Heat exchanger fouling prediction and mitigation methods
OCT 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Heat Exchanger Fouling Background and Objectives
Heat exchanger fouling represents one of the most persistent challenges in industrial operations, with a documented history spanning over a century. The phenomenon involves the accumulation of unwanted deposits on heat transfer surfaces, which progressively reduces thermal efficiency, increases pressure drop, and ultimately leads to significant operational and economic consequences across various industries.
The evolution of fouling research began in the early 20th century with rudimentary observations, progressing through empirical studies in the 1950s-60s, and advancing to more sophisticated modeling approaches by the 1980s. Recent decades have witnessed an integration of computational fluid dynamics, machine learning techniques, and real-time monitoring systems, marking significant technological progression in this field.
Current industry estimates suggest that fouling-related issues cost global industries billions of dollars annually, with the petrochemical sector alone facing expenses exceeding $4.5 billion per year in the United States. These costs manifest through increased energy consumption, maintenance requirements, production losses during downtime, and premature equipment replacement.
The technical objectives of this research focus on developing robust predictive models for fouling behavior across diverse operational conditions and heat exchanger designs. These models aim to incorporate multiple fouling mechanisms including crystallization, particulate deposition, chemical reaction fouling, biological growth, and corrosion products. The integration of real-time monitoring capabilities represents a critical advancement goal to enable proactive maintenance strategies.
Additionally, this research seeks to establish effective mitigation strategies that balance prevention and remediation approaches. Prevention techniques encompass design optimizations, operational adjustments, and chemical treatments, while remediation focuses on cleaning methodologies that minimize operational disruption. The ultimate objective is to develop a comprehensive framework that enables industries to optimize heat exchanger performance while minimizing fouling-related costs.
The technological trajectory indicates movement toward predictive maintenance systems utilizing artificial intelligence and Internet of Things (IoT) integration. These advanced systems promise to transform reactive maintenance paradigms into proactive management strategies, potentially revolutionizing industrial operations through significant reductions in energy consumption, maintenance costs, and environmental impact.
The evolution of fouling research began in the early 20th century with rudimentary observations, progressing through empirical studies in the 1950s-60s, and advancing to more sophisticated modeling approaches by the 1980s. Recent decades have witnessed an integration of computational fluid dynamics, machine learning techniques, and real-time monitoring systems, marking significant technological progression in this field.
Current industry estimates suggest that fouling-related issues cost global industries billions of dollars annually, with the petrochemical sector alone facing expenses exceeding $4.5 billion per year in the United States. These costs manifest through increased energy consumption, maintenance requirements, production losses during downtime, and premature equipment replacement.
The technical objectives of this research focus on developing robust predictive models for fouling behavior across diverse operational conditions and heat exchanger designs. These models aim to incorporate multiple fouling mechanisms including crystallization, particulate deposition, chemical reaction fouling, biological growth, and corrosion products. The integration of real-time monitoring capabilities represents a critical advancement goal to enable proactive maintenance strategies.
Additionally, this research seeks to establish effective mitigation strategies that balance prevention and remediation approaches. Prevention techniques encompass design optimizations, operational adjustments, and chemical treatments, while remediation focuses on cleaning methodologies that minimize operational disruption. The ultimate objective is to develop a comprehensive framework that enables industries to optimize heat exchanger performance while minimizing fouling-related costs.
The technological trajectory indicates movement toward predictive maintenance systems utilizing artificial intelligence and Internet of Things (IoT) integration. These advanced systems promise to transform reactive maintenance paradigms into proactive management strategies, potentially revolutionizing industrial operations through significant reductions in energy consumption, maintenance costs, and environmental impact.
Market Demand Analysis for Fouling Prevention Solutions
The global market for fouling prevention solutions in heat exchangers is experiencing robust growth, driven primarily by increasing industrial awareness of efficiency losses and maintenance costs associated with fouling. Current market valuations indicate that the heat exchanger fouling prevention sector reached approximately 8.2 billion USD in 2022, with projections suggesting a compound annual growth rate of 6.7% through 2030. This growth trajectory reflects the critical importance of fouling mitigation across multiple industries.
The oil and gas sector represents the largest market segment, accounting for roughly 32% of the total demand for fouling prevention solutions. This dominance stems from the sector's extensive use of heat exchangers in refining processes and the severe fouling challenges posed by crude oil processing. Following closely is the chemical processing industry, which constitutes about 27% of the market, where fouling prevention is essential for maintaining production efficiency and product quality.
Power generation facilities, particularly thermal and nuclear plants, form another significant market segment at approximately 18%. These facilities rely heavily on efficient heat transfer systems, making fouling prevention critical to operational sustainability. The food and beverage industry, though smaller at 12% of the market share, shows the fastest growth rate at 8.3% annually, driven by stringent hygiene requirements and increasing automation.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market with combined shares exceeding 60%, attributed to their mature industrial bases and stringent regulatory environments regarding energy efficiency and emissions. However, the Asia-Pacific region is demonstrating the most aggressive growth, with China and India at the forefront, expanding at rates exceeding 9% annually as their industrial sectors modernize and adopt more sophisticated heat exchange technologies.
Market research indicates a clear shift in customer preferences toward predictive and preventive solutions rather than reactive maintenance approaches. This trend is evidenced by the 23% increase in investment in real-time monitoring systems and predictive analytics platforms over the past three years. End-users increasingly demand integrated solutions that combine monitoring technology, predictive algorithms, and automated cleaning systems, reflecting a holistic approach to fouling management.
Economic analyses reveal that industries are willing to invest in premium fouling prevention solutions when demonstrable return on investment can be achieved within 18-24 months. This economic threshold has become a critical benchmark for solution providers developing new technologies in this space, driving innovation toward more cost-effective and efficient prevention methodologies.
The oil and gas sector represents the largest market segment, accounting for roughly 32% of the total demand for fouling prevention solutions. This dominance stems from the sector's extensive use of heat exchangers in refining processes and the severe fouling challenges posed by crude oil processing. Following closely is the chemical processing industry, which constitutes about 27% of the market, where fouling prevention is essential for maintaining production efficiency and product quality.
Power generation facilities, particularly thermal and nuclear plants, form another significant market segment at approximately 18%. These facilities rely heavily on efficient heat transfer systems, making fouling prevention critical to operational sustainability. The food and beverage industry, though smaller at 12% of the market share, shows the fastest growth rate at 8.3% annually, driven by stringent hygiene requirements and increasing automation.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market with combined shares exceeding 60%, attributed to their mature industrial bases and stringent regulatory environments regarding energy efficiency and emissions. However, the Asia-Pacific region is demonstrating the most aggressive growth, with China and India at the forefront, expanding at rates exceeding 9% annually as their industrial sectors modernize and adopt more sophisticated heat exchange technologies.
Market research indicates a clear shift in customer preferences toward predictive and preventive solutions rather than reactive maintenance approaches. This trend is evidenced by the 23% increase in investment in real-time monitoring systems and predictive analytics platforms over the past three years. End-users increasingly demand integrated solutions that combine monitoring technology, predictive algorithms, and automated cleaning systems, reflecting a holistic approach to fouling management.
Economic analyses reveal that industries are willing to invest in premium fouling prevention solutions when demonstrable return on investment can be achieved within 18-24 months. This economic threshold has become a critical benchmark for solution providers developing new technologies in this space, driving innovation toward more cost-effective and efficient prevention methodologies.
Current Fouling Prediction Technologies and Challenges
Fouling prediction in heat exchangers currently relies on several methodologies, each with varying degrees of accuracy and applicability. Traditional empirical models based on historical data remain widely used in industry settings. These models typically correlate fouling resistance with operating time using mathematical expressions derived from experimental observations. While practical for specific applications, they often lack generalizability across different operating conditions and fluid compositions.
Threshold models represent an advancement in prediction technology, identifying critical conditions beyond which fouling accelerates. These models incorporate parameters such as wall temperature, flow velocity, and fluid composition to determine when deposition becomes significant. However, they frequently struggle with complex fluid systems where multiple fouling mechanisms operate simultaneously.
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) has emerged as a powerful tool for fouling prediction, enabling detailed simulation of fluid flow patterns, temperature distributions, and particle trajectories within heat exchangers. CFD models can predict local fouling rates based on transport phenomena and surface attachment mechanisms. Despite their sophistication, these models require extensive computational resources and detailed input parameters that may not be readily available in industrial settings.
Machine learning approaches represent the cutting edge of fouling prediction technology. By analyzing large datasets from operational heat exchangers, algorithms can identify patterns and correlations invisible to traditional modeling approaches. Neural networks, support vector machines, and random forests have demonstrated promising results in predicting fouling rates and identifying key contributing factors. The primary limitation remains the requirement for substantial high-quality historical data for training.
Real-time monitoring systems using sensors for pressure drop, heat transfer coefficient, and fluid composition provide continuous data for dynamic fouling prediction. These systems can detect early signs of fouling before significant performance degradation occurs, enabling proactive maintenance scheduling.
Despite these advances, significant challenges persist in fouling prediction technology. The multiphysics nature of fouling phenomena—involving fluid dynamics, heat transfer, chemical reactions, and surface science—makes comprehensive modeling extremely difficult. Interactions between different fouling mechanisms (particulate, crystallization, biological, chemical reaction, corrosion) further complicate prediction efforts.
Scale-up issues represent another major challenge, as laboratory-derived models often fail to accurately predict behavior in industrial-scale equipment. Additionally, the stochastic nature of fouling initiation introduces inherent unpredictability that deterministic models struggle to capture. Time-dependent changes in fouling layer properties, including thermal conductivity, porosity, and mechanical strength, further complicate long-term predictions.
The diversity of industrial fluids and operating conditions necessitates customized prediction approaches, limiting the development of universal fouling prediction methodologies. This fragmentation of knowledge and approaches represents perhaps the most significant barrier to advancing the field.
Threshold models represent an advancement in prediction technology, identifying critical conditions beyond which fouling accelerates. These models incorporate parameters such as wall temperature, flow velocity, and fluid composition to determine when deposition becomes significant. However, they frequently struggle with complex fluid systems where multiple fouling mechanisms operate simultaneously.
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) has emerged as a powerful tool for fouling prediction, enabling detailed simulation of fluid flow patterns, temperature distributions, and particle trajectories within heat exchangers. CFD models can predict local fouling rates based on transport phenomena and surface attachment mechanisms. Despite their sophistication, these models require extensive computational resources and detailed input parameters that may not be readily available in industrial settings.
Machine learning approaches represent the cutting edge of fouling prediction technology. By analyzing large datasets from operational heat exchangers, algorithms can identify patterns and correlations invisible to traditional modeling approaches. Neural networks, support vector machines, and random forests have demonstrated promising results in predicting fouling rates and identifying key contributing factors. The primary limitation remains the requirement for substantial high-quality historical data for training.
Real-time monitoring systems using sensors for pressure drop, heat transfer coefficient, and fluid composition provide continuous data for dynamic fouling prediction. These systems can detect early signs of fouling before significant performance degradation occurs, enabling proactive maintenance scheduling.
Despite these advances, significant challenges persist in fouling prediction technology. The multiphysics nature of fouling phenomena—involving fluid dynamics, heat transfer, chemical reactions, and surface science—makes comprehensive modeling extremely difficult. Interactions between different fouling mechanisms (particulate, crystallization, biological, chemical reaction, corrosion) further complicate prediction efforts.
Scale-up issues represent another major challenge, as laboratory-derived models often fail to accurately predict behavior in industrial-scale equipment. Additionally, the stochastic nature of fouling initiation introduces inherent unpredictability that deterministic models struggle to capture. Time-dependent changes in fouling layer properties, including thermal conductivity, porosity, and mechanical strength, further complicate long-term predictions.
The diversity of industrial fluids and operating conditions necessitates customized prediction approaches, limiting the development of universal fouling prediction methodologies. This fragmentation of knowledge and approaches represents perhaps the most significant barrier to advancing the field.
Current Prediction Models and Mitigation Strategies
01 Mechanical cleaning systems for heat exchangers
Various mechanical systems have been developed to clean heat exchangers and prevent fouling. These include automated brushes, scrapers, and other physical cleaning mechanisms that can operate while the heat exchanger remains in service. These systems physically remove deposits from heat transfer surfaces, maintaining thermal efficiency and reducing the need for chemical treatments or system shutdowns.- Anti-fouling coatings and surface treatments: Various coatings and surface treatments can be applied to heat exchanger surfaces to prevent or reduce fouling. These include hydrophobic coatings, anti-adhesion materials, and specialized surface modifications that minimize the attachment of deposits. Such treatments create surfaces that are less prone to fouling accumulation, thereby maintaining heat transfer efficiency for longer periods and reducing the frequency of cleaning operations.
- Mechanical cleaning systems and methods: Mechanical systems for cleaning heat exchangers include automated brushes, scrapers, and flow-driven devices that physically remove fouling deposits from heat transfer surfaces. These systems can operate continuously or intermittently without requiring shutdown of the heat exchanger. By maintaining clean surfaces, these mechanical cleaning methods help preserve optimal heat transfer efficiency and extend the operational life of heat exchange equipment.
- Chemical cleaning and fouling inhibition: Chemical approaches to managing heat exchanger fouling include both cleaning agents for removing existing deposits and inhibitors that prevent fouling formation. These chemicals can be added to the process fluid or applied during cleaning cycles. Specialized formulations target specific types of fouling such as scale, biological growth, or particulate matter, dissolving or dispersing the deposits while protecting the heat exchanger materials from corrosion.
- Design modifications for fouling mitigation: Heat exchanger designs can be optimized to minimize fouling through features such as enhanced flow distribution, turbulence promotion, and self-cleaning geometries. These design modifications include specialized tube arrangements, altered flow paths, and optimized fluid velocities that reduce dead zones where deposits tend to accumulate. By addressing fouling through fundamental design principles, these approaches can significantly extend operational periods between maintenance.
- Monitoring and predictive maintenance systems: Advanced monitoring systems use sensors, data analytics, and predictive algorithms to detect fouling formation in heat exchangers before performance is significantly impacted. These systems track parameters such as pressure drop, temperature differentials, and flow rates to identify early signs of fouling. By enabling condition-based maintenance rather than scheduled interventions, these technologies optimize cleaning operations and minimize downtime while maximizing heat exchanger efficiency.
02 Chemical treatment methods for fouling prevention
Chemical treatments are widely used to prevent and control fouling in heat exchangers. These include scale inhibitors, dispersants, biocides, and specialized formulations that can prevent the formation of deposits or dissolve existing fouling. These chemicals can be continuously dosed or applied during periodic cleaning cycles to maintain heat transfer efficiency and extend the operational life of heat exchange equipment.Expand Specific Solutions03 Advanced monitoring and detection systems
Modern heat exchanger systems incorporate advanced monitoring technologies to detect fouling at early stages. These include sensors, imaging systems, and predictive algorithms that can identify changes in thermal performance, pressure drop, or flow characteristics indicative of fouling development. Early detection allows for timely intervention before significant efficiency losses occur.Expand Specific Solutions04 Design innovations to minimize fouling
Heat exchanger designs have evolved to inherently reduce fouling tendencies. These innovations include optimized flow patterns, self-cleaning geometries, enhanced surface materials, and specialized tube or plate configurations that minimize areas where deposits can accumulate. Such design improvements can significantly extend operational periods between cleaning requirements.Expand Specific Solutions05 Hybrid cleaning and maintenance approaches
Comprehensive fouling management often combines multiple techniques in hybrid approaches. These systems integrate mechanical cleaning with chemical treatments, periodic backflushing, ultrasonic cleaning, or other technologies to address different types of fouling simultaneously. Such integrated approaches provide more effective fouling control across various operating conditions and contaminant types.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies and Research Institutions in Fouling Management
Heat exchanger fouling prediction and mitigation is currently in a growth phase, with the global market expanding due to increasing industrial efficiency demands. The market size is estimated to reach several billion dollars by 2025, driven by energy conservation needs across petrochemical, power generation, and manufacturing sectors. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels, with companies like ExxonMobil, Siemens, and Saudi Aramco leading in advanced predictive analytics and AI-based solutions. Électricité de France and China National Petroleum are developing innovative monitoring systems, while specialized firms like SilcoTek and Solenis focus on anti-fouling coatings and chemical treatments. Academic-industry partnerships with institutions like King Fahd University and East China University of Science & Technology are accelerating research into novel fouling prevention technologies.
ExxonMobil Technology & Engineering Co.
Technical Solution: ExxonMobil has developed comprehensive fouling prediction models that integrate machine learning algorithms with traditional heat transfer principles. Their approach combines real-time monitoring systems with predictive analytics to forecast fouling rates in various heat exchanger configurations. The company utilizes proprietary HEAT (Heat Exchanger Analysis Technology) software that incorporates fluid dynamics simulations to predict deposit formation patterns based on operating conditions, fluid compositions, and surface characteristics. ExxonMobil's mitigation strategy employs a multi-faceted approach including specialized chemical treatments that modify surface properties to reduce adhesion of foulants, optimized flow distribution designs to minimize dead zones, and automated cleaning systems that can be deployed without full system shutdown. Their technology also includes advanced materials with anti-fouling properties for critical heat exchange surfaces.
Strengths: Comprehensive integration of real-time data with predictive models allows for proactive maintenance scheduling. Their extensive field experience across various industries provides robust validation of prediction accuracy. Weaknesses: Solutions are often proprietary and require significant customization for different applications, potentially increasing implementation costs.
Siemens AG
Technical Solution: Siemens has pioneered digital twin technology for heat exchanger fouling prediction, creating virtual replicas of physical heat exchangers that simulate real-time operating conditions. Their approach combines physics-based models with AI algorithms to predict fouling progression with high accuracy. The Siemens SIMATIC PCS 7 control system integrates with these digital twins to provide continuous monitoring and early warning of fouling conditions. For mitigation, Siemens has developed automated cleaning technologies including ultrasonic anti-fouling systems that create high-frequency vibrations to prevent deposit formation and dislodge existing fouling layers. Their heat exchanger designs incorporate computational fluid dynamics (CFD) optimization to create self-cleaning flow patterns that minimize dead zones where fouling typically initiates. Additionally, Siemens offers predictive maintenance services using their MindSphere IoT platform to analyze operational data and recommend optimal cleaning schedules before efficiency drops below critical thresholds.
Strengths: Digital twin technology provides highly accurate prediction capabilities without disrupting operations. Integration with existing control systems creates a seamless monitoring environment. Weaknesses: Implementation requires significant digital infrastructure and expertise, potentially limiting accessibility for smaller operations or facilities with legacy equipment.
Key Innovations in Fouling Detection and Prevention
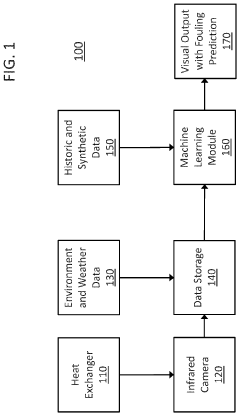
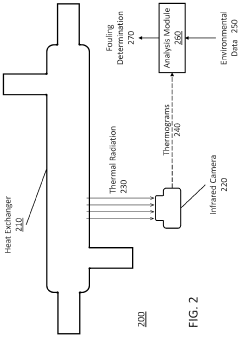
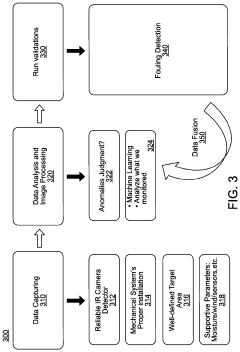
Heat exchanger fouling determination using thermography combined with machine learning methods
PatentActiveUS20210041347A1
Innovation
- A method combining thermography and machine learning to detect and predict polymer fouling by training a machine learning circuit using thermographic data from heat exchangers, allowing for non-destructive inspection and optimized maintenance scheduling.
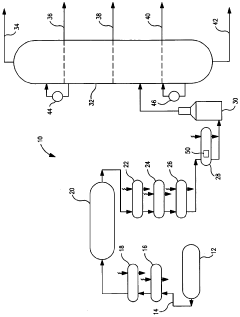
Crude oil pre-heat train with improved heat transfer and method of improving heat transfer
PatentWO2009045458A1
Innovation
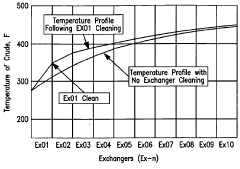
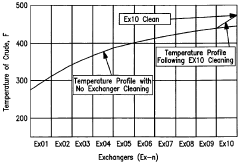
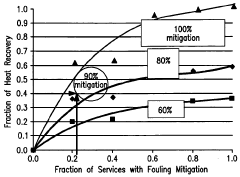
- Implementing an anti-fouling mechanism in select heat exchangers within the pre-heat train, such as those experiencing the highest temperatures or located adjacent to the furnace, using smoothed corrosion-resistant surfaces and vibration to inhibit fouling deposits, with the goal of achieving at least 75% to 90% mitigation of fouling, thereby reducing energy losses and maintenance costs.
Economic Impact of Fouling on Industrial Operations
Fouling in heat exchangers represents a significant economic burden across various industrial sectors, with annual costs estimated between 0.25% to 0.35% of the gross domestic product (GDP) in industrialized countries. This translates to approximately $26-30 billion in the United States alone and over €4.5 billion annually in the European Union. These substantial figures underscore the critical importance of effective fouling prediction and mitigation strategies.
The direct economic impacts of fouling manifest primarily through increased energy consumption. Fouled heat exchangers typically require 20-50% more energy input to maintain the same thermal performance as clean equipment. In petroleum refineries, fouling accounts for approximately 10% of the total energy consumption, while in food processing industries, this figure can reach up to 15% of operational energy costs.
Capital expenditure increases represent another significant economic consequence. Industries often overdesign heat exchangers by 30-40% to compensate for anticipated fouling, resulting in larger equipment footprints and higher initial investment costs. This overdesign practice adds an estimated 25% to the capital costs of new heat exchange systems across various industrial applications.
Maintenance and cleaning operations constitute a substantial portion of fouling-related expenses. The global market for industrial cleaning services specifically targeting heat exchanger fouling exceeds $8 billion annually. Individual cleaning operations for large industrial heat exchangers can cost between $40,000 to $100,000 per unit, with facilities typically requiring multiple cleanings per year depending on the severity of fouling conditions.
Production losses during downtime for cleaning and maintenance create perhaps the most severe economic impact. A typical petroleum refinery experiences 1-2.5% production loss annually due to fouling-related shutdowns, equating to approximately $12 million in lost revenue for a medium-sized facility. Chemical processing plants report similar figures, with production interruptions costing an average of $1.2 million per day during unscheduled shutdowns.
Environmental compliance costs further compound the economic burden. Increased energy consumption due to fouling directly correlates with higher carbon emissions, subjecting companies to carbon taxation in many jurisdictions. Additionally, the disposal of cleaning chemicals and fouling deposits must comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations, adding approximately 15-20% to the total fouling management costs in heavily regulated industries.
The direct economic impacts of fouling manifest primarily through increased energy consumption. Fouled heat exchangers typically require 20-50% more energy input to maintain the same thermal performance as clean equipment. In petroleum refineries, fouling accounts for approximately 10% of the total energy consumption, while in food processing industries, this figure can reach up to 15% of operational energy costs.
Capital expenditure increases represent another significant economic consequence. Industries often overdesign heat exchangers by 30-40% to compensate for anticipated fouling, resulting in larger equipment footprints and higher initial investment costs. This overdesign practice adds an estimated 25% to the capital costs of new heat exchange systems across various industrial applications.
Maintenance and cleaning operations constitute a substantial portion of fouling-related expenses. The global market for industrial cleaning services specifically targeting heat exchanger fouling exceeds $8 billion annually. Individual cleaning operations for large industrial heat exchangers can cost between $40,000 to $100,000 per unit, with facilities typically requiring multiple cleanings per year depending on the severity of fouling conditions.
Production losses during downtime for cleaning and maintenance create perhaps the most severe economic impact. A typical petroleum refinery experiences 1-2.5% production loss annually due to fouling-related shutdowns, equating to approximately $12 million in lost revenue for a medium-sized facility. Chemical processing plants report similar figures, with production interruptions costing an average of $1.2 million per day during unscheduled shutdowns.
Environmental compliance costs further compound the economic burden. Increased energy consumption due to fouling directly correlates with higher carbon emissions, subjecting companies to carbon taxation in many jurisdictions. Additionally, the disposal of cleaning chemicals and fouling deposits must comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations, adding approximately 15-20% to the total fouling management costs in heavily regulated industries.
Environmental Considerations in Fouling Treatment Methods
The environmental impact of fouling treatment methods has become increasingly significant in heat exchanger maintenance strategies. Traditional chemical cleaning approaches often involve harsh substances such as strong acids, caustic solutions, and organic solvents that pose substantial environmental risks when discharged without proper treatment. These chemicals can contaminate water bodies, disrupt aquatic ecosystems, and potentially enter the food chain, creating long-term environmental damage beyond their immediate application area.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide have evolved to address these concerns, with increasingly stringent discharge limitations and waste management requirements. Organizations like the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States and the European Environmental Agency have established comprehensive guidelines specifically targeting industrial cleaning processes. These regulations have driven the development of more environmentally responsible fouling mitigation approaches.
Green chemistry principles are now being integrated into modern fouling treatment solutions. Biodegradable surfactants and enzymes represent promising alternatives to conventional chemical cleaners, offering comparable cleaning efficiency while significantly reducing environmental footprint. These bio-based solutions naturally degrade after use, minimizing persistent environmental contamination and ecotoxicity concerns associated with traditional methods.
Water conservation has emerged as another critical environmental consideration in fouling management. Closed-loop cleaning systems that recycle cleaning solutions have gained traction, substantially reducing both freshwater consumption and wastewater generation. Advanced filtration and separation technologies enable the recovery and reuse of cleaning agents, further minimizing environmental impact while providing economic benefits through reduced resource consumption.
Energy efficiency considerations extend beyond the operational aspects of heat exchangers to their maintenance procedures. Traditional cleaning methods often require high temperatures or energy-intensive processes, contributing to carbon emissions. Modern approaches emphasize ambient-temperature cleaning solutions and mechanical methods that require minimal energy input, aligning fouling mitigation strategies with broader carbon reduction goals.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) methodologies are increasingly being applied to evaluate the comprehensive environmental impact of different fouling treatment options. These assessments consider factors including raw material extraction, manufacturing processes, operational requirements, and end-of-life disposal. Such holistic evaluation enables engineers to select fouling mitigation strategies that minimize environmental impact across the entire life cycle rather than simply addressing immediate operational concerns.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide have evolved to address these concerns, with increasingly stringent discharge limitations and waste management requirements. Organizations like the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States and the European Environmental Agency have established comprehensive guidelines specifically targeting industrial cleaning processes. These regulations have driven the development of more environmentally responsible fouling mitigation approaches.
Green chemistry principles are now being integrated into modern fouling treatment solutions. Biodegradable surfactants and enzymes represent promising alternatives to conventional chemical cleaners, offering comparable cleaning efficiency while significantly reducing environmental footprint. These bio-based solutions naturally degrade after use, minimizing persistent environmental contamination and ecotoxicity concerns associated with traditional methods.
Water conservation has emerged as another critical environmental consideration in fouling management. Closed-loop cleaning systems that recycle cleaning solutions have gained traction, substantially reducing both freshwater consumption and wastewater generation. Advanced filtration and separation technologies enable the recovery and reuse of cleaning agents, further minimizing environmental impact while providing economic benefits through reduced resource consumption.
Energy efficiency considerations extend beyond the operational aspects of heat exchangers to their maintenance procedures. Traditional cleaning methods often require high temperatures or energy-intensive processes, contributing to carbon emissions. Modern approaches emphasize ambient-temperature cleaning solutions and mechanical methods that require minimal energy input, aligning fouling mitigation strategies with broader carbon reduction goals.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) methodologies are increasingly being applied to evaluate the comprehensive environmental impact of different fouling treatment options. These assessments consider factors including raw material extraction, manufacturing processes, operational requirements, and end-of-life disposal. Such holistic evaluation enables engineers to select fouling mitigation strategies that minimize environmental impact across the entire life cycle rather than simply addressing immediate operational concerns.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!