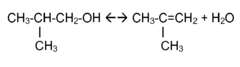Developments in Isobutane-Based Chemical Lubricants
JUL 24, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isobutane Lubricant Evolution and Objectives
Isobutane-based chemical lubricants have undergone significant evolution since their inception in the mid-20th century. Initially developed as alternatives to traditional petroleum-based lubricants, these compounds have gained prominence due to their unique properties and environmental advantages. The journey of isobutane lubricants began with the recognition of isobutane's potential as a base material for synthetic lubricants, offering improved stability and performance under extreme conditions.
The primary objective in the development of isobutane-based lubricants has been to enhance their performance characteristics while minimizing environmental impact. This dual focus has driven research and innovation in the field, leading to a series of technological advancements. Early formulations focused on improving thermal stability and reducing volatility, crucial factors in high-temperature applications such as automotive engines and industrial machinery.
As environmental concerns gained prominence, the objectives shifted towards developing more eco-friendly formulations. This led to the creation of biodegradable isobutane-based lubricants, designed to break down naturally without causing long-term environmental damage. Concurrently, efforts were made to improve the lubricants' efficiency, aiming to reduce friction and wear in mechanical systems, thereby enhancing energy efficiency and extending equipment lifespan.
Recent technological trends have focused on nano-engineered isobutane lubricants. These advanced formulations incorporate nanoparticles to further enhance lubrication properties, thermal conductivity, and wear resistance. The goal is to create 'smart' lubricants that can adapt to varying operational conditions, providing optimal performance across a wide range of applications.
Another key objective in the evolution of isobutane-based lubricants has been to expand their application range. From initial uses in automotive and industrial settings, these lubricants have found their way into diverse fields including aerospace, electronics, and even medical devices. This expansion has necessitated the development of specialized formulations tailored to meet the unique requirements of each application.
Looking forward, the objectives for isobutane-based chemical lubricants are multifaceted. There is a continued push towards developing 'green' lubricants with minimal environmental footprint, aligning with global sustainability goals. Simultaneously, researchers are exploring ways to enhance the lubricants' performance under extreme conditions, such as ultra-high temperatures or in vacuum environments. The integration of smart technologies, including self-healing and self-reporting capabilities, represents another frontier in lubricant development.
The primary objective in the development of isobutane-based lubricants has been to enhance their performance characteristics while minimizing environmental impact. This dual focus has driven research and innovation in the field, leading to a series of technological advancements. Early formulations focused on improving thermal stability and reducing volatility, crucial factors in high-temperature applications such as automotive engines and industrial machinery.
As environmental concerns gained prominence, the objectives shifted towards developing more eco-friendly formulations. This led to the creation of biodegradable isobutane-based lubricants, designed to break down naturally without causing long-term environmental damage. Concurrently, efforts were made to improve the lubricants' efficiency, aiming to reduce friction and wear in mechanical systems, thereby enhancing energy efficiency and extending equipment lifespan.
Recent technological trends have focused on nano-engineered isobutane lubricants. These advanced formulations incorporate nanoparticles to further enhance lubrication properties, thermal conductivity, and wear resistance. The goal is to create 'smart' lubricants that can adapt to varying operational conditions, providing optimal performance across a wide range of applications.
Another key objective in the evolution of isobutane-based lubricants has been to expand their application range. From initial uses in automotive and industrial settings, these lubricants have found their way into diverse fields including aerospace, electronics, and even medical devices. This expansion has necessitated the development of specialized formulations tailored to meet the unique requirements of each application.
Looking forward, the objectives for isobutane-based chemical lubricants are multifaceted. There is a continued push towards developing 'green' lubricants with minimal environmental footprint, aligning with global sustainability goals. Simultaneously, researchers are exploring ways to enhance the lubricants' performance under extreme conditions, such as ultra-high temperatures or in vacuum environments. The integration of smart technologies, including self-healing and self-reporting capabilities, represents another frontier in lubricant development.
Market Analysis for Isobutane-Based Lubricants
The market for isobutane-based chemical lubricants has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand across various industrial sectors. These lubricants offer superior performance characteristics, including excellent thermal stability, low volatility, and high viscosity index, making them ideal for applications in automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing industries.
The global isobutane-based lubricants market is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.5% over the next five years. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising adoption of high-performance lubricants in emerging economies and the increasing focus on energy efficiency and sustainability in developed markets.
In the automotive sector, isobutane-based lubricants are gaining traction due to their ability to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. As stringent environmental regulations continue to be implemented worldwide, the demand for these advanced lubricants is expected to surge. The aerospace industry is another key market driver, with isobutane-based lubricants being increasingly used in aircraft engines and hydraulic systems due to their superior thermal stability and low-temperature performance.
The manufacturing sector is also contributing to market growth, as isobutane-based lubricants are being utilized in various industrial applications, including metalworking, plastics processing, and textile manufacturing. These lubricants offer improved equipment longevity and reduced maintenance costs, making them an attractive option for industrial users.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific is expected to be the fastest-growing market for isobutane-based lubricants, driven by rapid industrialization and increasing automotive production in countries like China and India. North America and Europe remain significant markets, with a focus on high-performance and environmentally friendly lubricants.
Key market players in the isobutane-based lubricants industry include ExxonMobil, Shell, Chevron, and Total. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve product performance and expand their product portfolios. Additionally, there is a growing trend of strategic partnerships and collaborations between lubricant manufacturers and end-users to develop customized solutions for specific applications.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges such as fluctuating raw material prices and the increasing shift towards electric vehicles in the automotive sector may impact the growth of isobutane-based lubricants. However, ongoing technological advancements and the development of bio-based alternatives are expected to create new opportunities for market expansion in the coming years.
The global isobutane-based lubricants market is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.5% over the next five years. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising adoption of high-performance lubricants in emerging economies and the increasing focus on energy efficiency and sustainability in developed markets.
In the automotive sector, isobutane-based lubricants are gaining traction due to their ability to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. As stringent environmental regulations continue to be implemented worldwide, the demand for these advanced lubricants is expected to surge. The aerospace industry is another key market driver, with isobutane-based lubricants being increasingly used in aircraft engines and hydraulic systems due to their superior thermal stability and low-temperature performance.
The manufacturing sector is also contributing to market growth, as isobutane-based lubricants are being utilized in various industrial applications, including metalworking, plastics processing, and textile manufacturing. These lubricants offer improved equipment longevity and reduced maintenance costs, making them an attractive option for industrial users.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific is expected to be the fastest-growing market for isobutane-based lubricants, driven by rapid industrialization and increasing automotive production in countries like China and India. North America and Europe remain significant markets, with a focus on high-performance and environmentally friendly lubricants.
Key market players in the isobutane-based lubricants industry include ExxonMobil, Shell, Chevron, and Total. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve product performance and expand their product portfolios. Additionally, there is a growing trend of strategic partnerships and collaborations between lubricant manufacturers and end-users to develop customized solutions for specific applications.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges such as fluctuating raw material prices and the increasing shift towards electric vehicles in the automotive sector may impact the growth of isobutane-based lubricants. However, ongoing technological advancements and the development of bio-based alternatives are expected to create new opportunities for market expansion in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Isobutane Lubricant Technology
The development of isobutane-based chemical lubricants faces several significant challenges that hinder their widespread adoption and optimal performance. One of the primary issues is the thermal stability of these lubricants at high temperatures. While isobutane-based lubricants offer excellent low-temperature properties, their performance can degrade rapidly when exposed to elevated temperatures, leading to oxidation and breakdown of the lubricant structure.
Another critical challenge lies in the environmental impact of isobutane-based lubricants. As global regulations become increasingly stringent regarding emissions and environmental protection, there is a growing need to develop more eco-friendly formulations. The volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions associated with these lubricants pose a significant concern, particularly in enclosed or poorly ventilated environments.
Compatibility with various materials used in machinery and equipment presents another hurdle. Isobutane-based lubricants may interact adversely with certain elastomers and plastics, causing swelling, degradation, or other forms of material incompatibility. This limits their application in some industrial sectors and requires careful consideration in the design of lubricant systems.
The viscosity-temperature relationship of isobutane-based lubricants also presents challenges. While they perform well at low temperatures, maintaining optimal viscosity across a wide temperature range remains difficult. This can lead to reduced efficiency and increased wear in applications that experience significant temperature fluctuations.
Stability under high pressure is another area of concern, particularly in hydraulic systems and other high-pressure applications. Isobutane-based lubricants may experience shear thinning or other rheological changes under extreme pressure conditions, potentially compromising their protective properties.
Formulation complexity is a significant challenge in developing advanced isobutane-based lubricants. Balancing various additives to enhance performance characteristics while maintaining the base properties of the lubricant requires extensive research and testing. This complexity often leads to increased production costs and can limit the economic viability of these lubricants in certain markets.
Lastly, the storage and handling of isobutane-based lubricants present safety challenges due to their flammability and potential for gas formation. This necessitates specialized storage facilities and handling procedures, which can increase operational costs and complexity for end-users.
Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining advances in chemical engineering, materials science, and environmental technology. Ongoing research efforts focus on developing novel additives, improving molecular structures, and exploring hybrid formulations to overcome these limitations and expand the application range of isobutane-based chemical lubricants.
Another critical challenge lies in the environmental impact of isobutane-based lubricants. As global regulations become increasingly stringent regarding emissions and environmental protection, there is a growing need to develop more eco-friendly formulations. The volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions associated with these lubricants pose a significant concern, particularly in enclosed or poorly ventilated environments.
Compatibility with various materials used in machinery and equipment presents another hurdle. Isobutane-based lubricants may interact adversely with certain elastomers and plastics, causing swelling, degradation, or other forms of material incompatibility. This limits their application in some industrial sectors and requires careful consideration in the design of lubricant systems.
The viscosity-temperature relationship of isobutane-based lubricants also presents challenges. While they perform well at low temperatures, maintaining optimal viscosity across a wide temperature range remains difficult. This can lead to reduced efficiency and increased wear in applications that experience significant temperature fluctuations.
Stability under high pressure is another area of concern, particularly in hydraulic systems and other high-pressure applications. Isobutane-based lubricants may experience shear thinning or other rheological changes under extreme pressure conditions, potentially compromising their protective properties.
Formulation complexity is a significant challenge in developing advanced isobutane-based lubricants. Balancing various additives to enhance performance characteristics while maintaining the base properties of the lubricant requires extensive research and testing. This complexity often leads to increased production costs and can limit the economic viability of these lubricants in certain markets.
Lastly, the storage and handling of isobutane-based lubricants present safety challenges due to their flammability and potential for gas formation. This necessitates specialized storage facilities and handling procedures, which can increase operational costs and complexity for end-users.
Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining advances in chemical engineering, materials science, and environmental technology. Ongoing research efforts focus on developing novel additives, improving molecular structures, and exploring hybrid formulations to overcome these limitations and expand the application range of isobutane-based chemical lubricants.
Existing Isobutane Lubricant Formulations
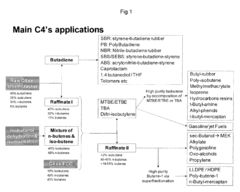
01 Synthesis of isobutane-based lubricants
Various methods for synthesizing isobutane-based lubricants are described, including alkylation processes and the use of catalysts. These processes aim to produce high-quality lubricants with improved properties such as viscosity and thermal stability.- Synthesis of isobutane-based lubricants: Various methods for synthesizing isobutane-based lubricants are described. These processes often involve the alkylation of isobutane with olefins or the isomerization of normal butane to produce isobutane-based compounds suitable for use as lubricants. The resulting products exhibit improved lubricating properties and thermal stability.
- Isobutane-based lubricant compositions: Lubricant compositions containing isobutane-derived compounds are formulated for specific applications. These compositions may include additives to enhance performance characteristics such as viscosity, wear resistance, and oxidation stability. The formulations are tailored to meet the requirements of various industrial and automotive applications.
- Production of isobutane-based refrigerants and lubricants: Processes for producing isobutane-based compounds that can serve as both refrigerants and lubricants are developed. These compounds offer advantages in terms of environmental friendliness and energy efficiency. The production methods focus on optimizing yield and purity while minimizing environmental impact.
- Isobutane-based lubricants for specific applications: Specialized isobutane-based lubricants are developed for specific industrial applications, such as metalworking, textile processing, and high-temperature operations. These lubricants are designed to provide superior performance under challenging conditions, offering benefits such as improved tool life, reduced friction, and enhanced cooling properties.
- Purification and quality improvement of isobutane-based lubricants: Methods for purifying and improving the quality of isobutane-based lubricants are described. These processes aim to remove impurities, enhance stability, and improve the overall performance of the lubricants. Techniques such as distillation, adsorption, and chemical treatment are employed to achieve higher purity and better lubricating properties.
02 Formulation of isobutane-based lubricant compositions
Isobutane-based lubricants are formulated with various additives and base oils to enhance their performance characteristics. These compositions may include other hydrocarbons, synthetic oils, or specific additives to improve lubricity, oxidation resistance, and other desirable properties.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications of isobutane-based lubricants
Isobutane-based lubricants find applications in various industries, including automotive, industrial machinery, and refrigeration systems. These lubricants are particularly useful in situations requiring low-temperature performance or compatibility with specific refrigerants.Expand Specific Solutions04 Production of isobutane derivatives for lubricants
Methods for producing isobutane derivatives, such as isobutylene or other branched hydrocarbons, which can be used as intermediates or components in lubricant formulations. These processes often involve catalytic reactions or isomerization techniques.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations
Research and development efforts focus on improving the environmental profile and safety aspects of isobutane-based lubricants. This includes developing biodegradable formulations, reducing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, and enhancing the overall sustainability of these lubricants.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Competitive Landscape
The development of isobutane-based chemical lubricants is in a growth phase, with increasing market size driven by demand in various industries. The technology is maturing, but still offers room for innovation. Key players like ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., and DuPont de Nemours are leading the field with advanced research and product development. BASF Corp. and The Lubrizol Corp. are also significant contributors, leveraging their expertise in chemical engineering to enhance lubricant performance. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established petrochemical giants and specialized chemical companies, each striving to develop more efficient and environmentally friendly lubricant solutions.
ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, Inc.
Technical Solution: ExxonMobil has developed advanced isobutane-based chemical lubricants with improved thermal stability and oxidation resistance. Their technology involves synthesizing complex esters from isobutanol and carboxylic acids, resulting in lubricants with enhanced performance at high temperatures[1]. The company has also introduced novel additive packages specifically designed for isobutane-based lubricants, which provide superior anti-wear and extreme pressure properties[2]. ExxonMobil's research has focused on optimizing the molecular structure of these lubricants to achieve a balance between volatility and lubricity, making them suitable for a wide range of applications from automotive to industrial machinery[3].
Strengths: Superior thermal stability, excellent oxidation resistance, and wide application range. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs and complexity in formulation compared to conventional mineral-based lubricants.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has made significant strides in isobutane-based chemical lubricants, focusing on environmentally friendly formulations. Their research has led to the development of bio-based isobutane lubricants derived from renewable resources, reducing reliance on petroleum-based products[4]. Sinopec has also pioneered a novel catalytic process for the efficient production of isobutane-based lubricants, improving yield and reducing energy consumption[5]. The company's lubricants feature enhanced biodegradability and reduced toxicity, aligning with global sustainability trends. Additionally, Sinopec has developed specialized isobutane-based lubricants for extreme temperature conditions, particularly suited for use in the rapidly growing Chinese industrial sector[6].
Strengths: Eco-friendly formulations, efficient production processes, and suitability for extreme conditions. Weaknesses: Potential limitations in global market penetration and higher initial costs for bio-based alternatives.
Innovative Patents in Isobutane Lubricant Chemistry
Process for making butenes from dry isobutanol
PatentInactiveEP2043971A2
Innovation
- A process involving the separation of dry isobutanol from fermentation broth, followed by contact with an acid catalyst at controlled temperatures and pressures to produce butenes, which can then be recovered and further converted into isoalkanes, alkyl aromatic compounds, and butyl alkyl ethers, facilitating the production of transportation fuels and fuel additives.
Simultaneous dehydration and skeletal isomerisation of isobutanol on acid catalysts
PatentInactiveEP2374781A1
Innovation
- Simultaneous dehydration and skeletal isomerization of isobutanol using crystalline silicates with high Si/Al ratios or modified alumina catalysts at elevated temperatures and moderate pressures, allowing for high isobutanol conversion and selectivity towards n-butenes and iso-butene, mimicking the composition of raffinate I from steam naphtha crackers.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The environmental impact and sustainability considerations of isobutane-based chemical lubricants have become increasingly important in recent years. As the industry moves towards more eco-friendly solutions, these lubricants are being scrutinized for their potential effects on the environment throughout their lifecycle.
One of the primary concerns is the volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions associated with isobutane-based lubricants. When released into the atmosphere, these compounds can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog, potentially impacting air quality and human health. Efforts are being made to develop formulations with lower VOC content or to implement more effective containment and recovery systems during manufacturing and application processes.
The production of isobutane-based lubricants also raises sustainability questions regarding resource consumption and energy efficiency. The petrochemical origin of isobutane means that these lubricants are derived from non-renewable resources, which may conflict with long-term sustainability goals. Industry leaders are exploring alternative feedstocks and production methods to reduce the carbon footprint associated with these lubricants.
Biodegradability is another critical factor in assessing the environmental impact of isobutane-based lubricants. Traditional formulations may persist in the environment for extended periods, potentially accumulating in ecosystems and affecting wildlife. Research is ongoing to enhance the biodegradability of these lubricants without compromising their performance characteristics.
Water contamination risks are also a significant concern, particularly in applications where lubricants may come into contact with aquatic environments. Efforts are being made to develop formulations that are less toxic to aquatic life and to improve spill prevention and cleanup protocols.
The end-of-life management of isobutane-based lubricants presents both challenges and opportunities for sustainability. Proper disposal and recycling methods are essential to minimize environmental impact. Some companies are implementing closed-loop systems to recover and reprocess used lubricants, reducing waste and conserving resources.
Regulatory pressures and consumer demand for greener products are driving innovation in this field. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to create more environmentally friendly alternatives that maintain or exceed the performance of traditional isobutane-based lubricants. This includes exploring bio-based additives, synthetic esters, and other novel compounds that offer improved environmental profiles.
As the industry evolves, life cycle assessments (LCAs) are becoming increasingly important tools for evaluating the overall environmental impact of isobutane-based lubricants. These assessments consider factors such as raw material extraction, production processes, use phase emissions, and end-of-life disposal to provide a comprehensive view of a product's environmental footprint.
One of the primary concerns is the volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions associated with isobutane-based lubricants. When released into the atmosphere, these compounds can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog, potentially impacting air quality and human health. Efforts are being made to develop formulations with lower VOC content or to implement more effective containment and recovery systems during manufacturing and application processes.
The production of isobutane-based lubricants also raises sustainability questions regarding resource consumption and energy efficiency. The petrochemical origin of isobutane means that these lubricants are derived from non-renewable resources, which may conflict with long-term sustainability goals. Industry leaders are exploring alternative feedstocks and production methods to reduce the carbon footprint associated with these lubricants.
Biodegradability is another critical factor in assessing the environmental impact of isobutane-based lubricants. Traditional formulations may persist in the environment for extended periods, potentially accumulating in ecosystems and affecting wildlife. Research is ongoing to enhance the biodegradability of these lubricants without compromising their performance characteristics.
Water contamination risks are also a significant concern, particularly in applications where lubricants may come into contact with aquatic environments. Efforts are being made to develop formulations that are less toxic to aquatic life and to improve spill prevention and cleanup protocols.
The end-of-life management of isobutane-based lubricants presents both challenges and opportunities for sustainability. Proper disposal and recycling methods are essential to minimize environmental impact. Some companies are implementing closed-loop systems to recover and reprocess used lubricants, reducing waste and conserving resources.
Regulatory pressures and consumer demand for greener products are driving innovation in this field. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to create more environmentally friendly alternatives that maintain or exceed the performance of traditional isobutane-based lubricants. This includes exploring bio-based additives, synthetic esters, and other novel compounds that offer improved environmental profiles.
As the industry evolves, life cycle assessments (LCAs) are becoming increasingly important tools for evaluating the overall environmental impact of isobutane-based lubricants. These assessments consider factors such as raw material extraction, production processes, use phase emissions, and end-of-life disposal to provide a comprehensive view of a product's environmental footprint.
Regulatory Framework for Chemical Lubricants
The regulatory framework for chemical lubricants, particularly those based on isobutane, is complex and multifaceted. It encompasses various international, national, and regional regulations that govern the production, distribution, and use of these substances. At the global level, the United Nations' Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) provides a standardized approach for communicating chemical hazards, which applies to isobutane-based lubricants.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating chemical lubricants under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). The TSCA requires manufacturers to submit premanufacture notices for new chemical substances, including novel isobutane-based lubricants, and to comply with reporting, record-keeping, and testing requirements. Additionally, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets standards for workplace exposure limits and safety protocols related to these chemicals.
The European Union's regulatory framework is particularly stringent, with the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation being the cornerstone of chemical management. REACH mandates that companies register chemical substances, including isobutane-based lubricants, and provide safety data to the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA). The Classification, Labelling, and Packaging (CLP) Regulation complements REACH by ensuring that hazards are clearly communicated to workers and consumers.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have their own regulatory systems. China's Measures for Environmental Management of New Chemical Substances and Japan's Chemical Substances Control Law (CSCL) both require registration and risk assessment of new chemicals, including lubricants. These regulations aim to protect human health and the environment while allowing for innovation in the chemical industry.
Specific to isobutane-based lubricants, regulations often focus on their volatile organic compound (VOC) content and potential environmental impact. Many jurisdictions have implemented VOC emission limits and require the use of low-VOC formulations in certain applications. Furthermore, as these lubricants can be flammable, regulations often address their storage, handling, and transportation to minimize fire and explosion risks.
The regulatory landscape is continuously evolving, with increasing emphasis on sustainability and environmental protection. This has led to the development of eco-labeling schemes and green certification programs that encourage the use of environmentally friendly lubricants. As research into isobutane-based lubricants progresses, regulators are likely to update their frameworks to address any newly identified risks or benefits associated with these substances.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating chemical lubricants under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). The TSCA requires manufacturers to submit premanufacture notices for new chemical substances, including novel isobutane-based lubricants, and to comply with reporting, record-keeping, and testing requirements. Additionally, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets standards for workplace exposure limits and safety protocols related to these chemicals.
The European Union's regulatory framework is particularly stringent, with the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation being the cornerstone of chemical management. REACH mandates that companies register chemical substances, including isobutane-based lubricants, and provide safety data to the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA). The Classification, Labelling, and Packaging (CLP) Regulation complements REACH by ensuring that hazards are clearly communicated to workers and consumers.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have their own regulatory systems. China's Measures for Environmental Management of New Chemical Substances and Japan's Chemical Substances Control Law (CSCL) both require registration and risk assessment of new chemicals, including lubricants. These regulations aim to protect human health and the environment while allowing for innovation in the chemical industry.
Specific to isobutane-based lubricants, regulations often focus on their volatile organic compound (VOC) content and potential environmental impact. Many jurisdictions have implemented VOC emission limits and require the use of low-VOC formulations in certain applications. Furthermore, as these lubricants can be flammable, regulations often address their storage, handling, and transportation to minimize fire and explosion risks.
The regulatory landscape is continuously evolving, with increasing emphasis on sustainability and environmental protection. This has led to the development of eco-labeling schemes and green certification programs that encourage the use of environmentally friendly lubricants. As research into isobutane-based lubricants progresses, regulators are likely to update their frameworks to address any newly identified risks or benefits associated with these substances.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!