Best Practices for QA/QC of Bio-Based Polyamide Batches in Manufacturing
AUG 20, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Bio-PA QA/QC Background
Bio-based polyamides, also known as bio-PAs or bio-nylons, have emerged as sustainable alternatives to conventional petroleum-derived polyamides in recent years. These materials are derived from renewable resources such as castor oil, sebacic acid, or other bio-based monomers. The growing demand for environmentally friendly and high-performance materials has driven the development and adoption of bio-PAs across various industries, including automotive, textiles, and consumer goods.
Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) play crucial roles in ensuring the consistency, reliability, and performance of bio-PA batches during manufacturing processes. The unique characteristics of bio-based raw materials and the potential variability in their composition present specific challenges for QA/QC practices in bio-PA production. These challenges necessitate the development and implementation of tailored quality management strategies to maintain product integrity and meet industry standards.
The QA/QC process for bio-PA batches typically encompasses several key aspects, including raw material inspection, in-process monitoring, and final product testing. Raw material inspection involves verifying the quality and consistency of bio-based monomers and additives, which can be influenced by factors such as crop variations and extraction methods. In-process monitoring focuses on controlling critical parameters during polymerization and extrusion stages to ensure optimal molecular weight distribution and polymer properties.
Final product testing for bio-PAs includes a range of physical, chemical, and mechanical analyses to verify compliance with specifications and performance requirements. These tests may include measurements of tensile strength, elongation at break, impact resistance, moisture absorption, and thermal properties. Additionally, specific tests for bio-based content and biodegradability may be conducted to validate the environmental claims associated with these materials.
The implementation of robust QA/QC practices for bio-PA manufacturing requires a combination of traditional polymer testing methods and specialized techniques adapted for bio-based materials. Advanced analytical tools such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, gel permeation chromatography (GPC), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) are often employed to characterize the molecular structure, composition, and thermal behavior of bio-PAs.
Establishing standardized protocols and acceptance criteria for bio-PA batches is essential for maintaining consistent quality across production runs. This involves defining key performance indicators (KPIs) and acceptable ranges for critical quality attributes. Continuous monitoring and statistical process control techniques are typically employed to identify and address any deviations from established quality parameters promptly.
Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) play crucial roles in ensuring the consistency, reliability, and performance of bio-PA batches during manufacturing processes. The unique characteristics of bio-based raw materials and the potential variability in their composition present specific challenges for QA/QC practices in bio-PA production. These challenges necessitate the development and implementation of tailored quality management strategies to maintain product integrity and meet industry standards.
The QA/QC process for bio-PA batches typically encompasses several key aspects, including raw material inspection, in-process monitoring, and final product testing. Raw material inspection involves verifying the quality and consistency of bio-based monomers and additives, which can be influenced by factors such as crop variations and extraction methods. In-process monitoring focuses on controlling critical parameters during polymerization and extrusion stages to ensure optimal molecular weight distribution and polymer properties.
Final product testing for bio-PAs includes a range of physical, chemical, and mechanical analyses to verify compliance with specifications and performance requirements. These tests may include measurements of tensile strength, elongation at break, impact resistance, moisture absorption, and thermal properties. Additionally, specific tests for bio-based content and biodegradability may be conducted to validate the environmental claims associated with these materials.
The implementation of robust QA/QC practices for bio-PA manufacturing requires a combination of traditional polymer testing methods and specialized techniques adapted for bio-based materials. Advanced analytical tools such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, gel permeation chromatography (GPC), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) are often employed to characterize the molecular structure, composition, and thermal behavior of bio-PAs.
Establishing standardized protocols and acceptance criteria for bio-PA batches is essential for maintaining consistent quality across production runs. This involves defining key performance indicators (KPIs) and acceptable ranges for critical quality attributes. Continuous monitoring and statistical process control techniques are typically employed to identify and address any deviations from established quality parameters promptly.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for bio-based polyamides has been steadily increasing due to growing environmental concerns and the push for sustainable materials in various industries. This trend is particularly evident in sectors such as automotive, textiles, and packaging, where there is a strong emphasis on reducing carbon footprint and enhancing product sustainability.
In the automotive industry, bio-based polyamides are gaining traction as manufacturers seek lightweight, durable, and eco-friendly materials for interior components, under-the-hood applications, and fuel system parts. The stringent regulations on vehicle emissions and fuel efficiency are driving the adoption of these materials, as they offer weight reduction benefits without compromising performance.
The textile sector is another significant market for bio-based polyamides, with increasing demand for sustainable fibers in apparel and sportswear. Consumers are becoming more environmentally conscious, leading to a preference for garments made from renewable resources. This shift in consumer behavior is prompting major textile manufacturers to incorporate bio-based polyamides into their product lines.
Packaging is emerging as a promising market for bio-based polyamides, especially in food packaging applications. The material's excellent barrier properties, combined with its renewable origin, make it an attractive option for manufacturers looking to reduce their reliance on petroleum-based plastics while maintaining product quality and shelf life.
The electronics industry is also showing interest in bio-based polyamides for applications such as connectors, housings, and cable insulation. The material's heat resistance, dimensional stability, and potential for reducing the overall environmental impact of electronic products are driving its adoption in this sector.
Market analysts project a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for bio-based polyamides that outpaces traditional petroleum-based counterparts. This growth is attributed to the increasing awareness of sustainability issues, government regulations promoting the use of bio-based materials, and technological advancements in production processes that are making these materials more cost-competitive.
However, challenges remain in terms of scaling up production to meet growing demand while maintaining consistent quality across batches. This is where robust QA/QC practices become crucial. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on developing and implementing stringent quality control measures to ensure that bio-based polyamide batches meet the high standards required by various industries.
The market demand for bio-based polyamides is also influencing research and development efforts. There is a growing focus on improving the mechanical properties, thermal stability, and processability of these materials to expand their application range and compete more effectively with traditional polyamides in high-performance applications.
In the automotive industry, bio-based polyamides are gaining traction as manufacturers seek lightweight, durable, and eco-friendly materials for interior components, under-the-hood applications, and fuel system parts. The stringent regulations on vehicle emissions and fuel efficiency are driving the adoption of these materials, as they offer weight reduction benefits without compromising performance.
The textile sector is another significant market for bio-based polyamides, with increasing demand for sustainable fibers in apparel and sportswear. Consumers are becoming more environmentally conscious, leading to a preference for garments made from renewable resources. This shift in consumer behavior is prompting major textile manufacturers to incorporate bio-based polyamides into their product lines.
Packaging is emerging as a promising market for bio-based polyamides, especially in food packaging applications. The material's excellent barrier properties, combined with its renewable origin, make it an attractive option for manufacturers looking to reduce their reliance on petroleum-based plastics while maintaining product quality and shelf life.
The electronics industry is also showing interest in bio-based polyamides for applications such as connectors, housings, and cable insulation. The material's heat resistance, dimensional stability, and potential for reducing the overall environmental impact of electronic products are driving its adoption in this sector.
Market analysts project a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for bio-based polyamides that outpaces traditional petroleum-based counterparts. This growth is attributed to the increasing awareness of sustainability issues, government regulations promoting the use of bio-based materials, and technological advancements in production processes that are making these materials more cost-competitive.
However, challenges remain in terms of scaling up production to meet growing demand while maintaining consistent quality across batches. This is where robust QA/QC practices become crucial. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on developing and implementing stringent quality control measures to ensure that bio-based polyamide batches meet the high standards required by various industries.
The market demand for bio-based polyamides is also influencing research and development efforts. There is a growing focus on improving the mechanical properties, thermal stability, and processability of these materials to expand their application range and compete more effectively with traditional polyamides in high-performance applications.
Current Challenges
The production of bio-based polyamides presents several significant challenges in quality assurance and quality control (QA/QC) processes. One of the primary issues is the inherent variability in bio-based raw materials. Unlike petroleum-based feedstocks, which are relatively consistent, bio-based materials can vary significantly in composition and quality depending on factors such as crop conditions, harvesting methods, and storage practices. This variability can lead to inconsistencies in the final product, making it difficult to maintain uniform quality across batches.
Another challenge lies in the complexity of the bio-based polyamide production process. The conversion of bio-based feedstocks into monomers and subsequent polymerization involves multiple steps, each of which can introduce potential quality issues. Controlling reaction conditions, such as temperature, pressure, and catalyst concentrations, becomes crucial to ensure consistent polymer properties. However, the sensitivity of bio-based materials to these conditions often requires more precise control than traditional petroleum-based processes, increasing the complexity of QA/QC procedures.
Contamination control is a critical concern in bio-based polyamide production. Biological impurities from the raw materials can persist through the manufacturing process and affect the final product quality. These impurities may include proteins, lipids, or other organic compounds that can impact the polymer's mechanical properties, color, or long-term stability. Developing effective purification and filtration methods to remove these contaminants without compromising the polymer's properties is an ongoing challenge.
The development of appropriate testing methods and standards for bio-based polyamides poses another significant hurdle. Traditional QA/QC tests designed for petroleum-based polyamides may not always be suitable or sufficient for their bio-based counterparts. New analytical techniques and quality parameters need to be established to accurately assess the unique characteristics of bio-based polyamides, including their bio-content, biodegradability, and potential for eco-toxicity.
Ensuring batch-to-batch consistency is particularly challenging for bio-based polyamides. The natural variations in raw materials can lead to differences in molecular weight distribution, crystallinity, and thermal properties between batches. This inconsistency can affect the processability and end-use performance of the polyamide, making it difficult to meet stringent customer specifications consistently. Developing robust process control strategies and implementing advanced statistical process control methods are essential to mitigate these variations.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape for bio-based materials is still evolving, creating uncertainty in QA/QC requirements. As new standards and regulations emerge, manufacturers must adapt their quality control processes to ensure compliance. This ongoing adaptation can be resource-intensive and may require frequent updates to testing protocols and documentation practices.
Another challenge lies in the complexity of the bio-based polyamide production process. The conversion of bio-based feedstocks into monomers and subsequent polymerization involves multiple steps, each of which can introduce potential quality issues. Controlling reaction conditions, such as temperature, pressure, and catalyst concentrations, becomes crucial to ensure consistent polymer properties. However, the sensitivity of bio-based materials to these conditions often requires more precise control than traditional petroleum-based processes, increasing the complexity of QA/QC procedures.
Contamination control is a critical concern in bio-based polyamide production. Biological impurities from the raw materials can persist through the manufacturing process and affect the final product quality. These impurities may include proteins, lipids, or other organic compounds that can impact the polymer's mechanical properties, color, or long-term stability. Developing effective purification and filtration methods to remove these contaminants without compromising the polymer's properties is an ongoing challenge.
The development of appropriate testing methods and standards for bio-based polyamides poses another significant hurdle. Traditional QA/QC tests designed for petroleum-based polyamides may not always be suitable or sufficient for their bio-based counterparts. New analytical techniques and quality parameters need to be established to accurately assess the unique characteristics of bio-based polyamides, including their bio-content, biodegradability, and potential for eco-toxicity.
Ensuring batch-to-batch consistency is particularly challenging for bio-based polyamides. The natural variations in raw materials can lead to differences in molecular weight distribution, crystallinity, and thermal properties between batches. This inconsistency can affect the processability and end-use performance of the polyamide, making it difficult to meet stringent customer specifications consistently. Developing robust process control strategies and implementing advanced statistical process control methods are essential to mitigate these variations.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape for bio-based materials is still evolving, creating uncertainty in QA/QC requirements. As new standards and regulations emerge, manufacturers must adapt their quality control processes to ensure compliance. This ongoing adaptation can be resource-intensive and may require frequent updates to testing protocols and documentation practices.
Existing QA/QC Methods
01 Improved mechanical properties of bio-based polyamides
Techniques for enhancing the mechanical properties of bio-based polyamides, including tensile strength, impact resistance, and flexibility. This involves optimizing the molecular structure, incorporating reinforcing agents, or using specific processing methods to achieve superior performance comparable to traditional petroleum-based polyamides.- Improved mechanical properties of bio-based polyamides: Techniques for enhancing the mechanical strength, impact resistance, and durability of bio-based polyamides through various methods such as reinforcement with fibers, optimizing molecular weight distribution, and incorporating specific additives. These improvements aim to make bio-based polyamides more competitive with traditional petroleum-based counterparts in high-performance applications.
- Enhanced thermal stability and flame retardancy: Methods to improve the thermal stability and flame retardant properties of bio-based polyamides, including the use of novel additives, nanocomposites, and chemical modifications. These advancements allow bio-based polyamides to meet stringent safety standards and expand their use in applications requiring high heat resistance.
- Optimized processing techniques for bio-based polyamides: Development of specialized processing techniques tailored for bio-based polyamides, including improved extrusion and injection molding methods, as well as novel approaches to enhance crystallization behavior and reduce cycle times. These advancements aim to improve the overall quality and consistency of bio-based polyamide products while increasing manufacturing efficiency.
- Enhanced barrier properties and chemical resistance: Innovations focused on improving the barrier properties and chemical resistance of bio-based polyamides, making them suitable for packaging applications and environments with exposure to harsh chemicals. This includes the development of multi-layer structures, surface treatments, and the incorporation of nanoparticles to enhance performance.
- Sustainable production and recycling of bio-based polyamides: Advancements in the sustainable production of bio-based polyamides, including the use of renewable feedstocks, energy-efficient manufacturing processes, and the development of effective recycling methods. These innovations aim to improve the overall environmental footprint of bio-based polyamides and enhance their circular economy potential.
02 Thermal stability and heat resistance enhancement
Methods to improve the thermal stability and heat resistance of bio-based polyamides, enabling their use in high-temperature applications. This may include the addition of heat stabilizers, cross-linking agents, or the development of novel monomer combinations to increase the melting point and maintain structural integrity at elevated temperatures.Expand Specific Solutions03 Moisture resistance and dimensional stability
Strategies to enhance the moisture resistance and dimensional stability of bio-based polyamides, reducing water absorption and improving performance in humid environments. This can involve surface treatments, the incorporation of hydrophobic additives, or modifications to the polymer structure to decrease hygroscopicity.Expand Specific Solutions04 Biodegradability and environmental impact
Techniques to optimize the biodegradability of bio-based polyamides while maintaining their functional properties. This includes developing composting methods, enhancing the polymer's susceptibility to microbial degradation, and ensuring that the breakdown products are environmentally benign.Expand Specific Solutions05 Processing and manufacturing quality control
Methods for improving the processing and manufacturing quality control of bio-based polyamides, ensuring consistent product properties and performance. This encompasses optimizing extrusion and molding parameters, developing in-line quality monitoring systems, and implementing advanced process control algorithms to maintain high-quality standards during production.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The market for bio-based polyamide manufacturing is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for sustainable materials. The global bio-based polyamide market is expected to expand significantly in the coming years, with a projected CAGR of over 15% through 2025. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Cathay Biotech, BASF, and Solvay leading innovation in synthetic biology and bio-manufacturing processes. These firms are developing new monomers and polymers from renewable sources, improving production efficiency, and enhancing material properties. However, challenges remain in scaling up production and ensuring consistent quality across batches, necessitating robust QA/QC practices. As the industry matures, collaboration between established chemical companies and biotech startups is likely to accelerate technological progress and market adoption.
Cathay Biotech, Inc.
Technical Solution: Cathay Biotech has developed a comprehensive QA/QC system for bio-based polyamide production. Their approach includes in-line monitoring of polymerization reactions using advanced spectroscopic techniques[1]. They employ a multi-stage quality control process, starting from raw material inspection to final product testing. The company utilizes automated sampling systems and rapid analytical methods to ensure batch-to-batch consistency. Cathay Biotech has also implemented a traceability system that allows for the tracking of each batch from feedstock to final product, enhancing their ability to identify and address any quality issues quickly[3].
Strengths: Advanced spectroscopic monitoring, comprehensive traceability system, and rapid analytical methods. Weaknesses: Potential high initial investment costs for advanced equipment and possible complexity in managing extensive data from multiple quality checkpoints.
Solvay Specialty Polymers USA LLC
Technical Solution: Solvay has developed a holistic approach to QA/QC for bio-based polyamide production. Their system integrates sustainable practices with rigorous quality control measures. Solvay employs a combination of in-line process monitoring and extensive laboratory testing. They have implemented a statistical process control (SPC) system that continuously analyzes production data to identify trends and potential quality issues[5]. Solvay's QC protocol includes advanced rheological testing to ensure consistent melt behavior and processability of bio-based polyamides. They also utilize accelerated aging tests to predict long-term performance and stability of their products[6]. Solvay has invested in developing bio-based reference materials for calibration of their analytical instruments, ensuring accurate and reliable measurements specific to bio-based polyamides.
Strengths: Integration of sustainability with quality control, advanced SPC implementation, and development of bio-based reference materials. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in maintaining consistent quality across a wide range of bio-based feedstocks.
Innovative QA/QC Tech
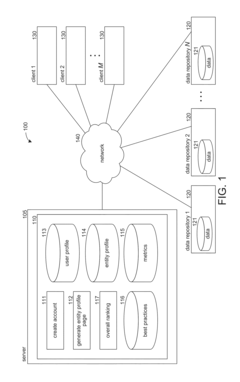
Using best practices customer adoption business intelligence data as input to enterprise resource planning (ERP)
PatentInactiveUS20180068245A1
Innovation
- A method and system that set and compare best practices attainment goals for customers, collect actual values, and adjust resource allocations based on whether these goals are met, using a processor to determine if actual values meet or exceed goals and reallocating resources as necessary, integrated with an enterprise resource planning system for effective resource management.
System and method for dissemination and assessment of performance metrics and related best practices information
PatentInactiveUS20130173355A1
Innovation
- A software facility that assesses performance metrics and disseminates related best practices information through a social networking and media platform, collecting data from various sources, ranking entities, and providing actionable tools for users to track, share, and collaborate on performance data to enhance quality of service and care.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance is a critical aspect of quality assurance and quality control (QA/QC) for bio-based polyamide batches in manufacturing. As the production of bio-based materials gains traction in the industry, manufacturers must navigate a complex landscape of regulations and standards to ensure their products meet legal requirements and customer expectations.
One of the primary regulatory bodies overseeing bio-based materials is the European Committee for Standardization (CEN). The CEN has developed specific standards for bio-based products, including EN 16785-1 and EN 16785-2, which outline methods for determining the bio-based content of products. Manufacturers must adhere to these standards to accurately label and market their bio-based polyamides.
In the United States, the USDA BioPreferred Program provides guidelines for bio-based product certification. This program requires manufacturers to undergo third-party testing to verify the bio-based content of their products. Compliance with this program can offer a competitive advantage in the market and may be necessary for government procurement contracts.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has also developed relevant standards, such as ISO 14021 for environmental labels and declarations. This standard provides guidelines for making claims about the bio-based content of products, ensuring transparency and preventing greenwashing.
Manufacturers must also consider regional regulations, such as REACH in the European Union, which governs the registration, evaluation, authorization, and restriction of chemicals. Bio-based polyamides, while derived from renewable resources, may still fall under the purview of such regulations depending on their chemical composition and properties.
Quality management systems play a crucial role in regulatory compliance. Implementing ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental management can help manufacturers establish robust processes for ensuring compliance with various regulations and standards. These systems provide a framework for documenting procedures, tracking changes, and conducting internal audits.
To maintain regulatory compliance, manufacturers should establish a dedicated team or designate personnel responsible for monitoring regulatory updates and ensuring ongoing adherence to relevant standards. This team should conduct regular assessments of the manufacturing process, from raw material sourcing to final product testing, to identify any potential compliance gaps.
Documentation is a key component of regulatory compliance. Manufacturers must maintain detailed records of their production processes, including raw material sources, processing conditions, and quality control test results. These records should be readily available for audits and inspections by regulatory bodies or certification organizations.
In conclusion, regulatory compliance for QA/QC of bio-based polyamide batches requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses adherence to international standards, regional regulations, and industry-specific guidelines. By implementing robust quality management systems and maintaining thorough documentation, manufacturers can ensure their products meet regulatory requirements and build trust with customers and stakeholders.
One of the primary regulatory bodies overseeing bio-based materials is the European Committee for Standardization (CEN). The CEN has developed specific standards for bio-based products, including EN 16785-1 and EN 16785-2, which outline methods for determining the bio-based content of products. Manufacturers must adhere to these standards to accurately label and market their bio-based polyamides.
In the United States, the USDA BioPreferred Program provides guidelines for bio-based product certification. This program requires manufacturers to undergo third-party testing to verify the bio-based content of their products. Compliance with this program can offer a competitive advantage in the market and may be necessary for government procurement contracts.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has also developed relevant standards, such as ISO 14021 for environmental labels and declarations. This standard provides guidelines for making claims about the bio-based content of products, ensuring transparency and preventing greenwashing.
Manufacturers must also consider regional regulations, such as REACH in the European Union, which governs the registration, evaluation, authorization, and restriction of chemicals. Bio-based polyamides, while derived from renewable resources, may still fall under the purview of such regulations depending on their chemical composition and properties.
Quality management systems play a crucial role in regulatory compliance. Implementing ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental management can help manufacturers establish robust processes for ensuring compliance with various regulations and standards. These systems provide a framework for documenting procedures, tracking changes, and conducting internal audits.
To maintain regulatory compliance, manufacturers should establish a dedicated team or designate personnel responsible for monitoring regulatory updates and ensuring ongoing adherence to relevant standards. This team should conduct regular assessments of the manufacturing process, from raw material sourcing to final product testing, to identify any potential compliance gaps.
Documentation is a key component of regulatory compliance. Manufacturers must maintain detailed records of their production processes, including raw material sources, processing conditions, and quality control test results. These records should be readily available for audits and inspections by regulatory bodies or certification organizations.
In conclusion, regulatory compliance for QA/QC of bio-based polyamide batches requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses adherence to international standards, regional regulations, and industry-specific guidelines. By implementing robust quality management systems and maintaining thorough documentation, manufacturers can ensure their products meet regulatory requirements and build trust with customers and stakeholders.
Sustainability Impact
The sustainability impact of implementing best practices for QA/QC of bio-based polyamide batches in manufacturing is significant and multifaceted. By ensuring consistent quality and performance of bio-based polyamides, these practices contribute to the broader adoption of sustainable materials in various industries.
Bio-based polyamides, derived from renewable resources, offer a more environmentally friendly alternative to their petroleum-based counterparts. The implementation of robust QA/QC practices enhances the reliability and consistency of these materials, thereby increasing their appeal to manufacturers and end-users. This, in turn, promotes the transition towards a more sustainable and circular economy.
One of the key sustainability benefits is the reduction in carbon footprint. Bio-based polyamides typically have a lower carbon footprint compared to conventional polyamides, as they utilize renewable resources that absorb CO2 during growth. Effective QA/QC practices ensure that the environmental benefits of these materials are consistently realized across production batches, maximizing their positive impact on climate change mitigation efforts.
Furthermore, stringent quality control measures can lead to reduced waste and improved resource efficiency in the manufacturing process. By identifying and addressing quality issues early in the production cycle, manufacturers can minimize the amount of off-spec material and reduce the need for energy-intensive reprocessing or disposal. This not only conserves raw materials but also reduces energy consumption and associated emissions.
The implementation of best practices in QA/QC also contributes to the longevity and performance of end products made from bio-based polyamides. By ensuring consistent material properties, these practices help create durable and long-lasting products, reducing the need for frequent replacements and thereby minimizing waste generation and resource consumption over the product lifecycle.
Moreover, robust QA/QC practices can facilitate the development of closed-loop recycling systems for bio-based polyamides. By maintaining consistent material quality, it becomes easier to recycle and reuse these materials at the end of their life, further enhancing their sustainability profile and supporting the principles of a circular economy.
In conclusion, the adoption of best practices for QA/QC in bio-based polyamide manufacturing plays a crucial role in realizing the full sustainability potential of these materials. It not only ensures the environmental benefits of bio-based alternatives but also contributes to resource efficiency, waste reduction, and the overall transition towards more sustainable manufacturing processes and products.
Bio-based polyamides, derived from renewable resources, offer a more environmentally friendly alternative to their petroleum-based counterparts. The implementation of robust QA/QC practices enhances the reliability and consistency of these materials, thereby increasing their appeal to manufacturers and end-users. This, in turn, promotes the transition towards a more sustainable and circular economy.
One of the key sustainability benefits is the reduction in carbon footprint. Bio-based polyamides typically have a lower carbon footprint compared to conventional polyamides, as they utilize renewable resources that absorb CO2 during growth. Effective QA/QC practices ensure that the environmental benefits of these materials are consistently realized across production batches, maximizing their positive impact on climate change mitigation efforts.
Furthermore, stringent quality control measures can lead to reduced waste and improved resource efficiency in the manufacturing process. By identifying and addressing quality issues early in the production cycle, manufacturers can minimize the amount of off-spec material and reduce the need for energy-intensive reprocessing or disposal. This not only conserves raw materials but also reduces energy consumption and associated emissions.
The implementation of best practices in QA/QC also contributes to the longevity and performance of end products made from bio-based polyamides. By ensuring consistent material properties, these practices help create durable and long-lasting products, reducing the need for frequent replacements and thereby minimizing waste generation and resource consumption over the product lifecycle.
Moreover, robust QA/QC practices can facilitate the development of closed-loop recycling systems for bio-based polyamides. By maintaining consistent material quality, it becomes easier to recycle and reuse these materials at the end of their life, further enhancing their sustainability profile and supporting the principles of a circular economy.
In conclusion, the adoption of best practices for QA/QC in bio-based polyamide manufacturing plays a crucial role in realizing the full sustainability potential of these materials. It not only ensures the environmental benefits of bio-based alternatives but also contributes to resource efficiency, waste reduction, and the overall transition towards more sustainable manufacturing processes and products.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!