while maintaining comparable weight. These materials provide excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical strength at elevated temperatures, extending operational lifespans in demanding environments.
Advanced polymer composites with thermally conductive fillers present weight reduction opportunities of up to 60% compared to metal alternatives. These materials offer design flexibility through injection molding and 3D printing processes, enabling complex geometries previously unachievable with traditional manufacturing methods.
High-entropy alloys (HEAs) represent a breakthrough material class, combining five or more principal elements in near-equiatomic proportions. These alloys demonstrate exceptional thermal stability, mechanical properties, and corrosion resistance across wide temperature ranges, making them ideal for extreme operating conditions in compact heat exchangers.
Surface modification technologies have also advanced significantly, with hydrophobic and hydrophilic coatings enhancing heat transfer coefficients by 15-30%. These treatments minimize fouling and scaling, maintaining performance over extended operational periods and reducing maintenance requirements.
Additive manufacturing has transformed material application in heat exchanger design, enabling lattice structures and topologically optimized geometries that maximize heat transfer while minimizing material usage. These manufacturing techniques allow for integrated multi-material solutions that strategically place high-performance materials only where needed, optimizing cost-effectiveness.
Phase change materials (PCMs) incorporated into heat exchanger designs provide thermal energy storage capabilities, smoothing load fluctuations and improving overall system efficiency. Recent developments in microencapsulation techniques have addressed previous limitations regarding containment and cycling stability.
These material advancements collectively enable compact heat exchangers with 30-50% higher energy efficiency than conventional designs while reducing material consumption, manufacturing costs, and environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle.
Sustainability Impact and Carbon Footprint Reduction Potential
Compact heat exchangers represent a significant opportunity for advancing sustainability goals across multiple industries. The implementation of these efficient thermal management solutions directly contributes to reduced energy consumption in heating, cooling, and power generation systems, with potential energy savings of 15-30% compared to conventional heat exchanger designs. This efficiency improvement translates to substantial reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, particularly in energy-intensive sectors such as manufacturing, power generation, and HVAC systems.
When analyzing the carbon footprint reduction potential, compact heat exchangers demonstrate impressive metrics. For every kilowatt-hour of energy saved through improved heat transfer efficiency, approximately 0.4-0.7 kg of CO2 emissions can be avoided, depending on the regional energy mix. In industrial applications, the cumulative impact becomes even more significant, with large-scale implementations potentially reducing carbon emissions by thousands of tons annually per facility.
The sustainability benefits extend beyond operational carbon reductions. Compact heat exchangers typically require 30-50% less raw material during manufacturing compared to traditional designs, reducing embodied carbon and resource depletion. Their smaller physical footprint also minimizes land use requirements and associated environmental disruption. Additionally, many modern compact designs utilize materials with higher recyclability rates, supporting circular economy principles and end-of-life sustainability considerations.
Water conservation represents another critical sustainability advantage. In applications where cooling water is required, compact heat exchangers can reduce water consumption by up to 40% through more efficient heat transfer and reduced fouling. This water-saving potential is particularly valuable in water-stressed regions and industries with high cooling demands.
The lifecycle assessment of compact heat exchangers reveals favorable sustainability metrics across multiple environmental impact categories. Beyond carbon emissions, these designs help reduce acidification potential, eutrophication impacts, and photochemical ozone creation potential. When properly maintained, their extended operational lifespan—often 20-25% longer than conventional designs—further enhances their sustainability profile by reducing replacement frequency and associated manufacturing impacts.
From a policy perspective, compact heat exchangers align with global sustainability frameworks including the Paris Agreement and various national energy efficiency standards. Their implementation supports organizational ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals and can contribute to compliance with increasingly stringent environmental regulations, potentially avoiding carbon taxes and penalties in jurisdictions with carbon pricing mechanisms.
When analyzing the carbon footprint reduction potential, compact heat exchangers demonstrate impressive metrics. For every kilowatt-hour of energy saved through improved heat transfer efficiency, approximately 0.4-0.7 kg of CO2 emissions can be avoided, depending on the regional energy mix. In industrial applications, the cumulative impact becomes even more significant, with large-scale implementations potentially reducing carbon emissions by thousands of tons annually per facility.
The sustainability benefits extend beyond operational carbon reductions. Compact heat exchangers typically require 30-50% less raw material during manufacturing compared to traditional designs, reducing embodied carbon and resource depletion. Their smaller physical footprint also minimizes land use requirements and associated environmental disruption. Additionally, many modern compact designs utilize materials with higher recyclability rates, supporting circular economy principles and end-of-life sustainability considerations.
Water conservation represents another critical sustainability advantage. In applications where cooling water is required, compact heat exchangers can reduce water consumption by up to 40% through more efficient heat transfer and reduced fouling. This water-saving potential is particularly valuable in water-stressed regions and industries with high cooling demands.
The lifecycle assessment of compact heat exchangers reveals favorable sustainability metrics across multiple environmental impact categories. Beyond carbon emissions, these designs help reduce acidification potential, eutrophication impacts, and photochemical ozone creation potential. When properly maintained, their extended operational lifespan—often 20-25% longer than conventional designs—further enhances their sustainability profile by reducing replacement frequency and associated manufacturing impacts.
From a policy perspective, compact heat exchangers align with global sustainability frameworks including the Paris Agreement and various national energy efficiency standards. Their implementation supports organizational ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals and can contribute to compliance with increasingly stringent environmental regulations, potentially avoiding carbon taxes and penalties in jurisdictions with carbon pricing mechanisms.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!