Design optimization of spiral heat exchangers
OCT 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Spiral Heat Exchanger Technology Background and Objectives
Spiral heat exchangers (SHEs) have evolved significantly since their inception in the early 20th century, representing a specialized category of heat transfer equipment characterized by their compact design and efficient thermal performance. The technology originated from the need to address limitations in conventional shell-and-tube heat exchangers, particularly in applications involving high-viscosity fluids, limited installation space, and fouling concerns. Early designs emerged in the 1930s, with significant commercial development occurring post-World War II as industrial processes demanded more efficient heat transfer solutions.
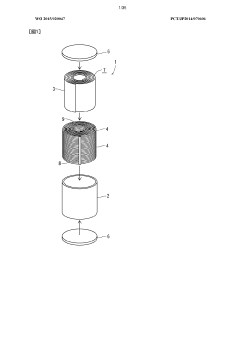
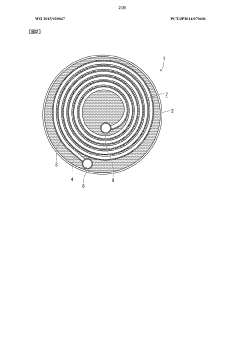
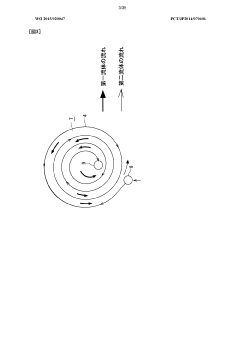
The fundamental architecture of spiral heat exchangers consists of two concentric spiral channels formed by metal sheets wound around a central core, creating separate flow paths for hot and cold fluids. This unique configuration enables counter-current flow patterns that maximize thermal efficiency while minimizing the required footprint. The evolution of manufacturing techniques, particularly in precision sheet metal forming and welding technologies, has been instrumental in advancing SHE capabilities over the decades.
Recent technological advancements have focused on enhancing the design optimization of spiral heat exchangers to meet increasingly stringent industrial requirements. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) modeling has revolutionized the understanding of complex flow patterns within spiral channels, enabling more precise prediction of pressure drops and heat transfer coefficients. Advanced materials science has contributed to the development of corrosion-resistant alloys and surface treatments that extend operational lifespans in aggressive environments.
The primary technical objectives in spiral heat exchanger optimization currently center around several key dimensions. Thermal efficiency enhancement remains paramount, with research directed toward optimizing spiral geometry, channel spacing, and flow distribution to maximize heat transfer rates while minimizing pressure losses. Size reduction represents another critical goal, particularly for applications in offshore platforms, pharmaceutical processing, and other space-constrained environments.
Fouling mitigation constitutes a significant focus area, with design innovations aimed at reducing deposit formation through optimized flow velocities and self-cleaning geometries. Energy efficiency improvements are being pursued through reduced pumping power requirements and enhanced heat recovery capabilities. Additionally, cost optimization through simplified manufacturing processes and standardized designs aims to improve the competitive positioning of spiral heat exchangers against alternative technologies.
The trajectory of spiral heat exchanger technology is increasingly influenced by sustainability considerations, with designs evolving to support low-carbon industrial processes, waste heat recovery systems, and renewable energy applications. As industrial decarbonization accelerates globally, the optimization of spiral heat exchangers represents a critical enabling technology for more efficient thermal management across diverse sectors including chemical processing, food production, wastewater treatment, and emerging green hydrogen systems.
The fundamental architecture of spiral heat exchangers consists of two concentric spiral channels formed by metal sheets wound around a central core, creating separate flow paths for hot and cold fluids. This unique configuration enables counter-current flow patterns that maximize thermal efficiency while minimizing the required footprint. The evolution of manufacturing techniques, particularly in precision sheet metal forming and welding technologies, has been instrumental in advancing SHE capabilities over the decades.
Recent technological advancements have focused on enhancing the design optimization of spiral heat exchangers to meet increasingly stringent industrial requirements. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) modeling has revolutionized the understanding of complex flow patterns within spiral channels, enabling more precise prediction of pressure drops and heat transfer coefficients. Advanced materials science has contributed to the development of corrosion-resistant alloys and surface treatments that extend operational lifespans in aggressive environments.
The primary technical objectives in spiral heat exchanger optimization currently center around several key dimensions. Thermal efficiency enhancement remains paramount, with research directed toward optimizing spiral geometry, channel spacing, and flow distribution to maximize heat transfer rates while minimizing pressure losses. Size reduction represents another critical goal, particularly for applications in offshore platforms, pharmaceutical processing, and other space-constrained environments.
Fouling mitigation constitutes a significant focus area, with design innovations aimed at reducing deposit formation through optimized flow velocities and self-cleaning geometries. Energy efficiency improvements are being pursued through reduced pumping power requirements and enhanced heat recovery capabilities. Additionally, cost optimization through simplified manufacturing processes and standardized designs aims to improve the competitive positioning of spiral heat exchangers against alternative technologies.
The trajectory of spiral heat exchanger technology is increasingly influenced by sustainability considerations, with designs evolving to support low-carbon industrial processes, waste heat recovery systems, and renewable energy applications. As industrial decarbonization accelerates globally, the optimization of spiral heat exchangers represents a critical enabling technology for more efficient thermal management across diverse sectors including chemical processing, food production, wastewater treatment, and emerging green hydrogen systems.
Market Demand Analysis for Spiral Heat Exchangers
The global market for spiral heat exchangers has been experiencing steady growth, driven primarily by increasing industrialization and the growing emphasis on energy efficiency across various sectors. Current market analysis indicates that the spiral heat exchanger market is valued at approximately 5.2 billion USD in 2023, with projections suggesting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% through 2030.
The oil and gas industry remains the largest consumer of spiral heat exchangers, accounting for roughly 35% of the total market share. This demand is fueled by the need for efficient heat transfer solutions in refining processes, natural gas processing, and petrochemical applications. The chemical processing industry follows closely, representing about 28% of the market, where spiral heat exchangers are valued for their ability to handle corrosive fluids and high-fouling applications.
Wastewater treatment represents a rapidly growing segment, currently at 15% of the market but expanding at nearly 8% annually. This growth is driven by increasingly stringent environmental regulations worldwide and the need for more efficient heat recovery systems in treatment facilities. The food and beverage industry accounts for approximately 12% of the market, utilizing spiral heat exchangers for pasteurization, sterilization, and general heating/cooling processes.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific dominates the market with a 38% share, propelled by rapid industrialization in China and India. North America and Europe follow with 27% and 24% respectively, where replacement of aging heat exchange infrastructure and focus on energy efficiency are key drivers.
Market research indicates that end-users are increasingly prioritizing design optimization factors such as reduced fouling, compact footprint, and lower maintenance requirements. A survey of industrial process engineers revealed that 72% consider thermal efficiency the most critical factor when selecting heat exchangers, followed by resistance to fouling (65%) and space requirements (58%).
The demand for customized spiral heat exchangers has grown by 22% over the past five years, reflecting the industry's need for application-specific solutions rather than one-size-fits-all approaches. This trend is particularly pronounced in specialized chemical processing and pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Energy efficiency regulations and sustainability initiatives are creating significant market pull for optimized spiral heat exchanger designs. Companies demonstrating verifiable energy savings of 15% or more through advanced heat exchanger designs are capturing premium market positions and commanding price premiums of up to 20% compared to standard offerings.
The oil and gas industry remains the largest consumer of spiral heat exchangers, accounting for roughly 35% of the total market share. This demand is fueled by the need for efficient heat transfer solutions in refining processes, natural gas processing, and petrochemical applications. The chemical processing industry follows closely, representing about 28% of the market, where spiral heat exchangers are valued for their ability to handle corrosive fluids and high-fouling applications.
Wastewater treatment represents a rapidly growing segment, currently at 15% of the market but expanding at nearly 8% annually. This growth is driven by increasingly stringent environmental regulations worldwide and the need for more efficient heat recovery systems in treatment facilities. The food and beverage industry accounts for approximately 12% of the market, utilizing spiral heat exchangers for pasteurization, sterilization, and general heating/cooling processes.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific dominates the market with a 38% share, propelled by rapid industrialization in China and India. North America and Europe follow with 27% and 24% respectively, where replacement of aging heat exchange infrastructure and focus on energy efficiency are key drivers.
Market research indicates that end-users are increasingly prioritizing design optimization factors such as reduced fouling, compact footprint, and lower maintenance requirements. A survey of industrial process engineers revealed that 72% consider thermal efficiency the most critical factor when selecting heat exchangers, followed by resistance to fouling (65%) and space requirements (58%).
The demand for customized spiral heat exchangers has grown by 22% over the past five years, reflecting the industry's need for application-specific solutions rather than one-size-fits-all approaches. This trend is particularly pronounced in specialized chemical processing and pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Energy efficiency regulations and sustainability initiatives are creating significant market pull for optimized spiral heat exchanger designs. Companies demonstrating verifiable energy savings of 15% or more through advanced heat exchanger designs are capturing premium market positions and commanding price premiums of up to 20% compared to standard offerings.
Current Technical Status and Design Challenges
Spiral heat exchangers (SHEs) represent a significant advancement in heat transfer technology, combining compact design with high thermal efficiency. Currently, the global market for SHEs is experiencing steady growth, with applications spanning across petrochemical, food processing, wastewater treatment, and HVAC industries. The technology has reached a mature stage in terms of basic design principles, but significant optimization challenges remain.
The current technical landscape shows that conventional SHE designs typically achieve thermal efficiencies of 70-85%, with pressure drop constraints limiting further performance improvements. Modern computational fluid dynamics (CFD) tools have enabled more sophisticated analysis of flow patterns within spiral channels, revealing complex secondary flows and recirculation zones that were previously difficult to characterize through experimental methods alone.
Material selection represents a critical aspect of current SHE technology. While stainless steel remains the predominant material for most applications, recent advancements in composite materials and specialized alloys have expanded design possibilities for corrosive environments. However, these advanced materials often introduce manufacturing complexities and cost premiums that limit widespread adoption.
Manufacturing techniques for SHEs have evolved significantly, with automated welding processes and precision forming equipment improving production consistency. Despite these advances, the fabrication of spiral channels with optimal geometrical parameters remains challenging, particularly for designs requiring tight curvature radios or variable channel spacing.
A significant technical challenge in SHE design optimization involves the trade-off between heat transfer enhancement and pressure drop. Current research indicates that while various enhancement techniques (such as surface roughening or flow disruptors) can improve thermal performance by 15-30%, they typically incur disproportionate pressure penalties, increasing pumping power requirements.
Fouling mitigation represents another persistent challenge, particularly in applications involving particulate-laden or high-viscosity fluids. Current anti-fouling strategies include specialized surface treatments and self-cleaning designs, but these solutions often compromise thermal performance or increase manufacturing complexity.
Geographical distribution of SHE technology development shows concentration in industrialized regions, with significant research clusters in Western Europe, North America, and East Asia. European manufacturers have traditionally led in high-precision SHE designs for pharmaceutical and food applications, while Asian manufacturers have gained market share through cost-competitive offerings for industrial applications.
The scaling challenge remains particularly acute for SHEs, as the thermal-hydraulic behavior observed in small-scale laboratory prototypes often fails to translate directly to industrial-scale units. This scaling discrepancy creates significant uncertainty in performance predictions for large installations, necessitating conservative design approaches that may sacrifice optimal efficiency.
The current technical landscape shows that conventional SHE designs typically achieve thermal efficiencies of 70-85%, with pressure drop constraints limiting further performance improvements. Modern computational fluid dynamics (CFD) tools have enabled more sophisticated analysis of flow patterns within spiral channels, revealing complex secondary flows and recirculation zones that were previously difficult to characterize through experimental methods alone.
Material selection represents a critical aspect of current SHE technology. While stainless steel remains the predominant material for most applications, recent advancements in composite materials and specialized alloys have expanded design possibilities for corrosive environments. However, these advanced materials often introduce manufacturing complexities and cost premiums that limit widespread adoption.
Manufacturing techniques for SHEs have evolved significantly, with automated welding processes and precision forming equipment improving production consistency. Despite these advances, the fabrication of spiral channels with optimal geometrical parameters remains challenging, particularly for designs requiring tight curvature radios or variable channel spacing.
A significant technical challenge in SHE design optimization involves the trade-off between heat transfer enhancement and pressure drop. Current research indicates that while various enhancement techniques (such as surface roughening or flow disruptors) can improve thermal performance by 15-30%, they typically incur disproportionate pressure penalties, increasing pumping power requirements.
Fouling mitigation represents another persistent challenge, particularly in applications involving particulate-laden or high-viscosity fluids. Current anti-fouling strategies include specialized surface treatments and self-cleaning designs, but these solutions often compromise thermal performance or increase manufacturing complexity.
Geographical distribution of SHE technology development shows concentration in industrialized regions, with significant research clusters in Western Europe, North America, and East Asia. European manufacturers have traditionally led in high-precision SHE designs for pharmaceutical and food applications, while Asian manufacturers have gained market share through cost-competitive offerings for industrial applications.
The scaling challenge remains particularly acute for SHEs, as the thermal-hydraulic behavior observed in small-scale laboratory prototypes often fails to translate directly to industrial-scale units. This scaling discrepancy creates significant uncertainty in performance predictions for large installations, necessitating conservative design approaches that may sacrifice optimal efficiency.
Current Design Optimization Methodologies
01 Geometric optimization of spiral channels
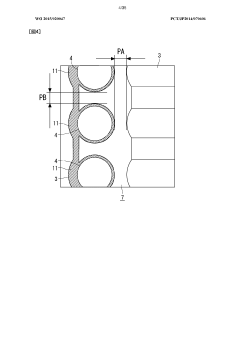
Optimization of the geometric parameters of spiral heat exchangers, including channel width, height, and curvature, can significantly improve heat transfer efficiency. By carefully designing the spiral geometry, fluid flow patterns can be enhanced to create better mixing and reduce pressure drop. These optimizations consider the trade-off between heat transfer performance and pressure loss, resulting in more efficient heat exchange systems.- Geometric optimization of spiral channels: Optimizing the geometric parameters of spiral heat exchangers can significantly improve heat transfer efficiency. This includes modifications to the spiral channel width, height, and curvature radius. By carefully designing these geometric features, fluid flow patterns can be optimized to enhance heat exchange while minimizing pressure drop. Advanced computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations are often used to determine optimal channel dimensions and spacing for specific applications.
- Flow pattern optimization techniques: Various techniques can be employed to optimize flow patterns within spiral heat exchangers. These include the implementation of turbulence promoters, flow disruptors, and specialized inlet/outlet configurations. By creating controlled turbulence or secondary flows, heat transfer coefficients can be significantly improved. Some designs incorporate vortex generators or surface modifications to enhance mixing while maintaining acceptable pressure drop characteristics.
- Material selection and surface treatment: The choice of materials and surface treatments plays a crucial role in spiral heat exchanger performance. High thermal conductivity materials can improve heat transfer rates, while corrosion-resistant alloys extend operational life in harsh environments. Surface modifications such as micro-texturing, coating applications, or chemical treatments can enhance heat transfer characteristics by increasing effective surface area or modifying wettability properties. These material optimizations must balance thermal performance with mechanical integrity and cost considerations.
- Computational modeling and simulation approaches: Advanced computational modeling and simulation techniques are essential tools for spiral heat exchanger design optimization. These include computational fluid dynamics (CFD), finite element analysis (FEA), and machine learning algorithms that can predict performance under various operating conditions. Multi-physics simulations that couple fluid flow, heat transfer, and structural mechanics enable comprehensive optimization of design parameters. These computational approaches reduce the need for costly physical prototyping and allow for rapid iteration of design concepts.
- Modular and adaptive design configurations: Innovative modular and adaptive design configurations allow for customization of spiral heat exchangers to specific operational requirements. These designs may feature adjustable spiral spacing, interchangeable components, or scalable architectures that can be optimized for different process conditions. Some advanced designs incorporate active control systems that can adjust flow characteristics in response to changing thermal loads. This approach enables optimization not just for a single operating point but across a range of conditions throughout the equipment lifecycle.
02 Flow distribution and turbulence enhancement
Techniques for improving flow distribution and enhancing turbulence in spiral heat exchangers can optimize heat transfer performance. These include the incorporation of flow disruptors, vortex generators, and specialized inlet/outlet configurations. By creating controlled turbulence and ensuring uniform flow distribution across the heat exchange surface, these design modifications can significantly increase thermal efficiency while minimizing pressure drop.Expand Specific Solutions03 Material selection and surface treatment
The choice of materials and surface treatments plays a crucial role in optimizing spiral heat exchangers. Advanced materials with superior thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and mechanical properties can enhance performance and durability. Surface modifications such as micro-structuring, coating applications, and roughness optimization can improve heat transfer coefficients and reduce fouling, leading to more efficient and longer-lasting heat exchange systems.Expand Specific Solutions04 Computational modeling and simulation techniques
Advanced computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and thermal modeling techniques are employed to optimize spiral heat exchanger designs. These simulation methods allow engineers to predict performance under various operating conditions, analyze flow patterns, and identify potential improvements without costly physical prototyping. Parametric studies and optimization algorithms can be used to determine the ideal configuration for specific applications, resulting in more efficient and cost-effective designs.Expand Specific Solutions05 Multi-phase and specialized application optimizations
Design optimizations for spiral heat exchangers handling multi-phase flows or specialized applications require unique considerations. These include phase separation features, condensation enhancement structures, and application-specific modifications. By tailoring the design to address the particular challenges of processes involving gas-liquid mixtures, phase changes, or extreme operating conditions, these optimizations can significantly improve performance in specialized industrial applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Competitive Landscape
The design optimization of spiral heat exchangers is currently in a growth phase, with an estimated global market size of $2.5-3 billion and projected annual growth of 5-7%. The technology has reached moderate maturity but continues to evolve with advanced computational methods and materials. Key industry players include Alfa Laval Corporate AB and Alfa Laval Spiral SAS, who dominate with comprehensive product portfolios and extensive R&D capabilities. Other significant competitors include SPIREC, Viessmann Group, and ECOTHERM Austria focusing on specialized applications. Academic institutions like Xi'an Jiaotong University, Chongqing University, and Beihang University contribute fundamental research advancing thermal efficiency and compact designs, while companies like Mitsubishi Electric and Panasonic integrate these exchangers into broader energy systems.
Xi'an Jiaotong University
Technical Solution: Xi'an Jiaotong University has developed innovative computational approaches for spiral heat exchanger optimization through their State Key Laboratory of Multiphase Flow. Their research combines advanced numerical simulation techniques with experimental validation to create comprehensive design methodologies. The university has pioneered novel mathematical models that accurately predict thermal-hydraulic performance across various operating conditions, incorporating both laminar and turbulent flow regimes. Their optimization approach utilizes genetic algorithms and machine learning techniques to identify optimal geometric parameters including spiral pitch, channel width variation, and entrance configurations. The research team has developed specialized correlations for heat transfer and pressure drop that account for curvature-induced secondary flows unique to spiral geometries, enabling more accurate performance prediction than traditional straight-channel correlations.
Strengths: Cutting-edge theoretical foundation based on fundamental research; comprehensive modeling approach incorporating multiple physical phenomena; innovative optimization algorithms. Weaknesses: Potentially limited industrial validation compared to commercial entities; focus may be more academic than practical implementation; possible gaps between theoretical models and manufacturing constraints.
Alfa Laval Corporate AB
Technical Solution: Alfa Laval has pioneered advanced computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling techniques for spiral heat exchanger optimization. Their approach combines 3D CFD simulations with proprietary algorithms to analyze flow distribution, pressure drop, and heat transfer characteristics. The company has developed specialized design software that optimizes spiral geometry based on specific process requirements, allowing for customization of channel spacing, plate thickness, and spiral curvature. Their technology incorporates thermal expansion compensation mechanisms and optimized flow distribution headers that minimize dead zones and maximize heat transfer efficiency. Alfa Laval's spiral heat exchangers feature self-cleaning designs with counter-current flow arrangements that achieve temperature approaches as close as 3°C, significantly outperforming traditional shell-and-tube exchangers in fouling applications.
Strengths: Superior thermal efficiency in limited footprint; excellent fouling resistance in challenging media; ability to handle multiple phases simultaneously. Weaknesses: Higher initial manufacturing costs compared to simpler heat exchanger designs; limited pressure ratings compared to some alternative technologies; complex maintenance procedures requiring specialized expertise.
Critical Patents and Technical Literature Review
Heat exchanger
PatentWO2015020047A1
Innovation
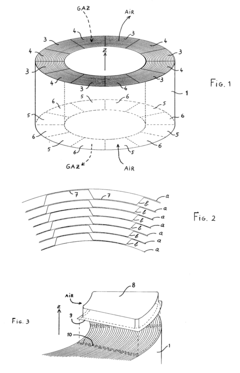
- A heat exchanger design featuring a spiral passage with equal passage widths in both the center and orthogonal directions to the spiral tube, ensuring even fluid flow and maximizing heat transfer area utilization, with a channel width ratio of 0.7 to 1.3, and incorporating features like wavy partition walls and projections to enhance flow uniformity and assembly efficiency.
Spiral heat exchanger
PatentInactiveEP0798527A1
Innovation
- A spiral-wound heat exchanger design where fluids circulate countercurrently along the axis of a cylindrical roll formed by a pair of sheets, eliminating internal cutouts and welding stresses by using external distributor-collectors and brazing only the sheets between which the higher-pressure fluid flows, ensuring local pressure retention without a pressurization enclosure.
Computational Fluid Dynamics Applications
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) has emerged as an indispensable tool in the design optimization of spiral heat exchangers (SHEs), offering detailed insights into complex flow patterns and heat transfer mechanisms that are difficult to capture through traditional experimental methods. The application of CFD techniques enables engineers to visualize and analyze the intricate fluid dynamics within the spiral channels, providing a comprehensive understanding of pressure drop, temperature distribution, and heat transfer coefficients.
Modern CFD software packages such as ANSYS Fluent, COMSOL Multiphysics, and OpenFOAM have been extensively utilized to simulate the performance of SHEs under various operating conditions. These simulations typically involve solving the Navier-Stokes equations coupled with energy equations, employing appropriate turbulence models such as k-ε, k-ω, or Reynolds Stress Model depending on the flow regime characteristics within the spiral channels.
The mesh generation for SHEs presents unique challenges due to their complex geometry. Structured hexahedral meshes are preferred for accuracy, but the curved nature of spiral channels often necessitates hybrid meshing approaches. Recent advancements in adaptive mesh refinement techniques have significantly improved the efficiency of CFD simulations for SHEs, allowing for finer resolution in critical regions while maintaining computational feasibility.
Parametric CFD studies have proven particularly valuable in optimizing geometric features of SHEs, including channel spacing, curvature radius, and entrance configurations. These studies have revealed that the centrifugal forces induced by the spiral geometry create secondary flows that can either enhance or impede heat transfer depending on the specific design parameters and operating conditions.
Multi-physics CFD simulations incorporating conjugate heat transfer, phase change phenomena, and even structural mechanics have advanced the holistic understanding of SHE performance. For instance, coupled fluid-structure interaction analyses help predict thermal stress distributions and potential deformation under extreme operating conditions, which is crucial for applications in high-temperature or high-pressure environments.
Machine learning techniques are increasingly being integrated with CFD for SHE optimization, creating surrogate models that can rapidly predict performance across a wide design space. This approach has dramatically reduced the computational resources required for comprehensive design optimization, enabling engineers to explore innovative configurations that might otherwise be overlooked using traditional design methodologies.
The validation of CFD results against experimental data remains essential, with recent studies showing good agreement between simulated and measured performance metrics when appropriate modeling approaches are employed. This validation process has established CFD as a reliable tool for the virtual prototyping of SHEs, substantially reducing development time and costs associated with physical testing.
Modern CFD software packages such as ANSYS Fluent, COMSOL Multiphysics, and OpenFOAM have been extensively utilized to simulate the performance of SHEs under various operating conditions. These simulations typically involve solving the Navier-Stokes equations coupled with energy equations, employing appropriate turbulence models such as k-ε, k-ω, or Reynolds Stress Model depending on the flow regime characteristics within the spiral channels.
The mesh generation for SHEs presents unique challenges due to their complex geometry. Structured hexahedral meshes are preferred for accuracy, but the curved nature of spiral channels often necessitates hybrid meshing approaches. Recent advancements in adaptive mesh refinement techniques have significantly improved the efficiency of CFD simulations for SHEs, allowing for finer resolution in critical regions while maintaining computational feasibility.
Parametric CFD studies have proven particularly valuable in optimizing geometric features of SHEs, including channel spacing, curvature radius, and entrance configurations. These studies have revealed that the centrifugal forces induced by the spiral geometry create secondary flows that can either enhance or impede heat transfer depending on the specific design parameters and operating conditions.
Multi-physics CFD simulations incorporating conjugate heat transfer, phase change phenomena, and even structural mechanics have advanced the holistic understanding of SHE performance. For instance, coupled fluid-structure interaction analyses help predict thermal stress distributions and potential deformation under extreme operating conditions, which is crucial for applications in high-temperature or high-pressure environments.
Machine learning techniques are increasingly being integrated with CFD for SHE optimization, creating surrogate models that can rapidly predict performance across a wide design space. This approach has dramatically reduced the computational resources required for comprehensive design optimization, enabling engineers to explore innovative configurations that might otherwise be overlooked using traditional design methodologies.
The validation of CFD results against experimental data remains essential, with recent studies showing good agreement between simulated and measured performance metrics when appropriate modeling approaches are employed. This validation process has established CFD as a reliable tool for the virtual prototyping of SHEs, substantially reducing development time and costs associated with physical testing.
Materials Science Advancements for Enhanced Performance
Recent advancements in materials science have significantly impacted the design optimization of spiral heat exchangers (SHEs). Traditional materials like carbon steel and stainless steel are being enhanced or replaced with innovative alternatives that offer superior thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and mechanical properties under extreme operating conditions.
Nanomaterial-enhanced metals represent a breakthrough in heat exchanger technology. The incorporation of carbon nanotubes and graphene into conventional metal matrices has demonstrated up to 45% improvement in thermal conductivity while maintaining structural integrity. These composite materials enable the design of more compact SHEs with enhanced heat transfer rates, particularly beneficial in space-constrained industrial applications.
Advanced polymer composites are emerging as viable alternatives in low to medium temperature applications. Reinforced thermoplastics with ceramic fillers offer excellent chemical resistance while providing adequate thermal performance. These materials reduce weight by up to 60% compared to metal counterparts and significantly lower manufacturing costs through simplified fabrication processes.
Surface engineering technologies have revolutionized the performance of existing materials. Hydrophobic and oleophobic coatings minimize fouling in SHEs, maintaining optimal heat transfer efficiency over extended operational periods. Studies indicate that these coatings can reduce maintenance frequency by up to 40% and extend service life by 3-5 years in challenging environments such as petrochemical processing.
Additive manufacturing has enabled the production of complex geometries with tailored material properties. 3D-printed SHEs with functionally graded materials optimize thermal performance by strategically varying material composition throughout the structure. This approach allows engineers to address specific thermal challenges in different regions of the exchanger, improving overall efficiency by 15-25%.
High-entropy alloys (HEAs) represent the cutting edge of metallurgical research for extreme environment applications. These multi-principal element alloys demonstrate exceptional stability at high temperatures and pressures while resisting corrosion from aggressive media. HEAs are particularly promising for SHEs in next-generation power plants and chemical processing facilities where conventional materials rapidly degrade.
Biomimetic materials inspired by natural heat exchange systems are gaining attention for their potential to revolutionize SHE design. Structures mimicking vascular networks in plants or thermoregulation mechanisms in animals have demonstrated remarkable efficiency in laboratory tests, suggesting a promising direction for future material development.
Nanomaterial-enhanced metals represent a breakthrough in heat exchanger technology. The incorporation of carbon nanotubes and graphene into conventional metal matrices has demonstrated up to 45% improvement in thermal conductivity while maintaining structural integrity. These composite materials enable the design of more compact SHEs with enhanced heat transfer rates, particularly beneficial in space-constrained industrial applications.
Advanced polymer composites are emerging as viable alternatives in low to medium temperature applications. Reinforced thermoplastics with ceramic fillers offer excellent chemical resistance while providing adequate thermal performance. These materials reduce weight by up to 60% compared to metal counterparts and significantly lower manufacturing costs through simplified fabrication processes.
Surface engineering technologies have revolutionized the performance of existing materials. Hydrophobic and oleophobic coatings minimize fouling in SHEs, maintaining optimal heat transfer efficiency over extended operational periods. Studies indicate that these coatings can reduce maintenance frequency by up to 40% and extend service life by 3-5 years in challenging environments such as petrochemical processing.
Additive manufacturing has enabled the production of complex geometries with tailored material properties. 3D-printed SHEs with functionally graded materials optimize thermal performance by strategically varying material composition throughout the structure. This approach allows engineers to address specific thermal challenges in different regions of the exchanger, improving overall efficiency by 15-25%.
High-entropy alloys (HEAs) represent the cutting edge of metallurgical research for extreme environment applications. These multi-principal element alloys demonstrate exceptional stability at high temperatures and pressures while resisting corrosion from aggressive media. HEAs are particularly promising for SHEs in next-generation power plants and chemical processing facilities where conventional materials rapidly degrade.
Biomimetic materials inspired by natural heat exchange systems are gaining attention for their potential to revolutionize SHE design. Structures mimicking vascular networks in plants or thermoregulation mechanisms in animals have demonstrated remarkable efficiency in laboratory tests, suggesting a promising direction for future material development.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!