Compact heat exchanger design for electric vehicles
OCT 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
EV Heat Exchanger Evolution and Objectives
Heat exchanger technology in electric vehicles has undergone significant evolution since the early 2010s when EVs began gaining mainstream market traction. Initially, EV thermal management systems were adapted from conventional internal combustion engine vehicles, with minimal optimization for electric powertrains. These early systems were characterized by bulky, heavy heat exchangers that occupied considerable space and added unnecessary weight to vehicles already burdened by heavy battery packs.
The technological trajectory shifted dramatically around 2015-2017 when dedicated EV platforms emerged, necessitating purpose-built thermal management solutions. This period marked the transition from single-function heat exchangers to integrated thermal management systems capable of addressing multiple cooling and heating requirements simultaneously. The industry recognized that EVs present unique thermal challenges, including battery temperature regulation, power electronics cooling, and cabin climate control, all without the abundant waste heat generated by combustion engines.
By 2020, compact heat exchanger designs became a critical focus area for EV manufacturers seeking to maximize interior space, reduce vehicle weight, and improve overall energy efficiency. The primary objective evolved from simply providing adequate cooling to optimizing the entire thermal ecosystem of the vehicle while minimizing energy consumption and spatial requirements.
Current technological objectives for compact heat exchangers in EVs center around several key parameters. First, volumetric efficiency has become paramount, with designs aiming to achieve maximum heat transfer capacity per unit volume. Second, weight reduction remains critical for extending vehicle range, with manufacturers targeting up to 30% weight reduction compared to previous generation heat exchangers. Third, multi-functionality has emerged as a design imperative, with modern systems expected to handle cooling for batteries, motors, power electronics, and cabin climate control within an integrated architecture.
Another significant objective is operational efficiency across the wide temperature range EVs experience, from sub-zero winter conditions to extreme summer heat. This has driven innovation in materials science, with advanced aluminum alloys, polymer composites, and novel manufacturing techniques like additive manufacturing gaining prominence in the industry.
Looking forward, the technological roadmap for EV heat exchangers aims to achieve further miniaturization while enhancing thermal performance, with particular emphasis on supporting ultra-fast charging capabilities that generate significant heat loads. Additionally, there is growing focus on developing heat exchangers that can facilitate waste heat recovery systems, potentially improving overall vehicle efficiency by 5-8% in cold weather conditions.
The technological trajectory shifted dramatically around 2015-2017 when dedicated EV platforms emerged, necessitating purpose-built thermal management solutions. This period marked the transition from single-function heat exchangers to integrated thermal management systems capable of addressing multiple cooling and heating requirements simultaneously. The industry recognized that EVs present unique thermal challenges, including battery temperature regulation, power electronics cooling, and cabin climate control, all without the abundant waste heat generated by combustion engines.
By 2020, compact heat exchanger designs became a critical focus area for EV manufacturers seeking to maximize interior space, reduce vehicle weight, and improve overall energy efficiency. The primary objective evolved from simply providing adequate cooling to optimizing the entire thermal ecosystem of the vehicle while minimizing energy consumption and spatial requirements.
Current technological objectives for compact heat exchangers in EVs center around several key parameters. First, volumetric efficiency has become paramount, with designs aiming to achieve maximum heat transfer capacity per unit volume. Second, weight reduction remains critical for extending vehicle range, with manufacturers targeting up to 30% weight reduction compared to previous generation heat exchangers. Third, multi-functionality has emerged as a design imperative, with modern systems expected to handle cooling for batteries, motors, power electronics, and cabin climate control within an integrated architecture.
Another significant objective is operational efficiency across the wide temperature range EVs experience, from sub-zero winter conditions to extreme summer heat. This has driven innovation in materials science, with advanced aluminum alloys, polymer composites, and novel manufacturing techniques like additive manufacturing gaining prominence in the industry.
Looking forward, the technological roadmap for EV heat exchangers aims to achieve further miniaturization while enhancing thermal performance, with particular emphasis on supporting ultra-fast charging capabilities that generate significant heat loads. Additionally, there is growing focus on developing heat exchangers that can facilitate waste heat recovery systems, potentially improving overall vehicle efficiency by 5-8% in cold weather conditions.
Market Demand Analysis for Compact EV Thermal Systems
The electric vehicle (EV) market is experiencing unprecedented growth globally, with a compound annual growth rate exceeding 21% between 2020-2025. This rapid expansion has created a significant demand for advanced thermal management systems, particularly compact heat exchangers that can efficiently handle the unique thermal challenges of electric powertrains.
Market research indicates that the global EV thermal management system market is projected to reach $13.6 billion by 2027, with compact heat exchangers representing approximately 30% of this segment. This growth is primarily driven by the increasing energy density of battery systems and the need for more efficient cooling solutions that can maintain optimal operating temperatures while minimizing space and weight.
Consumer preferences are shifting toward EVs with longer ranges and faster charging capabilities, both of which generate substantial heat that must be effectively managed. Survey data from major automotive markets reveals that over 65% of potential EV buyers consider thermal efficiency and battery longevity as critical factors in their purchasing decisions, highlighting the market pull for advanced thermal solutions.
Regional analysis shows varying demands across markets. In Europe, stringent emissions regulations are accelerating EV adoption, creating immediate demand for compact thermal systems. The North American market emphasizes performance and range, driving interest in high-efficiency cooling solutions. Meanwhile, the Asia-Pacific region, led by China, focuses on cost-effective thermal management systems for mass-market EVs.
Industry trends indicate a growing preference for integrated thermal management systems that can simultaneously address battery cooling, cabin climate control, and power electronics thermal regulation. This integration trend is creating market opportunities for compact, multi-functional heat exchangers that can operate across different temperature ranges and cooling requirements.
Fleet operators and ride-sharing companies represent an emerging market segment with specific thermal management needs. These commercial users prioritize system durability, maintenance intervals, and total cost of ownership, creating demand for robust heat exchanger designs that can withstand intensive duty cycles while maintaining efficiency.
Supply chain analysis reveals potential constraints in specialized materials required for high-performance compact heat exchangers, including advanced aluminum alloys and specialized polymers. These supply limitations could impact market growth and pricing dynamics, potentially creating premium segments for manufacturers who can secure reliable material sources.
Market research indicates that the global EV thermal management system market is projected to reach $13.6 billion by 2027, with compact heat exchangers representing approximately 30% of this segment. This growth is primarily driven by the increasing energy density of battery systems and the need for more efficient cooling solutions that can maintain optimal operating temperatures while minimizing space and weight.
Consumer preferences are shifting toward EVs with longer ranges and faster charging capabilities, both of which generate substantial heat that must be effectively managed. Survey data from major automotive markets reveals that over 65% of potential EV buyers consider thermal efficiency and battery longevity as critical factors in their purchasing decisions, highlighting the market pull for advanced thermal solutions.
Regional analysis shows varying demands across markets. In Europe, stringent emissions regulations are accelerating EV adoption, creating immediate demand for compact thermal systems. The North American market emphasizes performance and range, driving interest in high-efficiency cooling solutions. Meanwhile, the Asia-Pacific region, led by China, focuses on cost-effective thermal management systems for mass-market EVs.
Industry trends indicate a growing preference for integrated thermal management systems that can simultaneously address battery cooling, cabin climate control, and power electronics thermal regulation. This integration trend is creating market opportunities for compact, multi-functional heat exchangers that can operate across different temperature ranges and cooling requirements.
Fleet operators and ride-sharing companies represent an emerging market segment with specific thermal management needs. These commercial users prioritize system durability, maintenance intervals, and total cost of ownership, creating demand for robust heat exchanger designs that can withstand intensive duty cycles while maintaining efficiency.
Supply chain analysis reveals potential constraints in specialized materials required for high-performance compact heat exchangers, including advanced aluminum alloys and specialized polymers. These supply limitations could impact market growth and pricing dynamics, potentially creating premium segments for manufacturers who can secure reliable material sources.
Current Challenges in EV Heat Exchanger Technology
Despite significant advancements in electric vehicle thermal management systems, compact heat exchanger design faces several critical challenges that impede optimal performance and efficiency. The primary constraint remains the limited space availability within EV architectures, where power electronics, batteries, and motors compete for positioning. Engineers must design heat exchangers that deliver sufficient cooling capacity while maintaining minimal volume and weight profiles, a balance that becomes increasingly difficult as power densities rise in modern EVs.
Material limitations present another significant hurdle. Traditional aluminum heat exchangers struggle to meet the demanding thermal conductivity requirements of high-performance EVs, while more advanced materials like copper and specialized alloys introduce cost and manufacturing complexities. The industry continues to search for materials offering optimal thermal performance without compromising weight targets or production scalability.
The multi-temperature loop challenge further complicates heat exchanger design. Modern EVs require thermal management across vastly different temperature ranges – from battery systems operating optimally between 20-40°C to power electronics that may reach 85°C during operation. Designing compact exchangers capable of efficiently managing these diverse thermal requirements while maintaining system integration remains technically demanding.
Manufacturing complexity represents another substantial barrier. Advanced heat exchanger designs with intricate internal geometries that maximize heat transfer surface area often encounter production limitations. Techniques like additive manufacturing offer promising solutions but remain cost-prohibitive for mass production, creating a gap between theoretical optimal designs and commercially viable solutions.
Energy efficiency concerns are paramount as every watt consumed by thermal management systems directly impacts vehicle range. Current heat exchanger technologies often require supplementary pumps and fans that introduce parasitic energy losses. The industry seeks passive or low-energy cooling solutions that maintain thermal performance while minimizing auxiliary power consumption.
Durability and reliability under variable operating conditions pose additional challenges. Heat exchangers must withstand thermal cycling, vibration, and potential exposure to road contaminants while maintaining consistent performance throughout the vehicle's lifespan. This becomes particularly challenging when designing ultra-compact systems with minimal material thickness and complex flow paths.
Cost considerations ultimately constrain innovation pathways. While novel designs utilizing advanced manufacturing techniques and exotic materials demonstrate superior thermal performance in laboratory settings, their commercial viability remains limited by production economics. The industry continues to seek the optimal balance between performance, compactness, and cost-effectiveness to enable widespread adoption of next-generation thermal management solutions.
Material limitations present another significant hurdle. Traditional aluminum heat exchangers struggle to meet the demanding thermal conductivity requirements of high-performance EVs, while more advanced materials like copper and specialized alloys introduce cost and manufacturing complexities. The industry continues to search for materials offering optimal thermal performance without compromising weight targets or production scalability.
The multi-temperature loop challenge further complicates heat exchanger design. Modern EVs require thermal management across vastly different temperature ranges – from battery systems operating optimally between 20-40°C to power electronics that may reach 85°C during operation. Designing compact exchangers capable of efficiently managing these diverse thermal requirements while maintaining system integration remains technically demanding.
Manufacturing complexity represents another substantial barrier. Advanced heat exchanger designs with intricate internal geometries that maximize heat transfer surface area often encounter production limitations. Techniques like additive manufacturing offer promising solutions but remain cost-prohibitive for mass production, creating a gap between theoretical optimal designs and commercially viable solutions.
Energy efficiency concerns are paramount as every watt consumed by thermal management systems directly impacts vehicle range. Current heat exchanger technologies often require supplementary pumps and fans that introduce parasitic energy losses. The industry seeks passive or low-energy cooling solutions that maintain thermal performance while minimizing auxiliary power consumption.
Durability and reliability under variable operating conditions pose additional challenges. Heat exchangers must withstand thermal cycling, vibration, and potential exposure to road contaminants while maintaining consistent performance throughout the vehicle's lifespan. This becomes particularly challenging when designing ultra-compact systems with minimal material thickness and complex flow paths.
Cost considerations ultimately constrain innovation pathways. While novel designs utilizing advanced manufacturing techniques and exotic materials demonstrate superior thermal performance in laboratory settings, their commercial viability remains limited by production economics. The industry continues to seek the optimal balance between performance, compactness, and cost-effectiveness to enable widespread adoption of next-generation thermal management solutions.
State-of-the-Art Compact Heat Exchanger Solutions
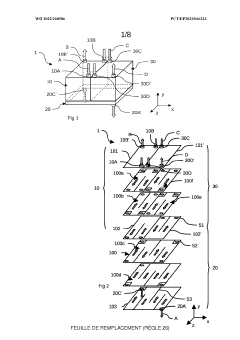
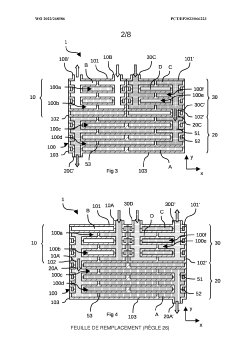
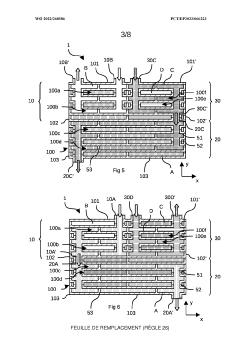
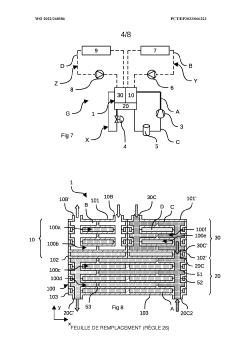
01 Compact heat exchanger designs with enhanced surface area
Heat exchangers can be made more compact by increasing the surface area available for heat transfer within a given volume. This can be achieved through the use of fins, corrugated plates, or other surface enhancements that maximize the contact area between the heat transfer medium and the exchanger surfaces. These designs allow for efficient heat transfer while minimizing the overall size of the heat exchanger.- Compact heat exchanger designs: Compact heat exchanger designs focus on maximizing heat transfer surface area while minimizing the overall volume. These designs often incorporate features such as fins, microchannels, or specialized geometries to increase the heat transfer efficiency in a limited space. The compactness factor is particularly important in applications where space constraints are significant, such as in automotive, aerospace, or portable systems.
- Advanced materials for heat exchanger compactness: The use of advanced materials with superior thermal conductivity properties enables the development of more compact heat exchangers. Materials such as high-conductivity metals, composites, or specialized alloys allow for thinner walls and more efficient heat transfer, reducing the overall size requirements. These materials can withstand higher operating temperatures and pressures while maintaining structural integrity, further contributing to the compactness of the heat exchanger design.
- Innovative flow arrangements for compact heat exchangers: Innovative flow arrangements, such as counter-flow, cross-flow, or multi-pass configurations, can significantly enhance the efficiency of compact heat exchangers. These arrangements optimize the temperature gradient between the fluids, maximizing heat transfer in a limited space. Advanced flow distribution techniques ensure uniform fluid distribution across the heat transfer surface, preventing hotspots and improving overall performance of compact heat exchangers.
- Additive manufacturing for complex compact geometries: Additive manufacturing technologies enable the production of heat exchangers with complex internal geometries that would be impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. These complex structures can include intricate channel networks, variable wall thicknesses, and integrated features that maximize heat transfer surface area while minimizing volume. The design freedom offered by additive manufacturing allows for highly optimized, application-specific compact heat exchangers with improved performance characteristics.
- Modular and stackable heat exchanger systems: Modular and stackable heat exchanger designs allow for flexible configuration while maintaining high compactness. These systems can be scaled according to specific application requirements without sacrificing efficiency. The modular approach enables easier maintenance, replacement of individual components, and adaptation to changing thermal management needs. Standardized connection interfaces between modules ensure reliable operation while minimizing the overall footprint of the heat exchange system.
02 Microchannel and mini-channel heat exchanger technology
Microchannel and mini-channel heat exchangers utilize very small flow passages to increase heat transfer efficiency while reducing the overall size of the unit. These designs feature multiple parallel channels with small hydraulic diameters that enhance heat transfer coefficients and reduce the required heat transfer area. This technology is particularly useful in applications where space constraints are significant and high thermal performance is required.Expand Specific Solutions03 Innovative materials for compact heat exchangers
Advanced materials with superior thermal conductivity properties can significantly improve heat exchanger compactness. Materials such as aluminum alloys, copper alloys, and composite materials allow for thinner walls and more efficient heat transfer, reducing the overall size requirements. Additionally, these materials often offer benefits such as corrosion resistance and reduced weight, further enhancing the performance of compact heat exchangers.Expand Specific Solutions04 Optimized flow arrangements and configurations
The arrangement of flow paths within heat exchangers can significantly impact their compactness. Innovative configurations such as counter-flow, cross-flow, or multi-pass arrangements can maximize heat transfer efficiency while minimizing the required size. Advanced computational fluid dynamics modeling helps optimize these flow patterns to achieve the highest possible heat transfer rates in the smallest possible volume.Expand Specific Solutions05 Additive manufacturing for complex heat exchanger geometries
Additive manufacturing techniques enable the production of heat exchangers with complex internal geometries that would be impossible to create using traditional manufacturing methods. These complex structures can incorporate features such as lattice structures, variable channel dimensions, and integrated flow distributors that maximize heat transfer efficiency while minimizing size. This approach allows for highly customized designs optimized for specific applications and space constraints.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Competitive Landscape
The compact heat exchanger market for electric vehicles is in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by the EV industry's expansion. The market is characterized by competition between established automotive thermal management players like Valeo, MAHLE, and Hanon Systems, alongside new entrants from EV manufacturers such as BYD and Polestar. Technical maturity varies, with traditional suppliers leveraging existing expertise while adapting to EV-specific requirements. Chinese companies including Sunwoda and Wuhu Hantway are rapidly advancing their capabilities, while European firms like Behr and Webasto maintain strong positions through innovation. The integration of digital technologies, exemplified by Huawei Digital Power's involvement, is pushing the industry toward more sophisticated thermal management solutions.
Valeo Thermal Systems Japan Corp.
Technical Solution: Valeo has developed an innovative compact heat exchanger design specifically for electric vehicles that utilizes a stacked plate architecture with enhanced surface area. Their solution incorporates micro-channel technology with optimized flow distribution to maximize heat transfer efficiency while minimizing size and weight. The design features aluminum alloy construction with specialized coatings to prevent corrosion and enhance durability. Valeo's system integrates seamlessly with battery thermal management systems, utilizing a smart control algorithm that adapts cooling/heating capacity based on real-time battery temperature monitoring. Their design achieves approximately 30% higher heat transfer coefficient compared to conventional designs while reducing the overall volume by up to 25%. The system is particularly effective for fast-charging applications, where thermal management is critical for battery longevity and safety.
Strengths: Superior heat transfer efficiency in a compact form factor, excellent integration with battery management systems, and proven reliability in extreme temperature conditions. Weaknesses: Higher manufacturing costs compared to traditional heat exchangers and requires specialized manufacturing processes that may limit production scalability.
Behr GmbH & Co. KG
Technical Solution: Behr (now part of MAHLE) has pioneered a compact heat exchanger design for EVs featuring a layered multi-material approach that optimizes thermal conductivity while reducing weight. Their technology employs a combination of aluminum and polymer components in a brazed plate design that maximizes surface area contact while minimizing fluid volume requirements. The heat exchanger incorporates turbulence-enhancing microstructures that improve heat transfer coefficients by up to 40% compared to conventional designs. Behr's solution is particularly notable for its integration capabilities, designed to function simultaneously with multiple vehicle systems including battery cooling, cabin climate control, and power electronics thermal management. The design features modular construction that allows for customization based on specific vehicle platform requirements while maintaining manufacturing efficiency. Their latest generation achieves a 35% reduction in size compared to previous designs while handling the increased thermal loads of fast-charging EV batteries.
Strengths: Exceptional thermal performance in a lightweight package, versatile integration with multiple vehicle systems, and modular design approach that supports platform flexibility. Weaknesses: Complex manufacturing process with higher initial tooling costs and potential challenges in serviceability due to the integrated design approach.
Key Patents and Innovations in EV Thermal Management
Advanced vehicle heat exchanger
PatentActiveUS20250100353A1
Innovation
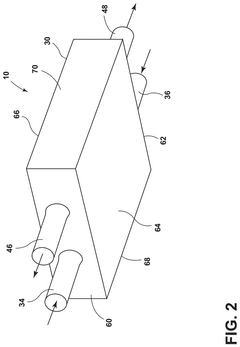
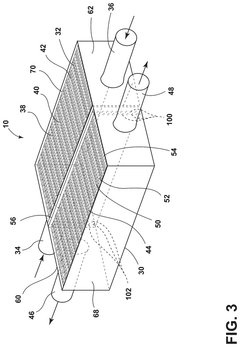
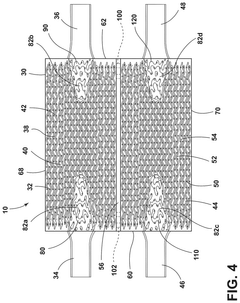
- A heat exchanger design featuring a housing with a first and second cooling block, each with gyroid structures defining coolant and refrigerant channels, and a perforated barrier plate for fluid communication between them, facilitating counter-flow configuration for enhanced thermal transfer.
Plate heat exchanger having a large number of heat exchange compartments
PatentWO2022268586A1
Innovation
- A compact plate heat exchanger design comprising multiple heat exchange compartments with specific circulation paths for different heat transfer fluids, allowing for efficient heat exchange between refrigerant and heat transfer fluids, and integrating functions like condensers and coolers within a single, stacked structure, reducing the need for multiple components and simplifying connections.
Materials Science Advancements for Thermal Efficiency
Recent advancements in materials science have revolutionized thermal management solutions for compact heat exchangers in electric vehicles. Novel composite materials with enhanced thermal conductivity properties are emerging as game-changers in this field. These materials, including metal matrix composites (MMCs) incorporating graphene, carbon nanotubes, and ceramic particles, demonstrate thermal conductivity values up to 40% higher than traditional aluminum alloys while maintaining comparable weight profiles.
Phase change materials (PCMs) represent another significant breakthrough, offering exceptional thermal energy storage capabilities. These materials can absorb and release large amounts of energy during phase transitions, effectively stabilizing temperature fluctuations in battery systems. Advanced PCMs with tailored melting points between 40-60°C are particularly suitable for EV battery thermal management systems, providing precise temperature control during high-load operations.
Surface treatment technologies have also evolved substantially, with hydrophobic and oleophobic coatings that significantly reduce fouling and scaling in heat exchanger channels. These treatments maintain optimal thermal performance over extended operational periods, reducing maintenance requirements and extending service intervals by up to 30% compared to conventional designs.
Additive manufacturing has enabled the development of complex microstructured surfaces that enhance heat transfer coefficients by creating controlled turbulence patterns. 3D-printed heat exchangers with biomimetic surface patterns inspired by natural systems demonstrate heat transfer improvements of 15-25% compared to traditional flat or simple finned surfaces.
Polymer-derived ceramics (PDCs) offer exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance while providing lower density alternatives to metal components. These materials withstand temperatures exceeding 300°C while offering corrosion resistance against coolants and other automotive fluids, making them ideal for next-generation cooling systems that must operate under increasingly demanding conditions.
Nanofluids, consisting of conventional heat transfer fluids with suspended nanoparticles, show thermal conductivity enhancements of up to 40% at relatively low particle concentrations. These advanced coolants are particularly promising for compact heat exchangers where space constraints demand maximum thermal performance from every component.
Shape memory alloys and thermally responsive polymers are being integrated into adaptive heat exchanger designs that can physically reconfigure based on thermal loads, optimizing flow patterns and heat transfer surfaces according to real-time operating conditions. This dynamic response capability represents a paradigm shift from static heat exchanger designs to intelligent thermal management systems that continuously adapt to changing vehicle demands.
Phase change materials (PCMs) represent another significant breakthrough, offering exceptional thermal energy storage capabilities. These materials can absorb and release large amounts of energy during phase transitions, effectively stabilizing temperature fluctuations in battery systems. Advanced PCMs with tailored melting points between 40-60°C are particularly suitable for EV battery thermal management systems, providing precise temperature control during high-load operations.
Surface treatment technologies have also evolved substantially, with hydrophobic and oleophobic coatings that significantly reduce fouling and scaling in heat exchanger channels. These treatments maintain optimal thermal performance over extended operational periods, reducing maintenance requirements and extending service intervals by up to 30% compared to conventional designs.
Additive manufacturing has enabled the development of complex microstructured surfaces that enhance heat transfer coefficients by creating controlled turbulence patterns. 3D-printed heat exchangers with biomimetic surface patterns inspired by natural systems demonstrate heat transfer improvements of 15-25% compared to traditional flat or simple finned surfaces.
Polymer-derived ceramics (PDCs) offer exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance while providing lower density alternatives to metal components. These materials withstand temperatures exceeding 300°C while offering corrosion resistance against coolants and other automotive fluids, making them ideal for next-generation cooling systems that must operate under increasingly demanding conditions.
Nanofluids, consisting of conventional heat transfer fluids with suspended nanoparticles, show thermal conductivity enhancements of up to 40% at relatively low particle concentrations. These advanced coolants are particularly promising for compact heat exchangers where space constraints demand maximum thermal performance from every component.
Shape memory alloys and thermally responsive polymers are being integrated into adaptive heat exchanger designs that can physically reconfigure based on thermal loads, optimizing flow patterns and heat transfer surfaces according to real-time operating conditions. This dynamic response capability represents a paradigm shift from static heat exchanger designs to intelligent thermal management systems that continuously adapt to changing vehicle demands.
Integration Strategies with Battery Management Systems
The integration of compact heat exchangers with Battery Management Systems (BMS) represents a critical advancement in electric vehicle thermal management. Effective integration strategies must address the bidirectional communication between thermal systems and BMS to optimize battery performance, safety, and longevity. Modern approaches incorporate real-time thermal data exchange, allowing the BMS to make informed decisions about battery charging rates, power output limitations, and thermal management resource allocation based on heat exchanger performance metrics.
Advanced integration architectures employ unified control algorithms that balance thermal management priorities with battery state-of-charge considerations. These systems utilize predictive modeling to anticipate thermal loads during various driving conditions, enabling proactive rather than reactive thermal management. For instance, when the BMS detects an imminent high-power demand scenario, it can signal the thermal management system to increase cooling capacity preemptively, preventing potential thermal runaway situations.
Hardware integration has evolved toward modular designs that physically incorporate compact heat exchangers within or adjacent to battery modules. This proximity minimizes thermal response lag and reduces the complexity of coolant routing throughout the vehicle. Some cutting-edge designs feature direct cooling interfaces between heat exchanger surfaces and battery cells, eliminating intermediate thermal barriers and significantly improving heat transfer efficiency.
Communication protocols between heat exchangers and BMS have been standardized in recent years, with CAN-bus remaining predominant while newer systems adopt automotive ethernet for higher bandwidth thermal data transmission. These protocols support sophisticated thermal management features such as cell-level temperature balancing, where cooling resources are dynamically allocated to address hotspots within battery packs.
Fault tolerance represents another crucial aspect of integration strategy. Advanced systems implement redundant thermal monitoring channels and failsafe modes that can maintain minimum cooling capacity even during partial system failures. This redundancy is particularly important for fast-charging scenarios where thermal loads can increase rapidly and unpredictably.
Energy efficiency considerations have driven the development of integration strategies that minimize parasitic power consumption. Smart control algorithms optimize pump and fan operations based on actual cooling needs rather than worst-case scenarios, reducing the energy overhead of thermal management systems. Some manufacturers have implemented machine learning approaches that adapt thermal management strategies based on driver behavior patterns and environmental conditions, further enhancing efficiency.
Advanced integration architectures employ unified control algorithms that balance thermal management priorities with battery state-of-charge considerations. These systems utilize predictive modeling to anticipate thermal loads during various driving conditions, enabling proactive rather than reactive thermal management. For instance, when the BMS detects an imminent high-power demand scenario, it can signal the thermal management system to increase cooling capacity preemptively, preventing potential thermal runaway situations.
Hardware integration has evolved toward modular designs that physically incorporate compact heat exchangers within or adjacent to battery modules. This proximity minimizes thermal response lag and reduces the complexity of coolant routing throughout the vehicle. Some cutting-edge designs feature direct cooling interfaces between heat exchanger surfaces and battery cells, eliminating intermediate thermal barriers and significantly improving heat transfer efficiency.
Communication protocols between heat exchangers and BMS have been standardized in recent years, with CAN-bus remaining predominant while newer systems adopt automotive ethernet for higher bandwidth thermal data transmission. These protocols support sophisticated thermal management features such as cell-level temperature balancing, where cooling resources are dynamically allocated to address hotspots within battery packs.
Fault tolerance represents another crucial aspect of integration strategy. Advanced systems implement redundant thermal monitoring channels and failsafe modes that can maintain minimum cooling capacity even during partial system failures. This redundancy is particularly important for fast-charging scenarios where thermal loads can increase rapidly and unpredictably.
Energy efficiency considerations have driven the development of integration strategies that minimize parasitic power consumption. Smart control algorithms optimize pump and fan operations based on actual cooling needs rather than worst-case scenarios, reducing the energy overhead of thermal management systems. Some manufacturers have implemented machine learning approaches that adapt thermal management strategies based on driver behavior patterns and environmental conditions, further enhancing efficiency.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!