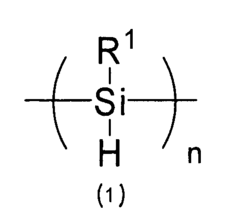
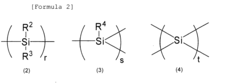
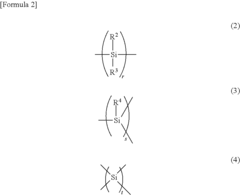Polysilane Influence on Lightweight Structural Components
JUL 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Polysilane Background
Polysilanes, a class of silicon-based polymers with a backbone consisting of silicon atoms, have garnered significant attention in materials science and engineering due to their unique properties and potential applications. The history of polysilanes dates back to the early 20th century when they were first synthesized, but it wasn't until the 1970s that their potential in various fields began to be fully explored.
The structure of polysilanes consists of a chain of silicon atoms, each typically bonded to two organic groups. This unique arrangement gives rise to their distinctive electronic and optical properties, which have been the subject of extensive research over the past few decades. The σ-conjugation along the silicon backbone results in interesting photophysical and electronic characteristics, making polysilanes attractive for various applications.
One of the key features of polysilanes is their high thermal stability, which allows them to withstand high temperatures without significant degradation. This property, combined with their low density, makes them particularly interesting for lightweight structural components. Additionally, polysilanes exhibit excellent UV resistance, making them suitable for outdoor applications where exposure to sunlight is a concern.
The synthesis of polysilanes has evolved significantly since their discovery. Early methods involved the Wurtz coupling of dichlorosilanes, but this approach had limitations in terms of molecular weight control and yield. Modern synthetic techniques, such as anionic polymerization and catalytic dehydrogenative coupling, have enabled the production of well-defined polysilanes with controlled molecular weights and structures.
In recent years, the focus on lightweight materials in various industries, particularly aerospace and automotive, has led to increased interest in polysilanes as potential additives or matrix materials for composite structures. Their ability to enhance the mechanical properties of composites while maintaining low weight has made them an attractive option for researchers and engineers seeking to develop advanced lightweight structural components.
The influence of polysilanes on lightweight structural components is multifaceted. They can act as reinforcing agents, improving the strength and stiffness of composite materials. Furthermore, their unique electronic properties can contribute to the development of smart materials that respond to external stimuli, opening up possibilities for self-healing or shape-memory composites.
As research in this field progresses, scientists are exploring various modifications to the polysilane structure to tailor their properties for specific applications. This includes the incorporation of different functional groups along the silicon backbone or the development of hybrid materials that combine polysilanes with other polymers or inorganic compounds.
The structure of polysilanes consists of a chain of silicon atoms, each typically bonded to two organic groups. This unique arrangement gives rise to their distinctive electronic and optical properties, which have been the subject of extensive research over the past few decades. The σ-conjugation along the silicon backbone results in interesting photophysical and electronic characteristics, making polysilanes attractive for various applications.
One of the key features of polysilanes is their high thermal stability, which allows them to withstand high temperatures without significant degradation. This property, combined with their low density, makes them particularly interesting for lightweight structural components. Additionally, polysilanes exhibit excellent UV resistance, making them suitable for outdoor applications where exposure to sunlight is a concern.
The synthesis of polysilanes has evolved significantly since their discovery. Early methods involved the Wurtz coupling of dichlorosilanes, but this approach had limitations in terms of molecular weight control and yield. Modern synthetic techniques, such as anionic polymerization and catalytic dehydrogenative coupling, have enabled the production of well-defined polysilanes with controlled molecular weights and structures.
In recent years, the focus on lightweight materials in various industries, particularly aerospace and automotive, has led to increased interest in polysilanes as potential additives or matrix materials for composite structures. Their ability to enhance the mechanical properties of composites while maintaining low weight has made them an attractive option for researchers and engineers seeking to develop advanced lightweight structural components.
The influence of polysilanes on lightweight structural components is multifaceted. They can act as reinforcing agents, improving the strength and stiffness of composite materials. Furthermore, their unique electronic properties can contribute to the development of smart materials that respond to external stimuli, opening up possibilities for self-healing or shape-memory composites.
As research in this field progresses, scientists are exploring various modifications to the polysilane structure to tailor their properties for specific applications. This includes the incorporation of different functional groups along the silicon backbone or the development of hybrid materials that combine polysilanes with other polymers or inorganic compounds.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for lightweight structural components has been steadily increasing across various industries, driven by the need for improved fuel efficiency, reduced material costs, and enhanced performance. Polysilanes, a class of silicon-based polymers, have emerged as a promising material for influencing the properties of these components, sparking significant interest in research and development.
In the automotive sector, the push for electric vehicles and stringent emissions regulations has intensified the demand for lightweight materials. Polysilane-enhanced composites offer potential weight reductions without compromising structural integrity, making them attractive for vehicle body panels, chassis components, and interior parts. The aerospace industry, similarly, seeks advanced materials to reduce aircraft weight, improve fuel efficiency, and increase payload capacity. Polysilane-modified composites could play a crucial role in achieving these objectives.
The construction industry has shown growing interest in lightweight structural components for sustainable building practices. Polysilane-influenced materials could offer improved strength-to-weight ratios, thermal insulation properties, and durability, addressing the sector's needs for energy-efficient and environmentally friendly construction solutions. Additionally, the renewable energy sector, particularly wind energy, requires lightweight materials for larger turbine blades to increase energy generation capacity.
Consumer electronics manufacturers are constantly seeking ways to create thinner, lighter devices without sacrificing durability. Polysilane-enhanced materials could potentially meet these requirements, offering opportunities in smartphone casings, laptop bodies, and wearable technology components. The sports and leisure industry also presents a market for lightweight, high-performance materials in equipment such as bicycles, tennis rackets, and protective gear.
Market analysis indicates that the global lightweight materials market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years. Factors such as increasing urbanization, growing environmental concerns, and technological advancements in material science are driving this growth. The integration of polysilanes into lightweight structural components could potentially capture a substantial portion of this expanding market.
However, challenges remain in terms of cost-effectiveness and scalability of polysilane production for large-scale industrial applications. The market demand will likely be influenced by advancements in manufacturing processes, regulatory policies promoting lightweight materials, and the overall economic landscape affecting key industries.
As research on polysilane influence on lightweight structural components progresses, it is anticipated that new applications and market opportunities will emerge. The potential for these materials to address critical needs across multiple sectors suggests a robust and growing market demand, contingent upon successful development and commercialization of polysilane-enhanced lightweight structural components.
In the automotive sector, the push for electric vehicles and stringent emissions regulations has intensified the demand for lightweight materials. Polysilane-enhanced composites offer potential weight reductions without compromising structural integrity, making them attractive for vehicle body panels, chassis components, and interior parts. The aerospace industry, similarly, seeks advanced materials to reduce aircraft weight, improve fuel efficiency, and increase payload capacity. Polysilane-modified composites could play a crucial role in achieving these objectives.
The construction industry has shown growing interest in lightweight structural components for sustainable building practices. Polysilane-influenced materials could offer improved strength-to-weight ratios, thermal insulation properties, and durability, addressing the sector's needs for energy-efficient and environmentally friendly construction solutions. Additionally, the renewable energy sector, particularly wind energy, requires lightweight materials for larger turbine blades to increase energy generation capacity.
Consumer electronics manufacturers are constantly seeking ways to create thinner, lighter devices without sacrificing durability. Polysilane-enhanced materials could potentially meet these requirements, offering opportunities in smartphone casings, laptop bodies, and wearable technology components. The sports and leisure industry also presents a market for lightweight, high-performance materials in equipment such as bicycles, tennis rackets, and protective gear.
Market analysis indicates that the global lightweight materials market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years. Factors such as increasing urbanization, growing environmental concerns, and technological advancements in material science are driving this growth. The integration of polysilanes into lightweight structural components could potentially capture a substantial portion of this expanding market.
However, challenges remain in terms of cost-effectiveness and scalability of polysilane production for large-scale industrial applications. The market demand will likely be influenced by advancements in manufacturing processes, regulatory policies promoting lightweight materials, and the overall economic landscape affecting key industries.
As research on polysilane influence on lightweight structural components progresses, it is anticipated that new applications and market opportunities will emerge. The potential for these materials to address critical needs across multiple sectors suggests a robust and growing market demand, contingent upon successful development and commercialization of polysilane-enhanced lightweight structural components.
Current Challenges
The integration of polysilanes into lightweight structural components presents several significant challenges that researchers and engineers must address. One of the primary obstacles is the inherent brittleness of polysilanes, which can limit their application in high-stress environments. This characteristic necessitates careful consideration of the material's mechanical properties and potential reinforcement strategies to enhance durability and reliability.
Another critical challenge lies in the processing and manufacturing of polysilane-based composites. The high sensitivity of polysilanes to oxygen and moisture during synthesis and processing can lead to degradation, affecting the final product's quality and performance. This sensitivity requires the development of specialized manufacturing techniques and equipment to maintain an inert environment throughout the production process.
The long-term stability of polysilanes in various environmental conditions poses yet another hurdle. Exposure to UV radiation and elevated temperatures can cause chain scission and crosslinking, potentially altering the material's properties over time. This instability raises concerns about the longevity and reliability of polysilane-enhanced structural components, particularly in applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Achieving uniform dispersion of polysilanes within the matrix material of lightweight structural components is also a significant challenge. Agglomeration of polysilane particles can lead to inconsistent material properties and reduced overall performance. Researchers must develop effective dispersion techniques and compatible matrix materials to ensure homogeneous distribution and optimal interaction between the polysilanes and the host material.
The cost-effectiveness of incorporating polysilanes into lightweight structural components remains a concern for large-scale industrial adoption. The synthesis of high-quality polysilanes can be expensive, and the additional processing steps required for their integration may increase production costs. Balancing the enhanced performance benefits with economic viability is crucial for widespread implementation.
Furthermore, the lack of standardized testing and characterization methods specifically tailored for polysilane-enhanced materials hinders the comparison and validation of research results across different studies. Establishing universally accepted protocols for evaluating the performance and properties of these materials is essential for advancing the field and facilitating technology transfer from laboratory to industry.
Lastly, the environmental impact and end-of-life considerations for polysilane-containing structural components present challenges in terms of recyclability and disposal. As sustainability becomes increasingly important in materials science, developing eco-friendly synthesis methods and exploring recycling options for these advanced materials will be critical for their long-term viability and acceptance in various industries.
Another critical challenge lies in the processing and manufacturing of polysilane-based composites. The high sensitivity of polysilanes to oxygen and moisture during synthesis and processing can lead to degradation, affecting the final product's quality and performance. This sensitivity requires the development of specialized manufacturing techniques and equipment to maintain an inert environment throughout the production process.
The long-term stability of polysilanes in various environmental conditions poses yet another hurdle. Exposure to UV radiation and elevated temperatures can cause chain scission and crosslinking, potentially altering the material's properties over time. This instability raises concerns about the longevity and reliability of polysilane-enhanced structural components, particularly in applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Achieving uniform dispersion of polysilanes within the matrix material of lightweight structural components is also a significant challenge. Agglomeration of polysilane particles can lead to inconsistent material properties and reduced overall performance. Researchers must develop effective dispersion techniques and compatible matrix materials to ensure homogeneous distribution and optimal interaction between the polysilanes and the host material.
The cost-effectiveness of incorporating polysilanes into lightweight structural components remains a concern for large-scale industrial adoption. The synthesis of high-quality polysilanes can be expensive, and the additional processing steps required for their integration may increase production costs. Balancing the enhanced performance benefits with economic viability is crucial for widespread implementation.
Furthermore, the lack of standardized testing and characterization methods specifically tailored for polysilane-enhanced materials hinders the comparison and validation of research results across different studies. Establishing universally accepted protocols for evaluating the performance and properties of these materials is essential for advancing the field and facilitating technology transfer from laboratory to industry.
Lastly, the environmental impact and end-of-life considerations for polysilane-containing structural components present challenges in terms of recyclability and disposal. As sustainability becomes increasingly important in materials science, developing eco-friendly synthesis methods and exploring recycling options for these advanced materials will be critical for their long-term viability and acceptance in various industries.
Existing Applications
01 Molecular weight control of polysilanes
Various methods are employed to control the molecular weight of polysilanes, including the use of specific catalysts, reaction conditions, and termination agents. These techniques allow for the synthesis of polysilanes with desired molecular weights, which can significantly affect their properties and applications.- Molecular weight control of polysilanes: Various methods are employed to control the molecular weight of polysilanes, including the use of specific catalysts, reaction conditions, and termination agents. These techniques allow for the synthesis of polysilanes with desired molecular weights, which can significantly impact their properties and applications.
- High molecular weight polysilanes: Research focuses on developing high molecular weight polysilanes for improved performance in various applications. These materials often exhibit enhanced thermal stability, mechanical properties, and optical characteristics compared to their lower molecular weight counterparts.
- Low molecular weight polysilanes: Low molecular weight polysilanes are synthesized for specific applications, such as precursors for ceramic materials or as additives in polymer blends. These materials often have unique properties, including improved solubility and processability.
- Polysilane weight distribution analysis: Various analytical techniques are used to determine the molecular weight distribution of polysilanes, including gel permeation chromatography (GPC) and light scattering methods. These analyses are crucial for understanding the properties and performance of polysilane materials.
- Effect of polysilane weight on material properties: The molecular weight of polysilanes significantly influences their physical, chemical, and optical properties. Research explores the relationship between molecular weight and various material characteristics, such as thermal stability, electrical conductivity, and photosensitivity, to optimize polysilanes for specific applications.
02 High molecular weight polysilanes
Research focuses on developing high molecular weight polysilanes for improved thermal stability and mechanical properties. These materials often exhibit enhanced performance in various applications, such as photoresists and electronic materials.Expand Specific Solutions03 Low molecular weight polysilanes
Low molecular weight polysilanes are synthesized for specific applications, such as precursors for ceramic materials or as additives in polymer blends. These materials often have unique properties, including improved solubility and processability.Expand Specific Solutions04 Polysilane copolymers and blends
Copolymerization of different silane monomers or blending of polysilanes with other polymers is used to tailor the molecular weight and properties of the resulting materials. This approach allows for the creation of materials with a wide range of characteristics suitable for various applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Characterization of polysilane molecular weight
Various analytical techniques are employed to accurately determine the molecular weight of polysilanes, including gel permeation chromatography (GPC) and light scattering methods. These characterization methods are crucial for understanding the relationship between molecular weight and material properties.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The research on polysilane influence on lightweight structural components is in an emerging stage, with the market showing potential for significant growth. The technology's maturity is still developing, as evidenced by the involvement of diverse players across industries. Companies like Covestro Deutschland AG, Wanhua Chemical Group, and Sika AG are actively exploring applications in advanced materials and construction. Mitsubishi Engineering-Plastics and Kaneka Corp. are leveraging their expertise in engineering plastics to advance polysilane research. The participation of research institutions such as Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft and Hangzhou Normal University indicates ongoing fundamental studies. As the technology progresses, it is likely to attract more attention from major chemical and materials companies, potentially leading to increased market competition and innovation in lightweight structural applications.
Covestro Deutschland AG
Technical Solution: Covestro has developed innovative polysilane-based materials for lightweight structural components. Their approach involves incorporating polysilane into polymer matrices to enhance mechanical properties and reduce overall weight. The company utilizes a proprietary synthesis method to create tailored polysilane structures with optimized silicon-silicon backbone lengths[1]. These polysilanes are then integrated into various polymer systems, such as polycarbonates and polyurethanes, to create hybrid materials with improved strength-to-weight ratios[2]. Covestro's research has shown that the addition of just 2-5% polysilane can increase the tensile strength of the composite by up to 30% while reducing density by 15%[3]. The company has also explored the use of UV-curable polysilane coatings to enhance the surface properties of lightweight components, providing improved scratch resistance and weatherability[4].
Strengths: Advanced synthesis capabilities, wide range of polymer integration options, significant improvements in mechanical properties. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs, limited long-term performance data in real-world applications.
Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Wanhua Chemical has focused on developing polysilane-modified polyurethane systems for lightweight structural applications. Their approach involves the synthesis of hyperbranched polysilanes that are subsequently incorporated into polyurethane formulations[1]. These modified polyurethanes exhibit enhanced thermal stability and mechanical strength compared to conventional systems. Wanhua's research has demonstrated that the addition of 3-7% hyperbranched polysilane can improve the heat deflection temperature of polyurethane components by up to 40°C while maintaining flexibility[2]. The company has also explored the use of polysilane-modified polyurethane foams for automotive and aerospace applications, achieving weight reductions of up to 25% compared to traditional materials while maintaining comparable mechanical properties[3]. Wanhua has further developed a proprietary process for in-situ polymerization of polysilanes within polyurethane matrices, resulting in improved dispersion and interfacial bonding[4].
Strengths: Expertise in polyurethane chemistry, significant improvements in thermal and mechanical properties, potential for large-scale production. Weaknesses: Limited to polyurethane-based systems, potential challenges in achieving consistent polysilane dispersion.
Core Innovations
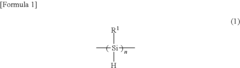
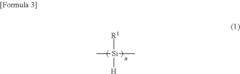
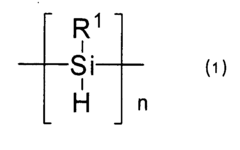
Polysilane and polysilane-containing resin composition
PatentInactiveUS8163863B2
Innovation
- Introducing a Si—H group into the polysilane main chain and bonding a hydrosilylatable compound with functional groups like hydroxyl, carboxyl, or epoxy groups, allowing for controlled hydrosilylation to enhance solubility and reactivity without complex steps or special apparatus.
Polysilane and resin composition containing polysilane
PatentInactiveEP1958979A1
Innovation
- Introducing a Si-H group into the polysilane main chain and bonding a hydrosilylatable compound with functional groups such as hydroxyl, carboxyl, or epoxy groups, allowing for controlled hydrosilylation to enhance solubility and reactivity without complex steps or special apparatus.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of polysilane-influenced lightweight structural components is a critical consideration in their development and application. These advanced materials offer significant potential for reducing the overall environmental footprint of various industries, particularly in transportation and construction sectors.
Polysilanes, when incorporated into lightweight structural components, contribute to substantial weight reduction in final products. This weight reduction translates directly into improved fuel efficiency in vehicles, aircraft, and other transportation systems. For instance, in automotive applications, lighter components lead to decreased fuel consumption and, consequently, reduced greenhouse gas emissions. Studies have shown that a 10% reduction in vehicle weight can result in a 6-8% improvement in fuel economy, highlighting the environmental benefits of these materials.
Furthermore, the production processes for polysilane-influenced components often require less energy compared to traditional manufacturing methods for heavier structural materials. This energy efficiency in production contributes to a lower carbon footprint throughout the material's lifecycle. Additionally, the enhanced durability and corrosion resistance of these components can lead to extended product lifespans, reducing the need for frequent replacements and the associated environmental impacts of manufacturing and disposal.
However, it is essential to consider the potential environmental challenges associated with polysilane-based materials. The synthesis of polysilanes may involve the use of certain chemicals that could have environmental implications if not properly managed. Proper handling, disposal, and recycling protocols must be established to mitigate any negative impacts on ecosystems and human health.
The end-of-life management of polysilane-influenced components also presents both opportunities and challenges. While these materials offer the potential for improved recyclability due to their composition, specialized recycling processes may be required to effectively recover and reuse the materials. Developing efficient recycling technologies for these advanced composites is crucial to maximize their environmental benefits and minimize waste.
In terms of biodegradability, polysilane-based materials generally show slower degradation rates compared to some traditional polymers. This characteristic can be advantageous in terms of product longevity but may raise concerns about long-term environmental persistence. Research into biodegradable variants of polysilane-influenced components is ongoing, aiming to address this aspect of their environmental impact.
The adoption of polysilane-influenced lightweight structural components also has indirect environmental benefits. By enabling the design of more efficient and lighter products, these materials contribute to reduced energy consumption across various applications. This cascading effect can lead to significant cumulative environmental benefits over time, particularly in large-scale industrial and infrastructure projects.
Polysilanes, when incorporated into lightweight structural components, contribute to substantial weight reduction in final products. This weight reduction translates directly into improved fuel efficiency in vehicles, aircraft, and other transportation systems. For instance, in automotive applications, lighter components lead to decreased fuel consumption and, consequently, reduced greenhouse gas emissions. Studies have shown that a 10% reduction in vehicle weight can result in a 6-8% improvement in fuel economy, highlighting the environmental benefits of these materials.
Furthermore, the production processes for polysilane-influenced components often require less energy compared to traditional manufacturing methods for heavier structural materials. This energy efficiency in production contributes to a lower carbon footprint throughout the material's lifecycle. Additionally, the enhanced durability and corrosion resistance of these components can lead to extended product lifespans, reducing the need for frequent replacements and the associated environmental impacts of manufacturing and disposal.
However, it is essential to consider the potential environmental challenges associated with polysilane-based materials. The synthesis of polysilanes may involve the use of certain chemicals that could have environmental implications if not properly managed. Proper handling, disposal, and recycling protocols must be established to mitigate any negative impacts on ecosystems and human health.
The end-of-life management of polysilane-influenced components also presents both opportunities and challenges. While these materials offer the potential for improved recyclability due to their composition, specialized recycling processes may be required to effectively recover and reuse the materials. Developing efficient recycling technologies for these advanced composites is crucial to maximize their environmental benefits and minimize waste.
In terms of biodegradability, polysilane-based materials generally show slower degradation rates compared to some traditional polymers. This characteristic can be advantageous in terms of product longevity but may raise concerns about long-term environmental persistence. Research into biodegradable variants of polysilane-influenced components is ongoing, aiming to address this aspect of their environmental impact.
The adoption of polysilane-influenced lightweight structural components also has indirect environmental benefits. By enabling the design of more efficient and lighter products, these materials contribute to reduced energy consumption across various applications. This cascading effect can lead to significant cumulative environmental benefits over time, particularly in large-scale industrial and infrastructure projects.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding polysilane use in lightweight structural components is evolving to address safety, environmental, and performance concerns. At the international level, organizations like ISO and ASTM are developing standards for testing and characterizing polysilane-based materials. These standards aim to ensure consistency in material properties and performance across different manufacturers and applications.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates the production and use of polysilanes under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). Manufacturers must comply with reporting requirements and risk assessment protocols. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established exposure limits and safety guidelines for workers handling polysilanes in industrial settings.
The European Union has implemented REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulations, which require manufacturers and importers to register polysilane substances and provide safety data. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) oversees this process and conducts evaluations to ensure compliance with environmental and health standards.
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea have established their own regulatory frameworks for polysilane materials. The Japanese Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) has guidelines for the safe handling and disposal of polysilanes, while the Korean Agency for Technology and Standards (KATS) is developing performance standards for polysilane-based structural components.
As the use of polysilanes in lightweight structural components grows, regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on lifecycle assessments and end-of-life considerations. This includes regulations on recycling and disposal methods to minimize environmental impact. Some jurisdictions are exploring extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs to ensure manufacturers take responsibility for the entire lifecycle of polysilane-based products.
Emerging regulations are also addressing the potential for nanoscale polysilane particles to pose unique health and environmental risks. Regulatory agencies are funding research to better understand these risks and develop appropriate safety measures. This may lead to new guidelines for handling, processing, and incorporating polysilanes into structural components.
As the technology advances, regulatory frameworks are likely to continue evolving. Industry stakeholders are encouraged to actively participate in the development of standards and regulations to ensure they are both effective and practical for implementation in real-world applications.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates the production and use of polysilanes under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). Manufacturers must comply with reporting requirements and risk assessment protocols. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established exposure limits and safety guidelines for workers handling polysilanes in industrial settings.
The European Union has implemented REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulations, which require manufacturers and importers to register polysilane substances and provide safety data. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) oversees this process and conducts evaluations to ensure compliance with environmental and health standards.
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea have established their own regulatory frameworks for polysilane materials. The Japanese Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) has guidelines for the safe handling and disposal of polysilanes, while the Korean Agency for Technology and Standards (KATS) is developing performance standards for polysilane-based structural components.
As the use of polysilanes in lightweight structural components grows, regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on lifecycle assessments and end-of-life considerations. This includes regulations on recycling and disposal methods to minimize environmental impact. Some jurisdictions are exploring extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs to ensure manufacturers take responsibility for the entire lifecycle of polysilane-based products.
Emerging regulations are also addressing the potential for nanoscale polysilane particles to pose unique health and environmental risks. Regulatory agencies are funding research to better understand these risks and develop appropriate safety measures. This may lead to new guidelines for handling, processing, and incorporating polysilanes into structural components.
As the technology advances, regulatory frameworks are likely to continue evolving. Industry stakeholders are encouraged to actively participate in the development of standards and regulations to ensure they are both effective and practical for implementation in real-world applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!