How Polysilane Shapes Next-Generation User Interfaces?
JUL 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Polysilane UI Evolution
The evolution of polysilane-based user interfaces represents a significant leap forward in human-computer interaction. This progression can be traced through several key stages, each marked by technological advancements and innovative applications.
In the early stages, polysilane materials were primarily explored for their unique optical and electronic properties. Researchers discovered that these silicon-based polymers exhibited excellent photoconductivity and electroluminescence, making them potential candidates for display technologies. This initial phase laid the groundwork for future developments in user interface design.
As the technology matured, the focus shifted towards integrating polysilane into flexible and transparent substrates. This breakthrough allowed for the creation of bendable and see-through displays, opening up new possibilities for wearable devices and augmented reality applications. The ability to conform to various shapes and surfaces marked a significant departure from traditional rigid interface designs.
The next phase saw the development of touch-sensitive polysilane films. By incorporating conductive nanoparticles into the polymer matrix, researchers created highly responsive touch interfaces that could be seamlessly integrated into various form factors. This advancement paved the way for more intuitive and interactive user experiences across a wide range of devices.
Recent years have witnessed the emergence of self-healing polysilane interfaces. These materials can repair minor scratches and damages autonomously, significantly enhancing the durability and longevity of user interface components. This self-repairing capability addresses one of the major challenges in maintaining the functionality and aesthetics of frequently used touch surfaces.
The latest frontier in polysilane UI evolution is the development of shape-shifting interfaces. By leveraging the material's unique molecular structure and responsiveness to external stimuli, researchers are creating interfaces that can dynamically change their physical form. This opens up possibilities for adaptive user interfaces that can morph to accommodate different user needs or environmental conditions.
Looking ahead, the integration of polysilane with other emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and haptic feedback systems promises to revolutionize the way we interact with digital devices. The potential for creating highly personalized, context-aware interfaces that can adapt in real-time to user preferences and environmental factors represents the next major milestone in the evolution of polysilane-based user interfaces.
In the early stages, polysilane materials were primarily explored for their unique optical and electronic properties. Researchers discovered that these silicon-based polymers exhibited excellent photoconductivity and electroluminescence, making them potential candidates for display technologies. This initial phase laid the groundwork for future developments in user interface design.
As the technology matured, the focus shifted towards integrating polysilane into flexible and transparent substrates. This breakthrough allowed for the creation of bendable and see-through displays, opening up new possibilities for wearable devices and augmented reality applications. The ability to conform to various shapes and surfaces marked a significant departure from traditional rigid interface designs.
The next phase saw the development of touch-sensitive polysilane films. By incorporating conductive nanoparticles into the polymer matrix, researchers created highly responsive touch interfaces that could be seamlessly integrated into various form factors. This advancement paved the way for more intuitive and interactive user experiences across a wide range of devices.
Recent years have witnessed the emergence of self-healing polysilane interfaces. These materials can repair minor scratches and damages autonomously, significantly enhancing the durability and longevity of user interface components. This self-repairing capability addresses one of the major challenges in maintaining the functionality and aesthetics of frequently used touch surfaces.
The latest frontier in polysilane UI evolution is the development of shape-shifting interfaces. By leveraging the material's unique molecular structure and responsiveness to external stimuli, researchers are creating interfaces that can dynamically change their physical form. This opens up possibilities for adaptive user interfaces that can morph to accommodate different user needs or environmental conditions.
Looking ahead, the integration of polysilane with other emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and haptic feedback systems promises to revolutionize the way we interact with digital devices. The potential for creating highly personalized, context-aware interfaces that can adapt in real-time to user preferences and environmental factors represents the next major milestone in the evolution of polysilane-based user interfaces.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for polysilane-based next-generation user interfaces is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing need for more intuitive, responsive, and versatile interaction methods across various industries. As consumers and businesses alike seek more immersive and efficient ways to interact with digital devices, polysilane technology offers promising solutions that could revolutionize the user interface landscape.
In the consumer electronics sector, there is a growing demand for flexible, transparent, and lightweight displays that can be integrated into wearable devices, smart home appliances, and automotive interfaces. Polysilane's unique properties, such as its ability to form thin, flexible films with excellent optical and electrical characteristics, position it as a key material for developing these advanced display technologies. This aligns with the trend towards more seamless and unobtrusive integration of technology into everyday objects and environments.
The automotive industry represents another significant market for polysilane-based interfaces. As vehicles become increasingly connected and autonomous, there is a rising demand for advanced human-machine interfaces that can provide drivers and passengers with intuitive and distraction-free interaction methods. Polysilane's potential to enable transparent, heads-up displays and touch-sensitive surfaces throughout the vehicle interior makes it an attractive option for next-generation automotive user interfaces.
In the healthcare sector, the need for more hygienic and efficient user interfaces in medical devices and hospital equipment is driving interest in polysilane technology. Its ability to create smooth, easy-to-clean surfaces that can incorporate touch and gesture recognition capabilities addresses the growing concern for infection control in healthcare settings while improving the user experience for both medical professionals and patients.
The industrial and manufacturing sectors are also showing increased demand for robust, responsive interfaces that can withstand harsh environments. Polysilane's durability and potential for creating flexible, touch-sensitive surfaces make it well-suited for developing user interfaces for industrial machinery, control panels, and wearable devices for workers in challenging environments.
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, there is a growing market for innovative user interfaces that can seamlessly connect and control multiple devices. Polysilane's versatility in creating various interface types, from transparent displays to touch-sensitive surfaces, positions it as a key enabling technology for developing unified control systems for smart homes, offices, and industrial settings.
The education and entertainment industries are also driving demand for more engaging and interactive user interfaces. Polysilane's potential to create large, flexible displays and touch-sensitive surfaces opens up new possibilities for interactive learning environments, immersive gaming experiences, and innovative art installations.
In the consumer electronics sector, there is a growing demand for flexible, transparent, and lightweight displays that can be integrated into wearable devices, smart home appliances, and automotive interfaces. Polysilane's unique properties, such as its ability to form thin, flexible films with excellent optical and electrical characteristics, position it as a key material for developing these advanced display technologies. This aligns with the trend towards more seamless and unobtrusive integration of technology into everyday objects and environments.
The automotive industry represents another significant market for polysilane-based interfaces. As vehicles become increasingly connected and autonomous, there is a rising demand for advanced human-machine interfaces that can provide drivers and passengers with intuitive and distraction-free interaction methods. Polysilane's potential to enable transparent, heads-up displays and touch-sensitive surfaces throughout the vehicle interior makes it an attractive option for next-generation automotive user interfaces.
In the healthcare sector, the need for more hygienic and efficient user interfaces in medical devices and hospital equipment is driving interest in polysilane technology. Its ability to create smooth, easy-to-clean surfaces that can incorporate touch and gesture recognition capabilities addresses the growing concern for infection control in healthcare settings while improving the user experience for both medical professionals and patients.
The industrial and manufacturing sectors are also showing increased demand for robust, responsive interfaces that can withstand harsh environments. Polysilane's durability and potential for creating flexible, touch-sensitive surfaces make it well-suited for developing user interfaces for industrial machinery, control panels, and wearable devices for workers in challenging environments.
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, there is a growing market for innovative user interfaces that can seamlessly connect and control multiple devices. Polysilane's versatility in creating various interface types, from transparent displays to touch-sensitive surfaces, positions it as a key enabling technology for developing unified control systems for smart homes, offices, and industrial settings.
The education and entertainment industries are also driving demand for more engaging and interactive user interfaces. Polysilane's potential to create large, flexible displays and touch-sensitive surfaces opens up new possibilities for interactive learning environments, immersive gaming experiences, and innovative art installations.
Technical Challenges
Polysilane technology, while promising for next-generation user interfaces, faces several significant technical challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption. One of the primary obstacles is the stability and durability of polysilane materials in various environmental conditions. Exposure to heat, light, and moisture can lead to degradation of the polymer structure, potentially compromising the performance and longevity of devices incorporating this technology.
Another critical challenge lies in the scalability of polysilane production. Current synthesis methods are often complex and yield relatively small quantities, making it difficult to meet the demands of large-scale manufacturing. Researchers are working on developing more efficient and cost-effective production techniques, but significant improvements are still needed to make polysilane-based interfaces commercially viable.
The integration of polysilane materials with existing electronic components and manufacturing processes presents another hurdle. Compatibility issues may arise when attempting to incorporate polysilane into conventional device architectures, requiring novel approaches to interface design and fabrication techniques. This integration challenge extends to ensuring seamless communication between polysilane-based components and traditional electronic systems.
Furthermore, the optimization of electrical and optical properties of polysilane materials for specific interface applications remains an ongoing challenge. While polysilanes exhibit promising characteristics, fine-tuning these properties to meet the diverse requirements of different user interface scenarios requires extensive research and development efforts.
The development of reliable and precise patterning techniques for polysilane materials is also crucial. Creating intricate and high-resolution patterns is essential for many interface applications, but achieving this with polysilane can be challenging due to its unique chemical and physical properties. Researchers are exploring various lithographic and printing methods to overcome these limitations.
Lastly, the long-term reliability and performance consistency of polysilane-based interfaces need to be thoroughly evaluated and improved. As a relatively new technology, there is limited data on how these materials behave over extended periods of use in real-world conditions. Addressing concerns about potential degradation, fatigue, or changes in performance characteristics over time is essential for building consumer and industry confidence in polysilane-based user interfaces.
Another critical challenge lies in the scalability of polysilane production. Current synthesis methods are often complex and yield relatively small quantities, making it difficult to meet the demands of large-scale manufacturing. Researchers are working on developing more efficient and cost-effective production techniques, but significant improvements are still needed to make polysilane-based interfaces commercially viable.
The integration of polysilane materials with existing electronic components and manufacturing processes presents another hurdle. Compatibility issues may arise when attempting to incorporate polysilane into conventional device architectures, requiring novel approaches to interface design and fabrication techniques. This integration challenge extends to ensuring seamless communication between polysilane-based components and traditional electronic systems.
Furthermore, the optimization of electrical and optical properties of polysilane materials for specific interface applications remains an ongoing challenge. While polysilanes exhibit promising characteristics, fine-tuning these properties to meet the diverse requirements of different user interface scenarios requires extensive research and development efforts.
The development of reliable and precise patterning techniques for polysilane materials is also crucial. Creating intricate and high-resolution patterns is essential for many interface applications, but achieving this with polysilane can be challenging due to its unique chemical and physical properties. Researchers are exploring various lithographic and printing methods to overcome these limitations.
Lastly, the long-term reliability and performance consistency of polysilane-based interfaces need to be thoroughly evaluated and improved. As a relatively new technology, there is limited data on how these materials behave over extended periods of use in real-world conditions. Addressing concerns about potential degradation, fatigue, or changes in performance characteristics over time is essential for building consumer and industry confidence in polysilane-based user interfaces.
Current UI Solutions
01 Polysilane-based electronic devices
Polysilanes are used in the development of electronic devices, including user interfaces. These materials exhibit unique electrical and optical properties, making them suitable for various applications in display technologies and touch-sensitive interfaces.- Polysilane-based materials for electronic devices: Polysilanes are used in the development of electronic devices, including user interfaces. These materials exhibit unique optical and electrical properties, making them suitable for various applications in display technologies and touch-sensitive surfaces.
- User interface design incorporating polysilane components: The integration of polysilane-based components in user interface design enhances functionality and performance. These materials can be used to create responsive and durable touch surfaces, improving user experience in various electronic devices.
- Polysilane synthesis and modification for UI applications: Advanced synthesis and modification techniques for polysilanes are developed to tailor their properties for specific user interface applications. This includes adjusting molecular weight, side-chain functionalization, and incorporating other elements to enhance performance in UI devices.
- Polysilane-based flexible and transparent UI elements: Polysilanes are utilized in the creation of flexible and transparent user interface elements. These materials enable the development of bendable displays, transparent touch panels, and other innovative UI components that can be integrated into various devices.
- Integration of polysilanes in next-generation UI technologies: Polysilanes play a crucial role in the development of next-generation user interface technologies. This includes their application in advanced haptic feedback systems, holographic displays, and other emerging UI concepts that require materials with unique optical and electrical properties.
02 User interface design for polysilane applications
Specific user interface designs are created to optimize the interaction with polysilane-based devices. These interfaces take advantage of the material's properties to enhance user experience and functionality in electronic devices and displays.Expand Specific Solutions03 Polysilane synthesis and modification for UI applications
Various methods for synthesizing and modifying polysilanes are developed to enhance their properties for use in user interfaces. These processes aim to improve the material's performance, durability, and compatibility with existing technologies.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration of polysilanes in touchscreen technologies
Polysilanes are incorporated into touchscreen technologies, leveraging their unique properties to create responsive and efficient user interfaces. This integration enhances the performance and functionality of touch-sensitive displays and input devices.Expand Specific Solutions05 Software development for polysilane-based UI systems
Specialized software is developed to optimize the performance and functionality of polysilane-based user interface systems. This software takes into account the unique properties of polysilanes to create more efficient and responsive user experiences.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The polysilane-based next-generation user interface technology is in an early development stage, with a growing but still limited market size. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established chemical companies and emerging materials technology firms. Key players like JSR Corp., Dow Silicones Corp., and Momentive Performance Materials are leveraging their expertise in silicone-based materials to develop polysilane applications. Research institutions such as South China University of Technology and Interuniversitair Micro-Electronica Centrum are contributing to technological advancements. While the technology shows promise, its maturity level varies among companies, with some still in the research phase and others moving towards commercialization.
JSR Corp.
Technical Solution: JSR Corp. has developed advanced polysilane materials for next-generation user interfaces. Their approach focuses on creating ultra-thin, flexible, and transparent polysilane films that can be integrated into various display technologies. These films offer improved optical properties, including high transparency and low haze, which are crucial for enhancing the visual quality of displays[1]. JSR's polysilane-based materials also demonstrate excellent thermal stability and adhesion properties, making them suitable for use in flexible and foldable devices[3]. The company has successfully incorporated their polysilane technology into OLED displays, resulting in improved efficiency and longer device lifetimes[5].
Strengths: Superior optical properties, flexibility, and durability. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs compared to traditional materials, and limited large-scale manufacturing experience.
3M Innovative Properties Co.
Technical Solution: 3M has developed a novel polysilane-based coating technology for next-generation user interfaces. Their approach utilizes polysilane nanocomposites to create ultra-thin, scratch-resistant coatings for touchscreens and displays. These coatings offer enhanced durability and improved touch sensitivity, while maintaining high transparency[2]. 3M's polysilane technology also incorporates self-healing properties, allowing minor scratches to disappear over time, thus extending the lifespan of devices[4]. Additionally, the company has developed polysilane-based anti-reflective coatings that significantly reduce glare and improve display visibility in various lighting conditions[6].
Strengths: Durability, self-healing properties, and enhanced touch sensitivity. Weaknesses: Potential for higher costs and complexity in manufacturing processes.
Polysilane Innovations
Dioxaborinane co-polymers and uses thereof
PatentInactiveUS20130261274A1
Innovation
- Development of dioxaborinane co-polymers with pendant dioxaborinane moieties and polymerizable groups, which can be combined with active moieties like hole transport agents or luminescent agents through Suzuki or Chan-Lam coupling reactions, allowing for the creation of flexible or stretchable user interfaces by adjusting polymer properties through co-polymerization with other monomers.
Light source with organic layer and photoluminescent layer
PatentInactiveUS6700322B1
Innovation
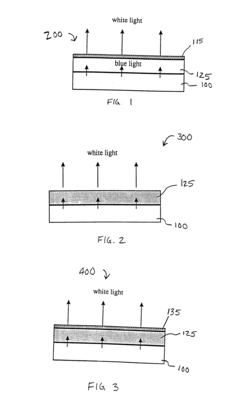
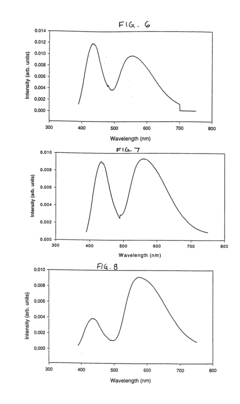
- Combining an organic light emitting device with a layer of photoluminescent material, such as phosphor particles, which absorbs and re-emits light to produce a mixed spectrum, enhancing color stability and uniformity by scattering the emitted light, thereby achieving a high color rendering index and consistent color temperature in the range of 3000-6500 K.
Material Safety Regs
As polysilane-based materials gain prominence in next-generation user interfaces, ensuring their safe use and handling becomes paramount. Material safety regulations for polysilanes are evolving to address the unique properties and potential risks associated with these innovative compounds. Regulatory bodies worldwide are developing guidelines to govern the production, transportation, storage, and application of polysilanes in consumer electronics and other interface technologies.
One key focus of material safety regulations is the potential for polysilane degradation under certain environmental conditions. Exposure to ultraviolet light or high temperatures can lead to the breakdown of polysilane chains, potentially releasing volatile organic compounds (VOCs). As a result, manufacturers are required to implement stringent quality control measures and provide appropriate packaging to minimize degradation risks during storage and transportation.
Occupational safety standards for workers handling polysilanes are also being established. These regulations typically mandate the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, goggles, and respiratory protection, when working with polysilane materials. Additionally, workplace ventilation requirements are being implemented to mitigate potential exposure to VOCs or other byproducts during manufacturing processes.
Environmental considerations play a significant role in polysilane safety regulations. Guidelines are being developed to address proper disposal methods for polysilane waste and recycling procedures for devices containing polysilane-based components. These measures aim to minimize the environmental impact of polysilane materials throughout their lifecycle.
As the application of polysilanes in user interfaces expands, regulatory bodies are also focusing on end-user safety. This includes setting limits on the permissible levels of polysilane-related compounds in consumer products and establishing testing protocols to ensure compliance. Manufacturers are required to provide safety data sheets and user guidelines detailing proper handling, maintenance, and disposal of polysilane-enabled devices.
International harmonization of polysilane safety regulations is an ongoing effort. Organizations such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) are working to develop consistent global standards for polysilane materials. This harmonization aims to facilitate international trade while ensuring uniform safety practices across different regions.
As research into polysilane applications continues, regulatory frameworks are expected to evolve. Ongoing studies on the long-term effects of polysilane exposure and potential environmental impacts will likely inform future updates to material safety regulations. This dynamic regulatory landscape underscores the importance of continued collaboration between industry stakeholders, researchers, and regulatory bodies to ensure the safe and responsible development of polysilane-based user interface technologies.
One key focus of material safety regulations is the potential for polysilane degradation under certain environmental conditions. Exposure to ultraviolet light or high temperatures can lead to the breakdown of polysilane chains, potentially releasing volatile organic compounds (VOCs). As a result, manufacturers are required to implement stringent quality control measures and provide appropriate packaging to minimize degradation risks during storage and transportation.
Occupational safety standards for workers handling polysilanes are also being established. These regulations typically mandate the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, goggles, and respiratory protection, when working with polysilane materials. Additionally, workplace ventilation requirements are being implemented to mitigate potential exposure to VOCs or other byproducts during manufacturing processes.
Environmental considerations play a significant role in polysilane safety regulations. Guidelines are being developed to address proper disposal methods for polysilane waste and recycling procedures for devices containing polysilane-based components. These measures aim to minimize the environmental impact of polysilane materials throughout their lifecycle.
As the application of polysilanes in user interfaces expands, regulatory bodies are also focusing on end-user safety. This includes setting limits on the permissible levels of polysilane-related compounds in consumer products and establishing testing protocols to ensure compliance. Manufacturers are required to provide safety data sheets and user guidelines detailing proper handling, maintenance, and disposal of polysilane-enabled devices.
International harmonization of polysilane safety regulations is an ongoing effort. Organizations such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) are working to develop consistent global standards for polysilane materials. This harmonization aims to facilitate international trade while ensuring uniform safety practices across different regions.
As research into polysilane applications continues, regulatory frameworks are expected to evolve. Ongoing studies on the long-term effects of polysilane exposure and potential environmental impacts will likely inform future updates to material safety regulations. This dynamic regulatory landscape underscores the importance of continued collaboration between industry stakeholders, researchers, and regulatory bodies to ensure the safe and responsible development of polysilane-based user interface technologies.
User Experience Impact
Polysilane technology is poised to revolutionize user interfaces, offering a transformative impact on user experience across various digital platforms. The integration of polysilane-based materials in next-generation interfaces promises to enhance interaction modalities, visual quality, and overall user engagement.
One of the most significant impacts of polysilane on user experience is the potential for more responsive and intuitive touch interfaces. The unique properties of polysilane allow for the development of ultra-thin, flexible touchscreens that can conform to various surfaces and shapes. This adaptability enables the creation of seamless, curved displays that provide a more natural and ergonomic interaction experience for users.
The improved optical properties of polysilane-based displays contribute to enhanced visual experiences. With higher contrast ratios, wider color gamuts, and improved brightness levels, users can enjoy more vivid and lifelike images. This advancement is particularly beneficial for applications such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), where immersive visual experiences are crucial for user engagement and satisfaction.
Polysilane's potential for creating transparent and flexible displays opens up new possibilities for ambient computing interfaces. These interfaces can be seamlessly integrated into everyday objects and environments, allowing for more natural and unobtrusive interactions. This shift towards ubiquitous computing interfaces could lead to a more intuitive and less technology-centric user experience, where digital interactions blend seamlessly with the physical world.
The energy efficiency of polysilane-based displays also contributes to improved user experience by extending battery life in mobile devices. Longer-lasting devices mean fewer interruptions for charging, leading to more continuous and satisfying user interactions. Additionally, the reduced power consumption aligns with growing user preferences for eco-friendly and sustainable technology solutions.
Polysilane's potential for creating highly responsive and low-latency interfaces could significantly enhance the user experience in gaming and other real-time interactive applications. The reduced input lag and smoother visual feedback can lead to more immersive and engaging experiences, potentially revolutionizing how users interact with digital content and virtual environments.
As polysilane technology matures, it is expected to enable new forms of haptic feedback in user interfaces. This could lead to more tactile and multi-sensory interactions, enriching the user experience by engaging multiple senses simultaneously. Such advancements could be particularly impactful in areas like accessibility, providing alternative interaction methods for users with visual or auditory impairments.
One of the most significant impacts of polysilane on user experience is the potential for more responsive and intuitive touch interfaces. The unique properties of polysilane allow for the development of ultra-thin, flexible touchscreens that can conform to various surfaces and shapes. This adaptability enables the creation of seamless, curved displays that provide a more natural and ergonomic interaction experience for users.
The improved optical properties of polysilane-based displays contribute to enhanced visual experiences. With higher contrast ratios, wider color gamuts, and improved brightness levels, users can enjoy more vivid and lifelike images. This advancement is particularly beneficial for applications such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), where immersive visual experiences are crucial for user engagement and satisfaction.
Polysilane's potential for creating transparent and flexible displays opens up new possibilities for ambient computing interfaces. These interfaces can be seamlessly integrated into everyday objects and environments, allowing for more natural and unobtrusive interactions. This shift towards ubiquitous computing interfaces could lead to a more intuitive and less technology-centric user experience, where digital interactions blend seamlessly with the physical world.
The energy efficiency of polysilane-based displays also contributes to improved user experience by extending battery life in mobile devices. Longer-lasting devices mean fewer interruptions for charging, leading to more continuous and satisfying user interactions. Additionally, the reduced power consumption aligns with growing user preferences for eco-friendly and sustainable technology solutions.
Polysilane's potential for creating highly responsive and low-latency interfaces could significantly enhance the user experience in gaming and other real-time interactive applications. The reduced input lag and smoother visual feedback can lead to more immersive and engaging experiences, potentially revolutionizing how users interact with digital content and virtual environments.
As polysilane technology matures, it is expected to enable new forms of haptic feedback in user interfaces. This could lead to more tactile and multi-sensory interactions, enriching the user experience by engaging multiple senses simultaneously. Such advancements could be particularly impactful in areas like accessibility, providing alternative interaction methods for users with visual or auditory impairments.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!