Exploring AGM Battery Applications in Logistics and Freight
AUG 7, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AGM Battery Evolution and Objectives
Absorbed Glass Mat (AGM) battery technology has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the 1980s. Initially developed for military and aircraft applications, AGM batteries have gradually found their way into various industries, including logistics and freight. The primary objective of exploring AGM battery applications in these sectors is to enhance operational efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and improve overall performance in transportation and warehousing operations.
The evolution of AGM batteries has been driven by the increasing demand for reliable, maintenance-free power sources in logistics and freight industries. These batteries have progressed from simple lead-acid designs to more advanced configurations, incorporating improved plate designs, enhanced electrolyte absorption, and better charge acceptance characteristics. The development of AGM technology has focused on addressing key challenges such as weight reduction, increased energy density, and improved cycle life to meet the specific needs of logistics and freight applications.
One of the primary objectives in applying AGM batteries to logistics and freight is to provide a stable and long-lasting power source for various equipment and vehicles. This includes powering forklifts, pallet jacks, and other material handling equipment in warehouses, as well as supporting auxiliary power systems in trucks and trailers. The goal is to minimize downtime, reduce maintenance requirements, and extend the operational life of equipment, ultimately leading to increased productivity and cost savings.
Another crucial objective is to support the transition towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly logistics operations. AGM batteries offer advantages over traditional flooded lead-acid batteries, such as being spill-proof and emitting fewer harmful gases during charging. This aligns with the growing emphasis on green logistics and the need to reduce the carbon footprint of transportation and warehousing activities.
The evolution of AGM batteries also aims to address the specific challenges faced in logistics and freight applications. These include the need for rapid recharging capabilities to minimize equipment downtime, improved performance in extreme temperatures to ensure reliability across diverse operating environments, and enhanced vibration resistance to withstand the rigors of transportation and material handling.
Furthermore, the development of AGM battery technology for logistics and freight applications seeks to integrate with emerging trends in the industry, such as automation and electrification. This includes supporting the power requirements of autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs) in warehouses and contributing to the electrification of commercial vehicles for last-mile delivery and short-haul transportation.
As the logistics and freight industries continue to evolve, the objectives for AGM battery applications expand to include compatibility with smart grid systems and renewable energy sources. This aims to create more resilient and sustainable power solutions for warehouses and distribution centers, potentially enabling energy storage and load balancing capabilities to optimize energy consumption and reduce operational costs.
The evolution of AGM batteries has been driven by the increasing demand for reliable, maintenance-free power sources in logistics and freight industries. These batteries have progressed from simple lead-acid designs to more advanced configurations, incorporating improved plate designs, enhanced electrolyte absorption, and better charge acceptance characteristics. The development of AGM technology has focused on addressing key challenges such as weight reduction, increased energy density, and improved cycle life to meet the specific needs of logistics and freight applications.
One of the primary objectives in applying AGM batteries to logistics and freight is to provide a stable and long-lasting power source for various equipment and vehicles. This includes powering forklifts, pallet jacks, and other material handling equipment in warehouses, as well as supporting auxiliary power systems in trucks and trailers. The goal is to minimize downtime, reduce maintenance requirements, and extend the operational life of equipment, ultimately leading to increased productivity and cost savings.
Another crucial objective is to support the transition towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly logistics operations. AGM batteries offer advantages over traditional flooded lead-acid batteries, such as being spill-proof and emitting fewer harmful gases during charging. This aligns with the growing emphasis on green logistics and the need to reduce the carbon footprint of transportation and warehousing activities.
The evolution of AGM batteries also aims to address the specific challenges faced in logistics and freight applications. These include the need for rapid recharging capabilities to minimize equipment downtime, improved performance in extreme temperatures to ensure reliability across diverse operating environments, and enhanced vibration resistance to withstand the rigors of transportation and material handling.
Furthermore, the development of AGM battery technology for logistics and freight applications seeks to integrate with emerging trends in the industry, such as automation and electrification. This includes supporting the power requirements of autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs) in warehouses and contributing to the electrification of commercial vehicles for last-mile delivery and short-haul transportation.
As the logistics and freight industries continue to evolve, the objectives for AGM battery applications expand to include compatibility with smart grid systems and renewable energy sources. This aims to create more resilient and sustainable power solutions for warehouses and distribution centers, potentially enabling energy storage and load balancing capabilities to optimize energy consumption and reduce operational costs.
Logistics Market Demand Analysis
The logistics and freight industry is experiencing a growing demand for reliable and efficient energy storage solutions, particularly in the realm of Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM) battery applications. This market demand is driven by several key factors that are reshaping the landscape of transportation and supply chain management.
Firstly, the increasing emphasis on sustainability and environmental responsibility has led to a surge in demand for cleaner energy alternatives in logistics operations. AGM batteries, known for their low maintenance requirements and minimal environmental impact, are well-positioned to meet this demand. They offer a more eco-friendly option compared to traditional lead-acid batteries, aligning with the industry's push towards greener practices.
The rise of e-commerce and the subsequent expansion of last-mile delivery services have also contributed significantly to the market demand for AGM batteries. These batteries are ideal for powering electric delivery vehicles, forklifts, and other equipment used in warehouses and distribution centers. Their ability to provide consistent power output and quick recharge capabilities makes them particularly suitable for the fast-paced nature of modern logistics operations.
Furthermore, the increasing automation in logistics and freight handling has created a need for reliable power sources that can support advanced technologies. AGM batteries are well-suited for powering automated guided vehicles (AGVs), robotic systems, and other smart logistics solutions that require stable and long-lasting energy storage.
The market demand is also influenced by the growing trend of electrification in the transportation sector. As more logistics companies transition to electric fleets for both short and long-haul operations, the demand for high-performance batteries like AGM is expected to rise. These batteries offer a balance of power, durability, and cost-effectiveness that is attractive to fleet operators looking to optimize their operations.
In addition, the global push for energy efficiency and cost reduction in logistics operations is driving the adoption of AGM batteries. Their low self-discharge rate and ability to perform well in a wide range of temperatures make them an economical choice for companies looking to minimize operational costs and maximize efficiency.
The market demand analysis also reveals a growing interest in AGM batteries for backup power systems in logistics facilities. With the increasing reliance on digital technologies and the need for uninterrupted operations, AGM batteries are being sought after for their reliability in providing emergency power during outages or grid instabilities.
As the logistics and freight industry continues to evolve, the demand for AGM battery applications is expected to grow further. This trend is likely to be reinforced by ongoing technological advancements, regulatory pressures for cleaner energy solutions, and the industry's pursuit of more efficient and sustainable operational practices.
Firstly, the increasing emphasis on sustainability and environmental responsibility has led to a surge in demand for cleaner energy alternatives in logistics operations. AGM batteries, known for their low maintenance requirements and minimal environmental impact, are well-positioned to meet this demand. They offer a more eco-friendly option compared to traditional lead-acid batteries, aligning with the industry's push towards greener practices.
The rise of e-commerce and the subsequent expansion of last-mile delivery services have also contributed significantly to the market demand for AGM batteries. These batteries are ideal for powering electric delivery vehicles, forklifts, and other equipment used in warehouses and distribution centers. Their ability to provide consistent power output and quick recharge capabilities makes them particularly suitable for the fast-paced nature of modern logistics operations.
Furthermore, the increasing automation in logistics and freight handling has created a need for reliable power sources that can support advanced technologies. AGM batteries are well-suited for powering automated guided vehicles (AGVs), robotic systems, and other smart logistics solutions that require stable and long-lasting energy storage.
The market demand is also influenced by the growing trend of electrification in the transportation sector. As more logistics companies transition to electric fleets for both short and long-haul operations, the demand for high-performance batteries like AGM is expected to rise. These batteries offer a balance of power, durability, and cost-effectiveness that is attractive to fleet operators looking to optimize their operations.
In addition, the global push for energy efficiency and cost reduction in logistics operations is driving the adoption of AGM batteries. Their low self-discharge rate and ability to perform well in a wide range of temperatures make them an economical choice for companies looking to minimize operational costs and maximize efficiency.
The market demand analysis also reveals a growing interest in AGM batteries for backup power systems in logistics facilities. With the increasing reliance on digital technologies and the need for uninterrupted operations, AGM batteries are being sought after for their reliability in providing emergency power during outages or grid instabilities.
As the logistics and freight industry continues to evolve, the demand for AGM battery applications is expected to grow further. This trend is likely to be reinforced by ongoing technological advancements, regulatory pressures for cleaner energy solutions, and the industry's pursuit of more efficient and sustainable operational practices.
AGM Technology Status and Challenges
AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) battery technology has made significant strides in recent years, particularly in logistics and freight applications. The current status of AGM batteries showcases their improved performance and reliability compared to traditional lead-acid batteries. These batteries offer higher energy density, faster charging capabilities, and enhanced cycle life, making them increasingly popular in the transportation sector.
One of the primary challenges facing AGM battery technology is the optimization of its performance in extreme temperature conditions. While AGM batteries generally perform better than flooded lead-acid batteries in cold environments, there is still room for improvement in both low and high-temperature scenarios. This is particularly crucial for logistics applications where batteries may be exposed to varied climatic conditions during transportation.
Another significant challenge is the balance between cost and performance. Although AGM batteries offer superior characteristics compared to traditional lead-acid batteries, their higher production costs can be a barrier to widespread adoption in cost-sensitive logistics operations. Manufacturers are continuously working on reducing production costs while maintaining or improving battery performance.
The weight of AGM batteries remains a concern, especially in freight applications where payload capacity is critical. While AGM batteries are lighter than flooded lead-acid batteries, further weight reduction without compromising power output is an ongoing challenge. This aspect is particularly important for electric forklifts and other material handling equipment used in warehouses and distribution centers.
Recycling and environmental impact present both a challenge and an opportunity for AGM battery technology. While these batteries are recyclable, improving the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of recycling processes is crucial for sustainable adoption in the logistics industry. Developing more environmentally friendly production methods and materials is also a focus area for researchers and manufacturers.
In terms of geographical distribution, AGM battery technology has seen widespread adoption in North America and Europe, with growing interest in Asia-Pacific regions. However, the technology's penetration in developing markets remains limited, presenting both a challenge and an opportunity for expansion.
The integration of smart battery management systems (BMS) with AGM batteries is an emerging trend that addresses some of the current challenges. Advanced BMS can optimize charging cycles, monitor battery health, and provide predictive maintenance capabilities, enhancing the overall performance and lifespan of AGM batteries in logistics applications.
Looking ahead, the development of hybrid systems combining AGM batteries with other energy storage technologies, such as lithium-ion or supercapacitors, is being explored to leverage the strengths of multiple technologies. This approach could potentially overcome some of the current limitations of AGM batteries while maintaining their cost-effectiveness for specific applications in the logistics and freight sector.
One of the primary challenges facing AGM battery technology is the optimization of its performance in extreme temperature conditions. While AGM batteries generally perform better than flooded lead-acid batteries in cold environments, there is still room for improvement in both low and high-temperature scenarios. This is particularly crucial for logistics applications where batteries may be exposed to varied climatic conditions during transportation.
Another significant challenge is the balance between cost and performance. Although AGM batteries offer superior characteristics compared to traditional lead-acid batteries, their higher production costs can be a barrier to widespread adoption in cost-sensitive logistics operations. Manufacturers are continuously working on reducing production costs while maintaining or improving battery performance.
The weight of AGM batteries remains a concern, especially in freight applications where payload capacity is critical. While AGM batteries are lighter than flooded lead-acid batteries, further weight reduction without compromising power output is an ongoing challenge. This aspect is particularly important for electric forklifts and other material handling equipment used in warehouses and distribution centers.
Recycling and environmental impact present both a challenge and an opportunity for AGM battery technology. While these batteries are recyclable, improving the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of recycling processes is crucial for sustainable adoption in the logistics industry. Developing more environmentally friendly production methods and materials is also a focus area for researchers and manufacturers.
In terms of geographical distribution, AGM battery technology has seen widespread adoption in North America and Europe, with growing interest in Asia-Pacific regions. However, the technology's penetration in developing markets remains limited, presenting both a challenge and an opportunity for expansion.
The integration of smart battery management systems (BMS) with AGM batteries is an emerging trend that addresses some of the current challenges. Advanced BMS can optimize charging cycles, monitor battery health, and provide predictive maintenance capabilities, enhancing the overall performance and lifespan of AGM batteries in logistics applications.
Looking ahead, the development of hybrid systems combining AGM batteries with other energy storage technologies, such as lithium-ion or supercapacitors, is being explored to leverage the strengths of multiple technologies. This approach could potentially overcome some of the current limitations of AGM batteries while maintaining their cost-effectiveness for specific applications in the logistics and freight sector.
Current AGM Solutions in Logistics
01 AGM battery design and structure
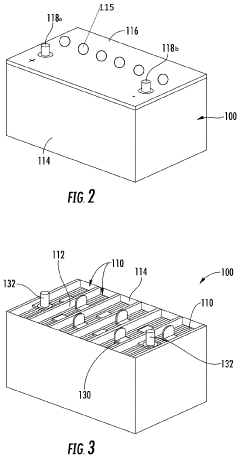
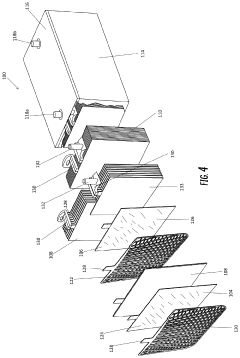
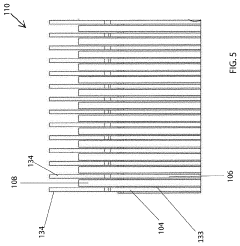
AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) batteries feature a unique design where the electrolyte is absorbed in a fiberglass mat separator. This design enhances the battery's performance, reduces internal resistance, and improves charge acceptance. The structure allows for better electrolyte distribution and prevents leakage, making AGM batteries suitable for various applications.- AGM battery structure and design: Advancements in AGM battery structure and design focus on improving performance and efficiency. This includes innovations in electrode configurations, separator materials, and overall battery construction to enhance capacity, cycle life, and charge acceptance.
- Electrolyte composition for AGM batteries: Research on electrolyte compositions aims to optimize AGM battery performance. This involves developing new formulations or additives to improve conductivity, reduce corrosion, and enhance overall battery efficiency and lifespan.
- Charging and management systems for AGM batteries: Innovations in charging and management systems for AGM batteries focus on improving charging efficiency, prolonging battery life, and enhancing overall performance. This includes advanced charging algorithms, monitoring systems, and intelligent battery management technologies.
- AGM battery applications in vehicles and energy storage: AGM batteries are being developed for various applications in vehicles and energy storage systems. This includes advancements in start-stop technology for automobiles, as well as innovations in large-scale energy storage solutions for renewable energy integration.
- Manufacturing processes for AGM batteries: Improvements in AGM battery manufacturing processes aim to enhance production efficiency, reduce costs, and improve product quality. This includes innovations in assembly techniques, automation, and quality control measures throughout the production process.
02 Improved electrolyte composition for AGM batteries
Advancements in electrolyte composition for AGM batteries focus on enhancing battery life, performance, and safety. These improvements may include additives to reduce sulfation, increase conductivity, or improve charge acceptance. Modified electrolyte formulations can also contribute to better temperature resistance and overall battery efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions03 AGM battery management systems
Battery management systems specifically designed for AGM batteries help optimize performance, extend battery life, and ensure safe operation. These systems may include advanced charging algorithms, temperature monitoring, and state-of-charge estimation. Intelligent management systems can also provide real-time data on battery health and performance.Expand Specific Solutions04 Manufacturing processes for AGM batteries
Innovative manufacturing processes for AGM batteries aim to improve production efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance product quality. These may include automated assembly techniques, advanced plate formation methods, and precise electrolyte filling processes. Improved manufacturing techniques can lead to more consistent and reliable AGM battery production.Expand Specific Solutions05 AGM battery applications and integration
AGM batteries are being integrated into various applications due to their superior performance characteristics. These applications may include automotive start-stop systems, renewable energy storage, and uninterruptible power supplies. The integration of AGM batteries often requires specialized designs and adaptations to maximize their benefits in specific use cases.Expand Specific Solutions
Key AGM Battery Manufacturers
The AGM battery market in logistics and freight is experiencing rapid growth, driven by increasing demand for reliable power sources in material handling equipment and electric vehicles. The industry is in an expansion phase, with a projected market size reaching billions of dollars globally. Technologically, AGM batteries are relatively mature, but innovations continue to improve performance and lifespan. Key players like Johnson Controls, Clarios, and Hoppecke Batterien are leading the market with advanced products. Emerging companies such as Stryten Energy and ArcActive are also making significant contributions to AGM battery technology. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established manufacturers and innovative startups, all vying to meet the growing needs of the logistics and freight sectors for efficient, long-lasting power solutions.
Hoppecke Batterien GmbH & Co. KG
Technical Solution: Hoppecke has developed the trak | air AGM battery series specifically for logistics and material handling applications. These batteries utilize advanced AGM technology with a unique electrolyte circulation system that ensures uniform acid distribution, reducing stratification and extending battery life[3]. The trak | air series incorporates a patented valve design that minimizes water loss and allows for maintenance-free operation. Hoppecke's AGM batteries also feature integrated temperature sensors and communication interfaces, enabling seamless integration with fleet management systems for optimized charging and utilization in logistics environments[4].
Strengths: Extended battery life, maintenance-free design, and advanced integration capabilities with fleet management systems. Weaknesses: Potentially higher upfront costs and limited flexibility in terms of capacity expansion compared to modular lithium-ion solutions.
Stryten Energy LLC
Technical Solution: Stryten Energy has developed the EcoVolt AGM battery line, specifically designed for material handling and logistics applications. These batteries utilize a proprietary AGM technology that enhances charge acceptance and provides faster recharge capabilities, crucial for high-throughput logistics operations[5]. Stryten's AGM batteries incorporate advanced lead alloys and separator materials that improve cycle life and reduce internal resistance, resulting in higher energy efficiency. The company has also implemented a unique manufacturing process that ensures consistent quality and performance across their AGM battery range, addressing the reliability concerns often associated with logistics applications[6].
Strengths: Fast recharge capabilities, high energy efficiency, and consistent performance. Weaknesses: Limited energy density compared to some newer battery technologies, and potential challenges in extreme temperature environments.
AGM Battery Innovations for Freight
Compact absorbent glass mat battery
PatentPendingUS20200212504A1
Innovation
- A compact AGM lead acid battery design with a reduced lead content and smaller size, utilizing a container with electrically connected cells and an absorbent glass mat interleaved between positive and negative plates, achieving improved cycle life and higher CCA performance.
Absorbent glass mat battery
PatentPendingUS20240222600A1
Innovation
- The development of a lead-acid battery with a negative electrode comprising a leady oxide, a synthetic organic expander, conductive carbons, and very fine particle barium sulfate, along with an absorbent glass mat separator, which enhances charge acceptance and cycling performance by improving the electrochemical active material composition and structure.
Environmental Impact of AGM Batteries
The environmental impact of AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) batteries in logistics and freight applications is a crucial consideration as the industry seeks more sustainable solutions. AGM batteries offer several environmental advantages over traditional lead-acid batteries, making them an attractive option for eco-conscious businesses.
One of the primary environmental benefits of AGM batteries is their sealed design, which eliminates the risk of acid spills and reduces the potential for environmental contamination. This feature is particularly important in logistics and freight operations, where batteries may be subjected to rough handling or accidents during transportation.
AGM batteries also have a longer lifespan compared to conventional lead-acid batteries, typically lasting up to 3-4 times longer. This extended service life translates to fewer battery replacements over time, reducing the overall environmental impact associated with battery production and disposal. In the context of logistics and freight, where large fleets of vehicles and equipment rely on batteries, this longevity can significantly decrease the industry's carbon footprint.
The improved energy efficiency of AGM batteries contributes to their environmental friendliness. They have lower internal resistance, allowing for faster charging and more efficient energy transfer. This efficiency reduces energy waste and can lead to lower overall power consumption in logistics operations, potentially decreasing the carbon emissions associated with electricity generation.
Recyclability is another key environmental aspect of AGM batteries. Like other lead-acid batteries, AGM batteries are highly recyclable, with up to 99% of their components being recoverable and reusable. This high recycling rate helps conserve natural resources and reduces the environmental impact of battery disposal.
In terms of manufacturing, AGM batteries require less lead than flooded lead-acid batteries, which can help reduce the environmental impact of lead mining and processing. Additionally, the production process for AGM batteries typically involves fewer hazardous materials, further minimizing potential environmental risks.
However, it's important to note that while AGM batteries offer environmental advantages, they still contain lead and sulfuric acid, which can be harmful if not properly handled or disposed of. Proper end-of-life management and recycling programs are crucial to fully realizing the environmental benefits of AGM batteries in logistics and freight applications.
As the logistics and freight industry continues to prioritize sustainability, the adoption of AGM batteries represents a step towards more environmentally friendly operations. Their improved performance, longer lifespan, and recyclability make them a viable option for companies looking to reduce their environmental impact while maintaining operational efficiency.
One of the primary environmental benefits of AGM batteries is their sealed design, which eliminates the risk of acid spills and reduces the potential for environmental contamination. This feature is particularly important in logistics and freight operations, where batteries may be subjected to rough handling or accidents during transportation.
AGM batteries also have a longer lifespan compared to conventional lead-acid batteries, typically lasting up to 3-4 times longer. This extended service life translates to fewer battery replacements over time, reducing the overall environmental impact associated with battery production and disposal. In the context of logistics and freight, where large fleets of vehicles and equipment rely on batteries, this longevity can significantly decrease the industry's carbon footprint.
The improved energy efficiency of AGM batteries contributes to their environmental friendliness. They have lower internal resistance, allowing for faster charging and more efficient energy transfer. This efficiency reduces energy waste and can lead to lower overall power consumption in logistics operations, potentially decreasing the carbon emissions associated with electricity generation.
Recyclability is another key environmental aspect of AGM batteries. Like other lead-acid batteries, AGM batteries are highly recyclable, with up to 99% of their components being recoverable and reusable. This high recycling rate helps conserve natural resources and reduces the environmental impact of battery disposal.
In terms of manufacturing, AGM batteries require less lead than flooded lead-acid batteries, which can help reduce the environmental impact of lead mining and processing. Additionally, the production process for AGM batteries typically involves fewer hazardous materials, further minimizing potential environmental risks.
However, it's important to note that while AGM batteries offer environmental advantages, they still contain lead and sulfuric acid, which can be harmful if not properly handled or disposed of. Proper end-of-life management and recycling programs are crucial to fully realizing the environmental benefits of AGM batteries in logistics and freight applications.
As the logistics and freight industry continues to prioritize sustainability, the adoption of AGM batteries represents a step towards more environmentally friendly operations. Their improved performance, longer lifespan, and recyclability make them a viable option for companies looking to reduce their environmental impact while maintaining operational efficiency.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of AGM Implementation
Implementing AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) batteries in logistics and freight operations requires a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis to determine the economic viability and long-term advantages. This analysis must consider both direct and indirect costs associated with AGM battery adoption, as well as the potential benefits that could offset these expenses.
The initial investment in AGM batteries is typically higher than traditional lead-acid batteries. However, this cost difference should be evaluated against the extended lifespan of AGM batteries, which can last up to three times longer than conventional alternatives. This longevity translates to reduced replacement frequency and associated labor costs, potentially resulting in significant savings over time.
Maintenance costs are another crucial factor to consider. AGM batteries require minimal maintenance, eliminating the need for regular water top-ups and reducing the risk of acid spills. This characteristic not only lowers ongoing maintenance expenses but also minimizes downtime and enhances operational efficiency in logistics and freight applications.
Energy efficiency is a key benefit of AGM batteries, as they have lower internal resistance and can charge faster than traditional batteries. This improved charging efficiency can lead to reduced energy consumption and lower electricity costs, particularly in high-usage scenarios common in logistics operations.
The enhanced performance of AGM batteries in extreme temperatures and their ability to withstand deep discharge cycles can result in improved reliability and reduced vehicle downtime. This increased uptime can have a substantial positive impact on operational efficiency and customer satisfaction in the logistics sector.
Safety considerations also play a role in the cost-benefit analysis. AGM batteries' sealed design reduces the risk of acid leaks and gas emissions, potentially lowering insurance premiums and improving workplace safety. This factor can contribute to long-term cost savings and reduced liability risks for logistics companies.
Environmental benefits, while not directly quantifiable in monetary terms, should be factored into the analysis. AGM batteries' longer lifespan and recyclability align with sustainability goals, potentially enhancing the company's reputation and opening doors to environmentally conscious clients or markets.
In conclusion, while the upfront costs of implementing AGM batteries in logistics and freight operations may be higher, the long-term benefits in terms of reduced maintenance, improved efficiency, enhanced reliability, and environmental sustainability can outweigh the initial investment. A thorough cost-benefit analysis should consider these factors over the entire lifecycle of the batteries to provide a comprehensive view of the economic impact of AGM implementation in the logistics and freight industry.
The initial investment in AGM batteries is typically higher than traditional lead-acid batteries. However, this cost difference should be evaluated against the extended lifespan of AGM batteries, which can last up to three times longer than conventional alternatives. This longevity translates to reduced replacement frequency and associated labor costs, potentially resulting in significant savings over time.
Maintenance costs are another crucial factor to consider. AGM batteries require minimal maintenance, eliminating the need for regular water top-ups and reducing the risk of acid spills. This characteristic not only lowers ongoing maintenance expenses but also minimizes downtime and enhances operational efficiency in logistics and freight applications.
Energy efficiency is a key benefit of AGM batteries, as they have lower internal resistance and can charge faster than traditional batteries. This improved charging efficiency can lead to reduced energy consumption and lower electricity costs, particularly in high-usage scenarios common in logistics operations.
The enhanced performance of AGM batteries in extreme temperatures and their ability to withstand deep discharge cycles can result in improved reliability and reduced vehicle downtime. This increased uptime can have a substantial positive impact on operational efficiency and customer satisfaction in the logistics sector.
Safety considerations also play a role in the cost-benefit analysis. AGM batteries' sealed design reduces the risk of acid leaks and gas emissions, potentially lowering insurance premiums and improving workplace safety. This factor can contribute to long-term cost savings and reduced liability risks for logistics companies.
Environmental benefits, while not directly quantifiable in monetary terms, should be factored into the analysis. AGM batteries' longer lifespan and recyclability align with sustainability goals, potentially enhancing the company's reputation and opening doors to environmentally conscious clients or markets.
In conclusion, while the upfront costs of implementing AGM batteries in logistics and freight operations may be higher, the long-term benefits in terms of reduced maintenance, improved efficiency, enhanced reliability, and environmental sustainability can outweigh the initial investment. A thorough cost-benefit analysis should consider these factors over the entire lifecycle of the batteries to provide a comprehensive view of the economic impact of AGM implementation in the logistics and freight industry.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!