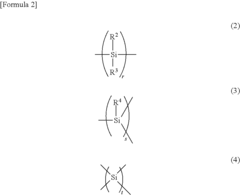Investigating New Directions for Polysilane Application
JUL 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Polysilane Evolution and Research Objectives
Polysilanes, a class of silicon-based polymers, have undergone significant evolution since their discovery in the mid-20th century. Initially considered as mere curiosities, these materials have gradually emerged as promising candidates for various technological applications. The journey of polysilanes from laboratory oddities to potential industrial materials reflects the broader trends in materials science and polymer chemistry.
The early research on polysilanes focused primarily on their synthesis and structural characterization. Scientists were intrigued by the unique silicon-silicon backbone, which differentiated these polymers from their carbon-based counterparts. As analytical techniques improved, researchers gained deeper insights into the electronic properties of polysilanes, particularly their σ-conjugation along the polymer chain.
The 1980s marked a turning point in polysilane research, with the discovery of their photoconductivity and photosensitivity. This revelation opened up new avenues for application, particularly in the field of photolithography and as photoresists in the semiconductor industry. The ability of polysilanes to undergo photodegradation under specific wavelengths of light made them attractive candidates for precision patterning in microelectronics manufacturing.
Concurrent with these developments, researchers began exploring the optical properties of polysilanes. The discovery of their strong UV absorption and efficient energy transfer mechanisms led to investigations into their potential as light-emitting materials and photonic devices. This shift in focus aligned with the growing interest in organic and polymer-based electronics, positioning polysilanes as potential alternatives to traditional inorganic semiconductors.
In recent years, the research objectives for polysilanes have expanded significantly. There is a growing interest in harnessing their unique properties for advanced applications in nanotechnology, energy storage, and biomedical fields. Scientists are now exploring ways to fine-tune the electronic and optical properties of polysilanes through molecular design and the incorporation of functional side groups.
One of the key research objectives is to enhance the processability and stability of polysilanes while maintaining their desirable properties. This includes developing new synthetic routes that allow for better control over molecular weight and polydispersity, as well as improving their resistance to oxidation and thermal degradation.
Another important goal is to expand the application scope of polysilanes beyond their traditional uses. Researchers are investigating their potential in areas such as gas sensing, catalysis, and as precursors for silicon carbide ceramics. There is also growing interest in exploring the biocompatibility of certain polysilane derivatives for drug delivery and tissue engineering applications.
As we look to the future, the research objectives for polysilanes are likely to focus on addressing global challenges. This includes exploring their role in sustainable technologies, such as solar energy harvesting and energy-efficient lighting. Additionally, there is a push to develop environmentally friendly synthesis methods and to investigate the biodegradability of polysilane-based materials.
The early research on polysilanes focused primarily on their synthesis and structural characterization. Scientists were intrigued by the unique silicon-silicon backbone, which differentiated these polymers from their carbon-based counterparts. As analytical techniques improved, researchers gained deeper insights into the electronic properties of polysilanes, particularly their σ-conjugation along the polymer chain.
The 1980s marked a turning point in polysilane research, with the discovery of their photoconductivity and photosensitivity. This revelation opened up new avenues for application, particularly in the field of photolithography and as photoresists in the semiconductor industry. The ability of polysilanes to undergo photodegradation under specific wavelengths of light made them attractive candidates for precision patterning in microelectronics manufacturing.
Concurrent with these developments, researchers began exploring the optical properties of polysilanes. The discovery of their strong UV absorption and efficient energy transfer mechanisms led to investigations into their potential as light-emitting materials and photonic devices. This shift in focus aligned with the growing interest in organic and polymer-based electronics, positioning polysilanes as potential alternatives to traditional inorganic semiconductors.
In recent years, the research objectives for polysilanes have expanded significantly. There is a growing interest in harnessing their unique properties for advanced applications in nanotechnology, energy storage, and biomedical fields. Scientists are now exploring ways to fine-tune the electronic and optical properties of polysilanes through molecular design and the incorporation of functional side groups.
One of the key research objectives is to enhance the processability and stability of polysilanes while maintaining their desirable properties. This includes developing new synthetic routes that allow for better control over molecular weight and polydispersity, as well as improving their resistance to oxidation and thermal degradation.
Another important goal is to expand the application scope of polysilanes beyond their traditional uses. Researchers are investigating their potential in areas such as gas sensing, catalysis, and as precursors for silicon carbide ceramics. There is also growing interest in exploring the biocompatibility of certain polysilane derivatives for drug delivery and tissue engineering applications.
As we look to the future, the research objectives for polysilanes are likely to focus on addressing global challenges. This includes exploring their role in sustainable technologies, such as solar energy harvesting and energy-efficient lighting. Additionally, there is a push to develop environmentally friendly synthesis methods and to investigate the biodegradability of polysilane-based materials.
Market Potential for Polysilane-Based Products
The market potential for polysilane-based products is significant and diverse, spanning multiple industries and applications. Polysilanes, a class of silicon-based polymers, have unique properties that make them attractive for various high-tech and industrial uses. In the electronics sector, polysilanes show promise as materials for organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) and photovoltaic cells. Their semiconductor properties and ability to form thin films make them suitable for next-generation display technologies and solar energy harvesting.
In the field of advanced materials, polysilanes are being explored for their potential in creating high-performance coatings and composites. Their thermal stability and resistance to harsh environments make them candidates for protective coatings in aerospace and automotive industries. The optical properties of polysilanes also open up opportunities in the photonics industry, where they could be used in optical waveguides and nonlinear optical devices.
The healthcare and biomedical sectors represent another promising market for polysilane-based products. Research is ongoing into using polysilanes as drug delivery systems, taking advantage of their biocompatibility and ability to be functionalized. Additionally, their potential as biosensors and imaging agents is being investigated, which could lead to advancements in medical diagnostics and treatment monitoring.
In the realm of nanotechnology, polysilanes are being studied for their ability to form nanostructures and nanocomposites. This property could lead to applications in areas such as water purification, where polysilane-based nanomembranes could offer improved filtration capabilities. The chemical industry is also exploring polysilanes as precursors for silicon carbide production, which has applications in high-temperature semiconductors and ceramic materials.
The growing focus on sustainable and environmentally friendly materials presents another market opportunity for polysilanes. Their potential biodegradability and the abundance of silicon as a raw material make them attractive alternatives to traditional petroleum-based polymers in certain applications. This aligns with the increasing demand for green technologies and materials across various industries.
While the market for polysilane-based products is still emerging, industry analysts project substantial growth in the coming years. The versatility of polysilanes and their potential to address challenges in multiple sectors suggest a broad and expanding market. However, realizing this potential will require overcoming technical challenges, scaling up production processes, and demonstrating clear advantages over existing materials in specific applications.
In the field of advanced materials, polysilanes are being explored for their potential in creating high-performance coatings and composites. Their thermal stability and resistance to harsh environments make them candidates for protective coatings in aerospace and automotive industries. The optical properties of polysilanes also open up opportunities in the photonics industry, where they could be used in optical waveguides and nonlinear optical devices.
The healthcare and biomedical sectors represent another promising market for polysilane-based products. Research is ongoing into using polysilanes as drug delivery systems, taking advantage of their biocompatibility and ability to be functionalized. Additionally, their potential as biosensors and imaging agents is being investigated, which could lead to advancements in medical diagnostics and treatment monitoring.
In the realm of nanotechnology, polysilanes are being studied for their ability to form nanostructures and nanocomposites. This property could lead to applications in areas such as water purification, where polysilane-based nanomembranes could offer improved filtration capabilities. The chemical industry is also exploring polysilanes as precursors for silicon carbide production, which has applications in high-temperature semiconductors and ceramic materials.
The growing focus on sustainable and environmentally friendly materials presents another market opportunity for polysilanes. Their potential biodegradability and the abundance of silicon as a raw material make them attractive alternatives to traditional petroleum-based polymers in certain applications. This aligns with the increasing demand for green technologies and materials across various industries.
While the market for polysilane-based products is still emerging, industry analysts project substantial growth in the coming years. The versatility of polysilanes and their potential to address challenges in multiple sectors suggest a broad and expanding market. However, realizing this potential will require overcoming technical challenges, scaling up production processes, and demonstrating clear advantages over existing materials in specific applications.
Current Polysilane Technology Landscape
Polysilanes have emerged as a significant class of materials in the field of polymer science and technology. The current polysilane technology landscape is characterized by a diverse range of applications and ongoing research efforts to expand their potential uses. Polysilanes are silicon-based polymers with a backbone consisting of silicon atoms bonded to organic side groups. This unique structure imparts them with interesting optical, electronic, and thermal properties.
In the realm of optoelectronics, polysilanes have shown promise as materials for organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) and photovoltaic devices. Their high electron mobility and tunable bandgap make them attractive candidates for these applications. Recent advancements have focused on improving the efficiency and stability of polysilane-based devices, with researchers exploring various side-group modifications to enhance performance.
The field of lithography has also seen significant developments in polysilane technology. These materials serve as effective photoresists due to their high sensitivity to UV light and their ability to undergo controlled degradation. Current research is aimed at developing polysilanes with enhanced resolution and improved resistance to etching processes, which are crucial for the production of increasingly miniaturized electronic components.
In the area of ceramics precursors, polysilanes have gained attention for their ability to form silicon carbide (SiC) upon pyrolysis. This property has led to their use in the production of high-performance ceramic fibers and coatings. Ongoing research is focused on optimizing the conversion process and exploring new precursor compositions to achieve desired material properties.
The current landscape also includes the exploration of polysilanes in biomedical applications. Their biocompatibility and potential for functionalization have opened up possibilities in drug delivery systems and tissue engineering scaffolds. However, this area is still in its early stages, with researchers investigating ways to improve the biodegradability and targeting capabilities of polysilane-based materials.
In the field of nanotechnology, polysilanes are being studied for their potential in creating nanostructured materials. Their ability to self-assemble into various morphologies has led to investigations into their use in templating and bottom-up fabrication of nanodevices. Current efforts are directed towards controlling the self-assembly process and integrating polysilanes with other nanomaterials to create hybrid structures with enhanced properties.
The industrial landscape for polysilane technology is characterized by a mix of established companies and emerging startups. Major chemical corporations are investing in polysilane research and development, particularly for applications in electronics and advanced materials. Meanwhile, specialized firms are focusing on niche applications, such as high-performance coatings and specialty polymers.
In the realm of optoelectronics, polysilanes have shown promise as materials for organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) and photovoltaic devices. Their high electron mobility and tunable bandgap make them attractive candidates for these applications. Recent advancements have focused on improving the efficiency and stability of polysilane-based devices, with researchers exploring various side-group modifications to enhance performance.
The field of lithography has also seen significant developments in polysilane technology. These materials serve as effective photoresists due to their high sensitivity to UV light and their ability to undergo controlled degradation. Current research is aimed at developing polysilanes with enhanced resolution and improved resistance to etching processes, which are crucial for the production of increasingly miniaturized electronic components.
In the area of ceramics precursors, polysilanes have gained attention for their ability to form silicon carbide (SiC) upon pyrolysis. This property has led to their use in the production of high-performance ceramic fibers and coatings. Ongoing research is focused on optimizing the conversion process and exploring new precursor compositions to achieve desired material properties.
The current landscape also includes the exploration of polysilanes in biomedical applications. Their biocompatibility and potential for functionalization have opened up possibilities in drug delivery systems and tissue engineering scaffolds. However, this area is still in its early stages, with researchers investigating ways to improve the biodegradability and targeting capabilities of polysilane-based materials.
In the field of nanotechnology, polysilanes are being studied for their potential in creating nanostructured materials. Their ability to self-assemble into various morphologies has led to investigations into their use in templating and bottom-up fabrication of nanodevices. Current efforts are directed towards controlling the self-assembly process and integrating polysilanes with other nanomaterials to create hybrid structures with enhanced properties.
The industrial landscape for polysilane technology is characterized by a mix of established companies and emerging startups. Major chemical corporations are investing in polysilane research and development, particularly for applications in electronics and advanced materials. Meanwhile, specialized firms are focusing on niche applications, such as high-performance coatings and specialty polymers.
Existing Polysilane Application Methods
01 Synthesis and properties of polysilanes
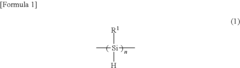
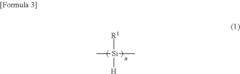
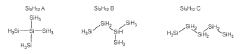
Polysilanes are silicon-based polymers with unique electronic and optical properties. They can be synthesized through various methods, including Wurtz coupling of dichlorosilanes. These materials exhibit high thermal stability and can be used in various applications such as photoresists and precursors for silicon carbide.- Synthesis and properties of polysilanes: Polysilanes are synthesized through various methods and exhibit unique properties. These silicon-based polymers have a backbone consisting of silicon atoms and can be modified with different substituents. They possess interesting optical and electronic properties, making them suitable for various applications in materials science and electronics.
- Applications of polysilanes in coatings and films: Polysilanes are utilized in the production of coatings and thin films. They can be applied to various substrates to create protective or functional layers. These coatings may exhibit properties such as improved adhesion, thermal stability, or optical characteristics, making them valuable in industries like electronics and automotive.
- Polysilanes in photoresist materials: Polysilanes are employed in the development of photoresist materials for lithography processes. Their photosensitive properties and ability to undergo photochemical reactions make them suitable for use in the fabrication of microelectronic devices and other applications requiring precise patterning.
- Functionalization and modification of polysilanes: Polysilanes can be functionalized or modified to enhance their properties or introduce new functionalities. This may involve the incorporation of various substituents or the creation of copolymers. Such modifications can lead to improved thermal stability, solubility, or specific optical or electronic characteristics.
- Polysilanes in semiconductor applications: Polysilanes find applications in semiconductor technology. They can be used as precursors for silicon-based materials or as components in electronic devices. Their unique electronic properties and ability to form stable films make them interesting candidates for various semiconductor applications.
02 Polysilane applications in electronics and optics
Polysilanes have applications in electronic and optical devices due to their unique properties. They can be used as photoresists in lithography processes, as well as in the fabrication of organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) and other optoelectronic devices. Their sigma-conjugation along the silicon backbone contributes to their interesting optical properties.Expand Specific Solutions03 Polysilane-based composite materials
Polysilanes can be incorporated into composite materials to enhance their properties. These composites may include polysilane-based coatings, films, or blends with other polymers. The addition of polysilanes can improve thermal stability, mechanical properties, and optical characteristics of the resulting materials.Expand Specific Solutions04 Modification and functionalization of polysilanes
Polysilanes can be modified or functionalized to tailor their properties for specific applications. This may involve the incorporation of various functional groups, copolymerization with other monomers, or post-polymerization modifications. These modifications can alter the solubility, reactivity, and electronic properties of the polysilanes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Polysilane processing and fabrication techniques
Various processing and fabrication techniques can be employed to create polysilane-based materials and devices. These may include solution processing, spin-coating, thermal evaporation, and lithographic patterning. The choice of processing method can significantly impact the final properties and performance of the polysilane materials.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Polysilane Research and Industry
The polysilane application market is in an early growth stage, characterized by ongoing research and development efforts across various industries. While the market size remains relatively small, it shows promising potential for expansion due to polysilanes' unique properties. The technology's maturity is still evolving, with companies like JSR Corp., Air Liquide SA, and Wacker Chemie AG leading the way in research and commercialization. These firms are exploring applications in electronics, photonics, and advanced materials. As the technology progresses, we can expect increased competition and diversification of applications, potentially driving market growth in the coming years.
JSR Corp.
Technical Solution: JSR Corp. has been at the forefront of polysilane research and application development. Their innovative approach focuses on utilizing polysilanes as precursors for silicon carbide (SiC) ceramics, which have applications in high-temperature environments[1]. The company has developed a proprietary process for synthesizing high-molecular-weight polysilanes with controlled structures, enabling the production of SiC fibers with enhanced mechanical properties[2]. JSR's polysilane-derived SiC materials demonstrate improved thermal stability and oxidation resistance compared to conventional ceramics[3], making them suitable for aerospace and energy sector applications.
Strengths: Advanced synthesis techniques for high-performance polysilanes; Expertise in SiC ceramic production. Weaknesses: Limited commercial scale production; High production costs compared to traditional materials.
Wacker Chemie AG
Technical Solution: Wacker Chemie AG has been exploring new directions for polysilane applications in the field of photovoltaics and electronics. Their research focuses on developing polysilane-based thin films for next-generation solar cells and organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs)[4]. Wacker's proprietary polysilane synthesis method allows for precise control over the silicon backbone structure, resulting in materials with tunable optoelectronic properties[5]. The company has successfully demonstrated polysilane thin films with high charge carrier mobility and improved light absorption characteristics, potentially leading to more efficient and cost-effective solar cells[6].
Strengths: Extensive experience in silicon chemistry; Strong R&D capabilities in optoelectronic materials. Weaknesses: Fierce competition in the photovoltaic market; Challenges in scaling up production for commercial applications.
Breakthrough Polysilane Synthesis Techniques
Polysilane and polysilane-containing resin composition
PatentInactiveUS8163863B2
Innovation
- Introducing a Si—H group into the polysilane main chain and bonding a hydrosilylatable compound with functional groups like hydroxyl, carboxyl, or epoxy groups, allowing for controlled hydrosilylation to enhance solubility and reactivity without complex steps or special apparatus.
Process for producing liquid polysilanes and isomer enriched higher silanes
PatentWO2020077183A1
Innovation
- The synthesis of higher silanes involves catalytic transformation of lower silanes using heterogeneous catalysts, such as Group I, II, or III element-based catalysts, to control temperature, residence time, and reactant ratios, resulting in isomerically enriched polysilanes with specific isomer ratios and high purity.
Environmental Impact of Polysilane Production
The production of polysilanes, while offering promising applications in various fields, raises significant environmental concerns that warrant careful consideration. The synthesis of polysilanes typically involves energy-intensive processes and the use of potentially hazardous chemicals, which can have adverse effects on the environment if not properly managed.
One of the primary environmental impacts of polysilane production is the generation of chemical waste. The synthesis often requires the use of alkali metals, such as sodium or potassium, which can react violently with water and pose disposal challenges. Additionally, the use of chlorosilanes as precursors can lead to the formation of hydrochloric acid as a by-product, necessitating proper neutralization and disposal procedures.
Energy consumption during polysilane production is another significant environmental factor. The high temperatures required for certain synthesis methods contribute to increased carbon emissions and energy costs. This aspect becomes particularly relevant when considering the scalability of polysilane production for industrial applications.
The potential for air and water pollution during the manufacturing process is also a concern. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) may be released during synthesis, potentially contributing to air quality issues if not adequately controlled. Similarly, improper handling or accidental release of chemicals used in polysilane production could lead to water contamination, affecting aquatic ecosystems and potentially human health.
Recycling and end-of-life considerations for polysilane-based products present additional environmental challenges. The stability of silicon-silicon bonds in polysilanes can make these materials resistant to natural degradation, potentially leading to long-term environmental persistence if not properly managed or recycled.
However, it is important to note that ongoing research is focused on developing more environmentally friendly synthesis methods for polysilanes. Green chemistry approaches, such as the use of less hazardous reagents and catalysts, are being explored to minimize the environmental impact of production processes. Additionally, efforts are being made to improve the energy efficiency of synthesis methods and to develop closed-loop systems that reduce waste generation and promote recycling.
The environmental impact of polysilane production must be weighed against the potential benefits of their applications. For instance, the use of polysilanes in photovoltaic technologies could contribute to the development of more efficient solar cells, potentially offsetting their production-related environmental costs through long-term renewable energy generation.
One of the primary environmental impacts of polysilane production is the generation of chemical waste. The synthesis often requires the use of alkali metals, such as sodium or potassium, which can react violently with water and pose disposal challenges. Additionally, the use of chlorosilanes as precursors can lead to the formation of hydrochloric acid as a by-product, necessitating proper neutralization and disposal procedures.
Energy consumption during polysilane production is another significant environmental factor. The high temperatures required for certain synthesis methods contribute to increased carbon emissions and energy costs. This aspect becomes particularly relevant when considering the scalability of polysilane production for industrial applications.
The potential for air and water pollution during the manufacturing process is also a concern. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) may be released during synthesis, potentially contributing to air quality issues if not adequately controlled. Similarly, improper handling or accidental release of chemicals used in polysilane production could lead to water contamination, affecting aquatic ecosystems and potentially human health.
Recycling and end-of-life considerations for polysilane-based products present additional environmental challenges. The stability of silicon-silicon bonds in polysilanes can make these materials resistant to natural degradation, potentially leading to long-term environmental persistence if not properly managed or recycled.
However, it is important to note that ongoing research is focused on developing more environmentally friendly synthesis methods for polysilanes. Green chemistry approaches, such as the use of less hazardous reagents and catalysts, are being explored to minimize the environmental impact of production processes. Additionally, efforts are being made to improve the energy efficiency of synthesis methods and to develop closed-loop systems that reduce waste generation and promote recycling.
The environmental impact of polysilane production must be weighed against the potential benefits of their applications. For instance, the use of polysilanes in photovoltaic technologies could contribute to the development of more efficient solar cells, potentially offsetting their production-related environmental costs through long-term renewable energy generation.
Polysilane Commercialization Challenges
The commercialization of polysilanes faces several significant challenges that have hindered their widespread adoption in industrial applications. One of the primary obstacles is the high production cost associated with synthesizing polysilanes on a large scale. Traditional methods of polysilane synthesis often involve complex and expensive processes, making it difficult to compete with more established materials in terms of cost-effectiveness.
Another major challenge is the limited stability of polysilanes under certain environmental conditions. Many polysilanes are sensitive to moisture and oxygen, which can lead to degradation and loss of their unique properties. This instability poses significant hurdles for long-term storage, transportation, and application in various industries, particularly those requiring exposure to ambient conditions.
The lack of standardized production methods and quality control measures also presents a barrier to commercialization. The properties of polysilanes can vary significantly depending on the synthesis method and conditions, making it challenging to achieve consistent performance across different batches. This variability hampers the development of reliable products and makes it difficult to meet the stringent quality requirements of potential industrial customers.
Furthermore, the limited understanding of structure-property relationships in polysilanes has impeded the development of tailored materials for specific applications. While polysilanes exhibit promising properties, such as high thermal stability and unique electronic characteristics, optimizing these properties for specific end-uses remains a challenge. This knowledge gap hinders the ability to design polysilanes with precisely controlled properties that meet the diverse needs of different industries.
Regulatory hurdles and safety concerns also play a role in slowing down the commercialization process. As relatively new materials, polysilanes may face additional scrutiny from regulatory bodies, requiring extensive testing and documentation to prove their safety and environmental impact. This process can be time-consuming and costly, further delaying market entry.
Lastly, the lack of established supply chains and manufacturing infrastructure for polysilanes presents logistical challenges for scaling up production. Developing efficient and cost-effective manufacturing processes, as well as building the necessary supply networks, requires significant investment and time. This infrastructure gap makes it difficult for polysilanes to compete with more established materials that already have well-developed production and distribution systems in place.
Another major challenge is the limited stability of polysilanes under certain environmental conditions. Many polysilanes are sensitive to moisture and oxygen, which can lead to degradation and loss of their unique properties. This instability poses significant hurdles for long-term storage, transportation, and application in various industries, particularly those requiring exposure to ambient conditions.
The lack of standardized production methods and quality control measures also presents a barrier to commercialization. The properties of polysilanes can vary significantly depending on the synthesis method and conditions, making it challenging to achieve consistent performance across different batches. This variability hampers the development of reliable products and makes it difficult to meet the stringent quality requirements of potential industrial customers.
Furthermore, the limited understanding of structure-property relationships in polysilanes has impeded the development of tailored materials for specific applications. While polysilanes exhibit promising properties, such as high thermal stability and unique electronic characteristics, optimizing these properties for specific end-uses remains a challenge. This knowledge gap hinders the ability to design polysilanes with precisely controlled properties that meet the diverse needs of different industries.
Regulatory hurdles and safety concerns also play a role in slowing down the commercialization process. As relatively new materials, polysilanes may face additional scrutiny from regulatory bodies, requiring extensive testing and documentation to prove their safety and environmental impact. This process can be time-consuming and costly, further delaying market entry.
Lastly, the lack of established supply chains and manufacturing infrastructure for polysilanes presents logistical challenges for scaling up production. Developing efficient and cost-effective manufacturing processes, as well as building the necessary supply networks, requires significant investment and time. This infrastructure gap makes it difficult for polysilanes to compete with more established materials that already have well-developed production and distribution systems in place.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!