Expanding Frontiers with Ethylene Vinyl Acetate Science
JUL 9, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
EVA Science Background and Objectives
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) has emerged as a versatile and innovative material in the field of polymer science. Its development can be traced back to the 1950s when researchers at DuPont first synthesized this copolymer. Since then, EVA has undergone significant advancements, evolving from a simple plastic to a high-performance material with diverse applications across multiple industries.
The primary objective of EVA science is to expand the frontiers of material properties and applications. Researchers aim to enhance the copolymer's characteristics, such as flexibility, toughness, and adhesion, while maintaining its low-temperature performance and resistance to environmental factors. This involves exploring various compositions of ethylene and vinyl acetate, as well as incorporating additives and fillers to tailor the material's properties for specific uses.
One of the key trends in EVA science is the development of sustainable and eco-friendly formulations. As environmental concerns grow, there is an increasing focus on creating biodegradable or recyclable EVA variants. This aligns with the global push towards circular economy principles and reduced environmental impact of plastic materials.
Another significant trend is the exploration of EVA in advanced applications, particularly in the fields of renewable energy and biomedical engineering. For instance, EVA is being investigated for its potential in solar panel encapsulation, where its transparency, weatherability, and electrical insulation properties are highly valuable. In the medical field, researchers are exploring EVA's biocompatibility for drug delivery systems and medical devices.
The evolution of EVA science also encompasses improvements in processing technologies. Advancements in extrusion, injection molding, and foam production techniques are enabling the creation of more complex and precise EVA-based products. This technological progress is crucial for expanding the material's applications in industries such as footwear, packaging, and automotive manufacturing.
As EVA science continues to evolve, interdisciplinary collaboration is becoming increasingly important. Materials scientists are working alongside chemists, physicists, and engineers to push the boundaries of EVA's capabilities. This collaborative approach is essential for addressing complex challenges and developing innovative solutions that can revolutionize various sectors.
In conclusion, the expanding frontiers of EVA science are driven by the need for advanced materials with tailored properties. The field's objectives encompass enhancing material performance, developing sustainable formulations, exploring new applications, and improving processing technologies. As research progresses, EVA is poised to play an even more significant role in shaping the future of materials science and technology.
The primary objective of EVA science is to expand the frontiers of material properties and applications. Researchers aim to enhance the copolymer's characteristics, such as flexibility, toughness, and adhesion, while maintaining its low-temperature performance and resistance to environmental factors. This involves exploring various compositions of ethylene and vinyl acetate, as well as incorporating additives and fillers to tailor the material's properties for specific uses.
One of the key trends in EVA science is the development of sustainable and eco-friendly formulations. As environmental concerns grow, there is an increasing focus on creating biodegradable or recyclable EVA variants. This aligns with the global push towards circular economy principles and reduced environmental impact of plastic materials.
Another significant trend is the exploration of EVA in advanced applications, particularly in the fields of renewable energy and biomedical engineering. For instance, EVA is being investigated for its potential in solar panel encapsulation, where its transparency, weatherability, and electrical insulation properties are highly valuable. In the medical field, researchers are exploring EVA's biocompatibility for drug delivery systems and medical devices.
The evolution of EVA science also encompasses improvements in processing technologies. Advancements in extrusion, injection molding, and foam production techniques are enabling the creation of more complex and precise EVA-based products. This technological progress is crucial for expanding the material's applications in industries such as footwear, packaging, and automotive manufacturing.
As EVA science continues to evolve, interdisciplinary collaboration is becoming increasingly important. Materials scientists are working alongside chemists, physicists, and engineers to push the boundaries of EVA's capabilities. This collaborative approach is essential for addressing complex challenges and developing innovative solutions that can revolutionize various sectors.
In conclusion, the expanding frontiers of EVA science are driven by the need for advanced materials with tailored properties. The field's objectives encompass enhancing material performance, developing sustainable formulations, exploring new applications, and improving processing technologies. As research progresses, EVA is poised to play an even more significant role in shaping the future of materials science and technology.
Market Demand Analysis for EVA Applications
The market demand for Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) applications has been experiencing significant growth across various industries. This versatile copolymer, known for its flexibility, durability, and excellent adhesion properties, has found widespread use in sectors such as packaging, footwear, solar panels, and automotive components.
In the packaging industry, EVA is increasingly sought after for its ability to create strong, flexible films and coatings. The rise of e-commerce and the need for sustainable packaging solutions have driven the demand for EVA-based materials that offer superior protection and reduced environmental impact. This trend is expected to continue as companies strive to meet consumer preferences for eco-friendly packaging options.
The footwear sector represents another substantial market for EVA applications. The material's lightweight nature, shock-absorbing properties, and resistance to wear and tear make it ideal for shoe soles and insoles. As the global athletic footwear market expands, driven by increasing health consciousness and sports participation, the demand for EVA in this sector is projected to grow steadily.
The renewable energy sector, particularly solar power, has emerged as a significant driver of EVA demand. EVA is a crucial component in the production of solar panels, where it serves as an encapsulant material. With the global push towards clean energy and the rapid expansion of solar installations worldwide, the demand for EVA in this application is expected to see robust growth in the coming years.
In the automotive industry, EVA is gaining traction due to its ability to enhance vehicle performance and efficiency. It is used in various applications, including gaskets, seals, and interior components. The trend towards lightweight materials in automotive manufacturing to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions is likely to further boost the demand for EVA-based products.
The construction sector also presents significant opportunities for EVA applications. The material's waterproofing properties and adhesive characteristics make it valuable in roofing membranes, flooring underlayments, and sealants. As the construction industry recovers from recent global challenges and focuses on sustainable building practices, the demand for EVA in this sector is expected to increase.
Overall, the market demand for EVA applications is driven by its versatility, cost-effectiveness, and ability to meet evolving industry requirements. The global EVA market is projected to grow at a steady rate, with Asia-Pacific emerging as a key region for demand growth due to rapid industrialization and urbanization. As industries continue to innovate and seek sustainable solutions, the applications for EVA are likely to expand, opening new avenues for market growth and technological advancements.
In the packaging industry, EVA is increasingly sought after for its ability to create strong, flexible films and coatings. The rise of e-commerce and the need for sustainable packaging solutions have driven the demand for EVA-based materials that offer superior protection and reduced environmental impact. This trend is expected to continue as companies strive to meet consumer preferences for eco-friendly packaging options.
The footwear sector represents another substantial market for EVA applications. The material's lightweight nature, shock-absorbing properties, and resistance to wear and tear make it ideal for shoe soles and insoles. As the global athletic footwear market expands, driven by increasing health consciousness and sports participation, the demand for EVA in this sector is projected to grow steadily.
The renewable energy sector, particularly solar power, has emerged as a significant driver of EVA demand. EVA is a crucial component in the production of solar panels, where it serves as an encapsulant material. With the global push towards clean energy and the rapid expansion of solar installations worldwide, the demand for EVA in this application is expected to see robust growth in the coming years.
In the automotive industry, EVA is gaining traction due to its ability to enhance vehicle performance and efficiency. It is used in various applications, including gaskets, seals, and interior components. The trend towards lightweight materials in automotive manufacturing to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions is likely to further boost the demand for EVA-based products.
The construction sector also presents significant opportunities for EVA applications. The material's waterproofing properties and adhesive characteristics make it valuable in roofing membranes, flooring underlayments, and sealants. As the construction industry recovers from recent global challenges and focuses on sustainable building practices, the demand for EVA in this sector is expected to increase.
Overall, the market demand for EVA applications is driven by its versatility, cost-effectiveness, and ability to meet evolving industry requirements. The global EVA market is projected to grow at a steady rate, with Asia-Pacific emerging as a key region for demand growth due to rapid industrialization and urbanization. As industries continue to innovate and seek sustainable solutions, the applications for EVA are likely to expand, opening new avenues for market growth and technological advancements.
EVA Technology Status and Challenges
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) technology has made significant strides in recent years, yet it still faces several challenges that hinder its full potential. The current status of EVA technology is characterized by its widespread use in various industries, including solar panel encapsulation, footwear manufacturing, and packaging materials. However, the technology's advancement is not uniform across all applications, with some sectors experiencing rapid growth while others lag behind.
One of the primary challenges in EVA technology is achieving consistent quality across different production batches. The copolymerization process of ethylene and vinyl acetate can be sensitive to slight variations in reaction conditions, leading to inconsistencies in the final product's properties. This variability can affect the performance of EVA-based products, particularly in high-precision applications such as photovoltaic modules.
Another significant challenge is the development of EVA formulations with enhanced thermal stability. While EVA copolymers offer excellent flexibility and transparency, they can suffer from degradation at elevated temperatures. This limitation restricts their use in certain high-temperature applications and necessitates the development of more thermally resistant EVA grades.
The environmental impact of EVA production and disposal remains a concern. Although EVA is recyclable, the recycling process is not as straightforward as with some other polymers due to its cross-linked structure in certain applications. Developing more environmentally friendly production methods and improving end-of-life recycling processes are crucial challenges that the industry must address.
In terms of geographical distribution, EVA technology development is concentrated in regions with strong polymer and materials science research capabilities. Countries like Japan, the United States, and Germany lead in EVA innovation, with emerging economies such as China rapidly catching up. This global distribution of expertise creates both opportunities for collaboration and challenges in terms of intellectual property protection and technology transfer.
The customization of EVA properties for specific applications presents both an opportunity and a challenge. While the ability to tailor EVA's characteristics by adjusting the vinyl acetate content and molecular weight distribution is a strength, it also requires significant research and development efforts to optimize formulations for each new application.
Lastly, the integration of EVA with other materials and technologies, such as nanotechnology and smart materials, represents a frontier that is both promising and challenging. Developing hybrid materials that combine the beneficial properties of EVA with those of other advanced materials could open up new applications but requires overcoming compatibility and processing hurdles.
One of the primary challenges in EVA technology is achieving consistent quality across different production batches. The copolymerization process of ethylene and vinyl acetate can be sensitive to slight variations in reaction conditions, leading to inconsistencies in the final product's properties. This variability can affect the performance of EVA-based products, particularly in high-precision applications such as photovoltaic modules.
Another significant challenge is the development of EVA formulations with enhanced thermal stability. While EVA copolymers offer excellent flexibility and transparency, they can suffer from degradation at elevated temperatures. This limitation restricts their use in certain high-temperature applications and necessitates the development of more thermally resistant EVA grades.
The environmental impact of EVA production and disposal remains a concern. Although EVA is recyclable, the recycling process is not as straightforward as with some other polymers due to its cross-linked structure in certain applications. Developing more environmentally friendly production methods and improving end-of-life recycling processes are crucial challenges that the industry must address.
In terms of geographical distribution, EVA technology development is concentrated in regions with strong polymer and materials science research capabilities. Countries like Japan, the United States, and Germany lead in EVA innovation, with emerging economies such as China rapidly catching up. This global distribution of expertise creates both opportunities for collaboration and challenges in terms of intellectual property protection and technology transfer.
The customization of EVA properties for specific applications presents both an opportunity and a challenge. While the ability to tailor EVA's characteristics by adjusting the vinyl acetate content and molecular weight distribution is a strength, it also requires significant research and development efforts to optimize formulations for each new application.
Lastly, the integration of EVA with other materials and technologies, such as nanotechnology and smart materials, represents a frontier that is both promising and challenging. Developing hybrid materials that combine the beneficial properties of EVA with those of other advanced materials could open up new applications but requires overcoming compatibility and processing hurdles.
Current EVA Formulation Techniques
01 Composition and properties of EVA
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) is a copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate. It exhibits properties such as flexibility, toughness, and resistance to UV radiation and stress-cracking. The ratio of ethylene to vinyl acetate in the copolymer can be varied to achieve different characteristics, making it suitable for various applications.- Composition and properties of EVA: Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) is a copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate. It exhibits properties such as flexibility, toughness, and resistance to stress-cracking. The composition and ratio of ethylene to vinyl acetate can be adjusted to achieve specific material characteristics for various applications.
- EVA in adhesive applications: EVA is widely used in adhesive formulations due to its excellent adhesion properties and compatibility with various substrates. It can be used in hot melt adhesives, pressure-sensitive adhesives, and as a base for other adhesive systems. The material's low melting point and good flow characteristics make it suitable for diverse bonding applications.
- EVA in foam and insulation products: EVA is utilized in the production of foam and insulation materials. Its closed-cell structure and low thermal conductivity make it an excellent choice for applications requiring thermal insulation, shock absorption, and buoyancy. EVA foams are used in various industries, including footwear, sports equipment, and packaging.
- EVA in solar panel encapsulation: EVA is a popular material for solar panel encapsulation due to its transparency, weather resistance, and electrical insulation properties. It helps protect solar cells from environmental factors and ensures long-term performance of photovoltaic modules. The material's ability to withstand UV radiation and maintain its properties over time makes it ideal for this application.
- EVA in film and packaging applications: EVA is used in the production of flexible films and packaging materials. Its clarity, toughness, and barrier properties make it suitable for food packaging, agricultural films, and other protective coverings. EVA can be blended with other polymers or additives to enhance specific properties such as gas permeability or heat-sealing characteristics.
02 EVA in adhesive applications
EVA is widely used in adhesive formulations due to its excellent adhesion properties and compatibility with various substrates. It is commonly employed in hot melt adhesives, pressure-sensitive adhesives, and sealants. The adhesive strength and thermal properties can be tailored by adjusting the vinyl acetate content and molecular weight of the EVA copolymer.Expand Specific Solutions03 EVA in foam and insulation materials
EVA is utilized in the production of foam and insulation materials due to its low density, good cushioning properties, and thermal insulation characteristics. It is commonly used in the manufacture of shoe soles, sports equipment, and building insulation. The foam structure can be controlled by adjusting the blowing agent and processing conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 EVA in solar panel encapsulation
EVA is a popular material for solar panel encapsulation due to its transparency, weatherability, and electrical insulation properties. It protects the solar cells from environmental factors and ensures long-term performance. The EVA formulation can be optimized to enhance UV stability and prevent yellowing over time.Expand Specific Solutions05 Modification and blending of EVA
EVA can be modified or blended with other polymers and additives to enhance its properties for specific applications. This includes crosslinking, grafting, and the addition of fillers or compatibilizers. Such modifications can improve mechanical strength, flame retardancy, or processability of EVA-based materials.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in EVA Industry
The ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) market is in a mature growth stage, characterized by steady demand across various industries. The global market size for EVA is substantial, driven by its versatile applications in packaging, footwear, and solar panels. Technologically, EVA production is well-established, with major players like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., Celanese International Corp., and Kuraray Co., Ltd. leading innovation. These companies, along with others such as DuPont de Nemours, Inc. and Saudi Basic Industries Corp., are continuously improving EVA properties and production processes. The competitive landscape is intense, with companies focusing on product differentiation and cost-effective manufacturing to maintain market share in this mature but still evolving sector.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has made significant strides in Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) science. Their approach involves advanced polymerization techniques to produce high-performance EVA copolymers. They utilize a proprietary catalyst system that allows for precise control over the vinyl acetate content, ranging from 10% to 40%[1]. This enables the production of EVA with tailored properties for specific applications. Sinopec has also developed a continuous solution polymerization process, which enhances production efficiency and product consistency[3]. Their research focuses on improving EVA's thermal stability and weatherability, crucial for applications in solar panel encapsulation and wire insulation[5]. Additionally, they are exploring the incorporation of nanofillers to enhance the mechanical and barrier properties of EVA films[7].
Strengths: Large-scale production capabilities, advanced catalyst technology, and a wide range of EVA grades. Weaknesses: Potential environmental concerns associated with petrochemical processes and competition from bio-based alternatives.
Celanese International Corp.
Technical Solution: Celanese International Corp. has been at the forefront of EVA innovation, particularly in the development of high-performance grades for demanding applications. Their approach centers on a proprietary high-pressure tubular reactor technology, which allows for the production of EVA with vinyl acetate content up to 50%[2]. This enables the creation of ultra-flexible and highly transparent EVA grades. Celanese has also pioneered the development of specialty EVA adhesives with enhanced thermal resistance and adhesion properties[4]. Their research extends to the modification of EVA with functional comonomers, improving compatibility with polar substrates and expanding its use in multilayer packaging[6]. Furthermore, Celanese is investing in sustainable EVA solutions, including grades with recycled content and bio-based alternatives[8].
Strengths: Diverse product portfolio, strong R&D capabilities, and focus on specialty grades. Weaknesses: Higher production costs for specialty grades and potential supply chain vulnerabilities for high-VA content products.
Innovative EVA Properties Research
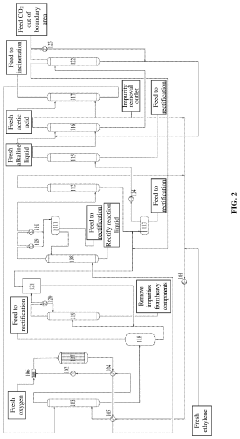
Ethane oxidative dehydrogenation with co-production of vinyl acetate
PatentWO2018114752A1
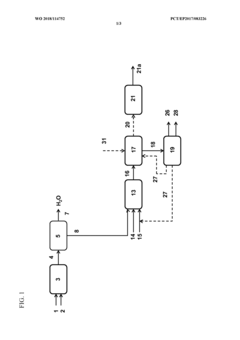
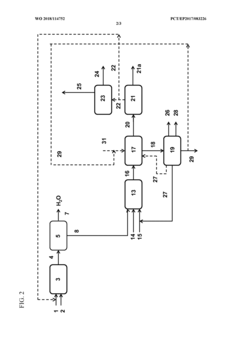
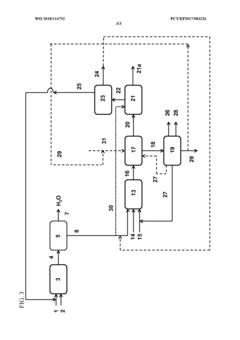
Innovation
- An integrated process where the effluent from the ethane oxidative dehydrogenation step is dewatered, and the dewatered ethylene and acetic acid are further converted to vinyl acetate using a vapor permeation unit and a vinyl acetate catalyst, allowing for the valorization of acetic acid and production of ethylene and vinyl acetate.
Vinyl acetate production process and device
PatentInactiveUS20230312456A1
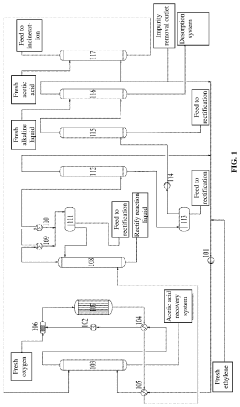
Innovation
- A process and device that includes a stabilizing process, acetic acid recovery system, and desorption system to optimize gas composition, increase oxygen concentration, and recover ethylene, reducing energy consumption and improving safety by segmenting material separation and recovering surplus heat.
Environmental Impact of EVA
The environmental impact of Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) is a critical consideration as its use continues to expand across various industries. EVA, a copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate, offers unique properties that make it valuable in applications ranging from solar panel encapsulation to footwear manufacturing. However, its widespread use raises concerns about its ecological footprint throughout its lifecycle.
During the production phase, EVA manufacturing processes contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption. The polymerization of ethylene and vinyl acetate monomers requires significant energy inputs, often derived from fossil fuels. Additionally, the use of chemical catalysts and additives in the production process can lead to potential environmental contamination if not properly managed.
In its use phase, EVA demonstrates both positive and negative environmental impacts. On the positive side, EVA's application in solar panel encapsulation contributes to the growth of renewable energy technologies, indirectly reducing carbon emissions. Its durability and weather resistance in this application also extend the lifespan of solar panels, reducing waste. However, the use of EVA in disposable products, such as packaging materials, contributes to the global plastic waste problem.
The end-of-life stage presents significant challenges for EVA materials. While EVA is theoretically recyclable, practical recycling efforts are often hindered by contamination and the difficulty of separating EVA from other materials in composite products. As a result, a large portion of EVA waste ends up in landfills or incinerators, contributing to soil and air pollution.
Biodegradability is another concern with EVA materials. Like many synthetic polymers, EVA does not readily biodegrade in natural environments. This persistence can lead to long-term accumulation in ecosystems, potentially affecting wildlife and marine environments through microplastic formation.
Efforts to mitigate the environmental impact of EVA are ongoing. Research into bio-based alternatives and improved recycling technologies shows promise for reducing the carbon footprint of EVA production and addressing end-of-life issues. Additionally, industry initiatives to implement more sustainable manufacturing processes and develop closed-loop recycling systems are gaining traction.
As the demand for EVA continues to grow, balancing its beneficial properties with environmental concerns becomes increasingly important. Future developments in EVA science must focus on enhancing its sustainability profile, from production to disposal, to ensure its continued use aligns with global environmental goals.
During the production phase, EVA manufacturing processes contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption. The polymerization of ethylene and vinyl acetate monomers requires significant energy inputs, often derived from fossil fuels. Additionally, the use of chemical catalysts and additives in the production process can lead to potential environmental contamination if not properly managed.
In its use phase, EVA demonstrates both positive and negative environmental impacts. On the positive side, EVA's application in solar panel encapsulation contributes to the growth of renewable energy technologies, indirectly reducing carbon emissions. Its durability and weather resistance in this application also extend the lifespan of solar panels, reducing waste. However, the use of EVA in disposable products, such as packaging materials, contributes to the global plastic waste problem.
The end-of-life stage presents significant challenges for EVA materials. While EVA is theoretically recyclable, practical recycling efforts are often hindered by contamination and the difficulty of separating EVA from other materials in composite products. As a result, a large portion of EVA waste ends up in landfills or incinerators, contributing to soil and air pollution.
Biodegradability is another concern with EVA materials. Like many synthetic polymers, EVA does not readily biodegrade in natural environments. This persistence can lead to long-term accumulation in ecosystems, potentially affecting wildlife and marine environments through microplastic formation.
Efforts to mitigate the environmental impact of EVA are ongoing. Research into bio-based alternatives and improved recycling technologies shows promise for reducing the carbon footprint of EVA production and addressing end-of-life issues. Additionally, industry initiatives to implement more sustainable manufacturing processes and develop closed-loop recycling systems are gaining traction.
As the demand for EVA continues to grow, balancing its beneficial properties with environmental concerns becomes increasingly important. Future developments in EVA science must focus on enhancing its sustainability profile, from production to disposal, to ensure its continued use aligns with global environmental goals.
EVA Recycling and Sustainability
As the global focus on sustainability intensifies, the recycling and sustainable management of Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) have become critical aspects of its lifecycle. EVA, widely used in various industries, presents unique challenges and opportunities in terms of recycling and environmental impact.
The recycling of EVA is complex due to its cross-linked structure, which makes it difficult to melt and reprocess using conventional methods. However, innovative techniques are emerging to address this challenge. Mechanical recycling, where EVA waste is ground into fine particles and reused in new products, is gaining traction. This method is particularly effective for EVA foam products, such as shoe soles and sports equipment.
Chemical recycling offers another promising avenue for EVA sustainability. This process involves breaking down EVA into its chemical components, which can then be used to create new polymers. Pyrolysis, a form of chemical recycling, has shown potential in converting EVA waste into valuable hydrocarbons and other chemical feedstocks.
The development of bio-based EVA alternatives is another significant trend in improving sustainability. Researchers are exploring the use of renewable resources, such as plant-based ethylene and acetic acid, to produce EVA with a lower carbon footprint. These bio-based alternatives aim to maintain the desirable properties of traditional EVA while reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Efforts to enhance the biodegradability of EVA are also underway. By incorporating biodegradable additives or modifying the polymer structure, scientists are working to create EVA products that can decompose more readily in natural environments. This approach is particularly relevant for single-use EVA applications, such as packaging materials.
The circular economy concept is driving innovations in EVA product design. Manufacturers are increasingly considering the end-of-life phase during product development, designing EVA products that are easier to disassemble and recycle. This shift towards design for recyclability is crucial for improving the overall sustainability of EVA use across industries.
Collaboration between industry stakeholders, including manufacturers, recyclers, and researchers, is essential for advancing EVA sustainability. Initiatives such as take-back programs and recycling partnerships are being established to create closed-loop systems for EVA products. These efforts not only reduce waste but also create new value streams in the EVA lifecycle.
As regulations around plastic waste and recycling become more stringent globally, the EVA industry is adapting to meet these challenges. Investments in recycling infrastructure and technologies are increasing, driven by both regulatory pressures and consumer demand for more sustainable products. The future of EVA sustainability lies in continued innovation, cross-sector collaboration, and a commitment to circular economy principles.
The recycling of EVA is complex due to its cross-linked structure, which makes it difficult to melt and reprocess using conventional methods. However, innovative techniques are emerging to address this challenge. Mechanical recycling, where EVA waste is ground into fine particles and reused in new products, is gaining traction. This method is particularly effective for EVA foam products, such as shoe soles and sports equipment.
Chemical recycling offers another promising avenue for EVA sustainability. This process involves breaking down EVA into its chemical components, which can then be used to create new polymers. Pyrolysis, a form of chemical recycling, has shown potential in converting EVA waste into valuable hydrocarbons and other chemical feedstocks.
The development of bio-based EVA alternatives is another significant trend in improving sustainability. Researchers are exploring the use of renewable resources, such as plant-based ethylene and acetic acid, to produce EVA with a lower carbon footprint. These bio-based alternatives aim to maintain the desirable properties of traditional EVA while reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Efforts to enhance the biodegradability of EVA are also underway. By incorporating biodegradable additives or modifying the polymer structure, scientists are working to create EVA products that can decompose more readily in natural environments. This approach is particularly relevant for single-use EVA applications, such as packaging materials.
The circular economy concept is driving innovations in EVA product design. Manufacturers are increasingly considering the end-of-life phase during product development, designing EVA products that are easier to disassemble and recycle. This shift towards design for recyclability is crucial for improving the overall sustainability of EVA use across industries.
Collaboration between industry stakeholders, including manufacturers, recyclers, and researchers, is essential for advancing EVA sustainability. Initiatives such as take-back programs and recycling partnerships are being established to create closed-loop systems for EVA products. These efforts not only reduce waste but also create new value streams in the EVA lifecycle.
As regulations around plastic waste and recycling become more stringent globally, the EVA industry is adapting to meet these challenges. Investments in recycling infrastructure and technologies are increasing, driven by both regulatory pressures and consumer demand for more sustainable products. The future of EVA sustainability lies in continued innovation, cross-sector collaboration, and a commitment to circular economy principles.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!