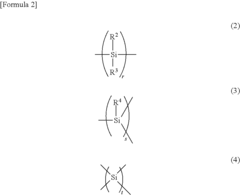How Polysilane Enables Superior Sensor Network Integration?
JUL 11, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Polysilane Sensor Evolution
The evolution of polysilane-based sensors represents a significant advancement in sensor network integration. This journey began in the late 1980s when researchers first recognized the unique electronic properties of polysilanes, particularly their sigma-conjugated backbone structure. These properties, including high electron mobility and photoconductivity, laid the foundation for their potential use in sensing applications.
In the 1990s, early experiments focused on utilizing polysilanes as photoresists and in optoelectronic devices. However, it was not until the early 2000s that researchers began to explore their potential in chemical and biological sensing. The breakthrough came with the discovery that certain polysilanes could change their optical and electrical properties in response to specific chemical stimuli, opening up new possibilities for highly sensitive and selective sensors.
The mid-2000s saw a surge in research aimed at optimizing polysilane structures for sensing applications. Scientists experimented with various side-chain modifications and copolymerization techniques to enhance sensitivity and selectivity. This period also marked the beginning of efforts to integrate polysilane sensors into miniaturized devices, paving the way for their use in sensor networks.
By the 2010s, polysilane sensors had evolved to incorporate advanced nanomaterials and fabrication techniques. The integration of polysilanes with carbon nanotubes and graphene led to hybrid sensors with enhanced performance characteristics, including improved sensitivity, faster response times, and greater stability. These advancements made polysilane-based sensors increasingly attractive for use in complex, multi-parameter sensing systems.
Recent years have seen a focus on developing polysilane sensors for specific applications, such as environmental monitoring, healthcare diagnostics, and industrial process control. The ability of polysilanes to be tailored for different sensing needs has led to their incorporation into diverse sensor network architectures. Researchers have also made significant progress in addressing challenges related to long-term stability and reproducibility, crucial factors for widespread adoption in sensor networks.
The latest developments in polysilane sensor evolution involve the integration of these materials with advanced data processing and communication technologies. Machine learning algorithms are being employed to enhance the interpretation of sensor data, while wireless communication protocols are enabling seamless integration of polysilane sensors into Internet of Things (IoT) networks. These advancements are pushing the boundaries of what is possible in terms of real-time, distributed sensing capabilities.
In the 1990s, early experiments focused on utilizing polysilanes as photoresists and in optoelectronic devices. However, it was not until the early 2000s that researchers began to explore their potential in chemical and biological sensing. The breakthrough came with the discovery that certain polysilanes could change their optical and electrical properties in response to specific chemical stimuli, opening up new possibilities for highly sensitive and selective sensors.
The mid-2000s saw a surge in research aimed at optimizing polysilane structures for sensing applications. Scientists experimented with various side-chain modifications and copolymerization techniques to enhance sensitivity and selectivity. This period also marked the beginning of efforts to integrate polysilane sensors into miniaturized devices, paving the way for their use in sensor networks.
By the 2010s, polysilane sensors had evolved to incorporate advanced nanomaterials and fabrication techniques. The integration of polysilanes with carbon nanotubes and graphene led to hybrid sensors with enhanced performance characteristics, including improved sensitivity, faster response times, and greater stability. These advancements made polysilane-based sensors increasingly attractive for use in complex, multi-parameter sensing systems.
Recent years have seen a focus on developing polysilane sensors for specific applications, such as environmental monitoring, healthcare diagnostics, and industrial process control. The ability of polysilanes to be tailored for different sensing needs has led to their incorporation into diverse sensor network architectures. Researchers have also made significant progress in addressing challenges related to long-term stability and reproducibility, crucial factors for widespread adoption in sensor networks.
The latest developments in polysilane sensor evolution involve the integration of these materials with advanced data processing and communication technologies. Machine learning algorithms are being employed to enhance the interpretation of sensor data, while wireless communication protocols are enabling seamless integration of polysilane sensors into Internet of Things (IoT) networks. These advancements are pushing the boundaries of what is possible in terms of real-time, distributed sensing capabilities.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for polysilane-enabled sensor network integration is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing need for advanced sensing technologies across various industries. Polysilanes, with their unique electronic and optical properties, offer superior capabilities in sensor network integration, addressing the growing demand for more efficient, reliable, and interconnected sensing systems.
In the automotive sector, there is a rising demand for polysilane-based sensors in advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous vehicles. These sensors provide enhanced accuracy and reliability in detecting obstacles, monitoring vehicle surroundings, and facilitating safe navigation. The automotive industry's shift towards electrification and autonomy is expected to further boost the demand for polysilane-enabled sensor networks.
The industrial sector is another key market for polysilane-enabled sensor networks. With the advent of Industry 4.0 and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), there is an increasing need for sophisticated sensor networks that can monitor and optimize manufacturing processes, equipment performance, and overall productivity. Polysilane-based sensors offer improved sensitivity, faster response times, and better integration capabilities, making them ideal for these applications.
In the healthcare and medical devices industry, polysilane-enabled sensor networks are gaining traction for their potential in wearable health monitoring devices, point-of-care diagnostics, and remote patient monitoring systems. The ability of polysilanes to enable miniaturization and enhanced sensitivity in biosensors is particularly valuable in this sector, as it allows for more accurate and non-invasive health monitoring solutions.
The environmental monitoring and smart city applications represent another growing market for polysilane-enabled sensor networks. These sensors can be used to monitor air quality, water pollution, and other environmental parameters with greater accuracy and reliability. The integration of these sensors into smart city infrastructure enables better resource management, improved public safety, and enhanced quality of life for urban residents.
The telecommunications industry is also showing interest in polysilane-enabled sensor networks for their potential in improving network performance and reliability. These sensors can be integrated into 5G and future 6G infrastructure to optimize signal transmission, monitor network health, and enhance overall connectivity.
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, the demand for polysilane-enabled sensor networks is expected to grow across various consumer applications. From smart homes to personal health devices, the superior integration capabilities of polysilane-based sensors offer improved functionality and user experience in connected devices.
The market for polysilane-enabled sensor network integration is projected to experience substantial growth in the coming years, driven by technological advancements, increasing adoption of IoT and smart technologies, and the growing need for more efficient and reliable sensing solutions across multiple industries. This trend is likely to continue as new applications and use cases for polysilane-based sensors emerge, further expanding the market potential.
In the automotive sector, there is a rising demand for polysilane-based sensors in advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous vehicles. These sensors provide enhanced accuracy and reliability in detecting obstacles, monitoring vehicle surroundings, and facilitating safe navigation. The automotive industry's shift towards electrification and autonomy is expected to further boost the demand for polysilane-enabled sensor networks.
The industrial sector is another key market for polysilane-enabled sensor networks. With the advent of Industry 4.0 and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), there is an increasing need for sophisticated sensor networks that can monitor and optimize manufacturing processes, equipment performance, and overall productivity. Polysilane-based sensors offer improved sensitivity, faster response times, and better integration capabilities, making them ideal for these applications.
In the healthcare and medical devices industry, polysilane-enabled sensor networks are gaining traction for their potential in wearable health monitoring devices, point-of-care diagnostics, and remote patient monitoring systems. The ability of polysilanes to enable miniaturization and enhanced sensitivity in biosensors is particularly valuable in this sector, as it allows for more accurate and non-invasive health monitoring solutions.
The environmental monitoring and smart city applications represent another growing market for polysilane-enabled sensor networks. These sensors can be used to monitor air quality, water pollution, and other environmental parameters with greater accuracy and reliability. The integration of these sensors into smart city infrastructure enables better resource management, improved public safety, and enhanced quality of life for urban residents.
The telecommunications industry is also showing interest in polysilane-enabled sensor networks for their potential in improving network performance and reliability. These sensors can be integrated into 5G and future 6G infrastructure to optimize signal transmission, monitor network health, and enhance overall connectivity.
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, the demand for polysilane-enabled sensor networks is expected to grow across various consumer applications. From smart homes to personal health devices, the superior integration capabilities of polysilane-based sensors offer improved functionality and user experience in connected devices.
The market for polysilane-enabled sensor network integration is projected to experience substantial growth in the coming years, driven by technological advancements, increasing adoption of IoT and smart technologies, and the growing need for more efficient and reliable sensing solutions across multiple industries. This trend is likely to continue as new applications and use cases for polysilane-based sensors emerge, further expanding the market potential.
Technical Challenges
The integration of polysilane into sensor networks presents several significant technical challenges that researchers and engineers must overcome to fully realize its potential. One of the primary obstacles is the optimization of polysilane's molecular structure and composition to enhance its sensing capabilities while maintaining stability and reliability in diverse environmental conditions. The complex nature of polysilane polymers requires precise control over their synthesis and processing to achieve consistent performance across large-scale sensor networks.
Another critical challenge lies in the development of efficient and scalable manufacturing techniques for polysilane-based sensors. Current production methods often involve complex chemical processes that are difficult to scale up for mass production. This limitation hinders the widespread adoption of polysilane sensors in large-scale network deployments. Researchers are exploring novel fabrication approaches, such as solution-based processing and roll-to-roll manufacturing, to address this issue.
The integration of polysilane sensors with existing network infrastructure and communication protocols poses additional technical hurdles. Ensuring seamless compatibility and interoperability between polysilane-based devices and conventional sensor network components is crucial for successful implementation. This challenge encompasses both hardware integration and software development to enable effective data collection, transmission, and analysis within the network.
Power management and energy efficiency represent significant concerns in polysilane-enabled sensor networks. While polysilane offers potential advantages in terms of low power consumption, optimizing the energy usage of individual sensors and the overall network remains a complex task. Researchers are investigating innovative power harvesting techniques and energy-efficient sensing algorithms to extend the operational lifespan of polysilane-based sensor nodes.
The long-term stability and reliability of polysilane sensors in real-world environments present ongoing challenges. Exposure to various environmental factors, such as temperature fluctuations, humidity, and UV radiation, can potentially degrade the performance and lifespan of polysilane-based devices. Developing robust encapsulation methods and protective coatings to shield the sensors from these external influences is crucial for ensuring their long-term viability in diverse applications.
Data processing and interpretation pose additional challenges in polysilane-enabled sensor networks. The unique properties of polysilane sensors may require specialized algorithms and data analysis techniques to extract meaningful information from the collected data. Developing efficient signal processing methods and machine learning algorithms tailored to polysilane sensor outputs is essential for maximizing the value of the sensor network.
Finally, addressing potential environmental and health concerns associated with the use of polysilane materials in widespread sensor deployments is a critical challenge. Ensuring the safety and sustainability of polysilane-based sensors throughout their lifecycle, from production to disposal, is crucial for their acceptance and adoption in various industries and applications.
Another critical challenge lies in the development of efficient and scalable manufacturing techniques for polysilane-based sensors. Current production methods often involve complex chemical processes that are difficult to scale up for mass production. This limitation hinders the widespread adoption of polysilane sensors in large-scale network deployments. Researchers are exploring novel fabrication approaches, such as solution-based processing and roll-to-roll manufacturing, to address this issue.
The integration of polysilane sensors with existing network infrastructure and communication protocols poses additional technical hurdles. Ensuring seamless compatibility and interoperability between polysilane-based devices and conventional sensor network components is crucial for successful implementation. This challenge encompasses both hardware integration and software development to enable effective data collection, transmission, and analysis within the network.
Power management and energy efficiency represent significant concerns in polysilane-enabled sensor networks. While polysilane offers potential advantages in terms of low power consumption, optimizing the energy usage of individual sensors and the overall network remains a complex task. Researchers are investigating innovative power harvesting techniques and energy-efficient sensing algorithms to extend the operational lifespan of polysilane-based sensor nodes.
The long-term stability and reliability of polysilane sensors in real-world environments present ongoing challenges. Exposure to various environmental factors, such as temperature fluctuations, humidity, and UV radiation, can potentially degrade the performance and lifespan of polysilane-based devices. Developing robust encapsulation methods and protective coatings to shield the sensors from these external influences is crucial for ensuring their long-term viability in diverse applications.
Data processing and interpretation pose additional challenges in polysilane-enabled sensor networks. The unique properties of polysilane sensors may require specialized algorithms and data analysis techniques to extract meaningful information from the collected data. Developing efficient signal processing methods and machine learning algorithms tailored to polysilane sensor outputs is essential for maximizing the value of the sensor network.
Finally, addressing potential environmental and health concerns associated with the use of polysilane materials in widespread sensor deployments is a critical challenge. Ensuring the safety and sustainability of polysilane-based sensors throughout their lifecycle, from production to disposal, is crucial for their acceptance and adoption in various industries and applications.
Current Integration Solutions
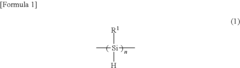
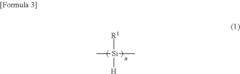
01 Polysilane synthesis and properties
Various methods for synthesizing polysilanes and their unique properties are explored. These polymers exhibit interesting electrical and optical characteristics, making them suitable for sensor applications. The synthesis techniques focus on improving the molecular weight, stability, and functionality of polysilanes.- Polysilane synthesis and properties: Various methods for synthesizing polysilanes and their unique properties are explored. These include techniques for creating high molecular weight polysilanes, improving their thermal stability, and enhancing their electrical conductivity. The resulting materials show potential for use in sensor networks due to their semiconducting properties and ability to be processed into thin films.
- Integration of polysilanes in sensor devices: Polysilanes are incorporated into sensor devices, leveraging their photosensitive and conductive properties. These materials are used to create thin-film transistors, photodetectors, and other sensing elements. The integration of polysilanes enhances the sensitivity and responsiveness of sensor networks, particularly in applications requiring light detection or electrical signal processing.
- Network architecture for polysilane-based sensors: Innovative network architectures are developed to optimize the performance of polysilane-based sensor networks. These designs focus on efficient data collection, processing, and transmission within the network. Considerations include power management, signal amplification, and noise reduction to ensure reliable operation of the polysilane sensors in various environmental conditions.
- Surface modification of polysilanes for improved sensing: Techniques for modifying the surface of polysilane materials are explored to enhance their sensing capabilities. These modifications include functionalization with specific chemical groups, creation of nanostructured surfaces, and incorporation of other materials to create hybrid sensors. The resulting sensors show improved selectivity, sensitivity, and stability in various sensing applications.
- Fabrication methods for polysilane-based sensor networks: Advanced fabrication methods are developed for creating integrated polysilane-based sensor networks. These techniques include novel deposition methods, patterning processes, and integration strategies to create large-scale, interconnected sensor arrays. The focus is on achieving uniform performance across the network while maintaining cost-effectiveness and scalability in production.
02 Polysilane-based sensor development
Polysilanes are utilized in the development of sensors due to their unique electronic and photonic properties. These sensors can detect various stimuli, including light, temperature, and chemical compounds. The integration of polysilanes into sensor devices enhances their sensitivity and response time.Expand Specific Solutions03 Network integration of polysilane sensors
The integration of polysilane-based sensors into network systems is explored. This involves developing communication protocols, data processing algorithms, and network architectures to enable efficient data collection and analysis from multiple polysilane sensors. The integration aims to create smart sensor networks for various applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Polysilane thin film fabrication
Techniques for fabricating polysilane thin films are investigated. These methods focus on creating uniform, stable films with controlled thickness and properties. The thin films are crucial for developing efficient sensors and integrating them into various devices and network systems.Expand Specific Solutions05 Functionalization of polysilanes for sensor applications
Methods for functionalizing polysilanes to enhance their sensing capabilities are explored. This includes the incorporation of specific functional groups or nanoparticles to improve selectivity and sensitivity towards target analytes. The functionalization techniques aim to expand the range of applications for polysilane-based sensors in network systems.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The integration of polysilane in sensor networks represents an emerging field in advanced materials and IoT technology. The market is in its early growth stage, with increasing research and development efforts driving innovation. While the market size is still relatively small, it is expected to expand rapidly as the technology matures and finds applications in various industries. Companies like Osaka Gas Co., Ltd. and Nippon Paint Co., Ltd. are exploring polysilane's potential in sensor applications, leveraging their expertise in materials science. Research institutions such as Hangzhou Normal University and the Chinese Academy of Sciences Institute of Acoustics are contributing to the fundamental understanding of polysilane properties. As the technology progresses, collaborations between industry leaders and academic institutions are likely to accelerate the development of polysilane-based sensor network solutions.
Wacker Chemie AG
Technical Solution: Wacker Chemie AG has developed advanced polysilane materials for superior sensor network integration. Their polysilane-based sensors offer enhanced sensitivity and stability, enabling more accurate and reliable data collection in complex environments. The company's proprietary synthesis methods result in high-purity polysilanes with tailored molecular structures, optimizing their performance for specific sensing applications[1]. These materials exhibit excellent photoconductivity and electroluminescence properties, making them ideal for optoelectronic sensors in integrated networks[2]. Wacker's polysilanes also demonstrate improved thermal stability and resistance to environmental factors, ensuring long-term reliability in diverse operating conditions[3].
Strengths: High-purity materials, tailored molecular structures, excellent optoelectronic properties. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs, limited commercial-scale production experience.
Capacitor Sciences, Inc.
Technical Solution: Capacitor Sciences, Inc. has developed innovative polysilane-based dielectric materials for advanced sensor network integration. Their proprietary polysilane formulations offer high dielectric constants and low loss tangents, enabling the creation of miniaturized, high-performance capacitive sensors[4]. These materials exhibit excellent temperature stability and low hysteresis, ensuring accurate and consistent measurements across a wide range of operating conditions[5]. The company's polysilane dielectrics also demonstrate superior compatibility with flexible substrates, facilitating the development of conformable and wearable sensor networks for IoT applications[6].
Strengths: High dielectric performance, excellent stability, compatibility with flexible substrates. Weaknesses: Limited track record in large-scale sensor network deployments, potential scalability challenges.
Core Polysilane Innovations
Polysilane and polysilane-containing resin composition
PatentInactiveUS8163863B2
Innovation
- Introducing a Si—H group into the polysilane main chain and bonding a hydrosilylatable compound with functional groups like hydroxyl, carboxyl, or epoxy groups, allowing for controlled hydrosilylation to enhance solubility and reactivity without complex steps or special apparatus.
Combined sensor and infusion set using separated sites
PatentActiveEP2190502A1
Innovation
- The development of a combined sensor and infusion apparatus with separate piercing members for the cannula and sensor, positioned in distinct in vivo environments, ensures that infused fluids do not contact the sensor, thereby preventing interference and stabilizing sensor readings by anchoring the apparatus to the skin.
Environmental Impact
The integration of polysilane-based sensor networks has significant implications for environmental sustainability and impact. Polysilane materials offer unique properties that enable the development of more efficient and environmentally friendly sensor systems. These networks can be deployed for various environmental monitoring applications, providing real-time data on air quality, water pollution, soil conditions, and ecosystem health.
One of the key environmental benefits of polysilane-enabled sensor networks is their potential for reduced energy consumption. The high charge carrier mobility and excellent photoconductivity of polysilanes allow for the creation of low-power sensors that can operate efficiently on minimal energy input. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in remote or off-grid locations, where traditional power sources may be limited or unavailable. By reducing the overall energy requirements of sensor networks, polysilane technology contributes to lower carbon emissions and a smaller ecological footprint.
Furthermore, the enhanced sensitivity and selectivity of polysilane-based sensors enable more accurate and comprehensive environmental monitoring. These sensors can detect a wide range of pollutants and contaminants at lower concentrations, allowing for earlier identification of potential environmental threats. This capability is crucial for proactive environmental management and the implementation of timely mitigation strategies.
The durability and stability of polysilane materials also contribute to their environmental benefits. Sensors constructed with polysilanes exhibit improved resistance to degradation from environmental factors such as UV radiation, temperature fluctuations, and chemical exposure. This increased longevity reduces the need for frequent sensor replacement, minimizing electronic waste and the associated environmental impact of manufacturing and disposing of sensor components.
Additionally, the versatility of polysilanes allows for the development of biodegradable or recyclable sensor materials. Research is ongoing to create polysilane-based sensors that can naturally decompose after their operational lifespan, reducing the accumulation of electronic waste in landfills. This approach aligns with circular economy principles and supports more sustainable practices in sensor network deployment.
The integration of polysilane-enabled sensor networks also has the potential to optimize resource management and conservation efforts. By providing high-resolution data on environmental conditions, these networks can inform more efficient use of water, energy, and other natural resources. For instance, in agriculture, polysilane sensors can enable precision farming techniques that minimize water usage and reduce the application of fertilizers and pesticides, thereby decreasing the environmental impact of agricultural practices.
In conclusion, the superior integration capabilities of polysilane-based sensor networks offer significant environmental benefits. From reduced energy consumption and improved monitoring accuracy to increased durability and potential biodegradability, these advanced sensor systems contribute to more sustainable environmental management practices and support global efforts to address climate change and ecological preservation.
One of the key environmental benefits of polysilane-enabled sensor networks is their potential for reduced energy consumption. The high charge carrier mobility and excellent photoconductivity of polysilanes allow for the creation of low-power sensors that can operate efficiently on minimal energy input. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in remote or off-grid locations, where traditional power sources may be limited or unavailable. By reducing the overall energy requirements of sensor networks, polysilane technology contributes to lower carbon emissions and a smaller ecological footprint.
Furthermore, the enhanced sensitivity and selectivity of polysilane-based sensors enable more accurate and comprehensive environmental monitoring. These sensors can detect a wide range of pollutants and contaminants at lower concentrations, allowing for earlier identification of potential environmental threats. This capability is crucial for proactive environmental management and the implementation of timely mitigation strategies.
The durability and stability of polysilane materials also contribute to their environmental benefits. Sensors constructed with polysilanes exhibit improved resistance to degradation from environmental factors such as UV radiation, temperature fluctuations, and chemical exposure. This increased longevity reduces the need for frequent sensor replacement, minimizing electronic waste and the associated environmental impact of manufacturing and disposing of sensor components.
Additionally, the versatility of polysilanes allows for the development of biodegradable or recyclable sensor materials. Research is ongoing to create polysilane-based sensors that can naturally decompose after their operational lifespan, reducing the accumulation of electronic waste in landfills. This approach aligns with circular economy principles and supports more sustainable practices in sensor network deployment.
The integration of polysilane-enabled sensor networks also has the potential to optimize resource management and conservation efforts. By providing high-resolution data on environmental conditions, these networks can inform more efficient use of water, energy, and other natural resources. For instance, in agriculture, polysilane sensors can enable precision farming techniques that minimize water usage and reduce the application of fertilizers and pesticides, thereby decreasing the environmental impact of agricultural practices.
In conclusion, the superior integration capabilities of polysilane-based sensor networks offer significant environmental benefits. From reduced energy consumption and improved monitoring accuracy to increased durability and potential biodegradability, these advanced sensor systems contribute to more sustainable environmental management practices and support global efforts to address climate change and ecological preservation.
Scalability and Cost Analysis
The scalability and cost analysis of polysilane-enabled sensor network integration reveals significant advantages over traditional approaches. Polysilane's unique properties allow for the creation of highly integrated and miniaturized sensor networks, offering substantial improvements in both scalability and cost-effectiveness.
From a scalability perspective, polysilane-based sensors can be fabricated using established semiconductor manufacturing processes, enabling mass production and easy integration into existing electronic systems. This compatibility with current manufacturing techniques facilitates rapid scaling of production to meet growing demand. Furthermore, the molecular structure of polysilanes can be easily modified, allowing for the development of a wide range of sensor types within the same manufacturing framework, enhancing the versatility and adaptability of sensor networks.
The cost analysis of polysilane-enabled sensor networks demonstrates notable economic benefits. The raw materials for polysilane synthesis are relatively inexpensive and abundant, contributing to lower overall production costs. Additionally, the ability to create multifunctional sensors using polysilanes reduces the need for multiple discrete components, leading to simplified system designs and decreased manufacturing complexity. This integration not only lowers material costs but also reduces assembly and testing expenses.
Energy efficiency is another crucial factor in the cost analysis of sensor networks. Polysilane-based sensors typically require less power to operate compared to conventional sensors, resulting in reduced energy consumption over the network's lifetime. This energy efficiency translates to lower operational costs and extended battery life for wireless sensor nodes, making polysilane-enabled networks particularly attractive for large-scale deployments in remote or hard-to-access locations.
The scalability of polysilane sensor networks is further enhanced by their potential for self-organization and adaptive behavior. Advanced polysilane formulations can incorporate self-healing properties, allowing for automatic repair of minor damages and extending the operational lifespan of the network. This self-maintenance capability reduces the need for frequent replacements or manual interventions, contributing to improved scalability and reduced long-term costs.
In terms of network expansion, polysilane-based sensors offer excellent compatibility with emerging communication protocols and data processing technologies. Their ability to integrate seamlessly with various wireless communication standards and edge computing platforms ensures that polysilane sensor networks can easily scale to accommodate increasing data volumes and evolving connectivity requirements without necessitating wholesale system replacements.
From a scalability perspective, polysilane-based sensors can be fabricated using established semiconductor manufacturing processes, enabling mass production and easy integration into existing electronic systems. This compatibility with current manufacturing techniques facilitates rapid scaling of production to meet growing demand. Furthermore, the molecular structure of polysilanes can be easily modified, allowing for the development of a wide range of sensor types within the same manufacturing framework, enhancing the versatility and adaptability of sensor networks.
The cost analysis of polysilane-enabled sensor networks demonstrates notable economic benefits. The raw materials for polysilane synthesis are relatively inexpensive and abundant, contributing to lower overall production costs. Additionally, the ability to create multifunctional sensors using polysilanes reduces the need for multiple discrete components, leading to simplified system designs and decreased manufacturing complexity. This integration not only lowers material costs but also reduces assembly and testing expenses.
Energy efficiency is another crucial factor in the cost analysis of sensor networks. Polysilane-based sensors typically require less power to operate compared to conventional sensors, resulting in reduced energy consumption over the network's lifetime. This energy efficiency translates to lower operational costs and extended battery life for wireless sensor nodes, making polysilane-enabled networks particularly attractive for large-scale deployments in remote or hard-to-access locations.
The scalability of polysilane sensor networks is further enhanced by their potential for self-organization and adaptive behavior. Advanced polysilane formulations can incorporate self-healing properties, allowing for automatic repair of minor damages and extending the operational lifespan of the network. This self-maintenance capability reduces the need for frequent replacements or manual interventions, contributing to improved scalability and reduced long-term costs.
In terms of network expansion, polysilane-based sensors offer excellent compatibility with emerging communication protocols and data processing technologies. Their ability to integrate seamlessly with various wireless communication standards and edge computing platforms ensures that polysilane sensor networks can easily scale to accommodate increasing data volumes and evolving connectivity requirements without necessitating wholesale system replacements.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!