Corrosion monitoring in high-temperature heat exchangers
OCT 14, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
High-Temperature Corrosion Monitoring Background and Objectives
Corrosion monitoring in high-temperature heat exchangers has evolved significantly over the past decades, transitioning from reactive maintenance approaches to sophisticated predictive monitoring systems. The historical development of this field began in the 1950s with basic visual inspections and weight loss measurements, progressing through electrochemical techniques in the 1970s, and advancing to real-time monitoring capabilities in the 2000s. This technological evolution has been driven by the critical need to ensure operational safety, extend equipment lifespan, and optimize maintenance schedules in industries where heat exchangers operate under extreme conditions.
The high-temperature environments present in petrochemical processing, power generation, and metallurgical industries create particularly aggressive corrosion conditions, with temperatures often exceeding 500°C. These extreme operating conditions accelerate various corrosion mechanisms including high-temperature oxidation, sulfidation, carburization, and molten salt corrosion, which collectively contribute to material degradation and potential catastrophic failures if left unmonitored.
Current technological trends in this field are moving toward integrated sensor networks, wireless monitoring capabilities, and advanced data analytics. The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) platforms with corrosion monitoring systems represents a significant advancement, allowing for continuous data collection and remote monitoring capabilities that were previously unattainable. Additionally, the development of corrosion-resistant materials and protective coatings continues to complement monitoring technologies, creating more comprehensive corrosion management systems.
The primary objectives of high-temperature corrosion monitoring research and development are multifaceted. First, there is a pressing need to develop sensors capable of withstanding extreme temperatures while maintaining measurement accuracy and reliability. Second, the industry requires monitoring systems that can provide real-time data on corrosion rates and mechanisms, enabling predictive maintenance rather than reactive repairs. Third, there is significant interest in developing non-intrusive monitoring techniques that can assess corrosion without disrupting operations.
From an economic perspective, effective corrosion monitoring aims to reduce the estimated $2.5 trillion annual global cost of corrosion (approximately 3.4% of global GDP) by enabling timely interventions before catastrophic failures occur. Furthermore, regulatory pressures and environmental concerns are driving the need for more sophisticated monitoring systems that can help prevent leaks and emissions resulting from corrosion-related failures.
The convergence of materials science, sensor technology, data analytics, and industrial automation is expected to revolutionize how high-temperature corrosion is monitored and managed in the coming decade, with significant implications for industrial efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
The high-temperature environments present in petrochemical processing, power generation, and metallurgical industries create particularly aggressive corrosion conditions, with temperatures often exceeding 500°C. These extreme operating conditions accelerate various corrosion mechanisms including high-temperature oxidation, sulfidation, carburization, and molten salt corrosion, which collectively contribute to material degradation and potential catastrophic failures if left unmonitored.
Current technological trends in this field are moving toward integrated sensor networks, wireless monitoring capabilities, and advanced data analytics. The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) platforms with corrosion monitoring systems represents a significant advancement, allowing for continuous data collection and remote monitoring capabilities that were previously unattainable. Additionally, the development of corrosion-resistant materials and protective coatings continues to complement monitoring technologies, creating more comprehensive corrosion management systems.
The primary objectives of high-temperature corrosion monitoring research and development are multifaceted. First, there is a pressing need to develop sensors capable of withstanding extreme temperatures while maintaining measurement accuracy and reliability. Second, the industry requires monitoring systems that can provide real-time data on corrosion rates and mechanisms, enabling predictive maintenance rather than reactive repairs. Third, there is significant interest in developing non-intrusive monitoring techniques that can assess corrosion without disrupting operations.
From an economic perspective, effective corrosion monitoring aims to reduce the estimated $2.5 trillion annual global cost of corrosion (approximately 3.4% of global GDP) by enabling timely interventions before catastrophic failures occur. Furthermore, regulatory pressures and environmental concerns are driving the need for more sophisticated monitoring systems that can help prevent leaks and emissions resulting from corrosion-related failures.
The convergence of materials science, sensor technology, data analytics, and industrial automation is expected to revolutionize how high-temperature corrosion is monitored and managed in the coming decade, with significant implications for industrial efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
Market Analysis for Heat Exchanger Monitoring Solutions
The global market for heat exchanger corrosion monitoring solutions is experiencing robust growth, driven primarily by increasing demands in critical industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, power generation, and metallurgy. Current market valuations indicate that the industrial corrosion monitoring segment reached approximately 3.9 billion USD in 2022, with heat exchanger-specific monitoring solutions comprising about 18% of this market. Industry analysts project a compound annual growth rate of 7.2% through 2028, significantly outpacing general industrial equipment markets.
Regional analysis reveals that North America currently holds the largest market share at 32%, followed by Europe at 28% and Asia-Pacific at 26%. However, the Asia-Pacific region is demonstrating the fastest growth trajectory, particularly in China and India, where rapid industrialization and increasing focus on operational efficiency are creating substantial market opportunities. The Middle East, with its extensive oil and gas infrastructure, represents another high-potential growth region.
Customer segmentation shows distinct market tiers with varying needs. Tier-one customers, primarily large multinational corporations in petrochemical and power generation sectors, prioritize comprehensive monitoring systems with advanced analytics capabilities and are willing to invest in premium solutions. Mid-market customers typically seek balanced cost-performance solutions with moderate implementation complexity, while smaller operations often prefer modular, scalable systems that can be expanded as needs evolve.
Pricing trends indicate a gradual decrease in per-unit monitoring costs, approximately 4-5% annually, as technology matures and competition intensifies. However, this is offset by increasing value-added services, particularly in data analytics and predictive maintenance capabilities, which command premium pricing. The average implementation cost for comprehensive heat exchanger monitoring systems ranges from 50,000 to 250,000 USD, depending on complexity and scale.
Market drivers include increasingly stringent regulatory requirements regarding industrial safety and environmental protection, rising awareness of total cost of ownership considerations, and the growing adoption of Industry 4.0 principles. The push toward predictive maintenance strategies is particularly significant, as organizations seek to minimize downtime and extend equipment lifespan. Additionally, the increasing complexity of industrial processes and the use of more aggressive process conditions create natural demand for more sophisticated monitoring solutions.
Barriers to market growth include high initial implementation costs, technical challenges in harsh operating environments, and organizational resistance to adopting new technologies. The fragmented nature of the market, with numerous specialized solution providers, also creates challenges for customers in selecting appropriate technologies.
Regional analysis reveals that North America currently holds the largest market share at 32%, followed by Europe at 28% and Asia-Pacific at 26%. However, the Asia-Pacific region is demonstrating the fastest growth trajectory, particularly in China and India, where rapid industrialization and increasing focus on operational efficiency are creating substantial market opportunities. The Middle East, with its extensive oil and gas infrastructure, represents another high-potential growth region.
Customer segmentation shows distinct market tiers with varying needs. Tier-one customers, primarily large multinational corporations in petrochemical and power generation sectors, prioritize comprehensive monitoring systems with advanced analytics capabilities and are willing to invest in premium solutions. Mid-market customers typically seek balanced cost-performance solutions with moderate implementation complexity, while smaller operations often prefer modular, scalable systems that can be expanded as needs evolve.
Pricing trends indicate a gradual decrease in per-unit monitoring costs, approximately 4-5% annually, as technology matures and competition intensifies. However, this is offset by increasing value-added services, particularly in data analytics and predictive maintenance capabilities, which command premium pricing. The average implementation cost for comprehensive heat exchanger monitoring systems ranges from 50,000 to 250,000 USD, depending on complexity and scale.
Market drivers include increasingly stringent regulatory requirements regarding industrial safety and environmental protection, rising awareness of total cost of ownership considerations, and the growing adoption of Industry 4.0 principles. The push toward predictive maintenance strategies is particularly significant, as organizations seek to minimize downtime and extend equipment lifespan. Additionally, the increasing complexity of industrial processes and the use of more aggressive process conditions create natural demand for more sophisticated monitoring solutions.
Barriers to market growth include high initial implementation costs, technical challenges in harsh operating environments, and organizational resistance to adopting new technologies. The fragmented nature of the market, with numerous specialized solution providers, also creates challenges for customers in selecting appropriate technologies.
Current Corrosion Monitoring Technologies and Challenges
Corrosion monitoring in high-temperature heat exchangers presents significant technical challenges due to the extreme operating conditions. Current monitoring technologies can be broadly categorized into offline and online methods, each with distinct advantages and limitations. Offline techniques include periodic visual inspections, ultrasonic thickness measurements, and metallographic examinations, which require operational shutdowns and provide only intermittent data points rather than continuous monitoring.
Online monitoring technologies have advanced considerably in recent years, with electrical resistance (ER) probes emerging as one of the most widely adopted solutions. These probes measure the increasing electrical resistance of a metal element as its cross-sectional area decreases due to corrosion. While effective, ER probes often struggle with accuracy in high-temperature environments above 600°C, where electrical properties of metals change independently of corrosion effects.
Electrochemical techniques such as Linear Polarization Resistance (LPR) and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) offer real-time corrosion rate data but face significant implementation challenges in high-temperature heat exchangers. The stability of reference electrodes and the integrity of electrical connections deteriorate rapidly in such harsh environments, limiting their practical application.
Weight loss coupons remain a traditional benchmark method, providing accurate time-averaged corrosion rates. However, they offer no real-time data and require extended exposure periods to yield meaningful results, making them unsuitable for dynamic process control or early warning systems.
Advanced non-destructive testing (NDT) methods including guided wave ultrasonic testing and acoustic emission monitoring show promise for detecting corrosion without process interruption. These techniques can identify corrosion-related anomalies by analyzing changes in wave propagation characteristics, though signal interpretation remains complex in multi-phase, high-temperature systems.
A significant challenge across all monitoring technologies is the heterogeneous nature of corrosion in heat exchangers. Localized phenomena such as pitting, crevice corrosion, and flow-accelerated corrosion often occur in specific regions that may be missed by point-measurement techniques, leading to unexpected failures despite monitoring efforts.
Material compatibility presents another major hurdle, as sensor components must withstand not only high temperatures but also potentially corrosive process fluids. Conventional sensor materials often degrade rapidly, compromising measurement accuracy and sensor longevity. Ceramic-based sensors and advanced alloys show promise but remain costly and sometimes unreliable over extended periods.
Data integration and interpretation represent the final frontier in corrosion monitoring. Current systems typically operate in isolation, with limited integration into broader asset management frameworks. The development of comprehensive corrosion management systems that incorporate real-time monitoring data with predictive analytics remains an active area of research with significant potential for improving heat exchanger reliability and operational efficiency.
Online monitoring technologies have advanced considerably in recent years, with electrical resistance (ER) probes emerging as one of the most widely adopted solutions. These probes measure the increasing electrical resistance of a metal element as its cross-sectional area decreases due to corrosion. While effective, ER probes often struggle with accuracy in high-temperature environments above 600°C, where electrical properties of metals change independently of corrosion effects.
Electrochemical techniques such as Linear Polarization Resistance (LPR) and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) offer real-time corrosion rate data but face significant implementation challenges in high-temperature heat exchangers. The stability of reference electrodes and the integrity of electrical connections deteriorate rapidly in such harsh environments, limiting their practical application.
Weight loss coupons remain a traditional benchmark method, providing accurate time-averaged corrosion rates. However, they offer no real-time data and require extended exposure periods to yield meaningful results, making them unsuitable for dynamic process control or early warning systems.
Advanced non-destructive testing (NDT) methods including guided wave ultrasonic testing and acoustic emission monitoring show promise for detecting corrosion without process interruption. These techniques can identify corrosion-related anomalies by analyzing changes in wave propagation characteristics, though signal interpretation remains complex in multi-phase, high-temperature systems.
A significant challenge across all monitoring technologies is the heterogeneous nature of corrosion in heat exchangers. Localized phenomena such as pitting, crevice corrosion, and flow-accelerated corrosion often occur in specific regions that may be missed by point-measurement techniques, leading to unexpected failures despite monitoring efforts.
Material compatibility presents another major hurdle, as sensor components must withstand not only high temperatures but also potentially corrosive process fluids. Conventional sensor materials often degrade rapidly, compromising measurement accuracy and sensor longevity. Ceramic-based sensors and advanced alloys show promise but remain costly and sometimes unreliable over extended periods.
Data integration and interpretation represent the final frontier in corrosion monitoring. Current systems typically operate in isolation, with limited integration into broader asset management frameworks. The development of comprehensive corrosion management systems that incorporate real-time monitoring data with predictive analytics remains an active area of research with significant potential for improving heat exchanger reliability and operational efficiency.
Existing High-Temperature Corrosion Monitoring Solutions
01 Electrochemical corrosion monitoring techniques
Electrochemical methods are widely used for monitoring corrosion in various environments. These techniques involve measuring electrical parameters such as potential, current, and impedance to assess corrosion rates and mechanisms. Electrochemical sensors can provide real-time data on corrosion activity, allowing for early detection of corrosion issues. These methods are particularly useful in industrial settings where continuous monitoring is required to prevent equipment failure.- Electrochemical corrosion monitoring techniques: Electrochemical methods are widely used for monitoring corrosion in various environments. These techniques involve measuring electrical parameters such as potential, current, and impedance to assess corrosion rates and mechanisms. Electrochemical sensors can provide real-time data on corrosion processes, allowing for early detection of corrosion issues. These methods are particularly useful in industrial settings where continuous monitoring is required to prevent equipment failure.
- Optical and visual corrosion monitoring systems: Optical monitoring systems use light-based technologies to detect and measure corrosion. These include fiber optic sensors, optical imaging, and spectroscopic techniques that can detect changes in material properties due to corrosion. Visual inspection systems may incorporate cameras and image processing algorithms to identify corrosion patterns and severity. These non-intrusive methods allow for monitoring of hard-to-reach areas and can provide detailed information about corrosion progression without disrupting operations.
- Wireless and IoT-based corrosion monitoring: Modern corrosion monitoring systems increasingly incorporate wireless technology and Internet of Things (IoT) capabilities. These systems use remote sensors that transmit corrosion data wirelessly to central monitoring stations or cloud platforms. This approach enables continuous monitoring of corrosion in remote or hazardous locations without requiring physical access. The integration with data analytics and artificial intelligence allows for predictive maintenance and early warning of potential corrosion-related failures.
- Corrosion monitoring in oil and gas applications: Specialized corrosion monitoring techniques have been developed for the oil and gas industry, where corrosion can lead to catastrophic failures. These include downhole monitoring tools, pipeline inspection gauges, and corrosion coupons designed to withstand harsh environments. Monitoring systems for this sector often combine multiple sensing technologies to provide comprehensive corrosion assessment in high-pressure, high-temperature, and chemically aggressive environments. These systems help maintain asset integrity and prevent environmental incidents.
- Corrosion rate measurement and analysis methods: Various techniques are employed to measure and analyze corrosion rates in different materials and environments. These include weight loss measurements, thickness measurements using ultrasonic techniques, electrical resistance methods, and chemical analysis of corrosion products. Advanced data processing algorithms help interpret the measurements and provide meaningful information about corrosion mechanisms and progression. These methods enable engineers to quantify corrosion damage and make informed decisions about maintenance and replacement schedules.
02 Optical and spectroscopic corrosion monitoring systems
Optical and spectroscopic techniques offer non-destructive methods for corrosion monitoring. These systems use light-based technologies such as fiber optics, laser, and spectroscopic analysis to detect and measure corrosion processes. The techniques can provide visual data on corrosion progression and are particularly valuable in hard-to-reach areas or harsh environments where traditional monitoring methods may be impractical. These systems can detect early signs of corrosion before significant damage occurs.Expand Specific Solutions03 Wireless and remote corrosion monitoring technologies
Wireless and remote monitoring technologies enable corrosion assessment in inaccessible or hazardous locations. These systems utilize wireless sensors that can transmit corrosion data to central monitoring stations without the need for physical connections. The technology allows for continuous monitoring without human intervention, improving safety and reducing inspection costs. Advanced systems incorporate IoT capabilities for real-time alerts and integration with maintenance management systems.Expand Specific Solutions04 Corrosion monitoring in oil and gas applications
Specialized corrosion monitoring techniques have been developed for the oil and gas industry, where corrosive environments pose significant challenges. These systems are designed to withstand high pressures, temperatures, and chemically aggressive environments found in wells, pipelines, and processing facilities. The monitoring techniques include downhole sensors, pipeline inspection tools, and specialized probes that can detect internal and external corrosion in critical infrastructure, helping to prevent leaks and failures.Expand Specific Solutions05 Data analysis and predictive corrosion monitoring
Advanced data analysis techniques and predictive algorithms are being applied to corrosion monitoring to forecast future corrosion behavior. These systems utilize machine learning, statistical analysis, and historical data to predict corrosion rates and remaining equipment life. By analyzing patterns in corrosion data, these systems can identify factors contributing to accelerated corrosion and recommend preventive measures. This approach enables condition-based maintenance strategies rather than time-based inspections, optimizing maintenance schedules and reducing costs.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies in Industrial Corrosion Monitoring
The corrosion monitoring market for high-temperature heat exchangers is currently in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by aging infrastructure and efficiency requirements. The global market size is estimated at $2-3 billion, expanding at 5-7% annually. Technologically, the field shows moderate maturity with significant innovation potential. Leading players include established industrial giants like GE, Siemens, and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries offering comprehensive monitoring solutions, alongside specialized companies like Xi'an Thermal Power Research Institute developing advanced sensors. Academic institutions such as Shanghai Jiao Tong University and West Virginia University contribute fundamental research, while oil and gas companies like Saudi Aramco drive application-specific innovations. The competitive landscape features a mix of traditional monitoring approaches and emerging AI/ML-enhanced predictive technologies.
General Electric Company
Technical Solution: General Electric has developed advanced corrosion monitoring systems for high-temperature heat exchangers utilizing electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) combined with wireless sensor networks. Their solution incorporates high-temperature resistant sensors capable of withstanding environments up to 1000°C, with specialized ceramic-based protective coatings that extend sensor lifespan in harsh conditions. GE's system employs real-time data analytics through their Predix platform, which uses machine learning algorithms to detect corrosion patterns before visible damage occurs. The technology includes multi-parameter monitoring (temperature, pressure, flow rate, and chemical composition) to correlate operating conditions with corrosion rates. Their Digital Twin technology creates virtual models of heat exchangers to predict remaining useful life based on corrosion progression data, enabling predictive maintenance scheduling rather than reactive repairs.
Strengths: Industry-leading integration with digital platforms for predictive analytics; comprehensive multi-parameter monitoring capability; extensive field validation across power generation applications. Weaknesses: Higher implementation costs compared to conventional monitoring systems; requires significant computational resources for full Digital Twin functionality; may need customization for specific industrial applications.
Saudi Arabian Oil Co.
Technical Solution: Saudi Aramco has developed a proprietary high-temperature corrosion monitoring system specifically designed for crude oil processing heat exchangers. Their technology employs multi-element electromagnetic sensors that can detect material thickness changes of less than 0.1mm in real-time while operating at temperatures up to 800°C. The system features specialized high-nickel alloy sensor housings with proprietary coatings that resist sulfidation and naphthenic acid corrosion common in petroleum processing. Aramco's solution incorporates a dual-monitoring approach combining electrical resistance techniques with hydrogen flux monitoring to detect both general and localized corrosion phenomena. Their system includes automated chemical injection control that responds to detected corrosion acceleration by adjusting inhibitor dosing rates. The technology integrates with Aramco's broader asset integrity management system, providing risk-based inspection scheduling based on actual corrosion rates rather than conservative time-based approaches. Field implementations have demonstrated 30-40% extension in heat exchanger service life and approximately 25% reduction in unplanned downtime across multiple facilities.
Strengths: Exceptional performance in high-sulfur crude processing environments; integrated chemical inhibitor control capabilities; extensive field validation in some of the world's largest refineries. Weaknesses: Proprietary technology with limited availability outside Aramco operations; requires specialized training for maintenance personnel; higher complexity compared to conventional monitoring approaches.
Key Innovations in Sensor Technology for Harsh Environments
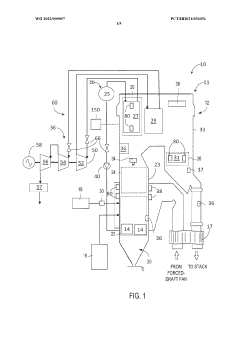
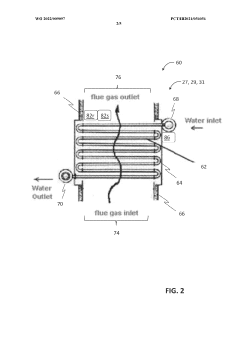
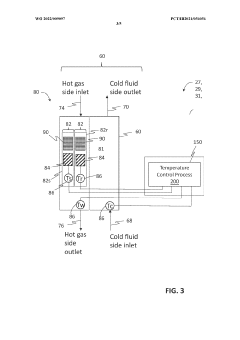
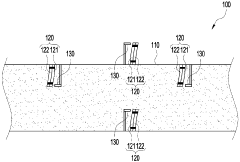
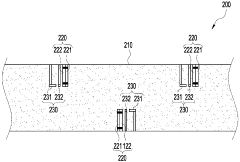
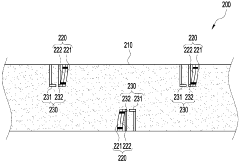
System and method for heat exchanger control based on real-time corrosion monitoring
PatentWO2022009097A1
Innovation
- A system and method for controlling corrosion in heat exchangers using a corrosion sensing device that measures corrosion rates and adjusts the cold side fluid inlet temperature based on real-time data, allowing for non-intrusive online monitoring and optimization of thermal efficiency while minimizing corrosion.
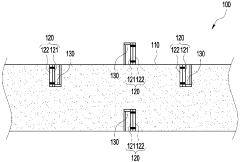
Erosion and high-temperature corrosion monitoring apparatus using the bimetal
PatentActiveKR1020190027669A
Innovation
- A bimetallic erosion and high-temperature corrosion monitoring device that uses a pair of metals with different properties to detect tube corrosion by measuring electrical contact or separation, allowing for economical and accurate determination of replacement timing.
Material Science Advancements for Corrosion Resistance
Recent advancements in material science have significantly contributed to enhancing corrosion resistance in high-temperature heat exchangers. The development of novel alloys with superior heat and corrosion resistance properties has been a focal point of research in this domain. Nickel-based superalloys, particularly those containing chromium, molybdenum, and tungsten, have demonstrated exceptional resistance to oxidation and sulfidation at elevated temperatures exceeding 800°C.
Ceramic coatings, especially thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) composed of yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ), have revolutionized the protection of metallic substrates in extreme environments. These coatings provide thermal insulation while simultaneously acting as a barrier against corrosive species. The integration of nanoparticles into these ceramic matrices has further enhanced their durability and resistance to thermal cycling.
Surface modification techniques have evolved substantially, with processes like pack cementation, chemical vapor deposition (CVD), and physical vapor deposition (PVD) enabling the formation of protective layers with tailored compositions. Aluminizing and chromizing treatments create diffusion layers that significantly improve oxidation resistance by forming stable Al2O3 or Cr2O3 scales upon exposure to high temperatures.
Self-healing materials represent a breakthrough in corrosion resistance technology. These innovative materials contain encapsulated healing agents that are released upon crack formation, automatically repairing damaged areas before corrosion can propagate. Micro-capsules containing reactive silicates or phosphates have shown promising results in laboratory tests, potentially extending heat exchanger service life by 30-40%.
Computational materials science has accelerated the discovery and optimization of corrosion-resistant materials. Machine learning algorithms can now predict corrosion behavior based on composition and microstructure, reducing the time and cost associated with experimental testing. This approach has led to the identification of several promising compositional ranges for next-generation heat exchanger materials.
Graphene and other two-dimensional materials have emerged as potential game-changers for corrosion protection. When applied as ultrathin coatings, these materials create an impermeable barrier that prevents the diffusion of corrosive species to the substrate. Research indicates that graphene-based coatings can reduce corrosion rates by up to 99% in certain environments, though challenges in large-scale application remain.
The development of in-situ monitoring capabilities within advanced materials themselves represents the frontier of this field. Embedding sensors or indicator particles that change properties in response to corrosion initiation allows for real-time assessment of material integrity without system shutdown.
Ceramic coatings, especially thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) composed of yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ), have revolutionized the protection of metallic substrates in extreme environments. These coatings provide thermal insulation while simultaneously acting as a barrier against corrosive species. The integration of nanoparticles into these ceramic matrices has further enhanced their durability and resistance to thermal cycling.
Surface modification techniques have evolved substantially, with processes like pack cementation, chemical vapor deposition (CVD), and physical vapor deposition (PVD) enabling the formation of protective layers with tailored compositions. Aluminizing and chromizing treatments create diffusion layers that significantly improve oxidation resistance by forming stable Al2O3 or Cr2O3 scales upon exposure to high temperatures.
Self-healing materials represent a breakthrough in corrosion resistance technology. These innovative materials contain encapsulated healing agents that are released upon crack formation, automatically repairing damaged areas before corrosion can propagate. Micro-capsules containing reactive silicates or phosphates have shown promising results in laboratory tests, potentially extending heat exchanger service life by 30-40%.
Computational materials science has accelerated the discovery and optimization of corrosion-resistant materials. Machine learning algorithms can now predict corrosion behavior based on composition and microstructure, reducing the time and cost associated with experimental testing. This approach has led to the identification of several promising compositional ranges for next-generation heat exchanger materials.
Graphene and other two-dimensional materials have emerged as potential game-changers for corrosion protection. When applied as ultrathin coatings, these materials create an impermeable barrier that prevents the diffusion of corrosive species to the substrate. Research indicates that graphene-based coatings can reduce corrosion rates by up to 99% in certain environments, though challenges in large-scale application remain.
The development of in-situ monitoring capabilities within advanced materials themselves represents the frontier of this field. Embedding sensors or indicator particles that change properties in response to corrosion initiation allows for real-time assessment of material integrity without system shutdown.
Economic Impact of Corrosion Prevention in Industrial Systems
The economic impact of corrosion in industrial systems, particularly in high-temperature heat exchangers, represents a significant financial burden across multiple sectors. Studies indicate that corrosion-related costs account for approximately 3-5% of GDP in industrialized nations, with heat exchanger failures contributing substantially to this figure. In petrochemical, power generation, and manufacturing industries, unplanned shutdowns due to corrosion-induced failures can cost facilities between $500,000 to $2 million per day in lost production alone.
Preventive maintenance strategies incorporating advanced corrosion monitoring technologies demonstrate compelling return on investment. Companies implementing comprehensive corrosion management programs report cost-benefit ratios ranging from 1:5 to 1:10, meaning every dollar spent on prevention saves five to ten dollars in potential damage and downtime costs. For high-temperature heat exchangers specifically, extending operational life through effective corrosion prevention can defer replacement costs that typically range from $100,000 to several million dollars depending on size and application.
The indirect economic benefits of corrosion prevention extend beyond immediate maintenance savings. Enhanced energy efficiency represents a significant economic advantage, as corrosion-free heat exchangers maintain optimal thermal transfer rates. Even minor corrosion-induced efficiency losses of 2-5% translate to substantial energy cost increases over equipment lifetime. Additionally, facilities with proven corrosion management programs often negotiate more favorable insurance premiums, reflecting reduced operational risk profiles.
Environmental compliance costs related to corrosion failures present another economic consideration. Leaks or failures in heat exchangers handling hazardous materials can result in regulatory fines exceeding $100,000 per incident, alongside mandatory remediation expenses. Proactive corrosion monitoring significantly mitigates these financial risks while supporting sustainability initiatives that increasingly influence corporate valuation.
Labor optimization represents a frequently overlooked economic benefit of advanced corrosion monitoring systems. Real-time monitoring technologies reduce the need for frequent manual inspections, allowing technical personnel to focus on higher-value activities. This workforce efficiency can generate annual savings of 15-25% in maintenance labor costs while improving overall productivity and safety metrics.
The economic case for investment in advanced corrosion monitoring technologies becomes particularly compelling when considering total lifecycle costs rather than initial implementation expenses. While sophisticated monitoring systems for high-temperature heat exchangers may require capital investment of $50,000-200,000, the extended equipment lifespan, reduced maintenance requirements, and prevention of catastrophic failures deliver positive economic returns typically within 12-24 months of deployment.
Preventive maintenance strategies incorporating advanced corrosion monitoring technologies demonstrate compelling return on investment. Companies implementing comprehensive corrosion management programs report cost-benefit ratios ranging from 1:5 to 1:10, meaning every dollar spent on prevention saves five to ten dollars in potential damage and downtime costs. For high-temperature heat exchangers specifically, extending operational life through effective corrosion prevention can defer replacement costs that typically range from $100,000 to several million dollars depending on size and application.
The indirect economic benefits of corrosion prevention extend beyond immediate maintenance savings. Enhanced energy efficiency represents a significant economic advantage, as corrosion-free heat exchangers maintain optimal thermal transfer rates. Even minor corrosion-induced efficiency losses of 2-5% translate to substantial energy cost increases over equipment lifetime. Additionally, facilities with proven corrosion management programs often negotiate more favorable insurance premiums, reflecting reduced operational risk profiles.
Environmental compliance costs related to corrosion failures present another economic consideration. Leaks or failures in heat exchangers handling hazardous materials can result in regulatory fines exceeding $100,000 per incident, alongside mandatory remediation expenses. Proactive corrosion monitoring significantly mitigates these financial risks while supporting sustainability initiatives that increasingly influence corporate valuation.
Labor optimization represents a frequently overlooked economic benefit of advanced corrosion monitoring systems. Real-time monitoring technologies reduce the need for frequent manual inspections, allowing technical personnel to focus on higher-value activities. This workforce efficiency can generate annual savings of 15-25% in maintenance labor costs while improving overall productivity and safety metrics.
The economic case for investment in advanced corrosion monitoring technologies becomes particularly compelling when considering total lifecycle costs rather than initial implementation expenses. While sophisticated monitoring systems for high-temperature heat exchangers may require capital investment of $50,000-200,000, the extended equipment lifespan, reduced maintenance requirements, and prevention of catastrophic failures deliver positive economic returns typically within 12-24 months of deployment.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!